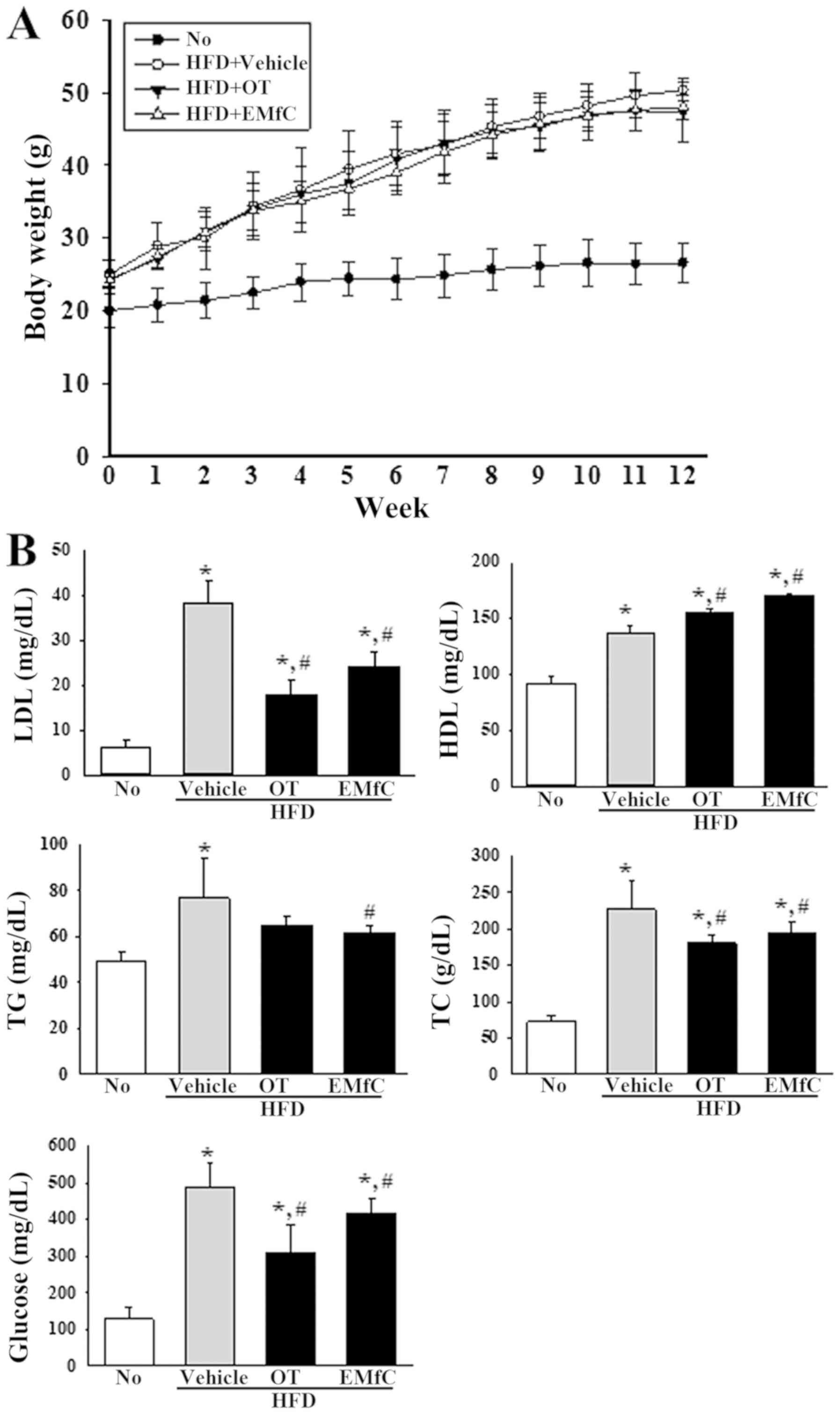
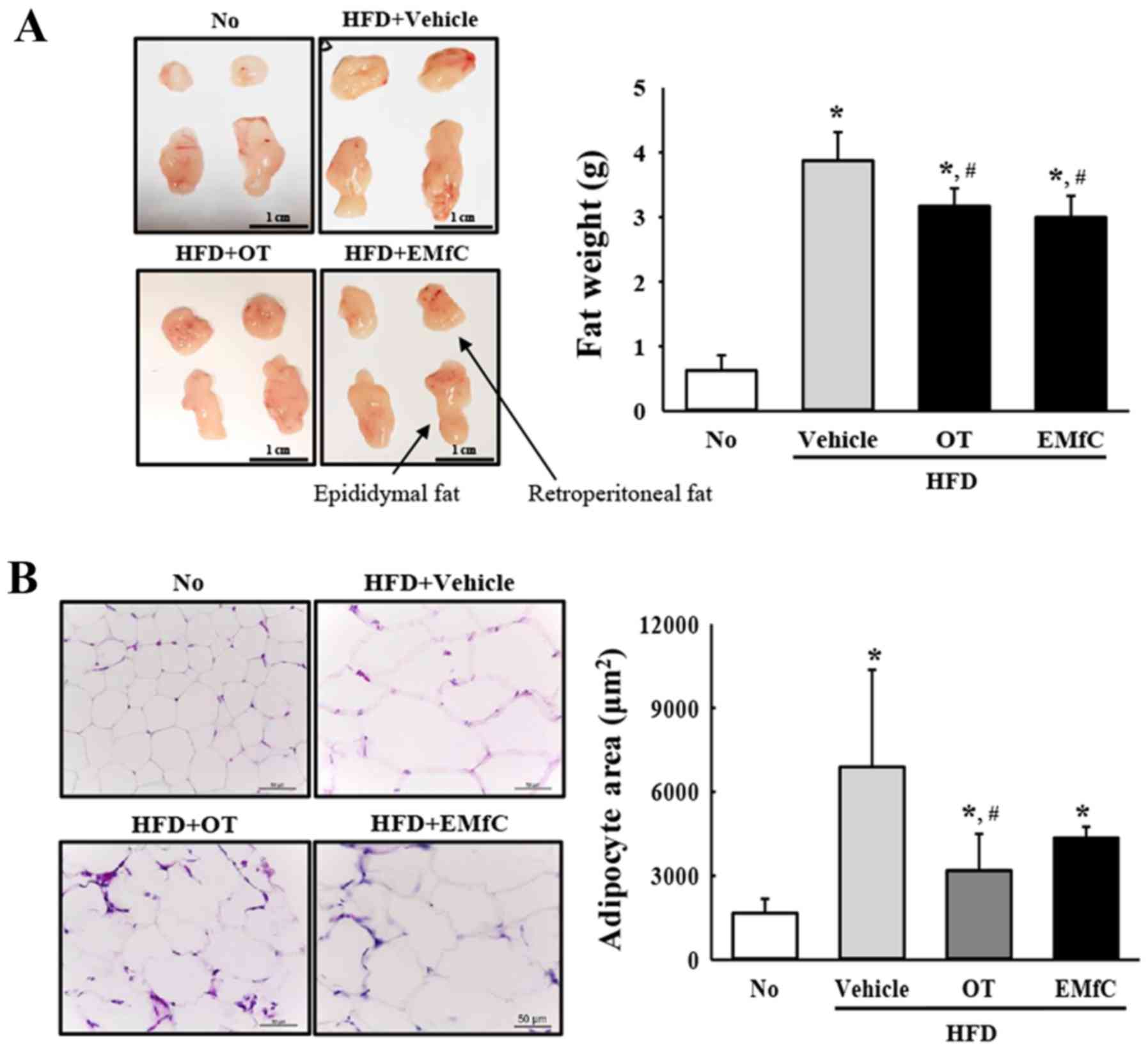
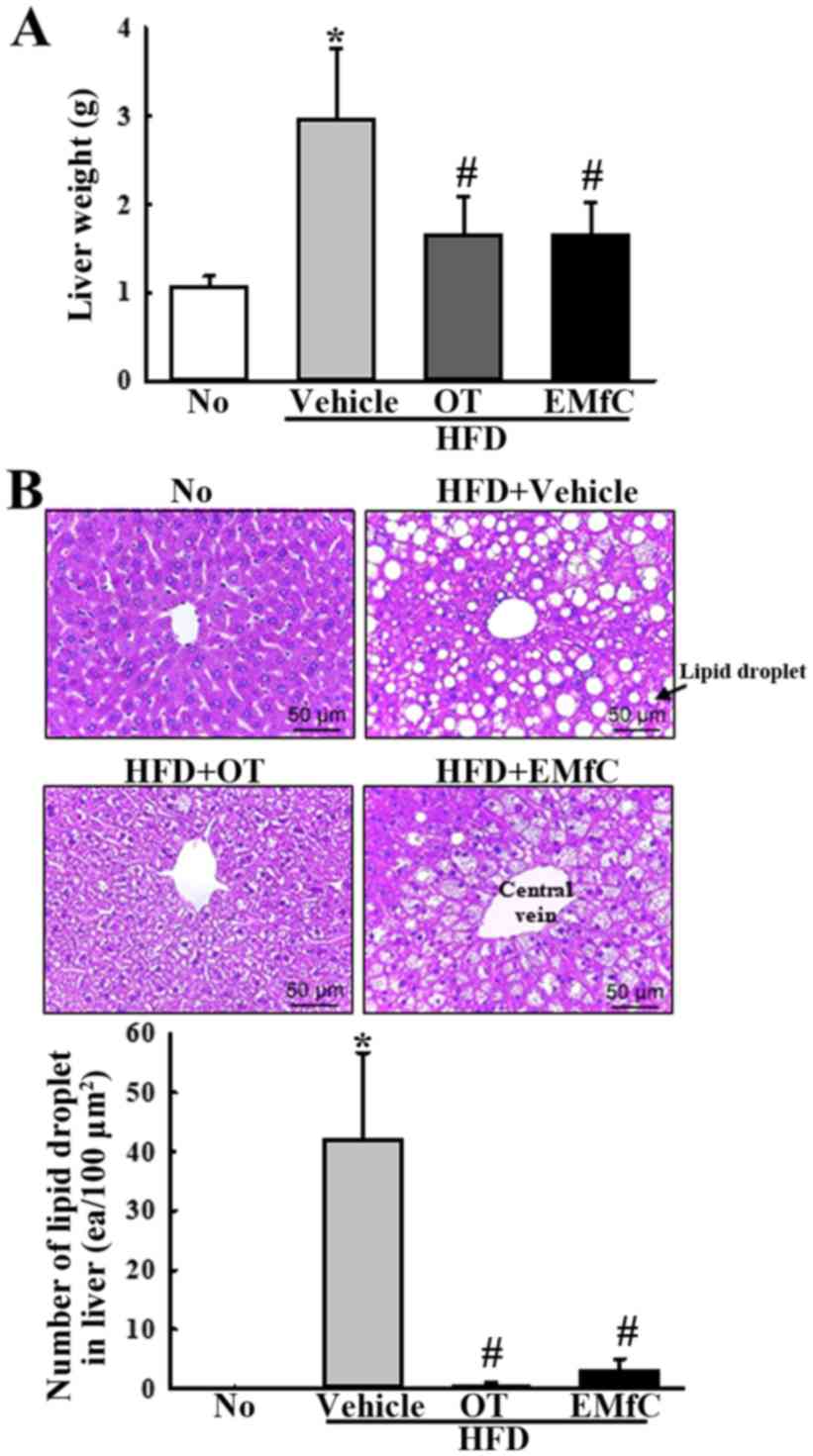
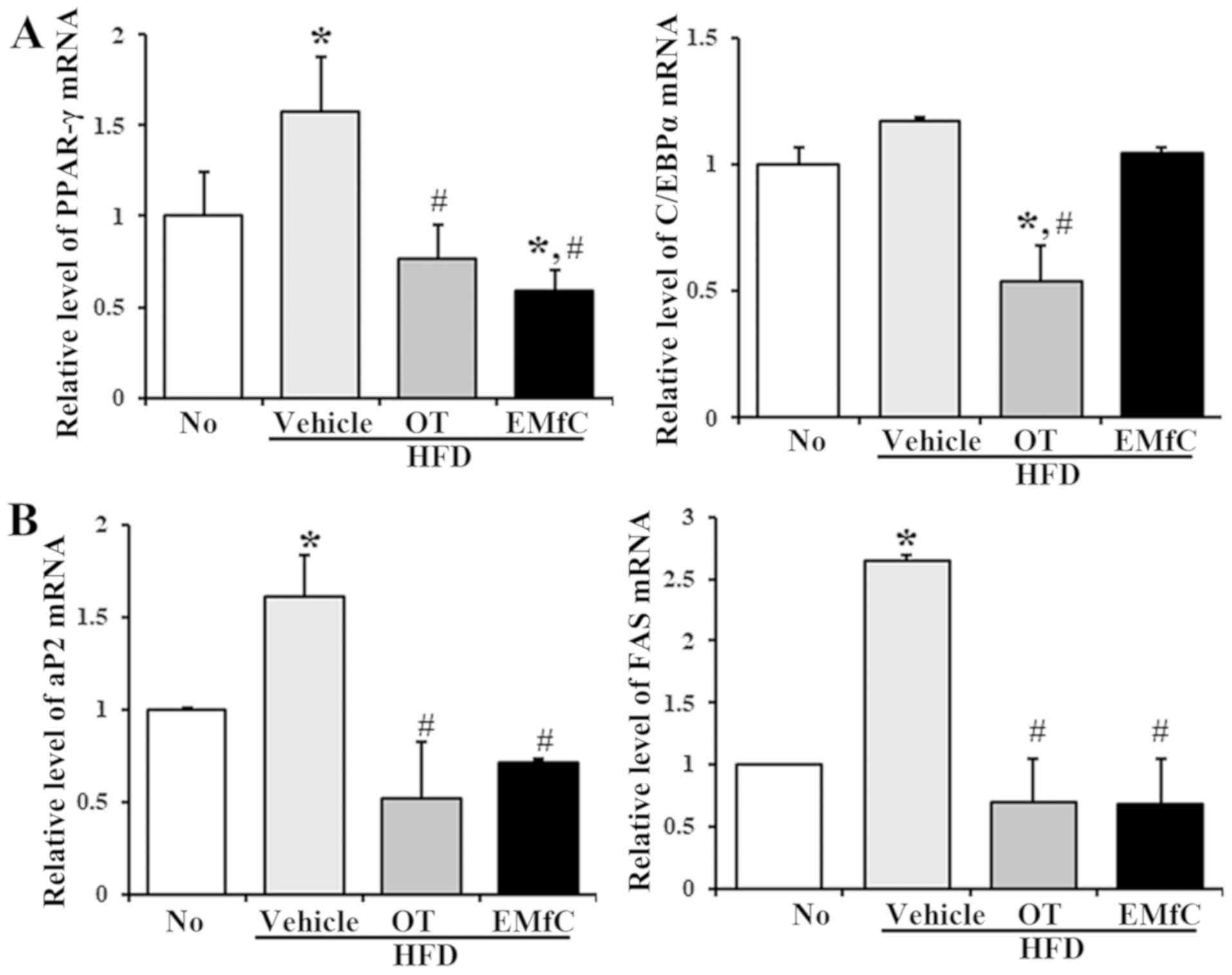
|
1
|
Haslam DW and James WP: Obesity. Lancet.
366:1197–1209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Després JP and Lemieux I: Abdominal
obesity and metabolic syndrome. Nature. 444:881–887. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC):
Worldwide trends in diabetes since 1980: A pooled analysis of 751
population-based studies with 4.4 million participants. Lancet.
387:1513–1530. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Maguire T and Haslam D: The Obesity
Epidemic and its Management. Matthew Wright: Pharmaceutical Press;
London: pp. 264–267. 2010
|
|
5
|
Pittler MH, Schmidt K and Ernst E: Adverse
events of herbal food supplements for body weight reduction:
Systematic review. Obes Rev. 6:93–111. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gunjal S, Ankola AV and Bhat K: In vitro
antibacterial activity of ethanolic extract of Morus alba
leaf against periodontal pathogens. Indian J Dent Res. 26:533–536.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Raman ST, Ganeshan AK, Chen C, Jin C, Li
SH, Chen HJ and Gui Z: In vitro in vivo antioxidant activity
of flavonoid extracted from mulberry fruit (Morus alba L.).
Pharmacogn Mag. 12:128–133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Xiang L, Wang C, Tang C and He X:
Antidiabetic and antioxidant effects and phytochemicals of mulberry
fruit (Morus alba L.) polyphenol enhanced extract. PLoS One.
8:e711442008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jo SP, Kim JK and Lim YH:
Antihyperlipidemic effects of stilbenoids isolated from Morus
alba in rats fed a high-cholesterol diet. Food Chem Toxicol.
65:213–218. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
El-Beshbishy HA, Singab AN, Sinkkonen J
and Pihlaja K: Hypolipidemic and antioxidant effects of Morus
alba L. (Egyptian mulberry) root bark fractions supplementation
in cholesterol-fed rats. Life Sci. 78:2724–2733. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Eo HJ, Park JH, Park GH, Lee MH, Lee JR,
Koo JS and Jeong JB: Anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer activity of
mulberry (Morus alba L.) root bark. BMC Complement Altern
Med. 14:2002014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chan EW, Lye PY and Wong SK:
Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and clinical trials of Morus
alba. Chin J Nat Med. 14:17–30. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kobayashi Y, Miyazawa M, Kamei A, Abe K
and Kojima T: Ameliorative effects of mulberry (Morus alba
L.) leaves on hyperlipidemia in rats fed a high-fat diet: Induction
of fatty acid oxidation, inhibition of lipogenesis, and suppression
of oxidative stress. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 74:2385–2395. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang SJ, Park NY and Lim Y:
Anti-adipogenic effect of mulberry leaf ethanol extract in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Nutr Res Pract. 8:613–617. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ann JY, Eo HY and Lim YS: Mulberry leaves
(Morus alba L.) ameliorate obesity-induced hepatic
lipogenesis, fibrosis, and oxidative stress in high-fat diet-fed
mice. Genes Nutr. 10:462015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Naowaboot J, Pannangpetch P,
Kukongviriyapan V, Prawan A, Kukongviriyapan U and Itharat A:
Mulberry leaf extract stimulates glucose uptake and GLUT4
translocation in rat adipocytes. Am J Chin Med. 40:163–175. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sugimoto M, Arai H, Taura Y, Murayama T,
Khaengkhan P, Nishio T, Ono K, Ariyasu H, Akamizu T, Ueda Y, et al:
Mulberry leaf ameliorates the expression profile of adipocytokines
by inhibiting oxidative stress in white adipose tissue in db/db
mice. Atherosclerosis. 204:388–394. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sung GH, Hywel-Jones NL, Sung JM,
Luangsa-Ard JJ, Shrestha B and Spatafora JW: Phylogenetic
classification of Cordyceps and the clavicipitaceous fungi.
Stud Mycol. 57:5–59. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De Silva DD, Rapior S, Sudarman E, Stadler
M, Xu J, Alias SA and Hyde KD: Bioactive metabolites from
macrofungi: Ethnopharmacology, biological activities and chemistry.
Fungal Divers. 62:1–40. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
De Silva DD, Rapior S, Fons F, Bahkali AH
and Hyde KD: Medicinal mushrooms in supportive cancer therapies: An
approach to anti-cancer effects and putative mechanisms of action.
Fungal Divers. 55:1–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pao HY, Pan BS, Leu SF and Huang BM:
Cordycepin stimulated steroidogenesis in MA-10 mouse Leydig tumor
cells through the protein kinase C Pathway. J Agric Food Chem.
60:4905–4913. 2102. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kim JR, Yeon SH, Kim HS and Ahn YJ:
Larvicidal activity against Plutella xylostella of
cordycepin from the fruiting body of Cordyceps militaris.
Pest Manag Sci. 58:713–717. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ramesh T, Yoo SK, Kim SW, Hwang SY, Sohn
SH, Kim IW and Kim SK: Cordycepin (3′-deoxyadenosine) attenuates
age-related oxidative stress and ameliorates antioxidant capacity
in rats. Exp Gerontol. 47:979–987. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Guo P, Kai Q, Gao J, Lian ZQ, Wu CM, Wu CA
and Zhu HB: Cordycepin prevents hyperlipidemia in hamsters fed a
high-fat diet via activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. J
Pharm Sci. 113:395–403. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kim SS, Lim KS, Kim HJ, Chong MS, Cho HE,
Choi YH, et al: Effects of extracts from mixed culture with
Tricholoma Matsutake mycelium and Cordyceps Militaris
mycelium on mlood glucose in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Korean J Orient Physiol Pathol. 22:365–370. 2008.
|
|
26
|
Hung YP and Lee CL: Higher anti-liver
fibrosis effect of cordyceps militaris-fermented product
cultured with deep ocean water via inhibiting proinflammatory
factors and fibrosis-related factors expressions. Mar Drugs.
15(pii): E1682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee MR, Kim JE, Yun WB, Choi JY, Park JJ,
Kim HR, Song BR, Choi YW, Kim KM and Hwang DY: Lipolytic effect of
novel extracts from mulberry (Morus alba) leaves fermented
with Cordyceps militaris in the primary adipocytes derived
from SD rats. Lab Anim Res. 33:270–279. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hofbauer KG, Nicholson JR and Boss O: The
obesity epidemic: Current and future pharmacological treatments.
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 47:565–592. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sharma B and Henderson DC: Sibutramine:
Current status as an anti-obesity drug and its future perspectives.
Expert Opin Pharmacother. 9:2161–2173. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lean ME: Pathophysiology of obesity. Proc
Nutr Soc. 59:331–336. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Apostolopoulou M, Savopoulos C, Michalakis
K, Coppack S, Dardavessis T and Hatzitolios A: Age, weight and
obesity. Maturitas. 71:115–119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Morimoto C, Kameda K, Tsujita T and Okuda
H: Relationships between lipolysis induced by various lipolytic
agents and hormone-sensitive lipase in rat fat cells. J Lipid Res.
42:120–127. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bray GA: Drug treatment of obesity. Rev
Endocr Metab Disord. 2:403–418. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mayer MA, Höcht C, Puyó A and Taira CA:
Recent advances in obesity pharmacotherapy. Curr Clin Pharmacol.
4:53–61. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vázquez-Vela ME, Torres N and Tovar AR:
White adipose tissue as endocrine organ and its role in obesity.
Arch Med Res. 39:715–728. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schoonjans K, Staels B and Auwerx J: The
peroxisome proliferator activated receptors (PPARS) and their
effects on lipid metabolism and adipocyte differentiation. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1302:93–109. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rosen ED, Walkey CJ, Puigserver P and
Spiegelman BM: Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Genes
Dev. 14:1293–1307. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kliewer SA and Willson TM: The nuclear
receptor PPARgamma-bigger than fat. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 8:576–581.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Spiegelman BM: PPAR-gamma: Adipogenic
regulator and thiazolidinedione receptor. Diabetes. 47:507–514.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Boizard M, Le Liepvre X, Lemarchand P,
Foufelle F, Ferré P and Dugail I: Obesity-related overexpression of
fatty-acid synthase gene in adipose tissue involves sterol
regulatory element-binding protein transcription factors. J Biol
Chem. 273:29164–29171. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Coe NR and Bernlohr DA: Physiological
properties and functions of intracellular fatty acid-binding
proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1391:287–306. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zimmermann R, Strauss JG, Haemmerle G,
Schoiswohl G, Birner-Gruenberger R, Riederer M, Lass A, Neuberger
G, Eisenhaber F, Hermetter A and Zechner R: Fat mobilization in
adipose tissue is promoted by adipose triglyceride lipase. Science.
306:1383–1386. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Haemmerle G, Lass A, Zimmermann R,
Gorkiewicz G, Meyer C, Rozman J, Heldmaier G, Maier R, Theussl C,
Eder S, et al: Defective lipolysis and altered energy metabolism in
mice lacking adipose triglyceride lipase. Science. 312:734–737.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ahmadian M, Duncan RE, Varady KA, Frasson
D, Hellerstein MK, Birkenfeld AL, Samuel VT, Shulman GI, Wang Y,
Kang C and Sul HS: Adipose overexpression of desnutrin promotes
fatty acid use and attenuates diet-induced obesity. Diabetes.
58:855–866. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tansey JT, Sztalryd C, Hlavin EM, Kimmel
AR and Londos C: The central role of perilipin a in lipid
metabolism and adipocyte lipolysis. IUBMB Life. 56:379–385. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Marcelin G and Chua S Jr: Contributions of
adipocyte lipid metabolism to body fat content and implications for
the treatment of obesity. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 10:588–593. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|