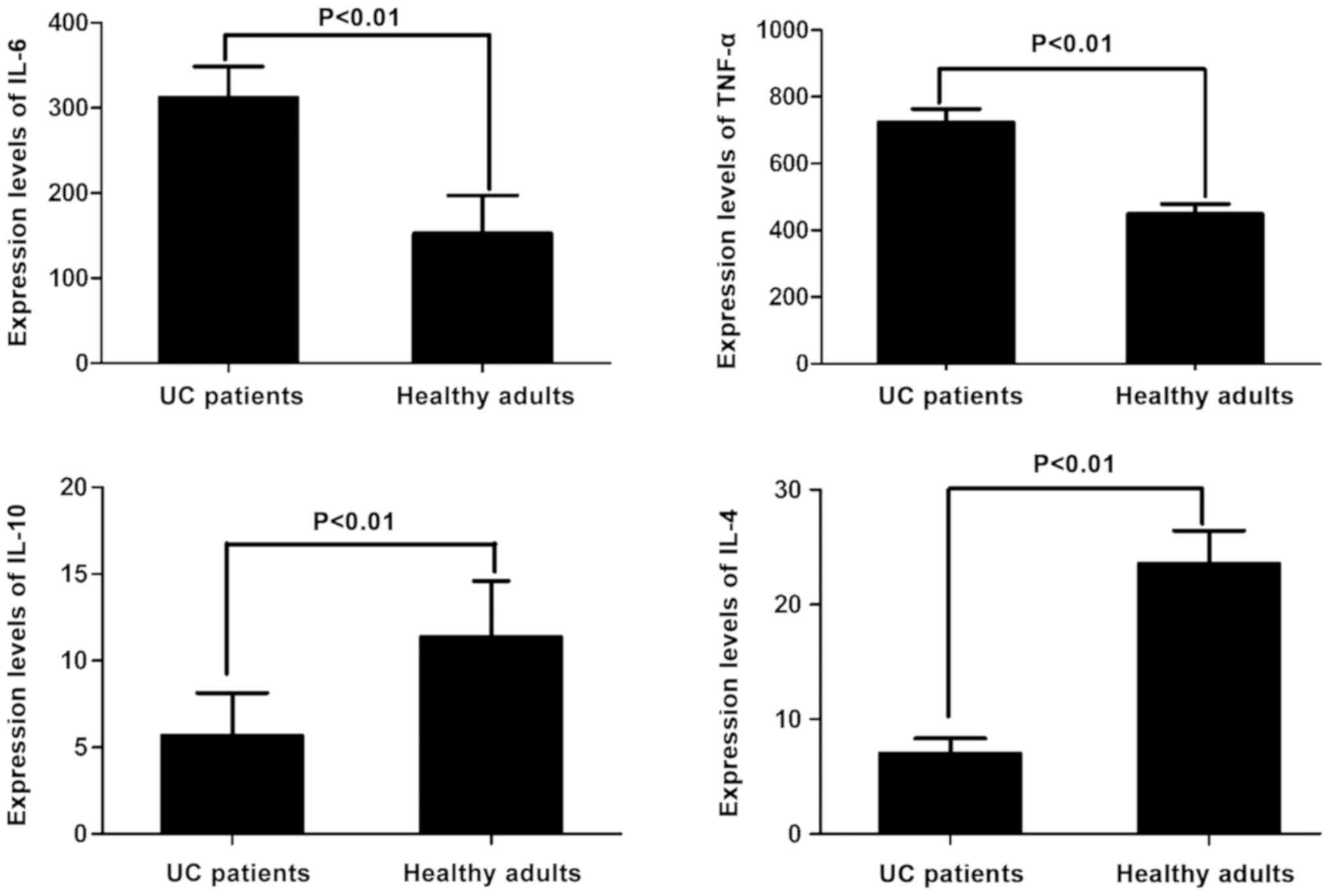
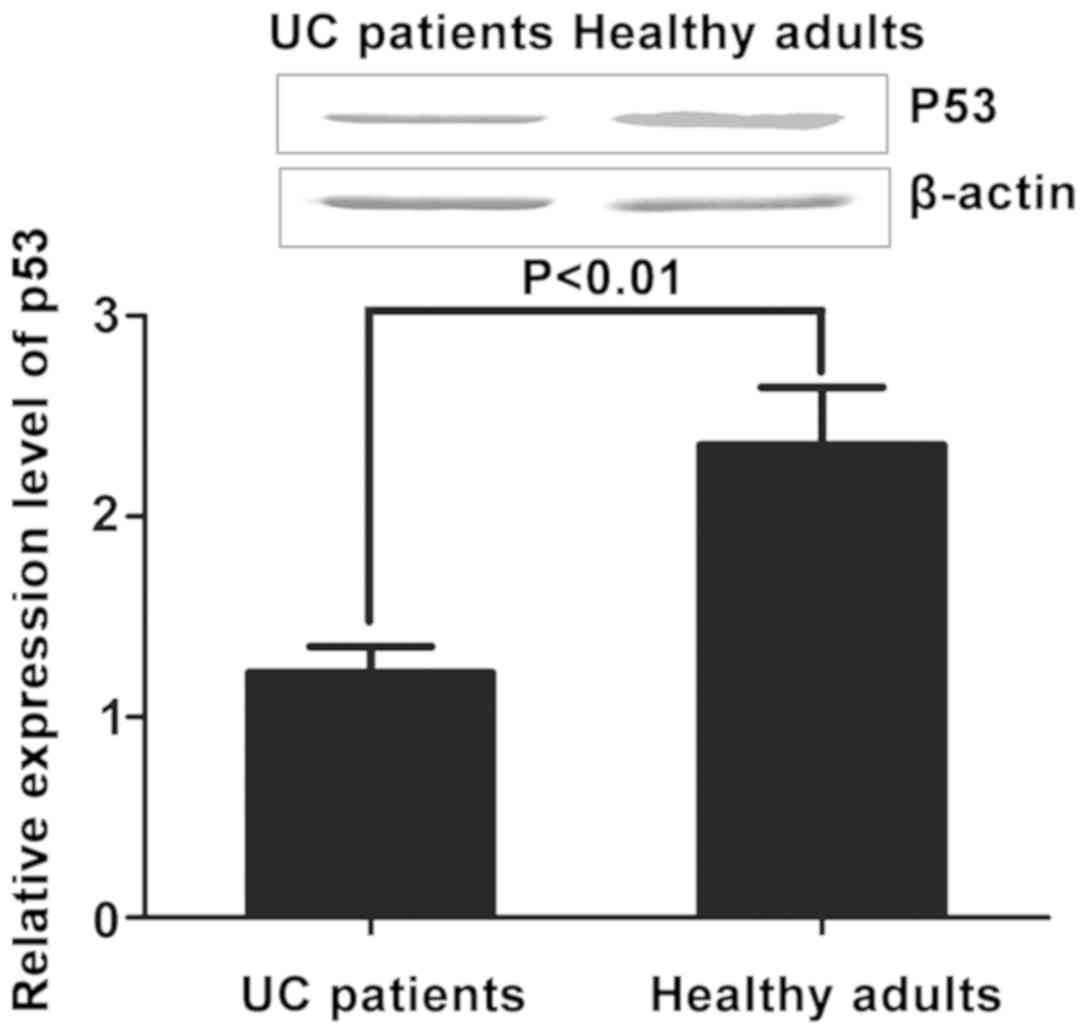
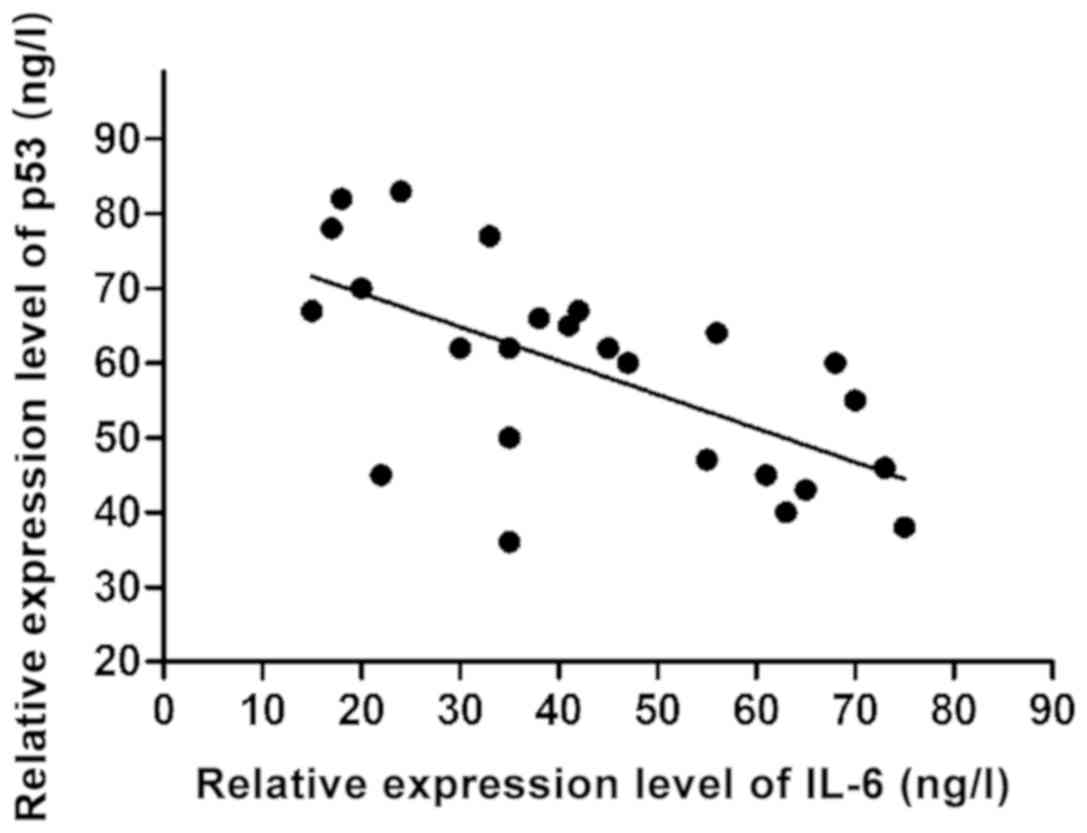
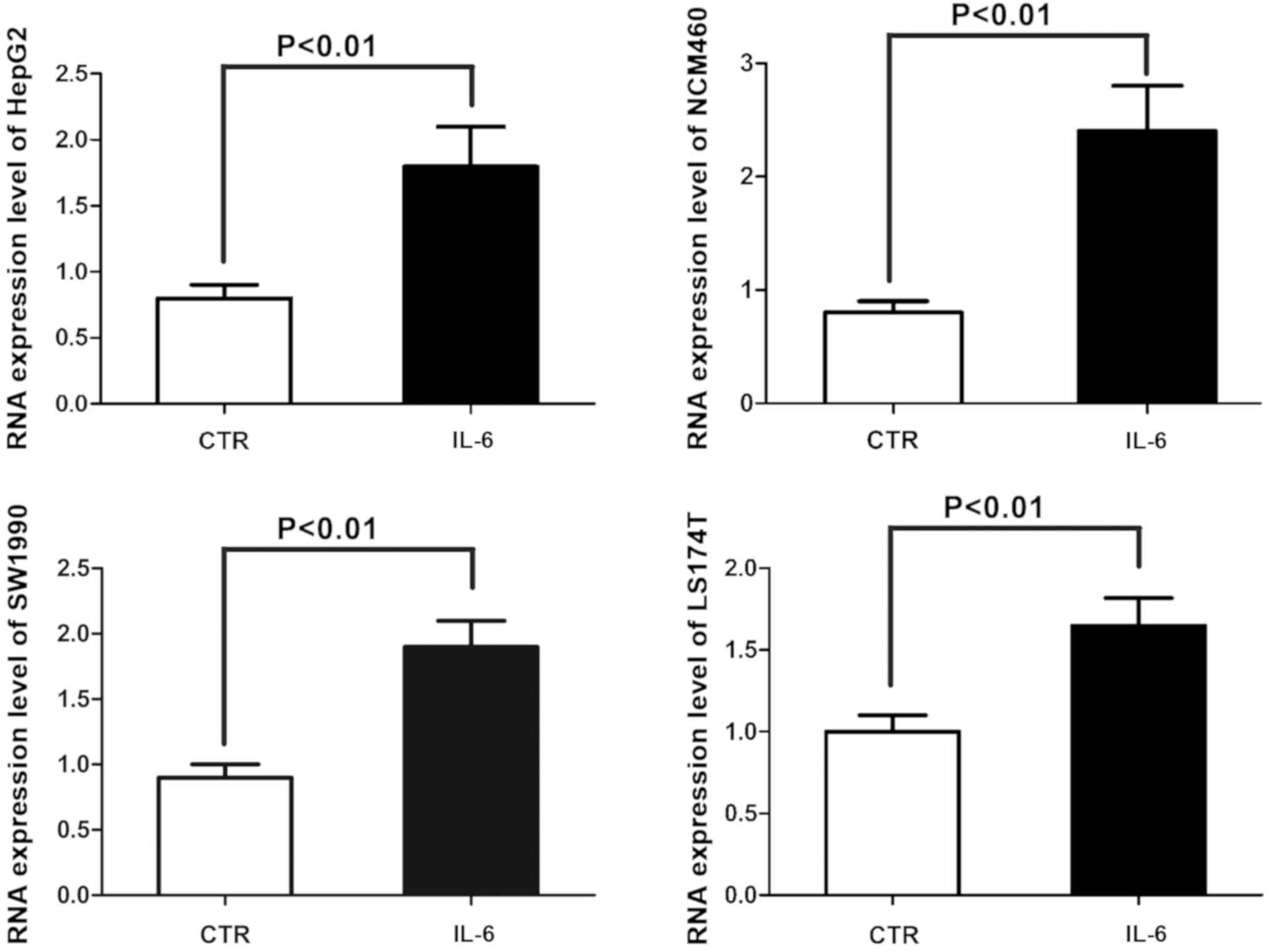
|
1
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mantovani A, Allavena P, Sica A and
Balkwill F: Cancer-related inflammation. Nature. 454:436–444. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lin WW and Karin M: A cytokine-mediated
link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J Clin
Invest. 117:1175–1183. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nakagawa H, Maeda S, Yoshida H, Tateishi
R, Masuzaki R, Ohki T, Hayakawa Y, Kinoshita H, Yamakado M, Kato N,
et al: Serum IL-6 levels and the risk for hepatocarcinogenesis in
chronic hepatitis C patients: An analysis based on gender
differences. Int J Cancer. 125:2264–2269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Terzić J, Grivennikov S, Karin E and Karin
M: Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology.
138:2101–2114.e5. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Derenzini M, Trerè D, Pession A, Montanaro
L, Sirri V and Ochs RL: Nucleolar function and size in cancer
cells. Am J Pathol. 152:1291–1297. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lennard-Jones JE: Classification of
inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. Suppl 170
(sup170):2 6, discussion. 16–19. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Faccioli S, Chieco P, Gramantieri L,
Stecca BA and Bolondi L: Cytometric measurement of cell
proliferation in echo-guided biopsies from focal lesions of the
liver. Mod Pathol. 9:120–125. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Canales RD, Luo Y, Willey JC, Austermiller
B, Barbacioru CC, Boysen C, Hunkapiller K, Jensen RV, Knight CR,
Lee KY, et al: Evaluation of DNA microarray results with
quantitative gene expression platforms. Nat Biotechnol.
24:1115–1122. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kurien BT and Scofield RH: Western
blotting. Methods. 38:283–293. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y and Lu H: Signaling to p53:
Ribosomal proteins find their way. Cancer Cell. 16:369–377. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deisenroth C and Zhang Y: Ribosome
biogenesis surveillance: Probing the ribosomal protein-Mdm2-p53
pathway. Oncogene. 29:4253–4260. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Montanaro L, Treré D and Derenzini M:
Nucleolus, ribosomes, and cancer. Am J Pathol. 173:301–310. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao C, Wang W, Yu W, Jou D, Wang Y, Ma H,
Xiao H, Qin H, Zhang C, Lü J, et al: A novel small molecule STAT3
inhibitor, LY5, inhibits cell viability, colony formation, and
migration of colon and liver cancer cells. Oncotarget.
7:12917–12926. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bollrath J, Phesse TJ, von Burstin VA,
Putoczki T, Bennecke M, Bateman T, Nebelsiek T, Lundgren-May T,
Canli O, Schwitalla S, et al: gp130-mediated Stat3 activation in
enterocytes regulates cell survival and cell-cycle progression
during colitis-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 15:91–102.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Grivennikov S, Karin E, Terzic J, Mucida
D, Yu GY, Vallabhapurapu S, Scheller J, Rose-John S, Cheroutre H,
Eckmann L, et al: IL-6 and Stat3 are required for survival of
intestinal epithelial cells and development of colitis-associated
cancer. Cancer Cell. 15:103–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park EJ, Lee JH, Yu GY, He G, Ali SR,
Holzer RG, Österreicher CH, Takahashi H and Karin M: Dietary and
genetic obesity promote liver inflammation and tumorigenesis by
enhancing IL-6 and TNF expression. Cell. 140:197–208. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He G and Karin M: NF-κB and STAT3 - key
players in liver inflammation and cancer. Cell Res. 21:159–168.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Risques RA, Lai LA, Himmetoglu C, Ebaee A,
Li L, Feng Z, Bronner MP, Al-Lahham B, Kowdley KV, Lindor KD, et
al: Ulcerative colitis-associated colorectal cancer arises in a
field of short telomeres, senescence, and inflammation. Cancer Res.
71:1669–1679. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu H, Pardoll D and Jove R: STATs in
cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat Rev
Cancer. 9:798–809. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Polyak K and Weinberg RA: Transitions
between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant
and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:265–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim S, Keku TO, Martin C, Galanko J,
Woosley JT, Schroeder JC, Satia JA, Halabi S and Sandler RS:
Circulating levels of inflammatory cytokines and risk of colorectal
adenomas. Cancer Res. 68:323–328. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|