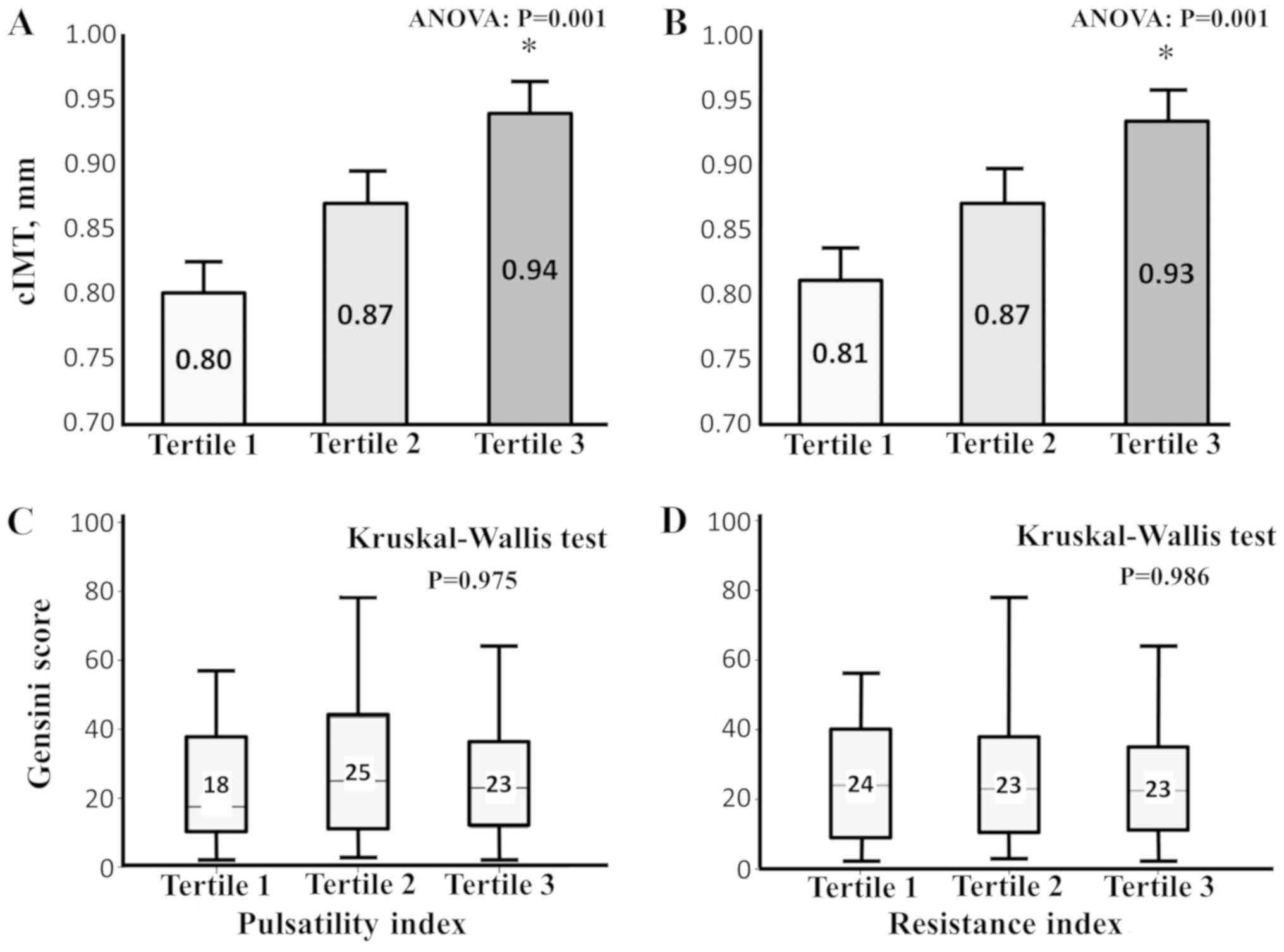
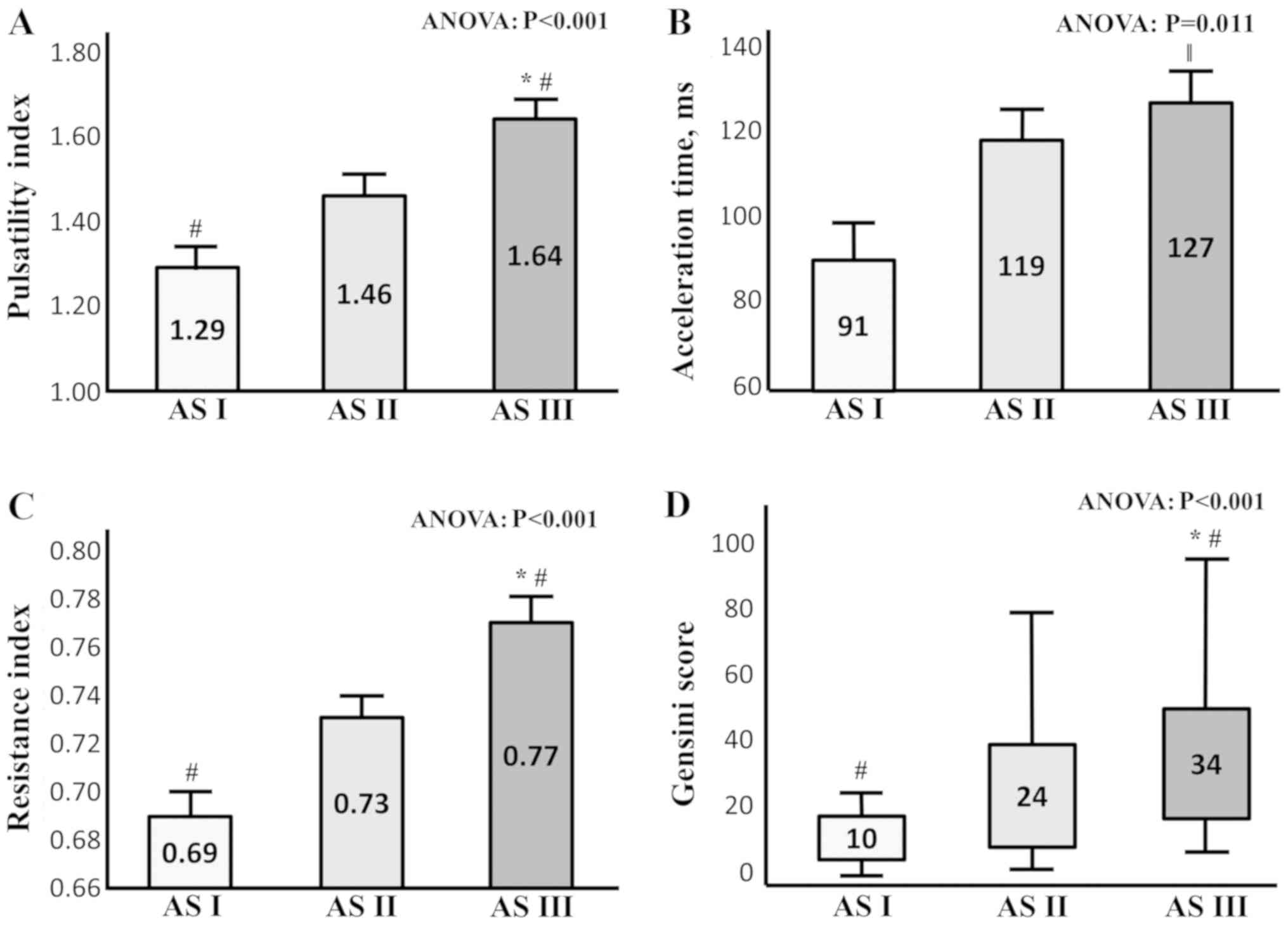
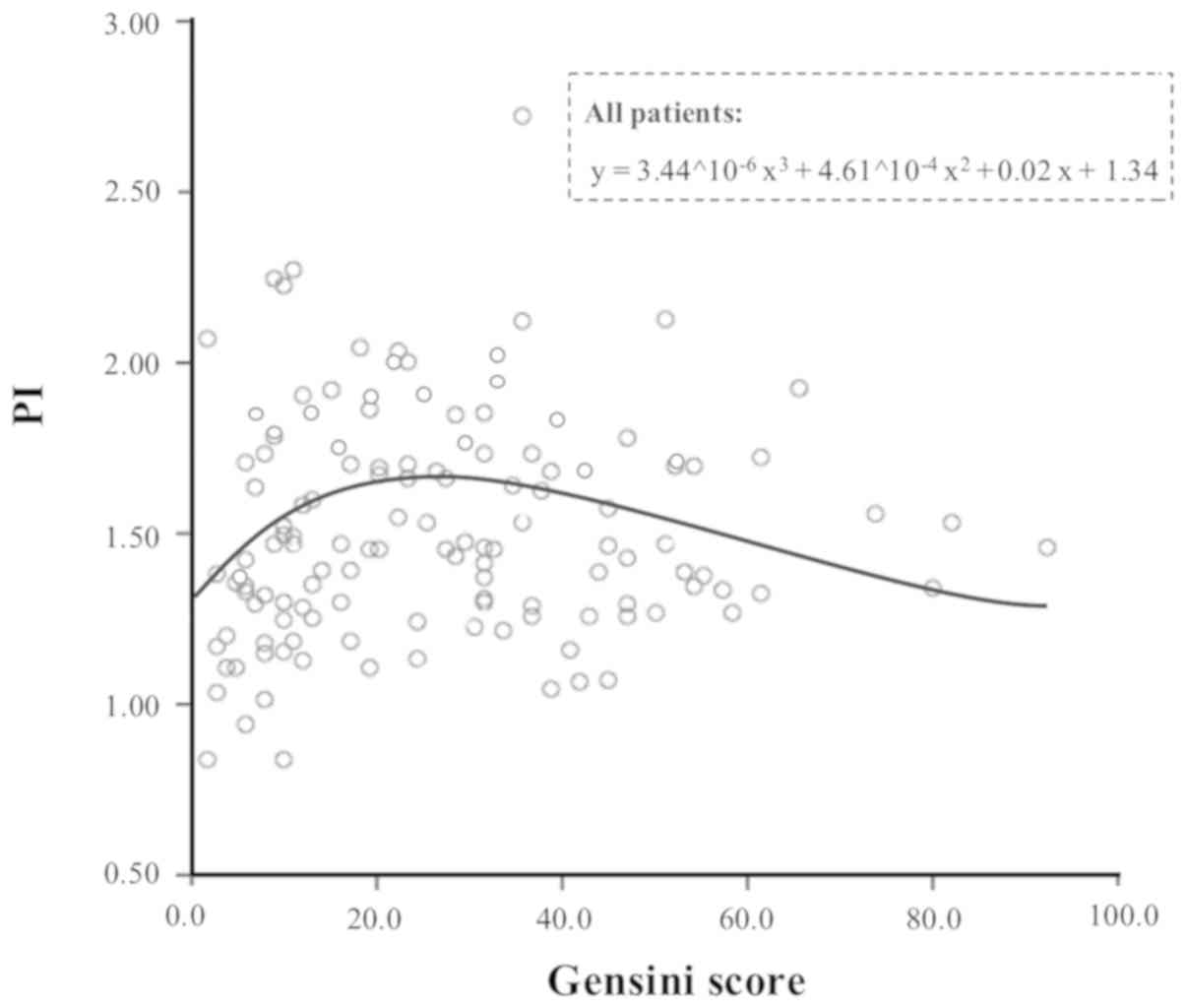
|
1
|
Huang Y, Su L, Cai X, Mai W, Wang S, Hu Y,
Wu Y, Tang H and Xu D: Association of all-cause and cardiovascular
mortality with prehypertension: A meta-analysis. Am Heart J.
167:160–168.e1. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li G, Zhang P, Wang J, An Y, Gong Q, Gregg
EW, Yang W, Zhang B, Shuai Y, Hong J, et al: Cardiovascular
mortality, all-cause mortality, and diabetes incidence after
lifestyle intervention for people with impaired glucose tolerance
in the da qing diabetes prevention study: A 23-year follow-up
study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2:474–480. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nakamura K, Nakagawa H, Murakami Y,
Kitamura A, Kiyama M, Sakata K, Tsuji I, Miura K, Ueshima H and
Okamura T; EPOCH-JAPAN research group, : Smoking increases the risk
of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with chronic
kidney disease. Kidney Int. 88:1144–1152. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nedkoff L, Knuiman M, Hung J and Briffa
TG: Long-term all-cause and cardiovascular mortality following
incident myocardial infarction in men and women with and without
diabetes: Temporal trends from 1998 to 2009. Eur J Prev Cardiol.
23:1273–1281. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xia X, He F, Wu X, Peng F, Huang F and Yu
X: Relationship between serum uric acid and all-cause and
cardiovascular mortality in patients treated with peritoneal
dialysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 64:257–264. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Capodanno D, Marcantoni C, Ministeri M,
Dipasqua F, Zanoli L, Rastelli S, Mangiafico S, Sanfilippo M,
Romano G and Tamburino C: Incorporating glomerular filtration rate
or creatinine clearance by the modification of diet in renal
disease equation or the cockcroft-gault equations to improve the
global accuracy of the age, creatinine, ejection fraction [ACEF]
score in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.
Int J Cardiol. 168:396–402. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rosei EA and Muiesan ML: Early target
organ damage and its reversibility: The heart. Clin Exp Hypertens.
26:673–687. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tublin ME, Bude RO and Platt JF: Review.
The resistive index in renal Doppler sonography: where do we stand?
AJR Am J Roentgenol. 180:885–892. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Geraci G, Mule G, Costanza G, Mogavero M,
Geraci C and Cottone S: Relationship between carotid
atherosclerosis and pulse pressure with renal hemodynamics in
hypertensive patients. Am J Hypertens. 29:519–527. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Geraci G, Mule G, Mogavero M, Geraci C,
D'Ignoti D, Guglielmo C and Cottone S: Renal haemodynamics and
severity of carotid atherosclerosis in hypertensive patients with
and without impaired renal function. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.
25:160–166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tedesco MA, Natale F, Mocerino R,
Tassinario G and Calabrò R: Renal resistive index and
cardiovascular organ damage in a large population of hypertensive
patients. J Hum Hypertens. 21:291–296. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Geraci G, Mule G, Geraci C, Mogavero M,
D'Ignoto F, Morreale M, Foraci AC and Cottone S: Association of
renal resistive index with aortic pulse wave velocity in
hypertensive patients. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 22:415–422. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mule G, Geraci G, Geraci C, Morreale M and
Cottone S: The renal resistive index: is it a misnomer? Intern
Emerg Med. 10:889–891. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Doi Y, Iwashima Y, Yoshihara F, Kamide K,
Takata H, Fujii T, Kubota Y, Nakamura S, Horio T and Kawano Y:
Association of renal resistive index with target organ damage in
essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens. 25:1292–1298.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pearce JD, Craven TE, Edwards MS, Corriere
MA, Crutchley TA, Fleming SH and Hansen KJ: Associations between
renal duplex parameters and adverse cardiovascular events in the
elderly: A prospective cohort study. Am J Kidney Dis. 55:281–290.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Toledo C, Thomas G, Schold JD, Arrigain S,
Gornik HL, Nally JV and Navaneethan SD: Renal resistive index and
mortality in chronic kidney disease. Hypertension. 66:382–388.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Doi Y, Iwashima Y, Yoshihara F, Kamide K,
Hayashi S, Kubota Y, Nakamura S, Horio T and Kawano Y: Renal
resistive index and cardiovascular and renal outcomes in essential
hypertension. Hypertension. 60:770–777. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ennezat PV, Maréchaux S, Six-Carpentier M,
Pinçon C, Sediri I, Delsart P, Gras M, Mounier-Véhier C, Gautier C,
Montaigne D, et al: Renal resistance index and its prognostic
significance in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection
fraction. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 26:3908–3913. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jashari F, Ibrahimi P, Nicoll R,
Bajraktari G, Wester P and Henein MY: Coronary and carotid
atherosclerosis: Similarities and differences. Atherosclerosis.
227:193–200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Inaba Y, Chen JA and Bergmann SR: Carotid
plaque, compared with carotid intima-media thickness, more
accurately predicts coronary artery disease events: A
meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis. 220:128–133. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Spence JD: Ultrasound measurement of
carotid plaque as a surrogate outcome for coronary artery disease.
Am J Cardiol. 89:10B–15B; discussion 15B-16B. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sinha AK, Eigenbrodt M and Mehta JL: Does
carotid intima media thickness indicate coronary atherosclerosis?
Curr Opin Cardiol. 17:526–530. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Komorovsky R and Desideri A: Carotid
ultrasound assessment of patients with coronary artery disease: A
useful index for risk stratification. Vasc Health Risk Manag.
1:131–136. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Granata A, Fiorini F, Andrulli S, Logias
F, Gallieni M, Romano G, Sicurezza E and Fiore CE: Doppler
ultrasound and renal artery stenosis: An overview. J Ultrasound.
12:133–143. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mancia G, Fagard R, Narkiewicz K, Redon J,
Zanchetti A, Böhm M, Christiaens T, Cifkova R, De Backer G,
Dominiczak A, et al: 2013 ESH/ESC guidelines for the management of
arterial hypertension: the task force for the management of
arterial hypertension of the european society of hypertension (ESH)
and of the european society of cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J.
34:2159–2219. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lang RM, Badano LP, Mor-Avi V, Afilalo J,
Armstrong A, Ernande L, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Goldstein SA,
Kuznetsova T, et al: Recommendations for cardiac chamber
quantification by echocardiography in adults: An update from the
american society of echocardiography and the european association
of cardiovascular imaging. Eur Hear J Cardiovasc Imaging.
16:233–270. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gensini GG: A more meaningful scoring
system for determining the severity of coronary heart disease. Am J
Cardiol. 51:6061983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Stergiou GS, Tzamouranis D, Protogerou A,
Nasothimiou E and Kapralos C: Validation of the microlife watch BP
office professional device for office blood pressure measurement
according to the International protocol. Blood Press Monit.
13:299–303. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL,
Castro AF III, Feldman HI, Kusek JW, Eggers P, Van Lente F, Greene
T, et al: A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate.
Ann Intern Med. 150:604–612. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nazzal MM, Hoballah JJ, Miller EV, Sharp
WJ, Kresowik TF and Corson J: Renal hilar doppler analysis is of
value in the management of patients with renovascular disease. Am J
Surg. 174:164–168. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Granata A, Zanoli L, Clementi S, Fatuzzo
P, Di Nicolò P and Fiorini F: Resistive intrarenal index: Myth or
reality? Br J Radiol. 87:201400042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Touboul PJ, Hennerici MG, Meairs S, Adams
H, Amarenco P, Bornstein N, Csiba L, Desvarieux M, Ebrahim S,
Hernandez Hernandez R, et al: Mannheim carotid intima-media
thickness and plaque consensus (2004-2006-2011). An update on
behalf of the advisory board of the 3rd, 4th and 5th watching the
risk symposia, at the 13th, 15th and 20th European stroke
conferences, Mannheim, Germany, 2004, Brussels, Belgium, 2006, and
Hamburg, Germany, 2011. Cerebrovasc Dis. 34:290–296. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Neale ML, Chambers JL, Kelly AT, Connard
S, Lawton MA, Roche J and Appleberg M: Reappraisal of duplex
criteria to assess significant carotid stenosis with special
reference to reports from the North American symptomatic carotid
endarterectomy trial and the European carotid surgery trial. J Vasc
Surg. 20:642–649. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Polak JF, Szklo M, Kronmal RA, Burke GL,
Shea S, Zavodni AE and O'Leary DH: The value of carotid artery
plaque and intima-media thickness for incident cardiovascular
disease: The multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis. J Am Heart
Assoc. 2:e0000872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wilson PW, Hoeg JM, D'Agostino RB,
Silbershatz H, Belanger AM, Poehlmann H, O'Leary D and Wolf PA:
Cumulative effects of high cholesterol levels, high blood pressure,
and cigarette smoking on carotid stenosis. N Engl J Med.
337:516–522. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Smith SC Jr, Dove JT, Jacobs AK, Kennedy
JW, Kereiakes D, Kern MJ, Kuntz RE, Popma JJ, Schaff HV, Williams
DO, et al: ACC/AHA guidelines for percutaneous coronary
intervention (revision of the 1993 PTCA guidelines)-executive
summary: A report of the American college of cardiology/American
Heart Association task force on practice guidelines (committee to
revise the 1993 guidelines for percutaneous transluminal coronary
angioplasty) endorsed by the society for cardiac angiography and
interventions. Circulation. 103:3019–3041. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Krämer B, Brill M, Brühn A and Kübler W:
Relationship between the degree of coronary artery disease and of
left ventricular function and the duration of the QT-interval in
ECG. Eur Heart J. 7:14–24. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zanoli L, Rastelli S, Marcantoni C,
Tamburino C, Laurent S, Boutouyrie P and Castellino P: Renal artery
diameter, renal function and resistant hypertension in patients
with low-to-moderate renal artery stenosis. J Hypertens.
30:600–607. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zanoli L, Rastelli S, Marcantoni C,
Capodanno D, Blanco J, Tamburino C, Laurent S, Boutouyrie P and
Castellino P: Non-hemodynamically significant renal artery stenosis
predicts cardiovascular events in persons with ischemic heart
disease. Am J Nephrol. 40:468–477. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bigé N, Lévy PP, Callard P, Faintuch JM,
Chigot V, Jousselin V, Ronco P and Boffa JJ: Renal arterial
resistive index is associated with severe histological changes and
poor renal outcome during chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol.
13:1392012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Florczak E, Januszewicz M, Januszewicz A,
Prejbisz A, Kaczmarska M, Michałowska I, Kabat M, Rywik T, Rynkun
D, Zieliński T, et al: Relationship between renal resistive index
and early target organ damage in patients with never-treated
essential hypertension. Blood Press. 18:55–61. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Granata A, Clementi A, Virzì GM, Brocca A,
de Cal M, Scarfia VR, Zanoli L, Ronco C, Corrao S and Malatino L:
Cardiorenal syndrome type 4: From chronic kidney disease to
cardiovascular impairment. Eur J Intern Med. 30:1–6. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Marcantoni C, Rastelli S, Zanoli L,
Tripepi G, Di Salvo M, Monaco S, Sgroi C, Capodanno D, Tamburino C
and Castellino P: Prevalence of renal artery stenosis in patients
undergoing cardiac catheterization. Intern Emerg Med. 8:401–408.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|