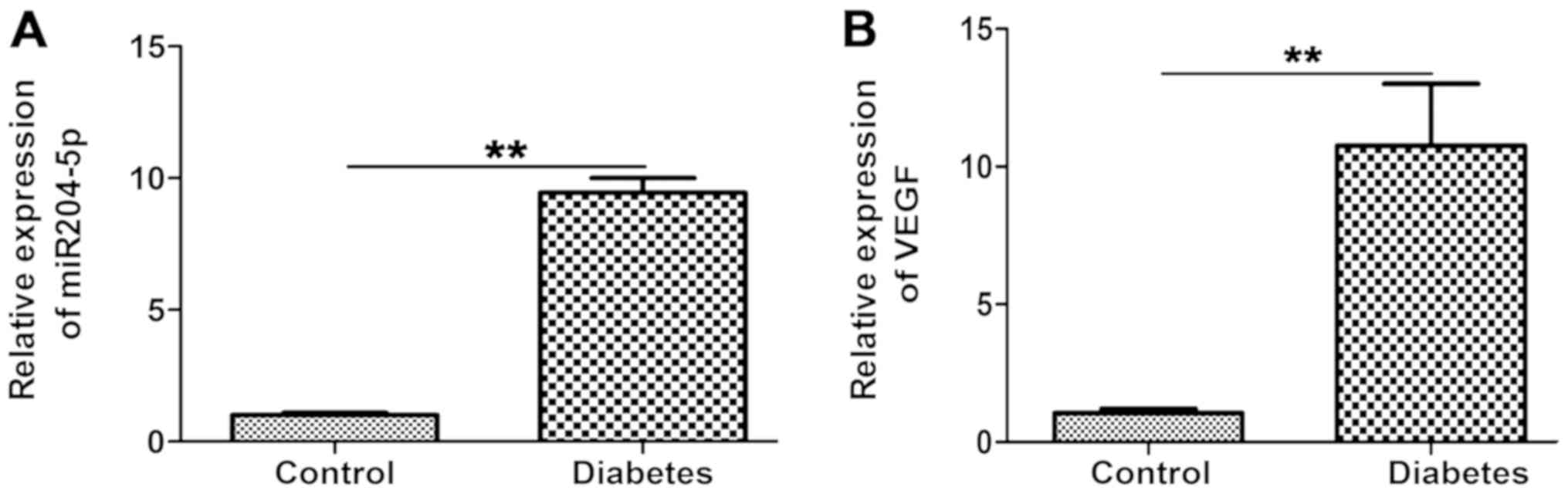
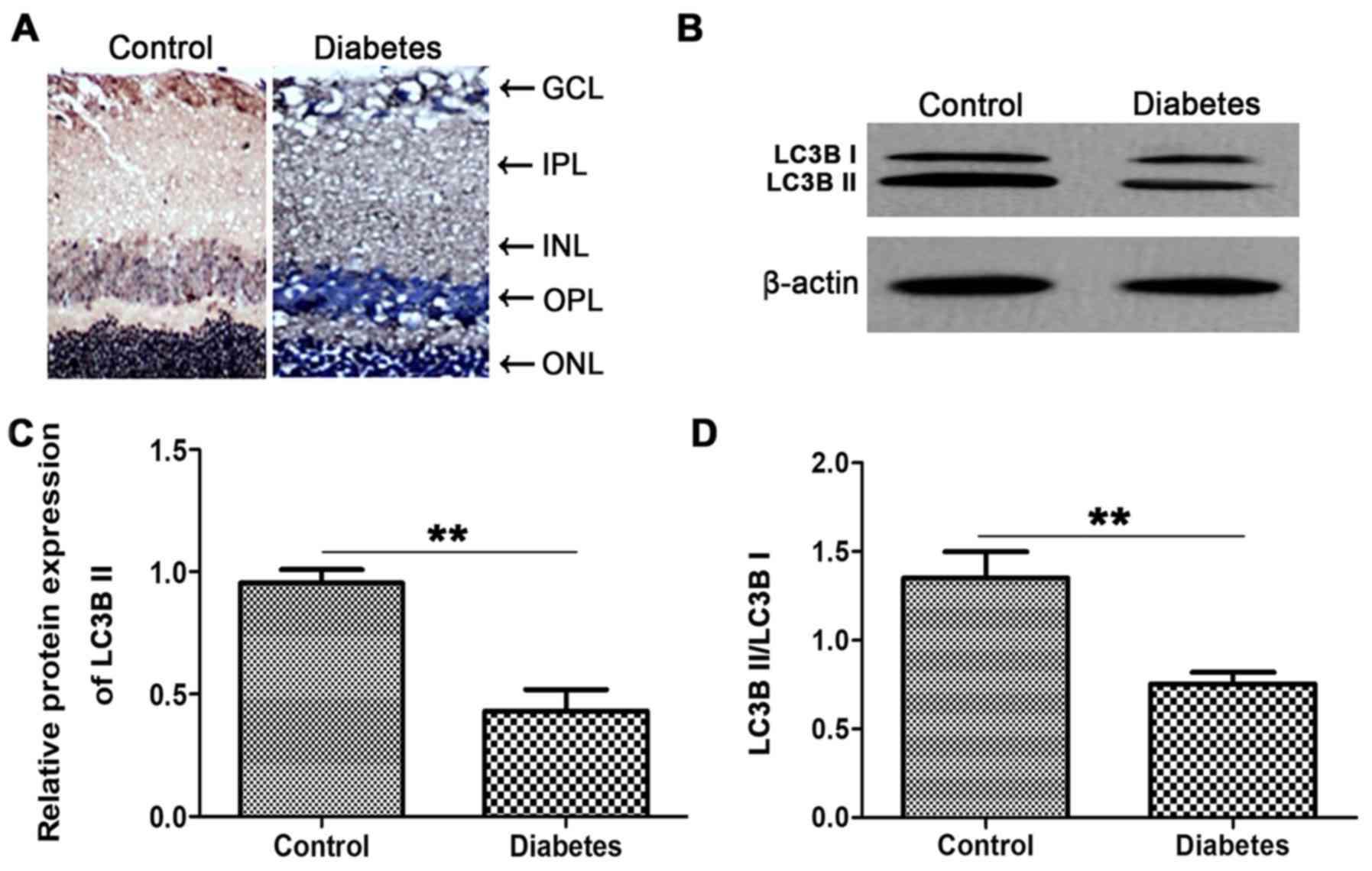
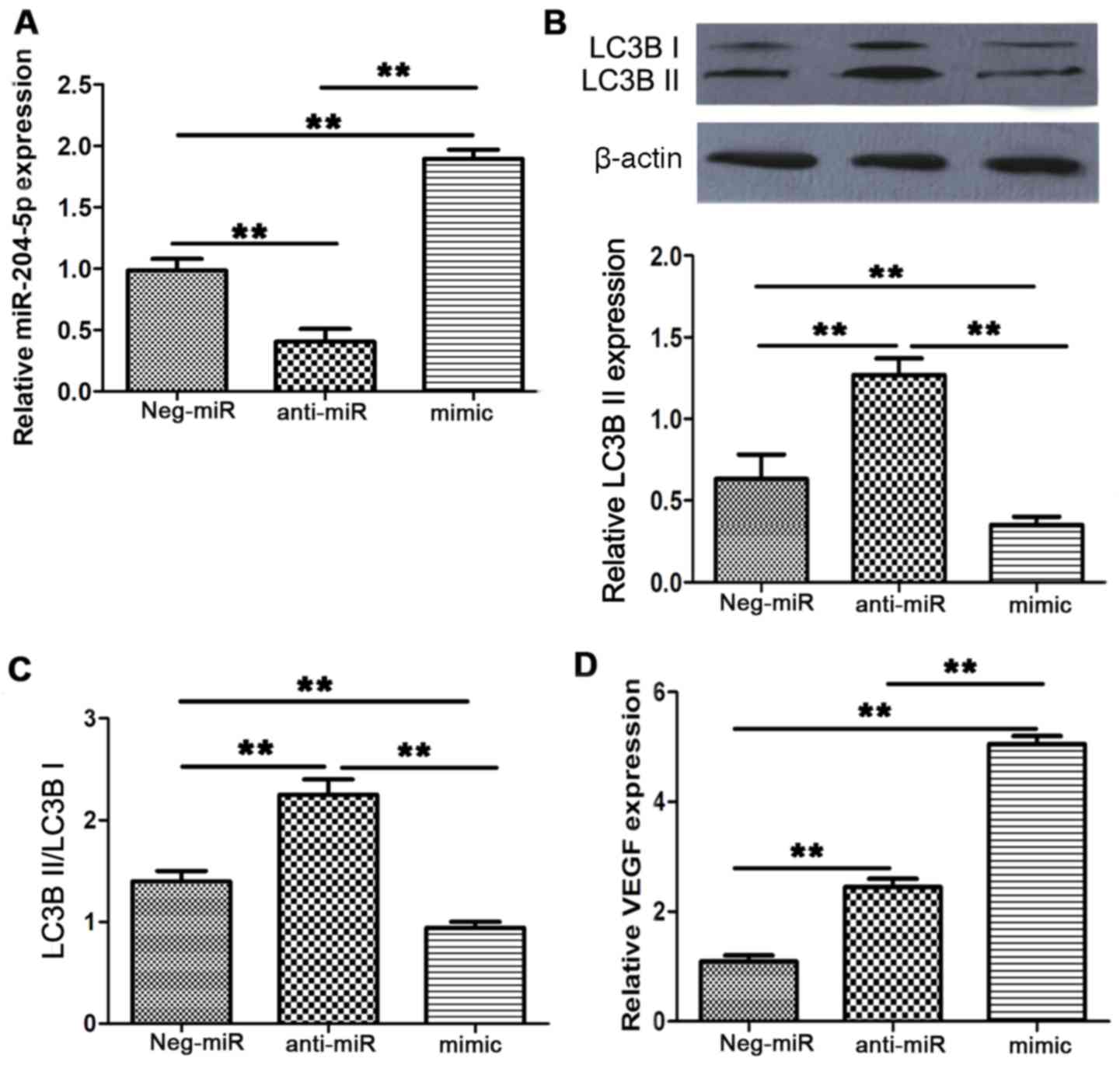
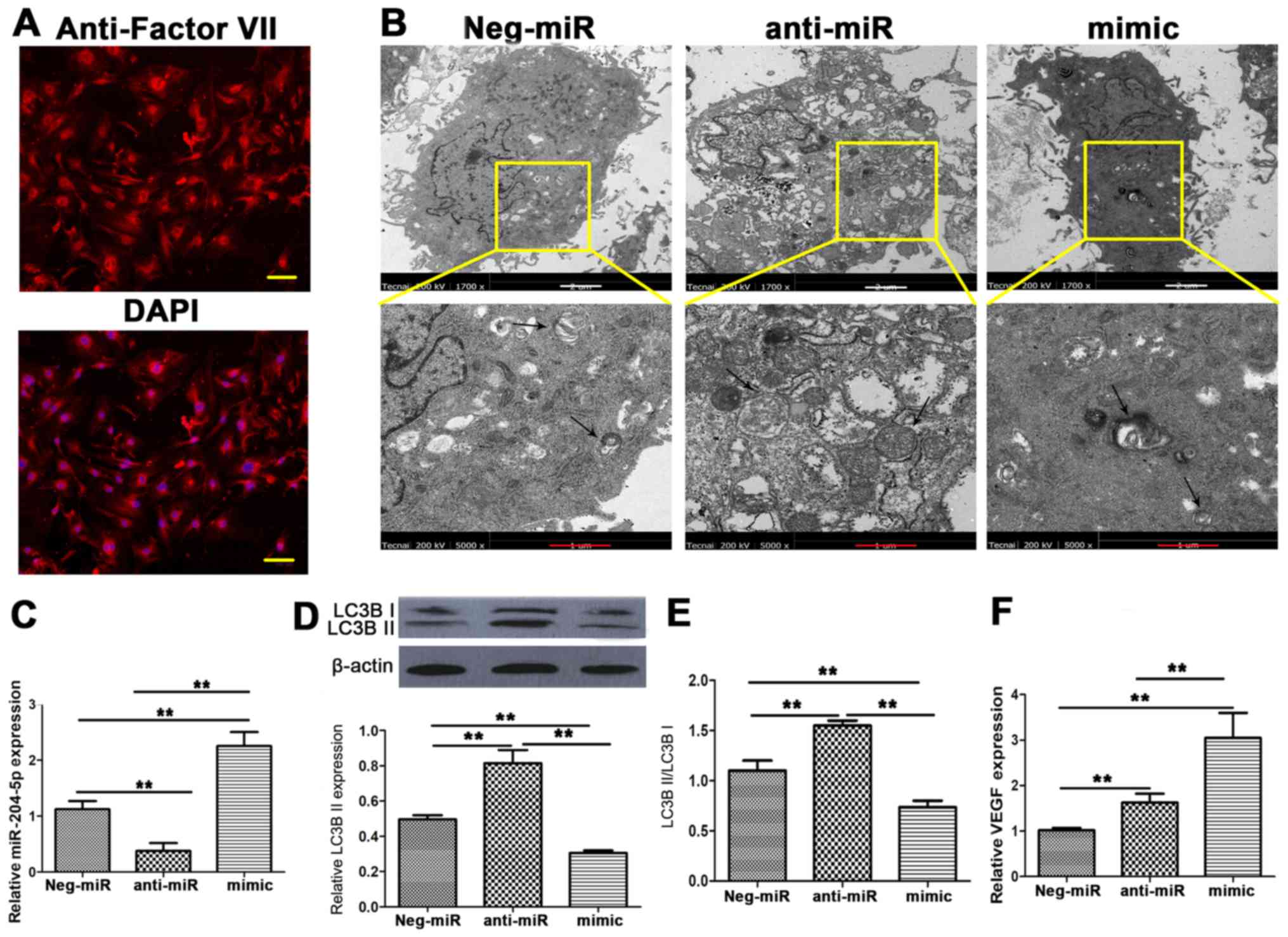
|
1
|
Santos LL, Lima FJC, Sousa-Rodrigues CF
and Barbosa FT: Use of SGLT-2 inhibitors in the treatment of type 2
diabetes mellitus. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 63:636–641. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Murchison AP, Hark L, Pizzi LT, Dai Y,
Mayro EL, Storey PP, Leiby BE and Haller JA: Non-adherence to eye
care in people with diabetes. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care.
5:e0003332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leasher JL, Bourne RR, Flaxman SR, Jonas
JB, Keeffe J, Naidoo N, Pesudovs K, Price H, White RA, Wong TY, et
al: Erratum. Global estimates on the number of people blind or
visually impaired by diabetic retinopathy: A meta-analysis from
1990–2010. Diabetes Care 2016;39:1643-1649. Diabetes Care.
39:20962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arroba AI, Campos-Caro A, Aguilar-Diosdado
M and Valverde AM: IGF-1, inflammation and retinal degeneration: A
close network. Front Aging Neurosci. 10:2032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hou L, Wei L, Zhu S, Wang J, Quan R, Li Z
and Liu J: Avian metapneumovirus subgroup C induces autophagy
through the ATF6 UPR pathway. Autophagy. 13:1709–1721. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang L, Feng D, Liu Y, Li S, Jiang L, Long
Z and Wu Y: Autophagy plays a protective role in motor neuron
degeneration following spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion-induced
spastic paralysis. Am J Transl Res. 9:4261–4270. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gao N, Wang H, Yin H and Yang Z:
Angiotensin II induces calcium-mediated autophagy in podocytes
through enhancing reactive oxygen species levels. Chem Biol
Interact. 277:110–118. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang T, Zhang L, Hu J, Duan Y, Zhang M,
Lin J, Man W, Pan X, Jiang Z, Zhang G, et al: Mst1 participates in
the atherosclerosis progression through macrophage autophagy
inhibition and macrophage apoptosis enhancement. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 98:108–116. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dehdashtian E, Mehrzadi S, Yousefi B,
Hosseinzadeh A, Reiter RJ, Safa M, Ghaznavi H and Naseripour M:
Diabetic retinopathy pathogenesis and the ameliorating effects of
melatonin; involvement of autophagy, inflammation and oxidative
stress. Life Sci. 193:20–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lopes de Faria JM, Duarte DA, Montemurro
C, Papadimitriou A, Consonni SR and Lopes de Faria JB: Defective
autophagy in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
57:4356–4366. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Alizadeh S, Mazloom H, Sadeghi A,
Emamgholipour S, Golestani A, Noorbakhsh F, Khoshniatnikoo M and
Meshkani R: Evidence for the link between defective autophagy and
inflammation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of type 2
diabetic patients. J Physiol Biochem. 74:369–379. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chandra S, Vimal D, Sharma D, Rai V, Gupta
SC and Chowdhuri DK: Role of miRNAs in development and disease:
Lessons learnt from small organisms. Life Sci. 185:8–14. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nadeem A, Ashraf MR, Javed M, Hussain T,
Tariq MS and Babar ME: Review-microRNAs: A new paradigm towards
mechanistic insight of diseases. Pak J Pharm Sci. 31:2017–2026.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gong Q, Xie J, Liu Y, Li Y and Su G:
Differentially expressed micrornas in the development of early
diabetic retinopathy. J Diabetes Res. 2017:47279422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Q, Qiu F, Zhou K, Matlock HG,
Takahashi Y, Rajala RVS, Yang Y, Moran E and Ma JX: Pathogenic role
of microRNA-21 in diabetic retinopathy through downregulation of
PPARα. Diabetes. 66:1671–1682. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Haque R, Iuvone PM, He L, Choi KSC, Ngo A,
Gokhale S, Aseem M and Park D: The MicroRNA-21 signaling pathway is
involved in prorenin receptor (PRR)-induced VEGF expression in
ARPE-19 cells under a hyperglycemic condition. Mol Vis. 23:251–262.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gomaa AR, Elsayed ET and Moftah RF:
MicroRNA-200b expression in the vitreous humor of patients with
proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmic Res. 58:168–175.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu JH, Gao Y, Ren AJ, Zhao SH, Zhong M,
Peng YJ, Shen W, Jing M and Liu L: Altered microRNA expression
profiles in retinas with diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmic Res.
47:195–201. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gao J, Wang Y, Zhao X, Chen P and Xie L:
MicroRNA-204-5p-mediated regulation of SIRT1 contributes to the
delay of epithelial cell cycle traversal in diabetic corneas.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 56:1493–1504. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Heine RJ,
Holman RR, Sherwin R and Zinman B: Management of hyperglycaemia in
type 2 diabetes: A consensus algorithm for the initiation and
adjustment of therapy. A consensus statement from the American
diabetes association and the european association for the study of
diabetes. Diab Tologia. 49:1711–1721. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rubsam A, Parikh S and Fort PE: Role of
Inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. Int J Mol Sci. 19(pii):
E9422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kaneko H and Terasaki H: Biological
involvement of MicroRNAs in proliferative vitreoretinopathy. Transl
Vis Sci Technol. 6:52017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wu D, Pan H, Zhou Y, Zhang Z, Qu P, Zhou J
and Wang W: Upregulation of microRNA-204 inhibits cell
proliferation, migration and invasion in human renal cell carcinoma
cells by downregulating SOX4. Mol Med Rep. 12:7059–7064. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu J and Li Y: Trichostatin A and
Tamoxifen inhibit breast cancer cell growth by miR-204 and ERalpha
reducing AKT/mTOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 467:242–247.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lorenzon L, Cippitelli C, Avantifiori R,
Uccini S, French D, Torrisi MR, Ranieri D, Mercantini P, Canu V,
Blandino G and Cavallini M: Down-regulated miRs specifically
correlate with non-cardial gastric cancers and Lauren's
classification system. J Surg Oncol. 116:184–194. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Palkina N, Komina A, Aksenenko M, Moshev
A, Savchenko A and Ruksha T: miR-204-5p and miR-3065-5p exert
antitumor effects on melanoma cells. Oncol Lett. 15:8269–8280.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gao W, Wu Y, He X, Zhang C, Zhu M, Chen B,
Liu Q, Qu X, Li W, Wen S and Wang B: MicroRNA-204-5p inhibits
invasion and metastasis of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma by
suppressing forkhead box C1. J Cancer. 8:2356–2368. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li H, Wang J, Liu X and Cheng Q:
MicroRNA-204-5p suppresses IL6-mediated inflammatory response and
chemokine generation in HK-2 renal tubular epithelial cells by
targeting IL6R. Biochem Cell Biol. 2018.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Volpe CMO, Villar-Delfino PH, Dos Anjos
PMF and Nogueira-Machado JA: Cellular death, reactive oxygen
species (ROS) and diabetic complications. Cell Death Dis.
9:1192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Levine B and Kroemer G: Autophagy in the
pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 132:27–42. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yoshii SR and Mizushima N: Monitoring and
measuring autophagy. Int J Mol Sci. 18(pii): E18652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li XC, Hu QK, Chen L, Liu SY, Su S, Tao H,
Zhang LN, Sun T and He LJ: HSPB8 promotes the fusion of
autophagosome and lysosome during autophagy in diabetic neurons.
Int J Med Sci. 14:1335–1341. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cai X, Li J, Wang M, She M, Tang Y, Li H
and Hui H: GLP-1 treatment improves diabetic retinopathy by
alleviating autophagy through GLP-1R-ERK1/2-HDAC6 signaling
pathway. Int J Med Sci. 14:1203–1212. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kobayashi S, Xu X, Chen K and Liang Q:
Suppression of autophagy is protective in high glucose-induced
cardiomyocyte injury. Autophagy. 8:577–592. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rodrigues M, Xin X, Jee K,
Babapoor-Farrokhran S, Kashiwabuchi F, Ma T, Bhutto I, Hassan SJ,
Daoud Y, Baranano D, et al: VEGF secreted by hypoxic muller cells
induces MMP-2 expression and activity in endothelial cells to
promote retinal neovascularization in proliferative diabetic
retinopathy. Diabetes. 62:3863–3873. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nishijima K, Ng YS, Zhong L, Bradley J,
Schubert W, Jo N, Akita J, Samuelsson SJ, Robinson GS, Adamis AP
and Shima DT: Vascular endothelial growth factor-A is a survival
factor for retinal neurons and a critical neuroprotectant during
the adaptive response to ischemic injury. Am J Pathol. 171:53–67.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gilbert RE, Vranes D, Berka JL, Kelly DJ,
Cox A, Wu LL, Stacker SA and Cooper ME: Vascular endothelial growth
factor and its receptors in control and diabetic rat eyes. Lab
Invest. 78:1017–1027. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bai Y, Ma JX, Guo J, Wang J, Zhu M, Chen Y
and Le YZ: Muller cell-derived VEGF is a significant contributor to
retinal neovascularization. J Pathol. 219:446–454. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|