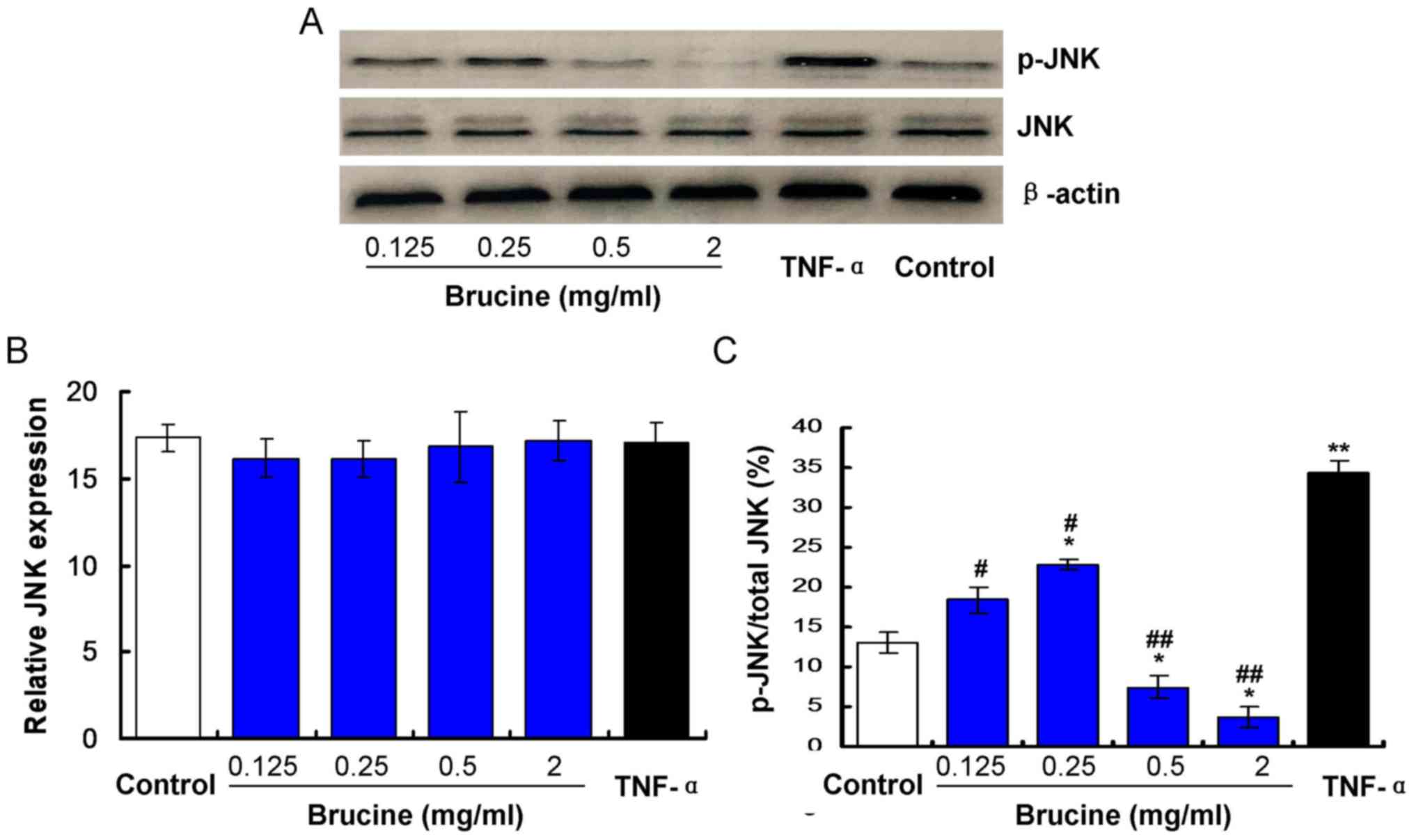
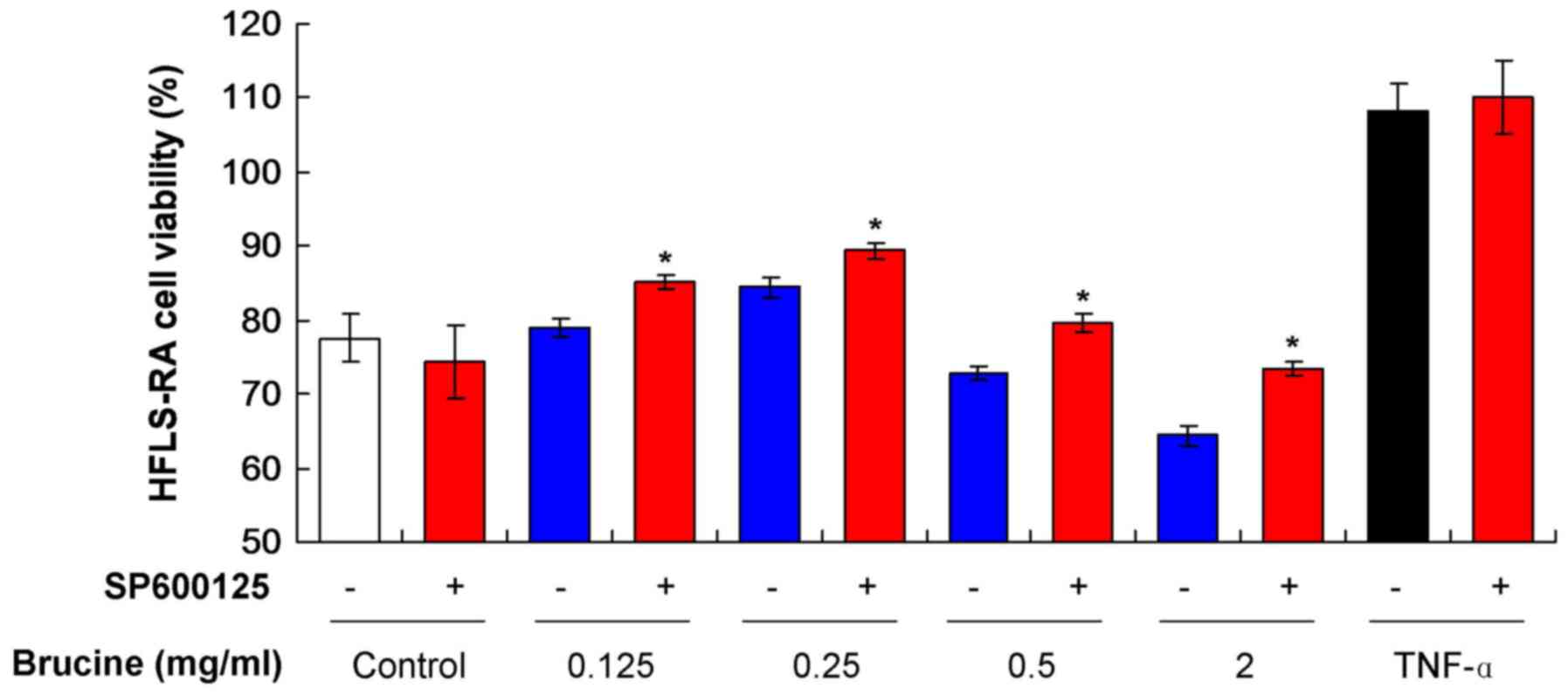
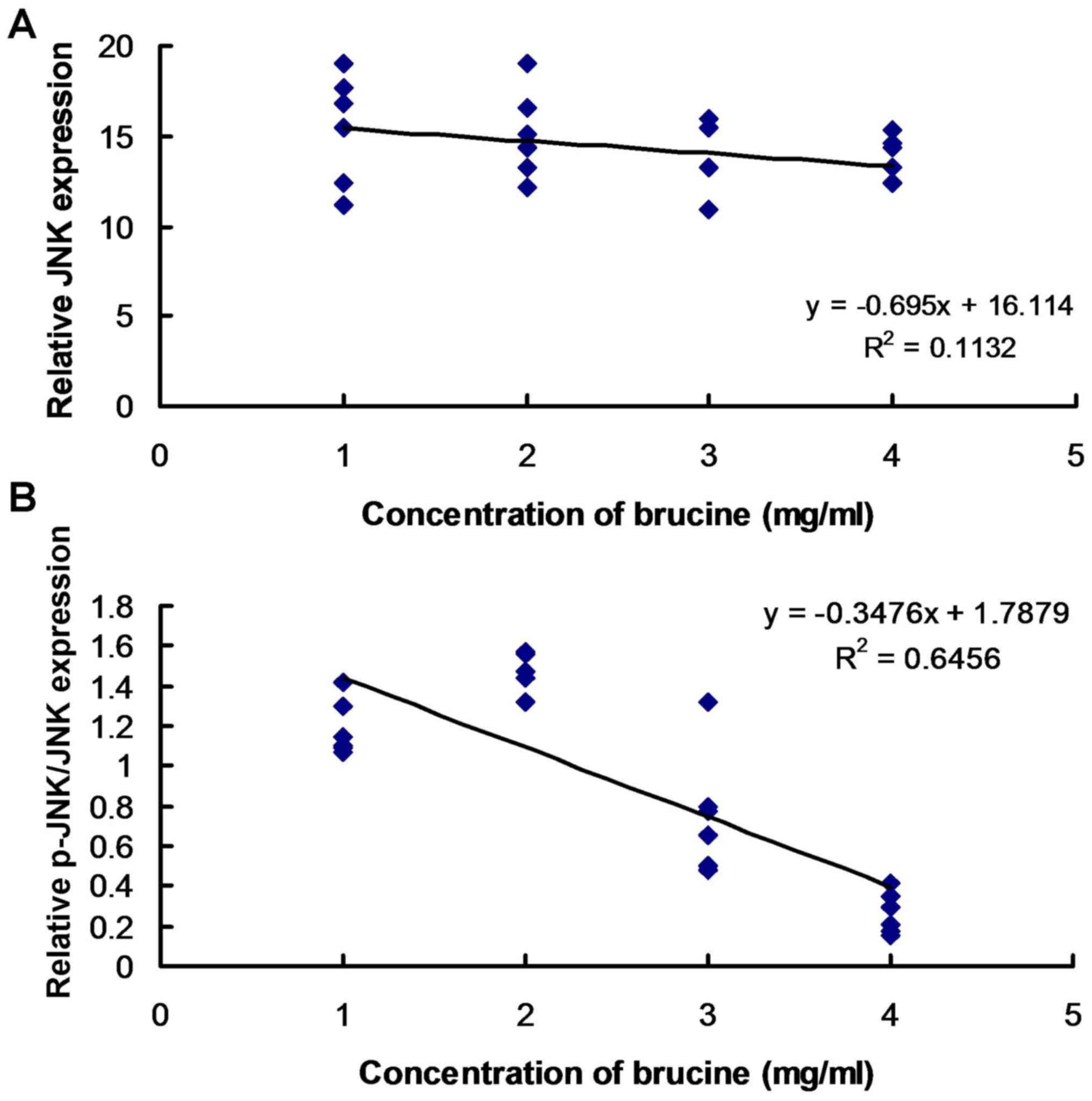
|
1
|
Muraki Y, Mizuno S, Nakatani K,
Wakabayashi H, Ishikawa E, Araki T, Taniguchi A, Isaji S and Okuda
M: Monitoring of peripheral blood cluster of differentiation
4+ adenosine triphosphate activity and CYP3A5 genotype
to determine the pharmacokinetics, clinical effects and
complications of tacrolimus in patients with autoimmune diseases.
Exp Ther Med. 15:532–538. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shiraishi T, Ishimoto H, Akata K, Kawanami
T, Yatera K and Mukae H: An autopsy case report of adult T-cell
leukemia accompanied by rheumatoid arthritis mimicking diffuse
panbronchiolitis. J UOEH. 39:55–61. 2017.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
van den Bemt BJ, Zwikker HE and van den
Ende CH: Medication adherence in patients with rheumatoid
arthritis: A critical appraisal of the existing literature. Expert
Rev Clin Immunol. 8:337–351. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen J, Qu Y, Wang D, Peng P, Cai H, Gao
Y, Chen Z and Cai B: Pharmacological evaluation of total alkaloids
from nux vomica: Effect of reducing strychnine contents.
Molecules. 19:4395–4408. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shu G, Mi X, Cai J, Zhang X, Yin W, Yang
X, Li Y, Chen L and Deng X: Brucine, an alkaloid from seeds of
Strychnos nux-vomica Linn., represses hepatocellular
carcinoma cell migration and metastasis: The role of hypoxia
inducible factor 1 pathway. Toxicol Lett. 222:91–101. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rao PS and Prasad MN: Strychnos
nux-vomica root extract induces apoptosis in the human multiple
myeloma cell line-U266B1. Cell Biochem Biophys. 66:443–450. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bhati R, Singh A, Saharan VA, Ram V and
Bhandari A: Strychnos nux-vomica seeds: Pharmacognostical
standardization, extraction, and antidiabetic activity. J Ayurveda
Integr Med. 3:80–84. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu P, Liang Q, Feng P, Li C, Yang C, Liang
H, Tang H and Shuai C: A novel brucine gel transdermal delivery
system designed for anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities. Int
J Mol Sci. 18:E7572017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qin JM, Yin PH, Li Q, Sa ZQ, Sheng X, Yang
L, Huang T, Zhang M, Gao KP, Chen QH, et al: Anti-tumor effects of
brucine immuno-nanoparticles on hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Nanomedicine. 7:369–379. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jakubík J, Krejcí A and Dolezal V:
Asparagine, valine, and threonine in the third extracellular loop
of muscarinic receptor have essential roles in the positive
cooperativity of strychnine-like allosteric modulators. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 313:688–696. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yin W, Wang TS, Yin FZ and Cai BC:
Analgesic and anti-inflammatory properties of brucine and brucine
N-oxide extracted from seeds of Strychnos nux-vomica. J
Ethnopharmacol. 88:205–214. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang J, Zhao F and Nie J: Anti-rheumatic
effects of Aconitum leucostomum Worosch. on human fibroblast-like
synoviocyte rheumatoid arthritis cells. Exp Ther Med. 14:453–460.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pan F, Zhu L, Lv H and Pei C: Quercetin
promotes the apoptosis of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in
rheumatoid arthritis by upregulating lncRNA MALAT1. Int J Mol Med.
38:1507–1514. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li H, Lei M, Yu C, Lv Y, Song Y and Yang
L: Mechano growth factor-E regulates apoptosis and inflammatory
responses in fibroblast-like synoviocytes of knee osteoarthritis.
Int Orthop. 39:2503–2509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kadkhoda Z, Amirzargar A, Esmaili Z,
Vojdanian M and Akbari S: Effect of TNF-α blockade in gingival
crevicular fluid on periodontal condition of patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. Iran J Immunol. 13:197–203. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Harigai M, Hara M, Kawamoto M, Kawaguchi
Y, Sugiura T, Tanaka M, Nakagawa M, Ichida H, Takagi K,
Higami-Ohsako S, et al: Amplification of the synovial inflammatory
response through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases
and nuclear factor kappaB using ligation of CD40 on CD14+ synovial
cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
50:2167–2177. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo W, Wang X, Zheng L, Zhan Y, Zhang D,
Zhang J and Zhang Y: Brucine suppresses colon cancer cells growth
via mediating KDR signaling pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 17:1316–3124.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Deng XK, Yin W, Li WD, Yin FZ, Lu XY,
Zhang XC, Hua ZC and Cai BC: The anti-tumor effects of alkaloids
from the seeds of Strychnos nux-vomica on HepG2 cells and
its possible mechanism. J Ethnopharmacol. 106:179–186. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Agrawal SS, Saraswati S, Mathur R and
Pandey M: Cytotoxic and antitumor effects of brucine on Ehrlich
ascites tumor and human cancer cell line. Life Sci. 89:147–158.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xin F, Wei W, Ji AF, Shen XL, Zhang GX,
Zhang MX, Li XX and Zhang HY: Inducing-apoptosis effect of brucine
on human monocytic leukemia cell line THP-1 and its mechanism.
Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 22:681–686. 2014.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zuo J, Xia Y, Li X, Ou-Yang Z and Chen JW:
Selective modulation of MAPKs contribute to the anti-proliferative
and anti-inflammatory activities of
1,7-dihydroxy-3,4-dimethoxyxanthone in rheumatoid arthritis-derived
fibroblast-like synoviocyte MH7A cells. J Ethnopharmacol.
168:248–254. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pan JX: LncRNA H19 promotes
atherosclerosis by regulating MAPK and NF-kB signaling pathway. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:322–328. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Knies N, Alankus B, Weilemann A, Tzankov
A, Brunner K, Ruff T, Kremer M, Keller UB, Lenz G and Ruland J:
Lymphomagenic CARD11/BCL10/MALT1 signaling drives malignant B-cell
proliferation via cooperative NF-κB and JNK activation. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 112:E7230–E7238. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|