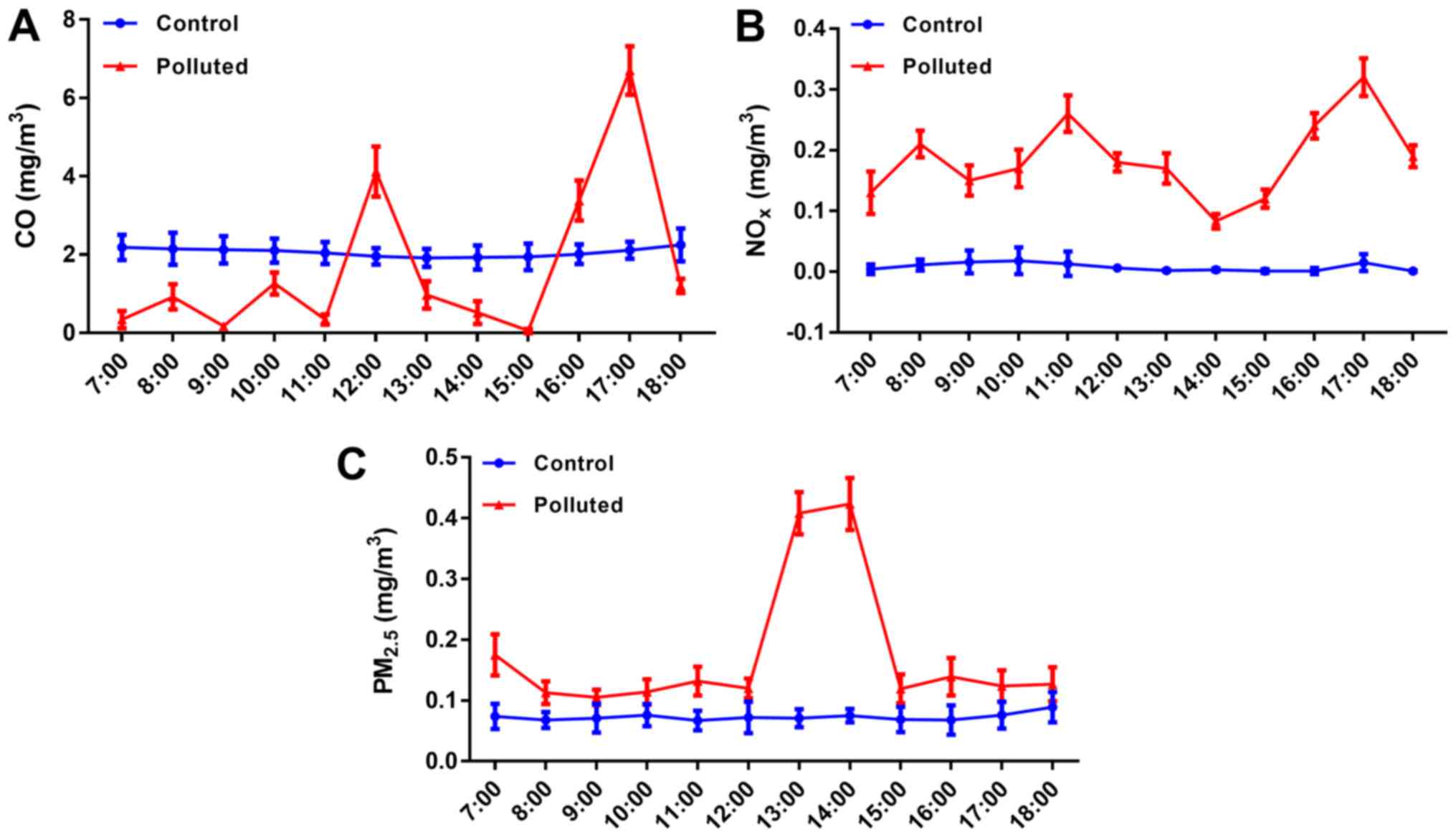
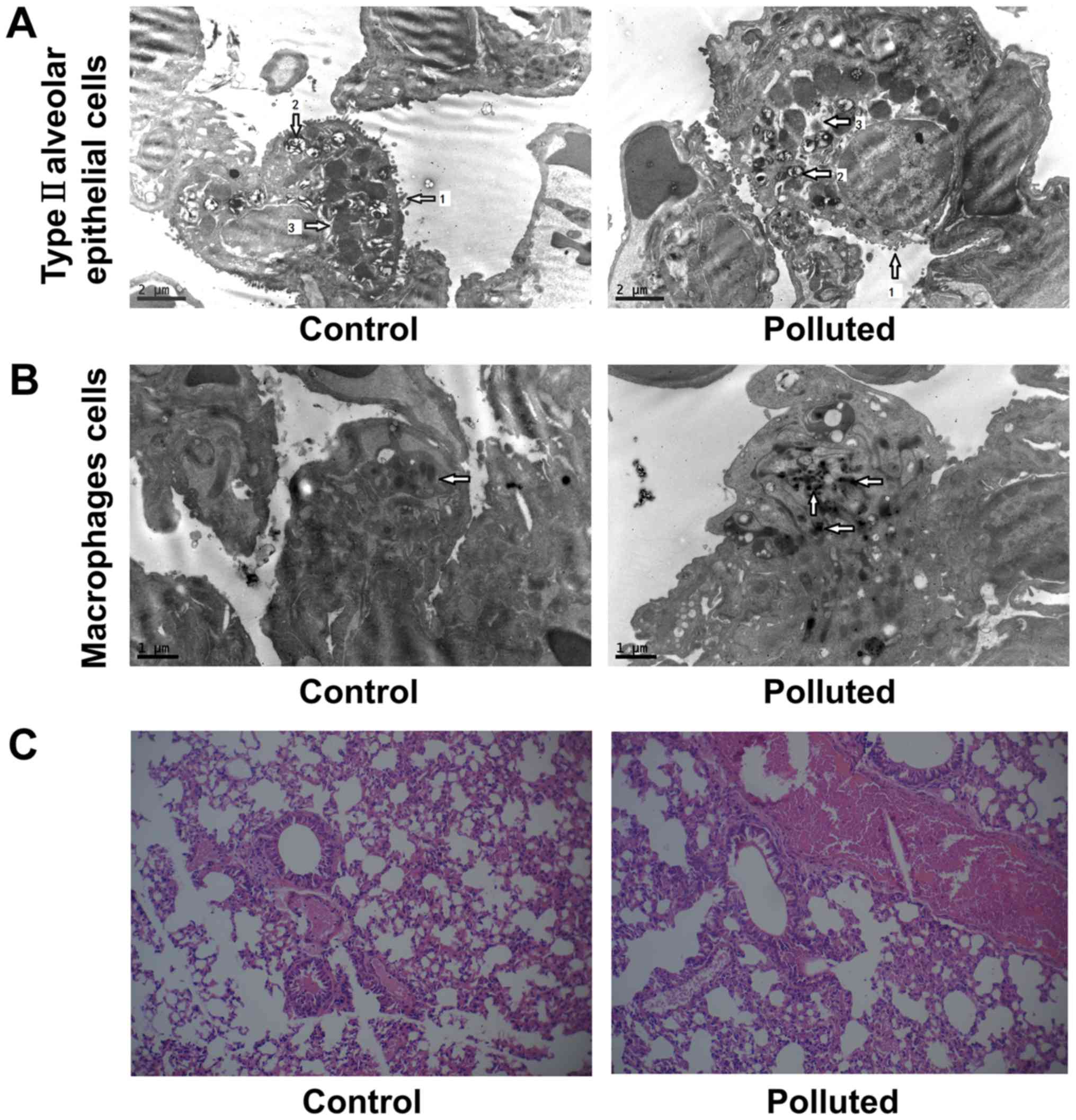
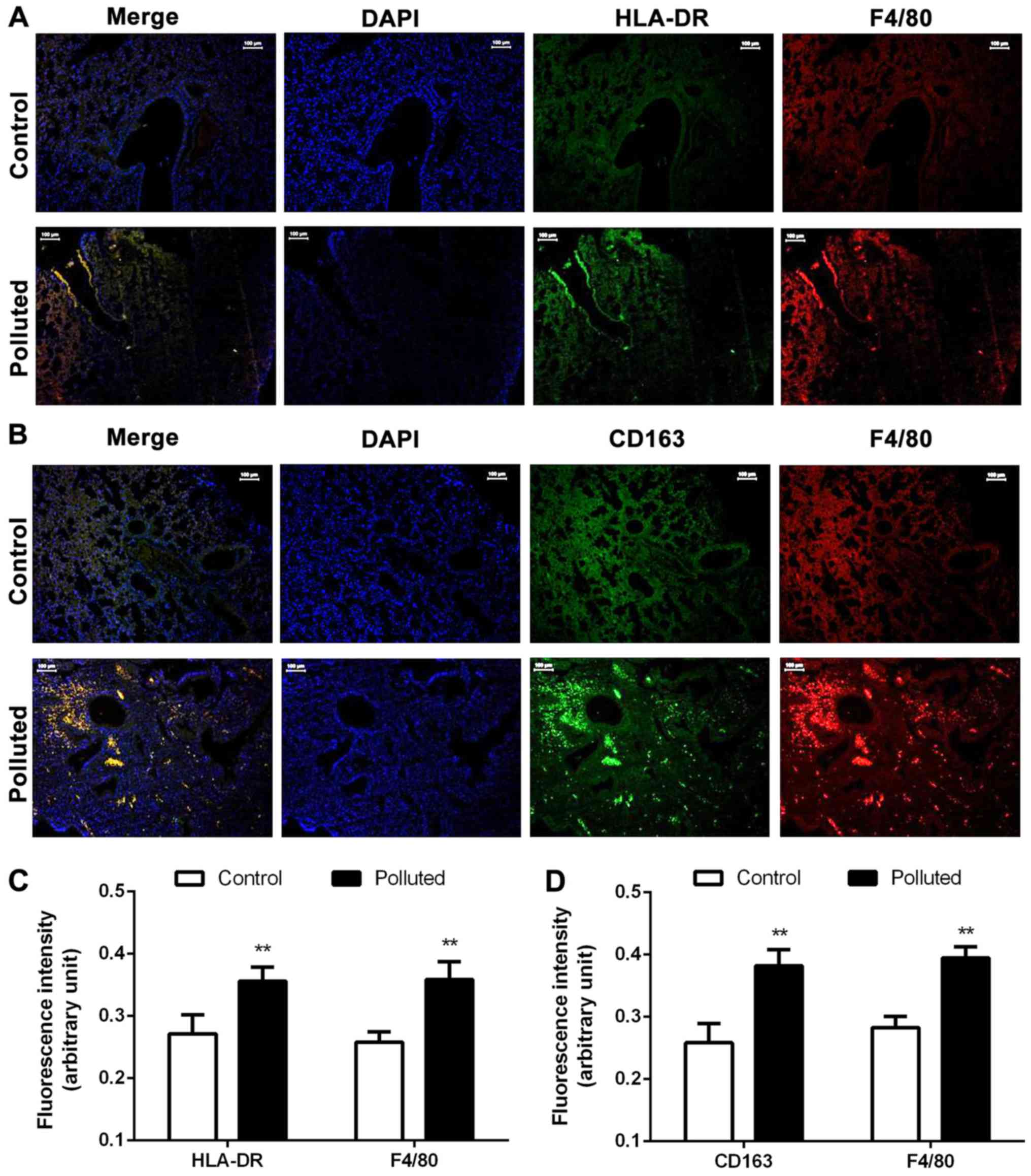
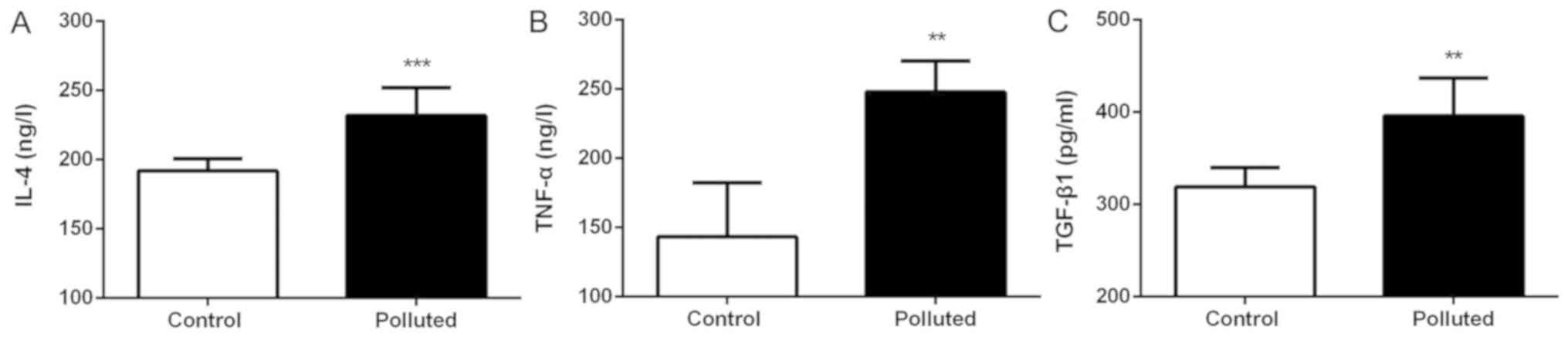
|
1
|
Brown MJ, Williams MD, Nelson MA and
Werley KA: QUIC transport and dispersion modeling of vehicle
emissions in cities for better public health assessments. Environ
Health Insights. 9 (Suppl 1):S55–S65. 2016.
|
|
2
|
Guan WJ, Zheng XY, Chung KF and Zhong NS:
Impact of air pollution on the burden of chronic respiratory
diseases in China: Time for urgent action. Lancet. 388:1939–1951.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pandey P, Patel DK, Khan AH, Barman SC,
Murthy RC and Kisku GC: Temporal distribution of fine particulates
(PM(2).(5):PM(1)(0)), potentially toxic metals, PAHs and
Metal-bound carcinogenic risk in the population of Lucknow City,
India. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng.
48:730–745. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Volk HE, Lurmann F, Penfold B,
Hertz-Picciotto I and McConnell R: Traffic-related air pollution,
particulate matter, and autism. JAMA Psychiatry. 70:71–77. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zielinska B, Sagebiel J, McDonald JD,
Whitney K and Lawson DR: Emission rates and comparative chemical
composition from selected in-use diesel and gasoline-fueled
vehicles. J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 54:1138–1150. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ezzati M, Lopez AD, Rodgers A, Vander
Hoorn S and Murray CJ; Comparative Risk Assessment Collaborating
Group, : Selected major risk factors and global and regional burden
of disease. Lancet. 360:1347–1360. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
IARC monographs on the evaluation of
carcinogenic risks to humans, . Diesel and gasoline engine exhausts
and some nitroarenes. International Agency for Research on Cancer.
IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 46:1–458. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Su R, Jin X, Zhang W, Li Z, Liu X and Ren
J: Particulate matter exposure induces the autophagy of macrophages
via oxidative stress-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Chemosphere.
167:444–453. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mitkus RJ, Powell JL, Zeisler R and Squibb
KS: Comparative physicochemical and biological characterization of
NIST interim reference material PM2.5 and SRM 1648 in human A549
and mouse RAW264.7 cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 27:2289–2298. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu XC, Li YJ, Wang YJ, Li Q, Yang Q, Weng
XG, Chen Ying, Cai WY, Guo Y, Kan XX, et al: Protection of Shenlian
extracts to PM2.5 infected RAW 264.7 cell damage. Zhongguo Zhong
Yao Za Zhi. 40:1977–1983. 2015.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yanamala N, Hatfield MK, Farcas MT,
Schwegler-Berry D, Hummer JA, Shurin MR, Birch ME, Gutkin DW, Kisin
E, Kagan VE, et al: Biodiesel versus diesel exposure: Enhanced
pulmonary inflammation, oxidative stress, and differential
morphological changes in the mouse lung. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
272:373–383. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhou H and Fan X: Changes of
Ca~(2+)-ATPase activity and oxygen free radicals in microsome
membranes of postharvest peach fruit. Acta Botanica
Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica. 27:1161–1166. 2007.
|
|
13
|
Libalova H, Uhlířová K, Kléma J, Machala
M, Šrám RJ, Ciganek M and Topinka J: Global gene expression changes
in human embryonic lung fibroblasts induced by organic extracts
from respirable air particles. Part Fibre Toxicol. 9:12012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dagher Z, Garçon G, Gosset P, Ledoux F,
Surpateanu G, Courcot D, Aboukais A, Puskaric E and Shirali P:
Pro-inflammatory effects of Dunkerque city air pollution
particulate matter 2.5 in human epithelial lung cells (L132) in
culture. J Appl Toxicol. 25:166–175. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xie Y, Zhang X, Tian Z, Jiang R, Chen R,
Song W and Zhao J: Preexposure to PM2.5 exacerbates acute viral
myocarditis associated with Th17 cell. Int J Cardiol.
168:3837–3845. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Furuyama A, Hirano S, Koike E and
Kobayashi T: Induction of oxidative stress and inhibition of
plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 production in endothelial cells
following exposure to organic extracts of diesel exhaust particles
and urban fine particles. Arch Toxicol. 80:154–162. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Furuyama A and Mochitate K: Hepatocyte
growth factor inhibits the formation of the basement membrane of
alveolar epithelial cells in vitro. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 286:L939–L946. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nerriere E, Zmirou-Navier D, Blanchard O,
Momas I, Ladner J, Le Moullec Y, Personnaz MB, Lameloise P, Delmas
V, Target A and Desqueyroux H: Can we use fixed ambient air
monitors to estimate population long-term exposure to air
pollutants? The case of spatial variability in the Genotox ER
study. Environ Res. 97:32–42. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hystad P, Demers PA, Johnson KC, Carpiano
RM and Brauer M: Long-term residential exposure to air pollution
and lung cancer risk. Epidemiology. 24:762–772. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Y, et al: Study on the morphological
changes of the rats' lung caused by exhausting of gasoline engine.
Xian Dai Yu Fang Yi Xue. 39:1349–1354. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
21
|
Ali BH, Al Za'abi M, Shalaby A, Manoj P,
Waly MI, Yasin J, Fahim M and Nemmar A: The effect of thymoquinone
treatment on the combined renal and pulmonary toxicity of cisplatin
and diesel exhaust particles. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
240:1698–1707. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Akopian AN, Fanick ER and Brooks EG: TRP
channels and traffic-related environmental pollution-induced
pulmonary disease. Semin Immunopathol. 38:331–338. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang J, Chen Y, Yu Z, Ding H and Ma Z:
Changes in gene expression in lungs of mice exposed to
traffic-related air pollution. Mol Cell Probes. 39:33–40. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li C, Shi M, Li S, Bai Z and Wang Z:
Combined use of land use regression and BenMAP for estimating
public health benefits of reducing PM 2.5 in Tianjin, China.
Atmospheric Environ. 152:16–23. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen Y, et al: A study on effect of
automobile exhaust pollutants in underground parking area on serum
inflammatory cytokines of mice. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Ji Jiu Za Zhi
2013. 353–356. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Wang G, Zhen L, Lü P, Jiang R and Song W:
Effects of ozone and fine particulate matter (PM2.5) on rat cardiac
autonomic nervous system and systemic inflammation. Wei Sheng Yan
Jiu. 42:554–560. 2013.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pei Y, Jiang R, Zou Y, Wang Y, Zhang S,
Wang G, Zhao J and Song W: Effects of fine particulate matter
(PM2.5) on systemic oxidative stress and cardiac function in
ApoE(−/−) mice. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 13:E4842016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang H, An J, Cheng M, Shen L, Zhu B, Li
Y, Wang Y, Duan Q, Sullivan A and Xia L: One year online
measurements of water-soluble ions at the industrially polluted
town of Nanjing, China: Sources, seasonal and diurnal variations.
Chemosphere. 148:526–536. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao G, Li S, Hong G, Li M, Wu B, Qiu Q
and Lu Z: The effect of resveratrol on paraquat-induced acute lung
injury in mice and its mechanism. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi
Xue. 28:33–37. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun CZ, Shen H, He XW, Bao L, Song Y,
Zhang Z and Qin HD: Effect of dobutamine on lung aquaporin 5 in
endotoxine shock-induced acute lung injury rabbit. J Thorac Dis.
7:1467–1477. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ten Have-Opbroek AA, Otto-Verberne CJ and
Dubbeldam JA: Ultrastructural characteristics of inclusion bodies
of type II cells in late embryonic mouse lung. Anat Embryol (Berl).
181:317–323. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dale D: Neutropenia and neutrophilia.
Lichtman M, Beutler E and Kipps TJ: Williams Hematology. Seventh.
McGraw-Hill Professional; New York, NY: pp. 701–708. 2006
|
|
33
|
Bronkhorst IH, Ly LV, Jordanova ES,
Vrolijk J, Versluis M, Luyten GP and Jager MJ: Detection of
M2-macrophages in uveal melanoma and relation with survival. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:643–650. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zeng Y, Yao X, Chen L, Yan Z, Liu J, Zhang
Y, Feng T, Wu J and Liu X: Sphingosine-1-phosphate induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma via
an MMP-7/syndecan-1/TGF-β autocrine loop. Oncotarget.
7:63324–63337. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schiechl G, Bauer B, Fuss I, Lang SA,
Moser C, Ruemmele P, Rose-John S, Neurath MF, Geissler EK, Schlitt
HJ, et al: Tumor development in murine ulcerative colitis depends
on MyD88 signaling of colonic F4/80+CD11bhighGr1low macrophages. J
Clin Invest. 121:1692–1708. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen L, Shi M, Gao S, Li S, Mao J, Zhang
H, Sun Y, Bai Z and Wang Z: Assessment of population exposure to
PM2.5 for mortality in China and its public health
benefit based on BenMAP. Environ Pollut. 221:311–317. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Long JF, Waldman WJ, Kristovich R,
Williams M, Knight D and Dutta PK: Comparison of ultrastructural
cytotoxic effects of carbon and carbon/iron particulates on human
monocyte-derived macrophages. Environ Health Perspect. 113:170–174.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Huang YC, Soukup J, Harder S and Becker S:
Mitochondrial oxidant production by a pollutant dust and
NO-mediated apoptosis in human alveolar macrophage. Ajp Cell
Physiol. 284:C24–C32. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Lee KI, Whang J, Choi HG, Son YJ, Jeon HS,
Back YW, Park HS, Paik S, Park JK, Choi CH and Kim HJ:
Mycobacterium avium MAV2054 protein induces macrophage apoptosis by
targeting mitochondria and reduces intracellular bacterial growth.
Sci Rep. 6:378042016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Suen YK, Fung KP, Lee CY and Kong SK:
Gliotoxin induces apoptosis in cultured macrophages via production
of reactive oxygen species and cytochrome c release without
mitochondrial depolarization. Free Radic Res. 35:1–10. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang X, Zhong W, Meng Q, Lin Q, Fang C,
Huang X, Li C, Huang Y and Tan J: Ambient PM2.5 exposure
exacerbates severity of allergic asthma in previously sensitized
mice. J Asthma. 52:785–794. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
He H, Buckley M, Britton B, Mu Y, Warner
K, Kumar S and Cory TJ: Polarized macrophage subsets differentially
express the drug efflux transporters MRP1 and BCRP, resulting in
altered HIV production. Antivir Chem Chemother.
26:2040206617745162018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu D, Whitehead J, Alfarra MR, Villegas
ER, Spracklen DV, Reddington CL, Kong S, Williams P, Haslett S,
Taylor JW, et al: Black-carbon absorption enhancement in the
atmosphere determined by particle mixing state. Nat Geosci.
10:184–188. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Huang H, Gao L, Xia D, Qiao L, Wang R, Su
G, Liu W, Liu G and Zheng M: Characterization of short- and
medium-chain chlorinated paraffins in outdoor/indoor
PM10/PM2.5/PM1.0 in Beijing, China. Environ Pollut. 225:674–680.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sui BL, Chen X, YU Y, Costa M and Wu H:
Effect of particle size on particulate matter emissions during
biosolid char combustion under air and oxyfuel conditions.
232:251–256. 2018.
|
|
47
|
Gu LZ, Sun H and Chen JH: Histone
deacetylases 3 deletion restrains PM2.5-induced mice lung injury by
regulating NF-κB and TGF-β/Smad2/3 signaling pathways. Biomed
Pharmacother. 85:756–762. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pirela S, Molina R, Watson C, Cohen JM,
Bello D, Demokritou P and Brain J: Effects of copy center particles
on the lungs: A toxicological characterization using a Balb/c mouse
model. Inhal Toxicol. 25:498–508. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Smith KR, Kim S, Recendez JJ, Teague SV,
Ménache MG, Grubbs DE, Sioutas C and Pinkerton KE: Airborne
particles of the california central valley alter the lungs of
healthy adult rats. Environ Health Perspect. 111:902–908. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mohammed MOA, Song WW, Ma YL, Liu LY, Ma
WL, Li WL, Li YF, Wang FY, Qi MY, Lv N, et al: Distribution
patterns, infiltration and health risk assessment of PM2.5-bound
PAHs in indoor and outdoor air in cold zone. Chemosphere.
155:70–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li M and Li YM: Fine particulate matter
and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za
Zhi. 24:713–715. 2016.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee CC and Kang JJ: Extract of motorcycle
exhaust particles induced macrophages apoptosis by
calcium-dependent manner. Chem Res Toxicol. 15:1534–1542. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Akbarshahi H, Menzel M, Posaric Bauden M,
Rosendahl A and Andersson R: Enrichment of murine CD68+ CCR2+ and
CD68+ CD206+ lung macrophages in acute pancreatitis-associated
acute lung injury. PLoS One. 7:e426542012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sun L, Chen B, Jiang R, Li J and Wang B:
Resveratrol inhibits lung cancer growth by suppressing M2-like
polarization of tumor associated macrophages. Cell Immunol.
331:86–93. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kimura Y and Sumiyoshi M: Resveratrol
prevents tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting
lymphangiogenesis and M2 macrophage activation and differentiation
in tumor-associated macrophages. Nutr Cancer. 68:667–678. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Clarke RW, Catalano PJ, Koutrakis P,
Murthy GG, Sioutas C, Paulauskis J, Coull B, Ferguson S and
Godleski JJ: Urban air particulate inhalation alters pulmonary
function and induces pulmonary inflammation in a rodent model of
chronic bronchitis. Inhal Toxicol. 11:637–656. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Aversa G, Punnonen J and de Vries JE: The
26-kD transmembrane form of tumor necrosis factor alpha on
activated CD4+ T cell clones provides a costimulatory signal for
human B cell activation. J Exp Med. 177:1575–1585. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Huang CZ, Yang J, Qiao HL and Jia LJ:
Polymorphisms and haplotype analysis of IL-4Rα Q576R and I75V in
patients with penicillin allergy. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 65:895–902.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Nygaard UC, Samuelsen M, Aase A and Løvik
M: The capacity of particles to increase allergic sensitization is
predicted by particle number and surface area, not by particle
mass. Toxicol Sci. 82:515–524. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Samuelsen M, Nygaard UC and Lovik M:
Allergy adjuvant effect of particles from wood smoke and road
traffic. Toxicology. 246:124–131. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lin ZM, Ma M, Li H, Qi Q, Liu YT, Yan YX,
Shen YF, Yang XQ, Zhu FH, He SJ, et al: Topical administration of
reversible SAHH inhibitor ameliorates imiquimod-induced
psoriasis-like skin lesions in mice via suppression of
TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced inflammatory response in keratinocytes and T
cell-derived IL-17. Pharmacol Res. 129:443–452. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Huang M, Su L, Yang L, Zhu L, Liu Z and
Duan R: Effect of exogenous TGF-β1 on the cadmium-induced
nephrotoxicity by inhibiting apoptosis of proximal tubular cells
through PI3K-AKT-mTOR signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact.
269:25–32. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Labour MN, Riffault M, Christensen ST and
Hoey DA: TGFβ1-induced recruitment of human bone mesenchymal stem
cells is mediated by the primary cilium in a SMAD3-dependent
manner. Sci Rep. 6:355422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhou X, Hu H, Balzar S, Trudeau JB and
Wenzel SE: MAPK regulation of IL-4/IL-13 receptors contributes to
the synergistic increase in CCL11/eotaxin-1 in response to TGF-β1
and IL-13 in human airway fibroblasts. J Immunol. 188:6046–6054.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ghavami S, Yeganeh B, Zeki AA, Shojaei S,
Kenyon NJ, Ott S, Samali A, Patterson J, Alizadeh J, Moghadam AR,
et al: Autophagy and the unfolded protein response promote
profibrotic effects of TGF-β1 in human lung fibroblasts. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 314:L493–L504. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Puerta-Arias JD, Pino-Tamayo PA, Arango JC
and González Á: Depletion of neutrophils promotes the resolution of
pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in mice infected with
paracoccidioides brasiliensis. PLoS One. 11:e01639852016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zaafan MA, Zaki HF, El-Brairy AI and
Kenawy SA: Pyrrolidinedithiocarbamate attenuates bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis in rats: Modulation of oxidative stress,
fibrosis, and inflammatory parameters. Exp Lung Res. 42:408–416.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|