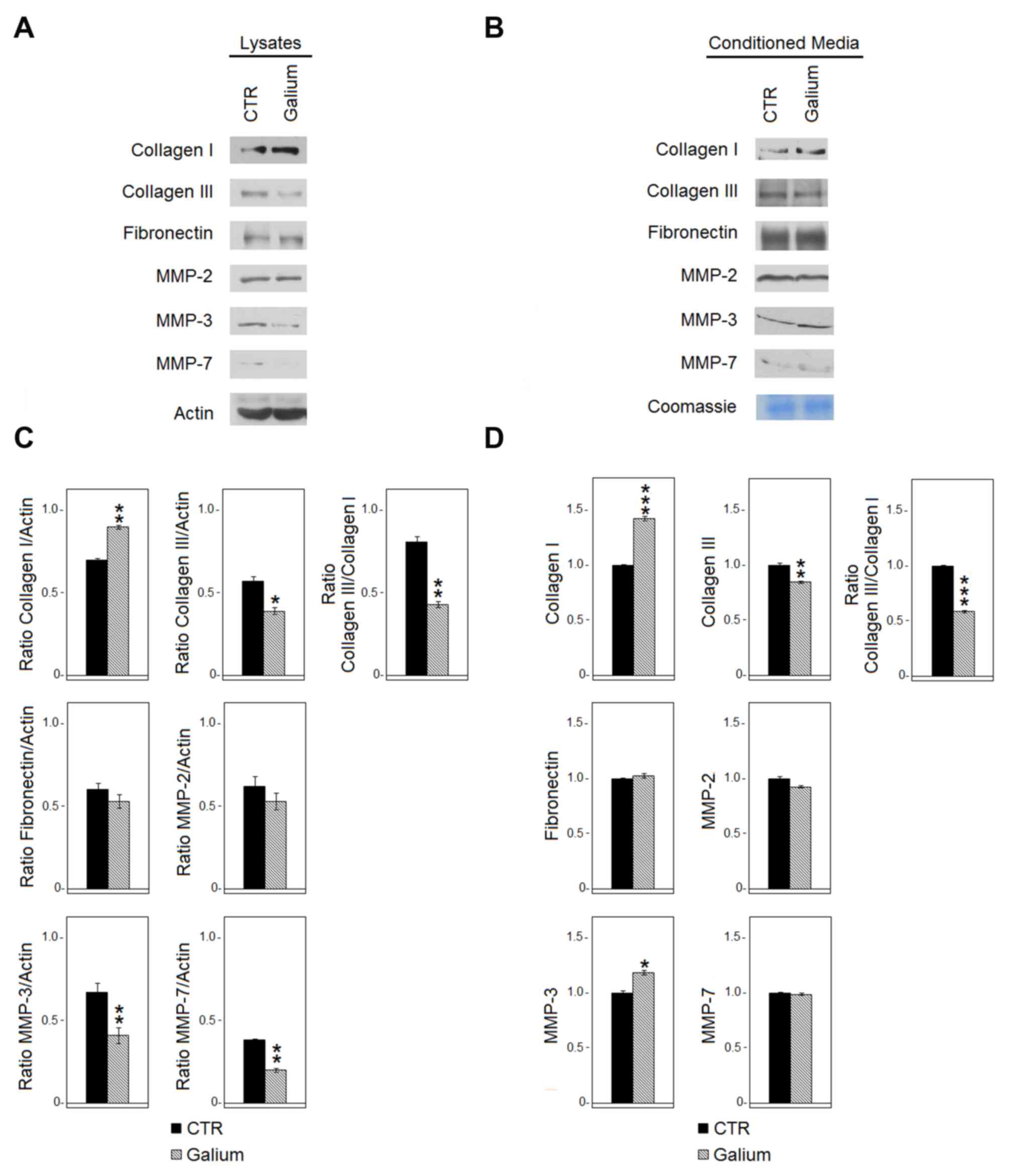
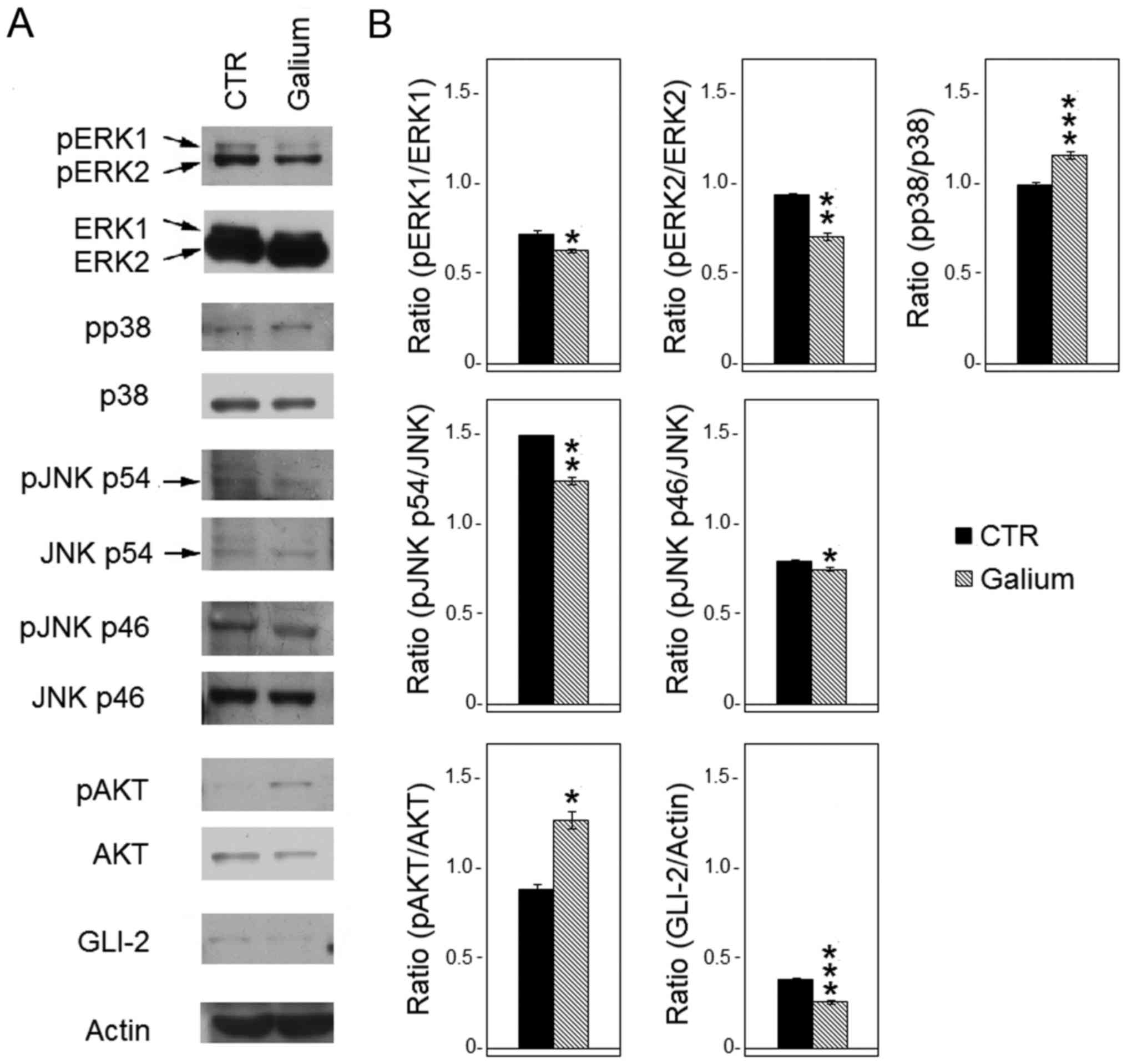
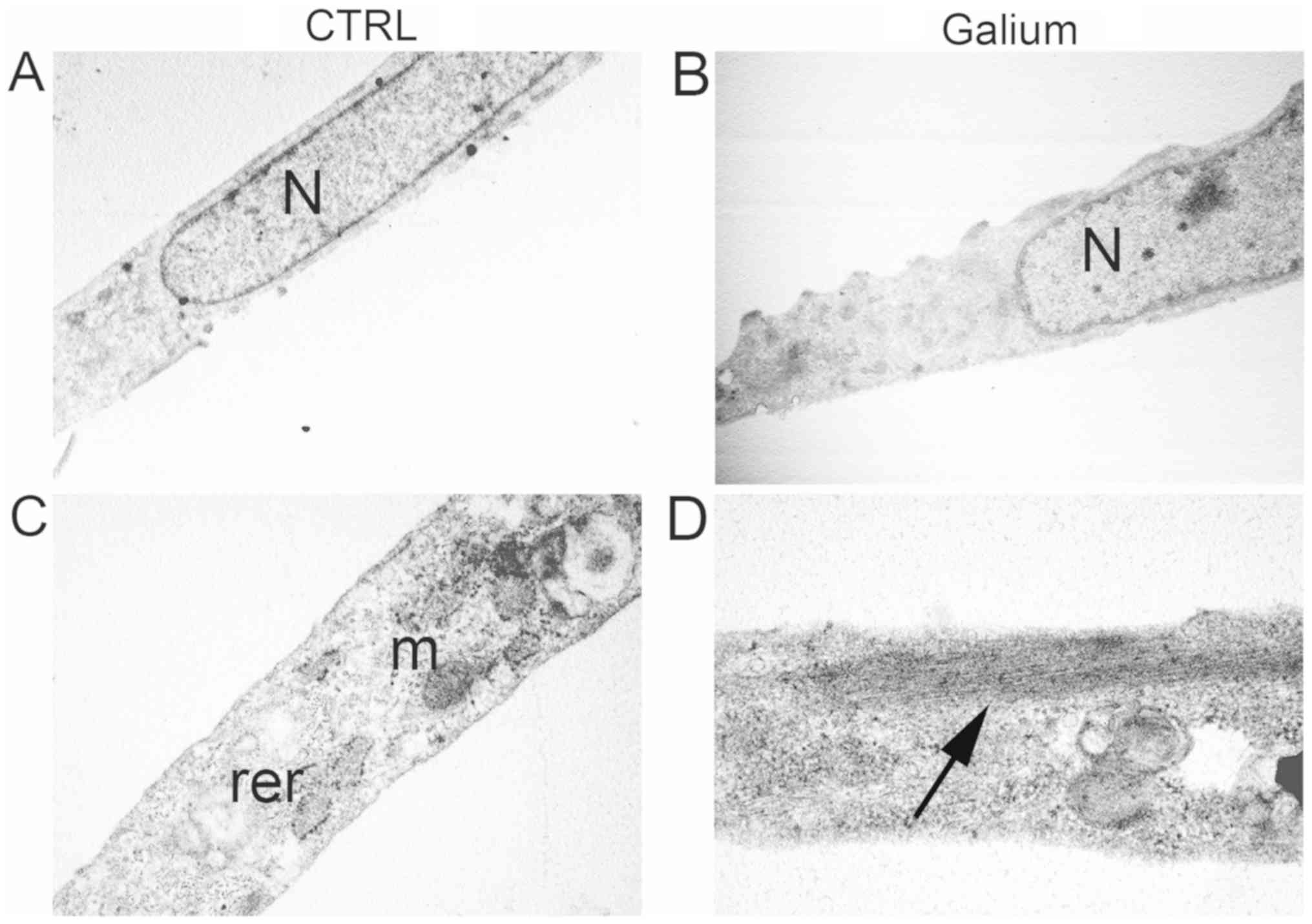
|
1
|
Nyström A and Bruckner-Tuderman L: Matrix
molecules and skin biology. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 89:136–146. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bei R, Masuelli L, Palumbo C, Tresoldi I,
Scardino A and Modesti A: Long-lasting tissue inflammatory
processes trigger autoimmune responses to extracellular matrix
molecules. Int Rev Immunol. 27:137–175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Iozzo RV and Gubbiotti MA: Extracellular
matrix: The driving force of mammalian diseases. Matrix Biol.
71-72:1–9. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Walker C, Mojares E and Del Río Hernández
A: Role of extracellular matrix in development and cancer
progression. Int J Mol Sci. 19(pii): E30282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li L, Zhao Q and Kong W: Extracellular
matrix remodeling and cardiac fibrosis. Matrix Biol. 68-69:490–506.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Minihane AM, Vinoy S, Russell WR, Baka A,
Roche HM, Tuohy KM, Teeling JL, Blaak EE, Fenech M, Vauzour D, et
al: Low-grade inflammation, diet composition and health: Current
research evidence and its translation. Br J Nutr. 114:999–1012.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Theocharis AD, Skandalis SS, Gialeli C and
Karamanos NK: Extracellular matrix structure. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
97:4–27. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Soylemezoglu O, Wild G, Dalley AJ, MacNeil
S, Milford-Ward A, Brown CB and el Nahas AM: Urinary and serum type
III collagen: Markers of renal fibrosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
12:1883–1889. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Arpino V, Brock M and Gill SE: The role of
TIMPs in regulation of extracellular matrix proteolysis. Matrix
Biol. 44-46:247–254. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Randelli F, Menon A, Giai Via A, Mazzoleni
MG, Sciancalepore F, Brioschi M and Gagliano N: Effect of a
collagen-based compound on morpho-functional properties of cultured
human tenocytes. Cells. 7(pii): E2462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Karsdal MA, Nielsen MJ, Sand JM, Henriksen
K, Genovese F, Bay-Jensen AC, Smith V, Adamkewicz JI, Christiansen
C and Leeming DJ: Extracellular matrix remodeling: The common
denominator in connective tissue diseases. Possibilities for
evaluation and current understanding of the matrix as more than a
passive architecture, but a key player in tissue failure. Assay
Drug Dev Technol. 11:70–92. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Barascuk N, Vassiliadis E, Larsen L, Wang
J, Zheng Q, Xing R, Cao Y, Crespo C, Lapret I, Sabatini M, et al:
Development and validation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
for the quantification of a specific MMP-9 mediated degradation
fragment of type III collagen-A novel biomarker of atherosclerotic
plaque remodeling. Clin Biochem. 44:900–906. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang Z, Li T, Jiang S, Xu J, Di W, Yang
Z, Hu W and Yang Y: AMPK: A novel target for treating hepatic
fibrosis. Oncotarget. 8:62780–62792. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang N, Wei WY, Li LL, Hu C and Tang QZ:
Therapeutic potential of polyphenols in cardiac fibrosis. Front
Pharmacol. 9:1222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Katoh M: Multi-layered prevention and
treatment of chronic inflammation, organ fibrosis and cancer
associated with canonical WNT/β catenin signaling activation
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 42:713–725. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Reale FR, GriYn TW, Compton JM, Graham S,
Townes PL and Bogden A: Characterization of a human malignant
mesothelioma cell line (H-MESO-1): A biphasic solid and ascitic
tumor model. Cancer Res. 47:3199–3205. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Masuelli L, Benvenuto M, Mattera R, Di
Stefano E, Zago E, Taffera G, Tresoldi I, Giganti MG, Frajese GV,
Berardi G, et al: In vitro and in vivo anti-tumoral effects of the
flavonoid apigenin in malignant mesotelioma. Front Pharmacol.
8:3732017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Strober W: Trypan blue exclusion test of
cell viability. Curr Protoc Immunol. 111:A3.B.1–3. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Benvenuto M, Mattera R, Sticca JI, Rossi
P, Cipriani C, Giganti MG, Volpi A, Modesti A, Masuelli L and Bei
R: Effect of the BH3 mimetic polyphenol (−)-Gossypol (AT-101) on
the in vitro and in vivo growth of malignant mesothelioma. Front
Pharmacol. 9:12692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Masuelli L, Pantanella F, La Regina G,
Benvenuto M, Fantini M, Mattera R, Di Stefano E, Mattei M,
Silvestri R, Schippa S, et al: Violacein, an indole-derived
purple-colored natural pigment produced by Janthinobacterium
lividum, inhibits the growth of head and neck carcinoma cell lines
both in vitro and in vivo. Tumour Biol. 37:3705–3717. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Benvenuto M, Mattera R, Masuelli L,
Taffera G, Andracchio O, Tresoldi I, Lido P, Giganti MG, Godos J,
Modesti A and Bei R: (±)-Gossypol induces apoptosis and autophagy
in head and neck carcinoma cell lines and inhibits the growth of
transplanted salivary gland cancer cells in BALB/c mice. Int J Food
Sci Nutr. 68:298–312. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Masuelli L, Benvenuto M, Di Stefano E,
Mattera R, Fantini M, De Feudis G, De Smaele E, Tresoldi I, Giganti
MG, Modesti A and Bei R: Curcumin blocks autophagy and activates
apoptosis of malignant mesothelioma cell lines and increases the
survival of mice intraperitoneally transplanted with a malignant
mesothelioma cell line. Oncotarget. 8:34405–34422. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Masuelli L, Granato M, Benvenuto M,
Mattera R, Bernardini R, Mattei M, d'Amati G, D'Orazi G, Faggioni
A, Bei R and Cirone M: Chloroquine supplementation increases the
cytotoxic effect of curcumin against Her2/neu overexpressing breast
cancer cells in vitro and in vivo in nude mice while counteracts it
in immune competent mice. OncoImmunology. 6:e13561512017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Angelucci C, D'Alessio A, Lama G, Binda E,
Mangiola A, Vescovi AL, Proietti G, Masuelli L, Bei R, Fazi B, et
al: Cancer stem cells from peritumoral tissue of glioblastoma
multiforme: The possible missing link between tumor development and
progression. Oncotarget. 9:28116–28130. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stanković M, Radojević I, Ćurčić M, Vasić
S, Topuzović M, Čomić L and Marković S: Evaluation of biological
activities of goldmoss stonecrop (Sedum acre L.). Turk J
Biol. 36:580–588. 2012.
|
|
26
|
Sentjurc M, Nemec M, Connor HD and Abram
V: Antioxidant activity of Sempervivum tectorum and its
components. J Agric Food Chem. 51:2766–2771. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Marrassini C, Acevedo C, Miño J, Ferraro G
and Gorzalczany S: Evaluation of antinociceptive, antinflammatory
activities and phytochemical analysis of aerial parts of Urtica
urens L. Phytother Res. 24:1807–1812. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lu P, Takai K, Weaver VM and Werb Z:
Extracellular matrix degradation and remodeling in development and
disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 3(pii):
a0050582011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sanchavanakit N, Saengtong W,
Manokawinchoke J and Pavasant P: TNF-α stimulates MMP-3 production
via PGE2 signalling through the NF-kB and p38 MAPK pathway in a
murine cementoblast cell line. Arch Oral Biol. 60:1066–1074. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang H, Gao F, Li X, Wang J, Liu H and
Zheng Z: TGF-β1 antagonizes TNF-α induced up-regulation of matrix
metalloproteinase 3 in nucleus pulposus cells: Role of the ERK1/2
pathway. Connect Tissue Res. 56:461–468. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Saed GM, Zhang W, Chegini N, Holmdahl L
and Diamond MP: Alteration of type I and III collagen expression in
human peritoneal mesothelial cells in response to hypoxia and
transforming growth factor-beta1. Wound Repair Regen. 7:504–510.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Forel JM, Guervilly C, Farnarier C, Donati
SY, Hraiech S, Persico N, Allardet-Servent J, Coiffard B, Gainnier
M, Loundou A, et al: Transforming growth factor-β1 in predicting
early lung fibroproliferation in patients with acute respiratory
distress syndrome. PLoS One. 13:e02061052018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rojkind M, Giambrone MA and Biempica L:
Collagen types in normal and cirrhotic liver. Gastroenterology.
76:710–719. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Javelaud D, Pierrat MJ and Mauviel A:
Crosstalk between TGF-β and hedgehog signaling in cancer. FEBS
Lett. 586:2016–2025. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liang R, Šumová B, Cordazzo C, Mallano T,
Zhang Y, Wohlfahrt T, Dees C, Ramming A, Krasowska D,
Michalska-Jakubus M, et al: The transcription factor GLI2 as a
downstream mediator of transforming growth factor-β-induced
fibroblast activation in SSc. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:756–764. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Moncada S and Higgs A: The
L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. N Engl J Med. 329:2002–2012. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xia W, Szomor Z, Wang Y and Murrell GA:
Nitric oxide enhances collagen synthesis in cultured human tendon
cells. J Orthop Res. 24:159–172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lundberg JO, Weitzberg E and Gladwin MT:
The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and
therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:156–167. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gilkes DM, Semenza GL and Wirtz D: Hypoxia
and the extracellular matrix: Drivers of tumour metastasis. Nat Rev
Cancer. 14:430–439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Negahdary M, Chelongar R, Zadeh SK and
Ajdary M: The antioxidant effects of silver, gold, and zinc oxide
nanoparticles on male mice in in vivo condition. Adv Biomed Res.
4:692015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hashimoto M, Sasaki JI, Yamaguchi S, Kawai
K, Kawakami H, Iwasaki Y and Imazato S: Gold nanoparticles inhibit
matrix metalloproteases without cytotoxicity. J Dent Res.
94:1085–1091. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Veerendhar A, Reich R and Breuer E:
Phosphorus based inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases. C R Chim.
13:1191–1202. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Slompo C, Buzalaf CP, Damante CA, Martins
GM, Hannas AR, Buzalaf MA and Oliveira RC: Fluoride modulates
preosteoblasts viability and matrix metalloproteinases-2 and −9
activities. Braz Dent J. 23:629–634. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Suszko A and Obmińska-Mrukowicz B: Effects
of polysaccharide fractions isolated from Caltha palustris
L. on the activity of phagocytic cells & humoral immune
response in mice with collagen-induced arthritis: A comparison with
methotrexate. Indian J Med Res. 145:229–236. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Han X and Parker TL: Anti-inflammatory
activity of Juniper (Juniperus communis) berry essential oil
in human dermal fibroblasts. Cogent Med. 4:13062002017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Rastogi S, Pandey MM and Kumar Singh Rawat
A: Medicinal plants of the genus Betula-traditional uses and a
phytochemical-pharmacological review. J Ethnopharmacol. 159:62–83.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ra HJ, Lee HJ, Jo HS, Nam DC, Lee YB, Kang
BH, Moon DK, Kim DH, Lee CJ and Hwang SC: Betulin suppressed
interleukin-1β-induced gene expression, secretion and proteolytic
activity of matrix metalloproteinase in cultured articular
chondrocytes and production of matrix metalloproteinase in the knee
joint of rat. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 21:19–26. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Silacci P, Dayer JM, Desgeorges A, Peter
R, Manueddu C and Guerne PA: Interleukin (IL)-6 and its soluble
receptor induce TIMP-1 expression in synoviocytes and chondrocytes,
and block IL-1-induced collagenolytic activity. J Biol Chem.
273:13625–13629. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Offergeld R, Reinecker C, Gumz E, Schrum
S, Treiber R, Neth RD and Gohla SH: Mitogenic activity of high
molecular polysaccharide fractions isolated from the cuppressaceae
Thuja occidentalis L. enhanced cytokine-production by
thyapolysaccharide, g-fraction (TPSg). Leukemia. 6 (Suppl
3):189S–191S. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sunila ES, Hamsa TP and Kuttan G: Effect
of Thuja occidentalis and its polysaccharide on
cell-mediated immune responses and cytokine levels of metastatic
tumor-bearing animals. Pharm Biol. 49:1065–1073. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Masuelli L, Marzocchella L, Focaccetti C,
Tresoldi I, Palumbo C, Izzi V, Benvenuto M, Fantini M, Lista F,
Tarantino U, et al: Resveratrol and diallyl disulfide enhance
curcumin-induced sarcoma cell apoptosis. Front Biosci (Landmark
Ed). 17:498–508. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Masuelli L, Di Stefano E, Fantini M,
Mattera R, Benvenuto M, Marzocchella L, Sacchetti P, Focaccetti C,
Bernardini R, Tresoldi I, et al: Resveratrol potentiates the in
vitro and in vivo anti-tumoral effects of curcumin in head and neck
carcinomas. Oncotarget. 5:10745–10762. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Fantini M, Benvenuto M, Masuelli L,
Frajese GV, Tresoldi I, Modesti A and Bei R: In vitro and in vivo
antitumoral effects of combinations of polyphenols, or polyphenols
and anticancer drugs: Perspectives on cancer treatment. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:9236–9282. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Rhee S: Fibroblasts in three dimensional
matrices: Cell migration and matrix remodelling. Exp Mol Med.
41:858–865. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Langevin HM, Bouffard NA, Fox JR, Palmer
BM, Wu J, Iatridis JC, Barnes WD, Badger GJ and Howe AK: Fibroblast
cytoskeletal remodeling contributes to connective tissue tension. J
Cell Physiol. 226:1166–1175. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|