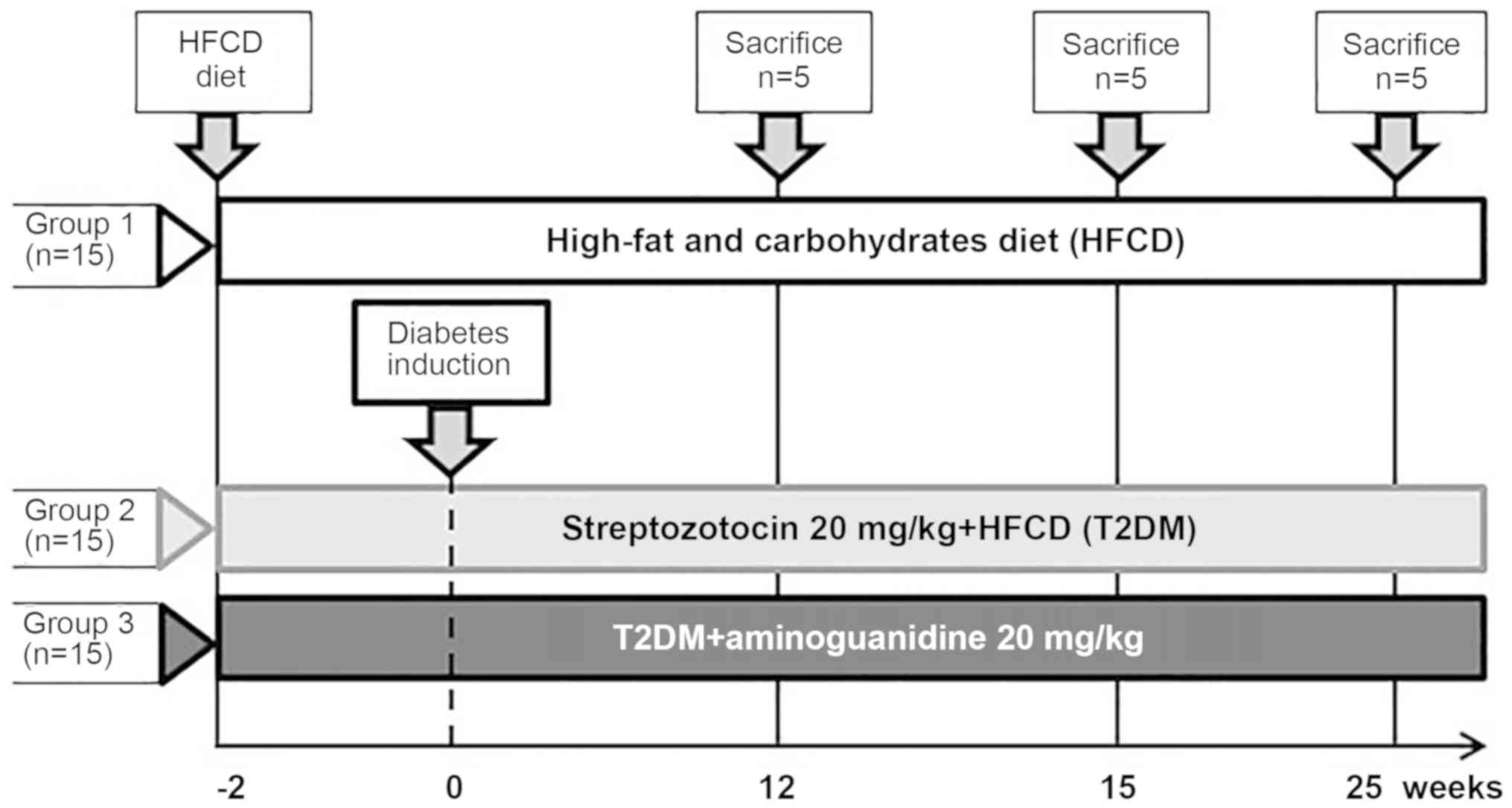
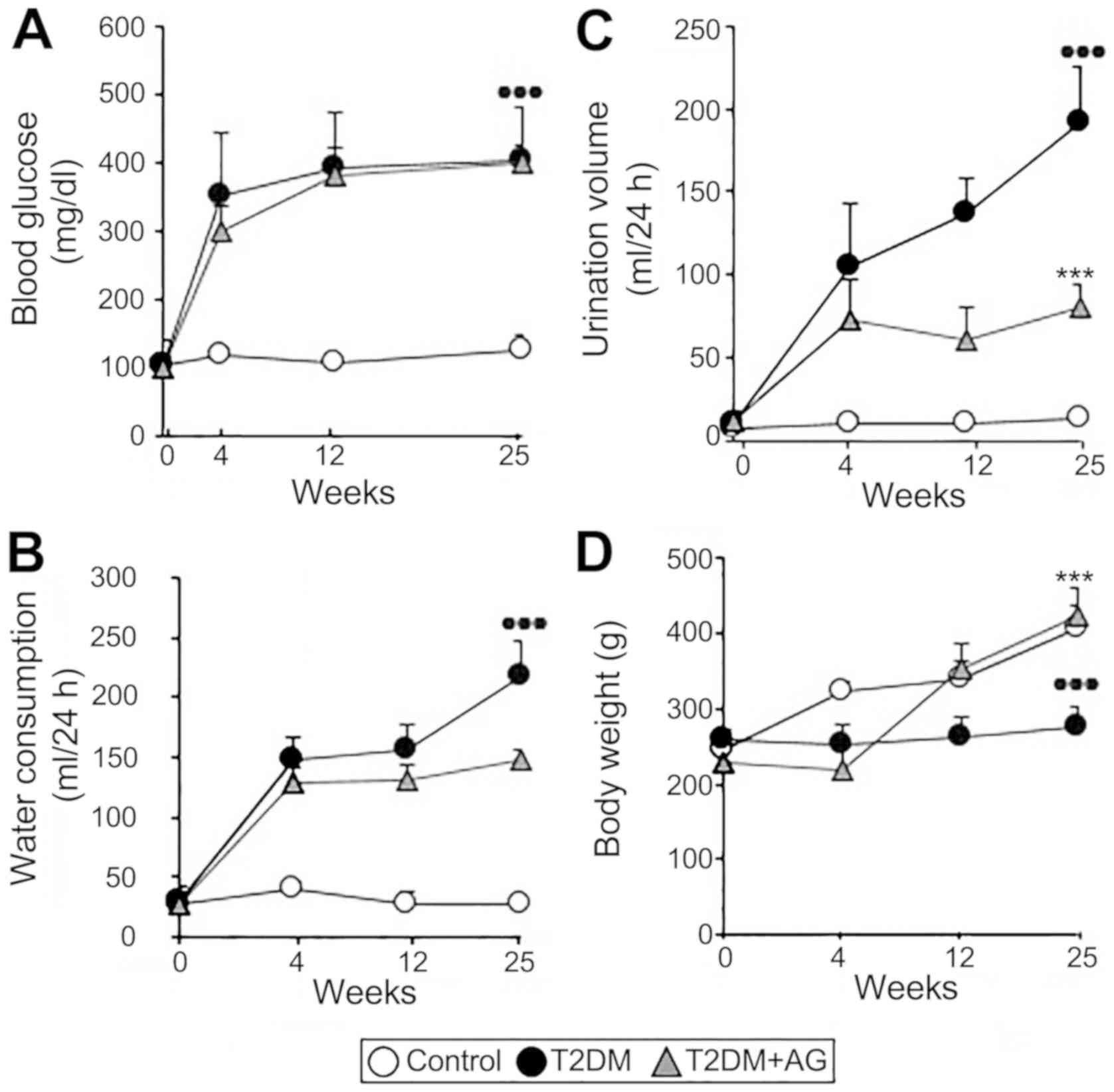
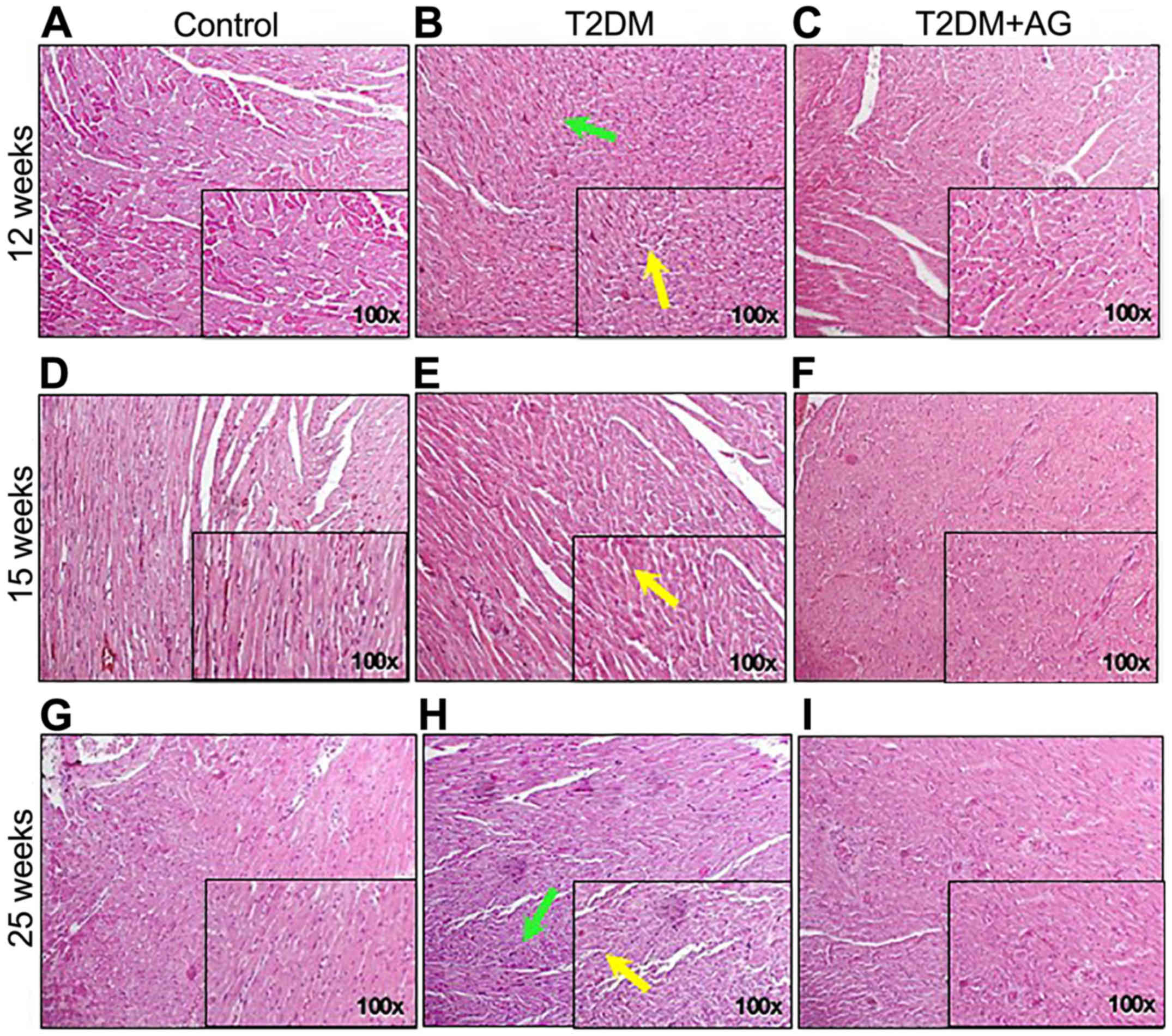
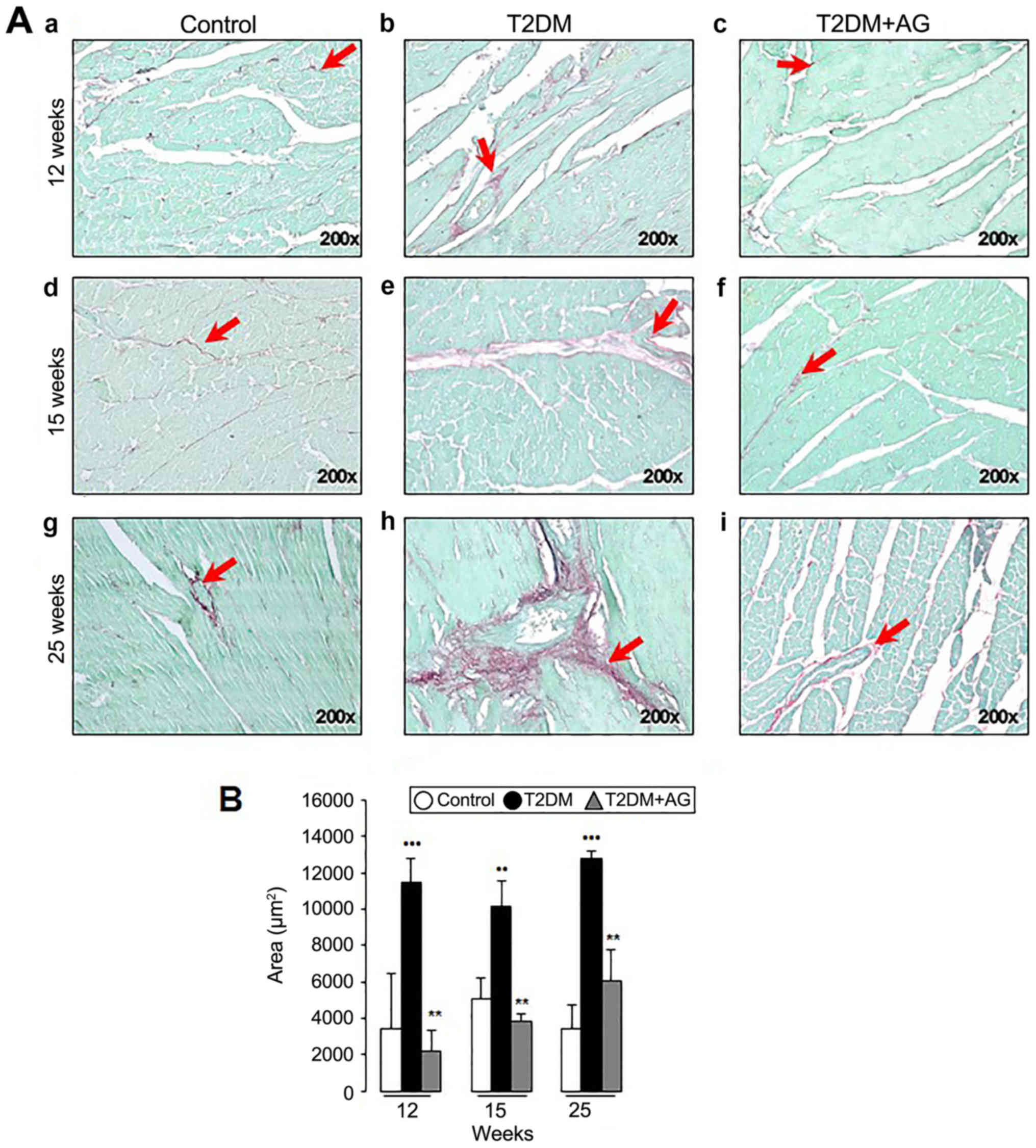
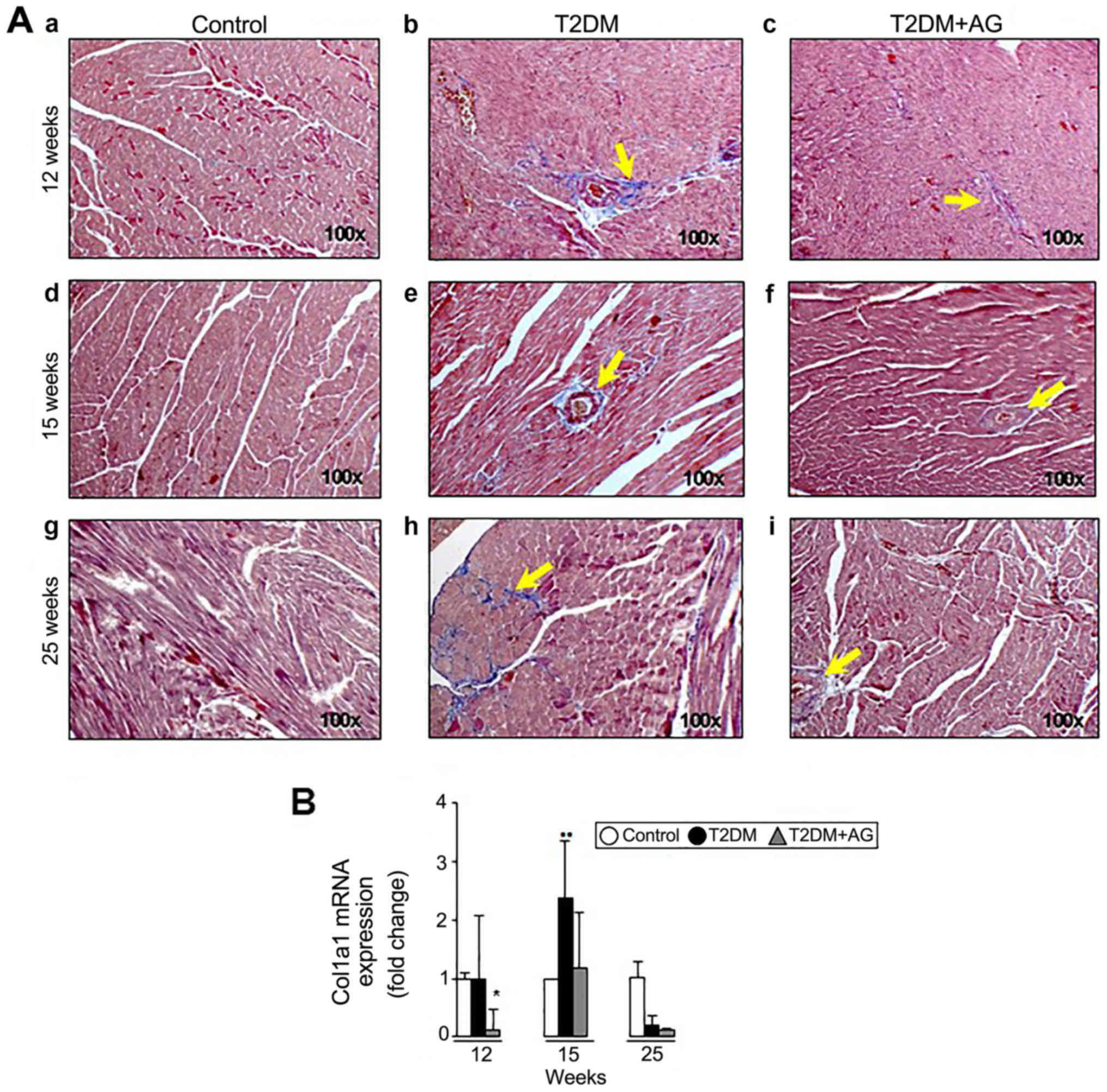
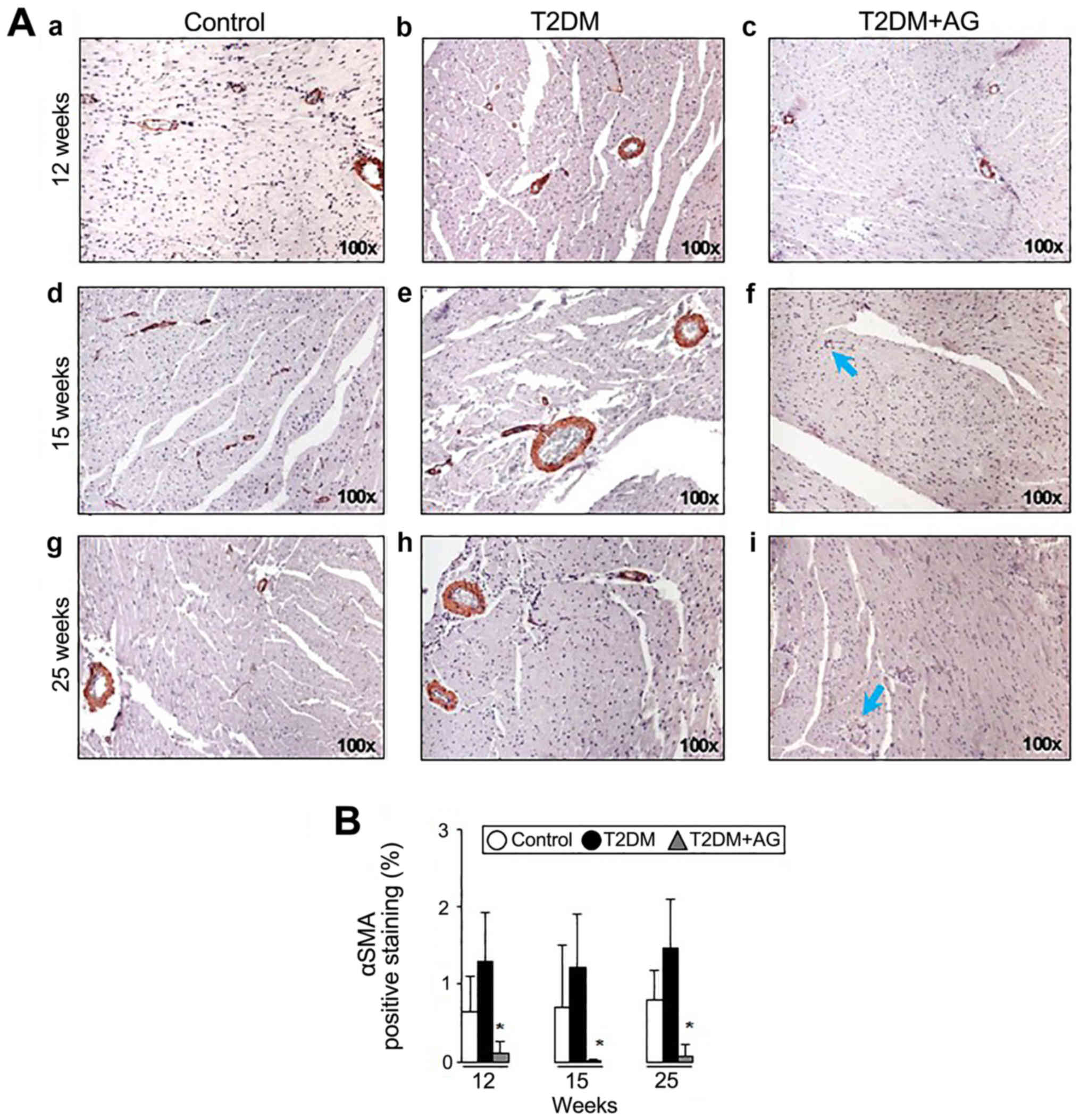
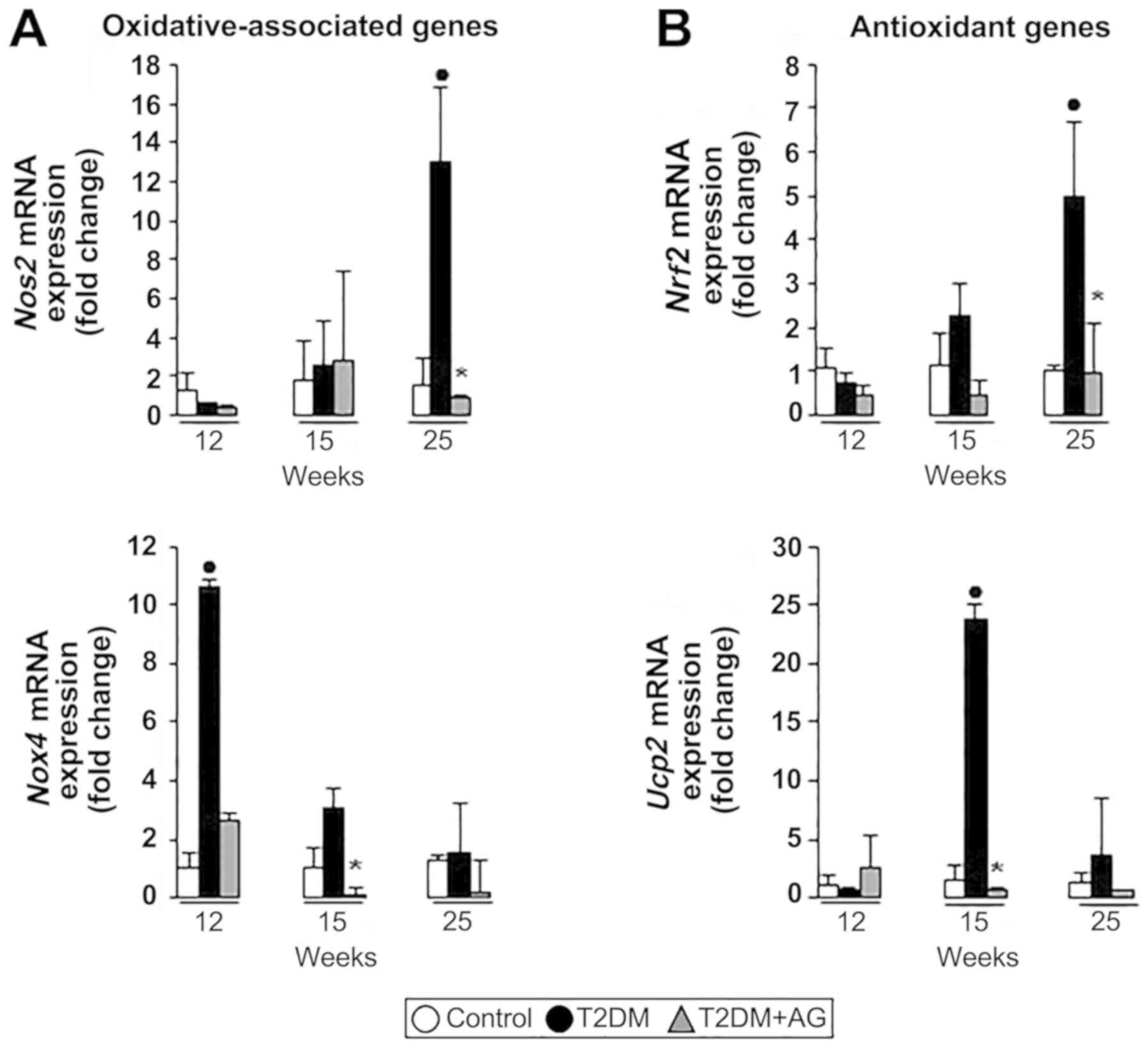
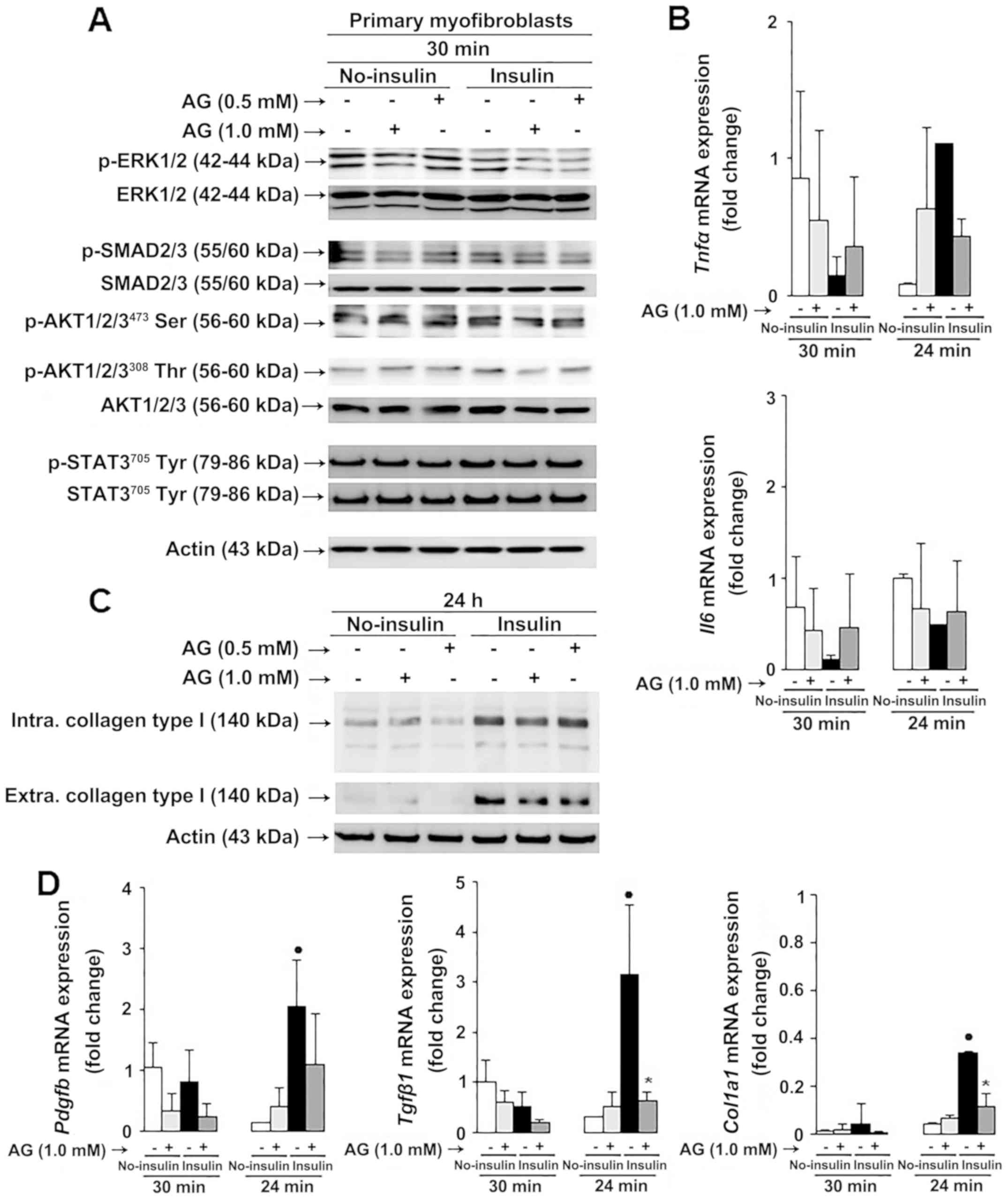
|
1
|
Patel D, Kumar R, Laloo D and Hemalatha S:
Diabetes mellitus: An overview on its pharmacological aspects and
reported medicinal plants having antidiabetic activity. Asian Pac J
Trop Biomed. 2:411–420. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kayama Y, Raaz U, Jagger A, Adam M,
Schellinger IN, Sakamoto M, Suzuki H, Toyama K, Spin JM and Tsao
PS: Diabetic cardiovascular disease induced by oxidative stress.
Int J Mol Sci. 16:25234–25263. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kumar S, Singh R, Vasudeva N and Sharma S:
Acute and chronic animal models for the evaluation of anti-diabetic
agents. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 11:92012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang HJ, Jin YX, Shen W, Neng J, Wu T, Li
YJ and Fu ZW: Low dose streptozotocin (STZ) combined with high
energy intake can effectively induce type 2 diabetes through
altering the related gene expression. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 16
(Suppl 1):S412–S417. 2007.
|
|
5
|
Malfitano C, de Souza Junior AL, Carbonaro
M, Bolsoni-Lopes A, Figueroa D, de Souza LE, Silva KA,
Consolim-Colombo F, Curi R and Irigoyen MC: Glucose and fatty acid
metabolism in infarcted heart from streptozotocin-induced diabetic
rats after 2 weeks of tissue remodeling. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
14:1492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nugent DA, Smith DM and Jones HB: A review
of islet of Langerhans degeneration in rodent models of type 2
diabetes. Toxicol Pathol. 36:529–551. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Serban AI, Stanca L, Geicu OI, Munteanu
MC, Costache M and Dinischiotu A: Extracellular matrix is modulated
in advanced glycation end products milieu via a RAGE receptor
dependent pathway boosted by transforming growth factor-β1 RAGE. J
Diabetes. 7:114–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Du AJ, Ren B, Gao XW, Yang L, Fu Y and
Zhao XD: Effects of aminoguanidine on retinal apoptosis in mice
with oxygen-induced retinopathy. Int J Ophthalmol. 6:436–441.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Serhiyenko VA and Serhiyenko AA: Diabetic
cardiac autonomic neuropathy: Do we have any treatment
perspectives? World J Diabetes. 6:245–258. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Thornalley PJ: Use of aminoguanidine
(Pimagedine) to prevent the formation of advanced glycation
endproducts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 419:31–40. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Soliman M: Preservation of myocardial
contractile function by aminoguanidine, a nitric oxide synthase
inhibitors, in a rat model of hemorrhagic shock. Pak J Med Sci.
29:1415–1419. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Niki T, Rombouts K, De Bleser P, De Smet
K, Rogiers V, Schuppan D, Yoshida M, Gabbiani G and Geerts A: A
histone deacetylase inhibitor, trichostatin A, suppresses
myofibroblastic differentiation of rat hepatic stellate cells in
primary culture. Hepatology. 29:858–867. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rombouts K, Niki T, Greenwel P,
Vandermonde A, Wielant A, Hellemans K, De Bleser P, Yoshida M,
Schuppan D, Rojkind M and Geerts A: Trichostatin A, a histone
deacetylase inhibitor, suppresses collagen synthesis and prevents
TGF-beta(1)-induced fibrogenesis in skin fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res.
278:184–197. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Grabiec K, Gajewska M, Milewska M,
Blaszczyk M and Grzelkowska-Kowalczyk K: The influence of high
glucose and high insulin on mechanisms controlling cell cycle
progression and arrest in mouse C2C12 myoblasts: The comparison
with IGF-I effect. J Endocrinol Invest. 37:233–245. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang CC, Gurevich I and Draznin B: Insulin
affects vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype and migration via
distinct signaling pathways. Diabetes. 52:2562–2569. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Boateng SY, Hartman TJ, Ahluwalia N,
Vidula H, Desai TA and Russell B: Inhibition of fibroblast
proliferation in cardiac myocyte cultures by surface
microtopography. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 285:C171–C182. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li M and Hagerman AE: Effect of
(−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on glucose-induced human serum
albumin glycation. Free Radic Res. 49:946–953. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Johnson PD and Besselsen DG: Practical
aspects of experimental design in animal research. ILAR J.
43:202–206. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Festing MF and Altman DG: Guidelines for
the design and statistical analysis of experiments using laboratory
animals. ILAR J. 43:244–258. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lattouf R, Younes R, Lutomski D, Naaman N,
Godeau G, Senni K and Changotade S: Picrosirius red staining: A
useful tool to appraise collagen networks in normal and
pathological tissues. J Histochem Cytochem. 62:751–758. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Halban PA, Polonsky KS, Bowden DW, Hawkins
MA, Ling C, Mather KJ, Powers AC, Rhodes CJ, Sussel L and Weir GC:
β-cell failure in type 2 diabetes: Postulated mechanisms and
prospects for prevention and treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
99:1983–1992. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rao KB, Malathi N, Narashiman S and Rajan
ST: Evaluation of myofibroblasts by expression of alpha smooth
muscle actin: A marker in fibrosis, dysplasia and carcinoma. J Clin
Diagn Res. 8:ZC14–ZC17. 2014.
|
|
24
|
Lijnen PJ, van Pelt JF and Fagard RH:
Stimulation of reactive oxygen species and collagen synthesis by
angiotensin II in cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovasc Ther. 30:e1–e8.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ma ZA, Zhao Z and Turk J: Mitochondrial
dysfunction and β-cell failure in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp
Diabetes Res. 2012:7035382012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tian XY, Wong WT, Xu A, Lu Y, Zhang Y,
Wang L, Cheang WS, Wang Y, Yao X and Huang Y: Uncoupling protein-2
protects endothelial function in diet-induced obese mice. Circ Res.
110:1211–1216. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Parthasarathy A, Gopi V, Devi K M S,
Balaji N and Vellaichamy E: Aminoguanidine inhibits ventricular
fibrosis and remodeling process in isoproterenol-induced
hypertrophied rat hearts by suppressing ROS and MMPs. Life Sci.
118:15–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chowdhury P, Soulsby ME and Scott JL:
Effects of aminoguanidine on tissue oxidative stress induced by
hindlimb unloading in rats. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 39:64–70.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cigremis Y, Parlakpinar H, Polat A, Colak
C, Ozturk F, Sahna E, Ermis N and Acet A: Beneficial role of
aminoguanidine on acute cardiomyopathy related to
doxorubicin-treatment. Mol Cell Biochem. 285:149–154. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wegner M, Neddermann D,
Piorunska-Stolzmann M and Jagodzinski PP: Role of epigenetic
mechanisms in the development of chronic complications of diabetes.
Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 105:164–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bertacca A, Ciccarone A, Cecchetti P,
Vianello B, Laurenza I, Maffei M, Chiellini C, Del Prato S and
Benzi L: Continually high insulin levels impair Akt phosphorylation
and glucose transport in human myoblasts. Metabolism. 54:1687–163.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lu TC, Wang ZH, Feng X, Chuang PY, Fang W,
Shen Y, Levy DE, Xiong H, Chen N and He JC: Knockdown of Stat3
activity in vivo prevents diabetic glomerulopathy. Kidney Int.
76:63–71. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yahiaoui L, Gvozdic D, Danialou G, Mack M
and Petrof BJ: CC family chemokines directly regulate myoblast
responses to skeletal muscle injury. J Physiol. 586:3991–4004.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tang M, Zhang W, Lin H, Jiang H, Dai H and
Zhang Y: High glucose promotes the production of collagen types I
and III by cardiac fibroblasts through a pathway dependent on
extracellular-signal-regulated kinase 1/2. Mol Cell Biochem.
301:109–114. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dong Y, Lakhia R, Thomas SS, Dong Y, Wang
XH, Silva KA and Zhang L: Interactions between p-Akt and Smad3 in
injured muscles initiate myogenesis or fibrogenesis. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 305:E367–E375. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schiaffino S and Mammucari C: Regulation
of skeletal muscle growth by the IGF1-Akt/PKB pathway: Insights
from genetic models. Skelet Muscle. 1:42011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sakai M, Oimomi M and Kasuga M:
Experimental studies on the role of fructose in the development of
diabetic complications. Kobe J Med Sci. 48:125–136. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang XL, Lau WB, Yuan YX, Wang YJ, Yi W,
Christopher TA, Lopez BL, Liu HR and Ma XL: Methylglyoxal increases
cardiomyocyte ischemia-reperfusion injury via glycative inhibition
of thioredoxin activity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
299:E207–E214. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ding WY, Liu L, Wang ZH, Tang MX, Ti Y,
Han L, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Zhong M and Zhang W: FP-receptor gene
silencing ameliorates myocardial fibrosis and protects from
diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Mol Med (Berl). 92:629–640. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu W, Wu J, Cai F, Xiang J, Zha W, Fan D,
Guo S, Ming Z and Liu C: Curcumin alleviates diabetic
cardiomyopathy in experimental diabetic rats. PLoS One.
7:e520132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rajesh M, Mukhopadhyay P, Bátkai S, Patel
V, Saito K, Matsumoto S, Kashiwaya Y, Horváth B, Mukhopadhyay B,
Becker L, et al: Cannabidiol attenuates cardiac dysfunction,
oxidative stress, fibrosis, and inflammatory and cell death
signaling pathways in diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol.
56:2115–2125. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
King AJ: The use of animal models in
diabetes research. Br J Pharmacol. 166:877–894. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Y, Babcock SA, Hu N, Maris JR, Wang
H and Ren J: Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH2) protects
against streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy: Role of
GSK3β and mitochondrial function. BMC Med. 10:402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Asbun J and Villarreal FJ: The
pathogenesis of myocardial fibrosis in the setting of diabetic
cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol. 47:693–700. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vijan S: In the clinic. Type 2 diabetes.
Ann Intern Med. 152:ITC31–ITC15, ITC316. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ježek P, Olejár T, Smolková K, Jezek J,
Dlasková A, Plecitá-Hlavatá L, Zelenka J, Špaček T, Engstová H,
Pajuelo Reguera D and Jabůrek M: Antioxidant and regulatory role of
mitochondrial uncoupling protein UCP2 in pancreatic beta-cells.
Physiol Res. 63 (Suppl 1):S73–S91. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Baldelli S, Aquilano K and Ciriolo MR:
Punctum on two different transcription factors regulated by PGC-α:
Nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2 and nuclear respiratory
factor 2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1830:4137–4146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li B, Liu S, Miao L and Cai L: Prevention
of diabetic complications by activation of Nrf2: Diabetic
cardiomyopathy and nephropathy. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012:2165122012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lasségue B and Griendling KK: NADPH
oxidases: Functions and pathologies in the vasculature.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:653–661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen F, Haigh S, Barman S and Fulton DJ:
From form to function: The role of Nox4 in the cardiovascular
system. Front Physiol. 3:4122012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Pendyala S and Natarajan V: Redox
regulation of Nox proteins. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 174:265–271.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Brewer AC, Murray TV, Arno M, Zhang M,
Anilkumar NP, Mann GE and Shah AM: Nox4 regulates Nrf2 and
glutathione redox in cardiomyocytes in vivo. Free Radic Biol Med.
51:205–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dusting GJ and Triggle C: Are we over
oxidized? Oxidative stress, cardiovascular disease, and the future
of intervention studies with antioxidants. Vasc Health Risk Manag.
1:93–97. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Kazakov A, Hall R, Jagoda P, Bachelier K,
Müller-Best P, Semenov A, Lammert F, Böhm M and Laufs U: Inhibition
of endothelial nitric oxide synthase induces and enhances
myocardial fibrosis. Cardiovasc Res. 100:211–221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Oak JH, Youn JY and Cai H: Aminoguanidine
inhibits aortic hydrogen peroxide production, VSMC NOX activity and
hypercontractility in diabetic mice. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 8:652009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li W, Cui M, Wei Y, Kong X, Tang L and Xu
D: Inhibition of the expression of TGF-β1 and CTGF in human
mesangial cells by exendin-4, a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
agonist. Cell Physiol Biochem. 30:749–757. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yokoi H, Kasahara M, Mori K, Kuwabara T,
Toda N, Yamada R, Namoto S, Yamamoto T, Seki N, Souma N, et al:
Peritoneal fibrosis and high transport are induced in mildly
pre-injured peritoneum by 3,4-dideoxyglucosone-3-ene in mice. Perit
Dial Int. 33:143–154. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dhar A, Dhar I, Desai KM and Wu L:
Methylglyoxal scavengers attenuate endothelial dysfunction induced
by methylglyoxal and high concentrations of glucose. Br J
Pharmacol. 161:1843–1856. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Eika B, Levin RM and Longhurst PA:
Modulation of urinary bladder function by sex hormones in
streptozotocin-diabetic rats. J Urol. 152:537–543. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Youssef S, Nguyen DT, Soulis T,
Panagiotopoulos S, Jerums G and Cooper ME: Effect of diabetes and
aminoguanidine therapy on renal advanced glycation end-product
binding. Kidney Int. 55:907–916. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wilkinson-Berka JL, Kelly DJ, Koerner SM,
Jaworski K, Davis B, Thallas V and Cooper ME: ALT-946 and
aminoguanidine, inhibitors of advanced glycation, improve severe
nephropathy in the diabetic transgenic (mREN-2)27 rat. Diabetes.
51:3283–3289. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Han DC, Isono M, Hoffman BB and Ziyadeh
FN: High glucose stimulates proliferation and collagen type I
synthesis in renal cortical fibroblasts: Mediation by autocrine
activation of TGF-beta. J Am Soc Nephrol. 10:1891–1899.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Aguilar H, Fricovsky E, Ihm S, Schimke M,
Maya-Ramos L, Aroonsakool N, Ceballos G, Dillmann W, Villarreal F
and Ramirez-Sanchez I: Role for high-glucose-induced protein
O-GlcNAcylation in stimulating cardiac fibroblast collagen
synthesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 306:C794–C804. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Fiaschi T, Magherini F, Gamberi T,
Lucchese G, Faggian G, Modesti A and Modesti PA: Hyperglycemia and
angiotensin II cooperate to enhance collagen I deposition by
cardiac fibroblasts through a ROS-STAT3-dependent mechanism.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1843:2603–2610. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kojima H, Fujimiya M, Matsumura K,
Nakahara T, Hara M and Chan L: Extrapancreatic insulin-producing
cells in multiple organs in diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2458–2463. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Phadnis SM, Ghaskadbi SM, Hardikar AA and
Bhonde RR: Mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow of
diabetic patients portrait unique markers influenced by the
diabetic microenvironment. Rev Diabet Stud. 6:260–270. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wang CC, Goalstone ML and Draznin B:
Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance that impact
cardiovascular biology. Diabetes. 53:2735–2740. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Grzebyk E and Piwowar A: Inhibitory
actions of selected natural substances on formation of advanced
glycation endproducts and advanced oxidation protein products. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 16:3812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Islas-Carbajal MC, Covarrubias A, Grijalva
G, Alvarez-Rodriguez A, Armendáriz-Borunda J and Rincón-Sánchez AR:
Nitric oxide synthases inhibition results in renal failure
improvement in cirrhotic rats. Liver Int. 25:131–140. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Corbett JA, Tilton RG, Chang K, Hasan KS,
Ido Y, Wang JL, Sweetland MA, Lancaster JR Jr, Williamson JR and
McDaniel ML: Aminoguanidine, a novel inhibitor of nitric oxide
formation, prevents diabetic vascular dysfunction. Diabetes.
41:552–556. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ara C, Karabulut AB, Kirimlioglu H, Yilmaz
M, Kirimliglu V and Yilmaz S: Protective effect of aminoguanidine
against oxidative stress in an experimental peritoneal adhesion
model in rats. Cell Biochem Funct. 24:443–448. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Stadler K, Jenei V, Somogyi A and Jakus J:
Beneficial effects of aminoguanidine on the cardiovascular system
of diabetic rats. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 21:189–196. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Richardson MA, Furlani RE, Podell BK,
Ackart DF, Haugen JD, Melander RJ, Melander C and Basaraba RJ:
Inhibition and breaking of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs)
with bis-2-aminoimidazole derivatives. Tetrahedron Lett.
56:3406–3409. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Giardino I, Fard AK, Hatchell DL and
Brownlee M: Aminoguanidine inhibits reactive oxygen species
formation, lipid peroxidation, and oxidant-induced apoptosis.
Diabetes. 47:1114–1120. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Oldfield MD, Bach LA, Forbes JM,
Nikolic-Paterson D, McRobert A, Thallas V, Atkins RC, Osicka T,
Jerums G and Cooper ME: Advanced glycation end products cause
epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation via the receptor for
advanced glycation end products (RAGE). J Clin Invest.
108:1853–1863. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Khazaei M, Karimi J, Sheikh N, Goodarzi
MT, Saidijam M, Khodadadi I and Moridi H: Effects of resveratrol on
receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) expression and
oxidative stress in the liver of rats with type 2 diabetes.
Phytother Res. 30:66–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Tan Y, Ichikawa T, Li J, Si Q, Yang H,
Chen X, Goldblatt CS, Meyer CJ, Li X, Cai L and Cui T: Diabetic
downregulation of Nrf2 activity via ERK contributes to oxidative
stress-induced insulin resistance in cardiac cells in vitro and in
vivo. Diabetes. 60:625–633. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|