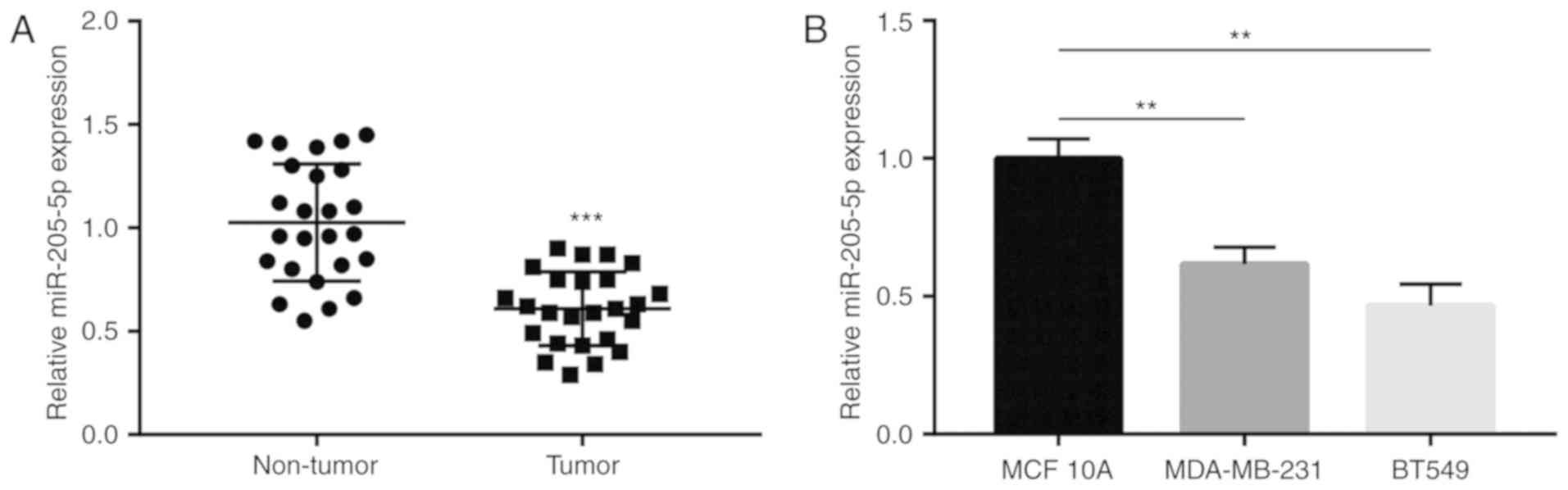
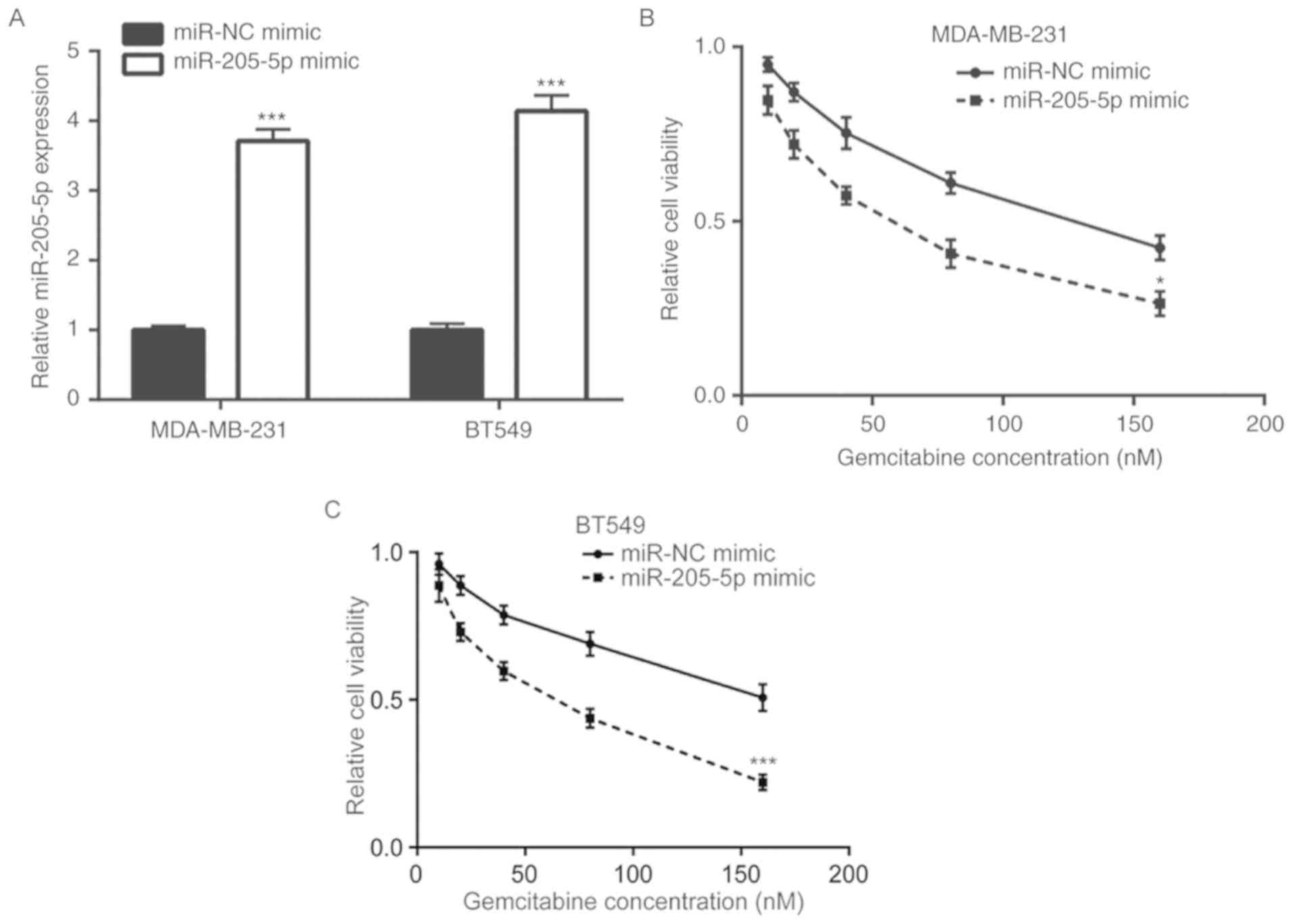
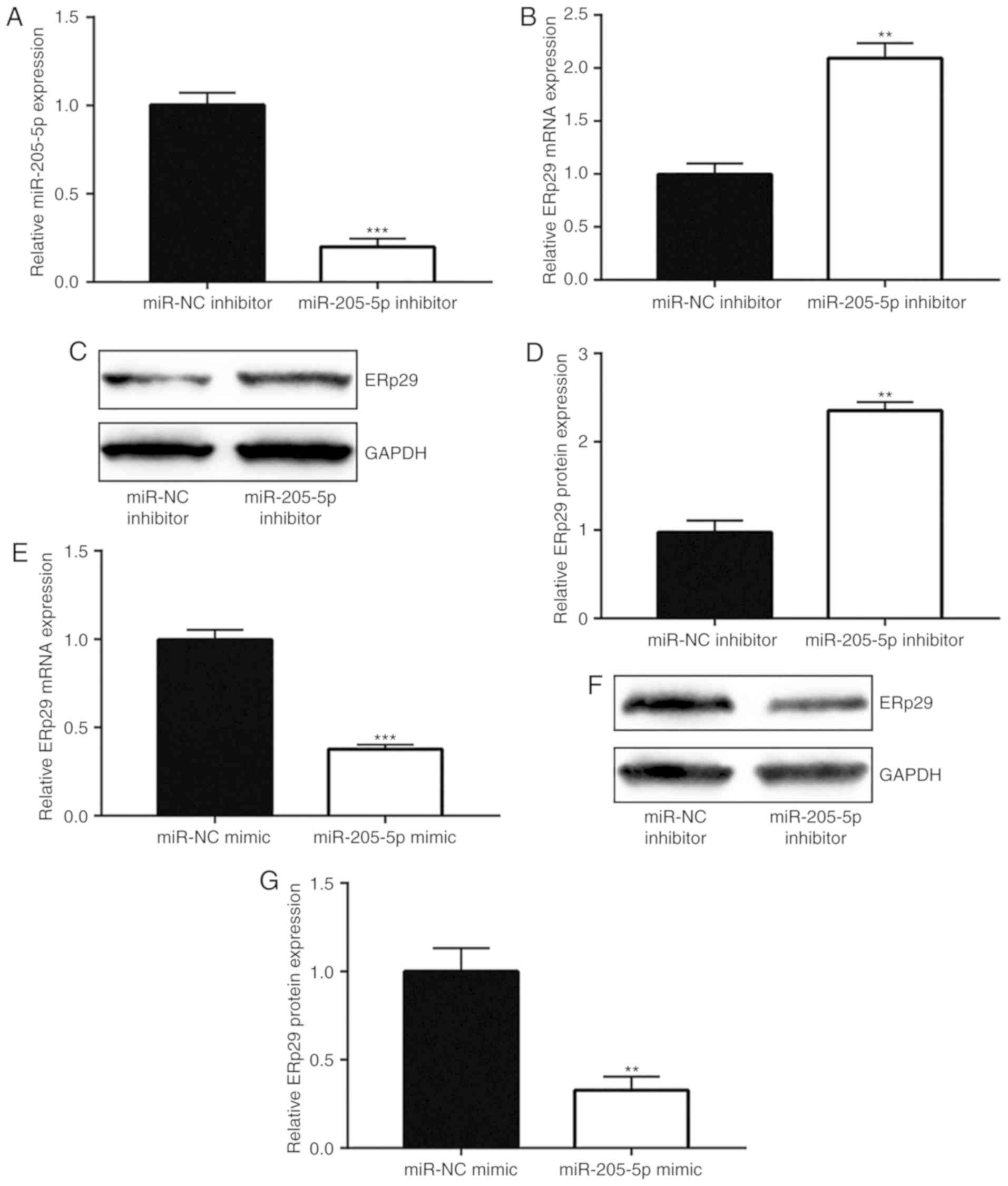
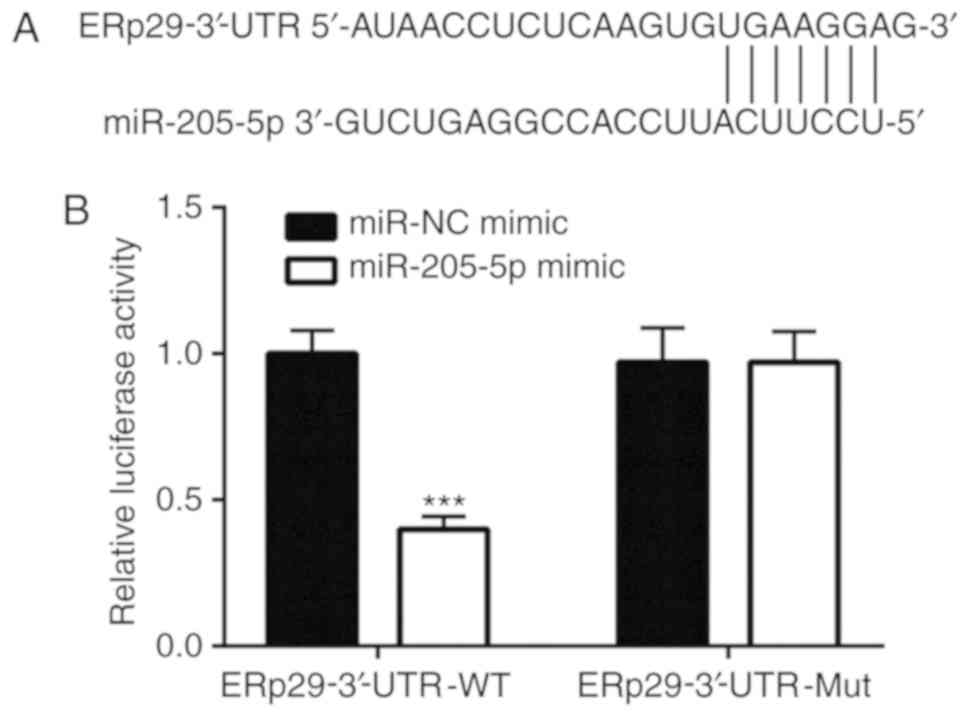
|
1
|
Smith IE, Dowsett M, Ebbs SR, Dixon JM,
Skene A, Blohmer JU, Ashley SE, Francis S, Boeddinghaus I and Walsh
G; IMPACT Trialists Group, : Neoadjuvant treatment of
postmenopausal breast cancer with anastrozole, tamoxifen, or both
in combination: The immediate preoperative anastrozole, tamoxifen,
or combined with tamoxifen (IMPACT) multicenter double-blind
randomized trial. J Clin Oncol. 23:5108–5116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gralow JR, Burstein HJ, Wood W, Hortobagyi
GN, Gianni L, von Minckwitz G, Buzdar AU, Smith IE, Symmans WF,
Singh B and Winer EP: Preoperative therapy in invasive breast
cancer: Pathologic assessment and systemic therapy issues in
operable disease. J Clin Oncol. 26:814–819. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tripathy D: Gemcitabine as single-agent
therapy for advanced breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 1
(Suppl):S8–S11. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Spielmann M: Single-agent gemcitabine as
first line therpy in patient with metastatic breast cancer.
Oncology. 62:2–8. 2011.
|
|
5
|
Blackstein M, Vogel CL, Ambinder R, Cowan
J, Iglesias J and Melemed A: Gemcitabin as first-line therapy in
patient with metastatic breast cancer: A phase II trail. Oncology.
62:2–8. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
CACA-CBCS, Chinese Anti-Cancer
Association, Committee of Breast Cancer Society, . Guidelines for
diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer in China (2017). China
Oncol. 27:1007–3639. 2017.
|
|
7
|
Vincenzi B, Santini D, Spoto S, Finolezzi
E, D'Angelillo RM, La Cesa A and Tonini G: The antineoplastic
treatment in the elderly. Clin Ter. 153:207–215. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu ZH, Lin C, Liu MM, Zhang J, Tao Z and
Hu XC: Src inhibition can synergize with gemcitabine and reverse
resistance in triple negative breast cancer cells via the AKT/c-Jun
pathway. PLoS One. 11:e01692302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang D and Richardson DR: Endoplasmic
reticulum protein 29 (ERp29): An emerging role in cancer. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 43:33–36. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martin C, Ardizzoni A and Rosso R:
Gemcitabine: Safety profile and efficacy in non-small cell lung
cancer unaffected by age. Aging (Milano). 9:297–303.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu P, Zhang H, Qi L, Tang Q, Tang Y, Xie
Z, Lv Y, Zhao S and Jiang W: Identification of ERp29 as a biomarker
for predicting nasopharyngeal carcinoma response to radiotherapy.
Oncol Rep. 27:987–994. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang D and Putti TC: Over-expression of
ERp29 attenuates doxorubicin-induced cell apoptosis through
up-regulation of Hsp27 in breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res Dec.
316:3522–3531. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mori-Iwamoto S, Kuramitsu Y, Ryozawa S,
Mikuria K, Fujimoto M, Maehara S, Maehara Y, Okita K, Nakamura K
and Sakaida I: Proteomics finding heat shock protein 27 as a
biomarker for resistance of pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine.
Int J Oncol. 31:1345–1350. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Hu Y, Wang JL, Yao H, Wang H,
Liang L, Li C, Shi H, Chen Y, Fang JY and Xu J: Proteomic
identification of ERP29 as a key chemoresistant factor activated by
the aggregating p53 mutant Arg282Trp. Oncogene. 36:5473–5483. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hammond SM: An overview of microRNAs. Adv
Drug Deliv Rev. 87:3–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Calin GA and Konopleva M: Small gene, big
number, many effects. Blood. 120:240–241. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Farmer DT, Shariat N, Park CY, Liu HJ,
Mavropoulos A and McManus MT: Partially penetrant postnatal
lethality of an epithelial specific MicroRNA in a mouse knockout.
PLoS One. 8:e766342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Greene SB, Gunaratne PH, Hammond SM and
Rosen JM: A putative role for microRNA-205 in mammary epithelial
cell progenitors. J Cell Sci. 123:606–618. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wu H, Zhu S and Mo YY: Suppression of cell
growth and invasion by miR-205 in breast cancer. Cell Res.
19:439–448. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
De Cola A, Volpe S, Budani MC, Ferracin M,
Lattanzio R, Turdo A, D'Agostino D, Capone E, Stassi G, Todaro M,
et al: MIR-205-5p-mediated downregulation of ErbB/HER receptors in
breast cancer stem cells results in targeted therapy resistance.
Cell Death. 6:e18232015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qi L, Wu P, Zhang X, Qiu Y, Jiang W, Huang
D, Liu Y, Tan P and Tian Y: Inhibiting ERp29 expression enhances
radiosensitivity in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell lines. Med
Oncol. 29:721–728. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dyawanapelly S, Kumar A and Chourasia MK:
Lessons learned from gemcitabine: Impact of therapeutic carrier
systems and Gemcitabine's drug conjugates on cancer therapy. Crit
Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 34:63–96. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ying SY, Chang DC and Lin SL: The microRNA
(miRNA): Overview of the RNA genes that modulate gene function. Mol
Biotechnol. 38:257–268. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lou W, Liu J, Gao Y, Zhong G, Ding B, Xu L
and Fan W: MicroRNA regulation of liver cancer stem cells. Am J
Cancer Res. 8:1126–1141. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang W, Liu J and Wang G: The role of
microRNAs in human breast cancer progression. Tumour Biol.
35:6235–6244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu SJ, Yang L, Hong Q, Kuang XY, Di GH and
Shao ZM: MicroRNA-200a confers chemoresistance by antagonizing
TP53INP1 and YAP1 in human breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 18:742018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gregory PA, Bracken CP, Bert AG and
Goodall GJ: MicroRNAs as regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Cell Cycle. 7:3112–3118. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li L and Li S: miR-205-5p inhibits cell
migration and invasion in prostatic carcinoma by targeting ZEB1.
Oncol Lett. 16:1715–1721. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Okamoto K, Miyoshi K and Murawaki Y:
miR-29b, miR-205 and miR-221 enhance chemosensitivity to
gemcitabine in HuH28 human cholangiocarcinoma cells. PLoS One.
8:e776232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bambang IF, Lee YK, Richardson DR and
Zhang D: Endoplasmic reticulum protein 29 regulates epithelial cell
integrity during the mesenchymal-epithelial transition in breast
cancer cells. Oncogene. 32:1240–1251. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Deng YJ, Tang N, Liu C, Zhang JY, An SL,
Peng YL, Ma LL, Li GQ, Jiang Q, Hu CT, et al: CLIC4, ERp29, and
Smac/DIABLO derived from metastatic cancer stem-like cells stratify
prognostic risks of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
20:3809–3817. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bambang IF, Xu S, Zhou J, Salto-Tellez M,
Sethi SK and Zhang D: Overexpression of endoplasmic reticulum
protein 29 regulates mesenchymal-epithelial transition and
suppresses xenograft tumor growth of invasive breast cancer cells.
Lab Invest. 89:1229–1242. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shnyder SD, Mangum JE and Hubbard MJ:
Triplex profiling of functionally distinct chaperones
(ERp29/PDI/BiP) reveals marked heterogeneity of the endoplasmic
reticulum proteome in cancer. J Proteome Res. 7:3364–3372. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Farmaki E, Mkrtchian S, Papazian I,
Papavassiliou AG and Kiaris H: ERp29 regulates response to
doxorubicin by a PERK-mediated mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1813:1165–1171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|