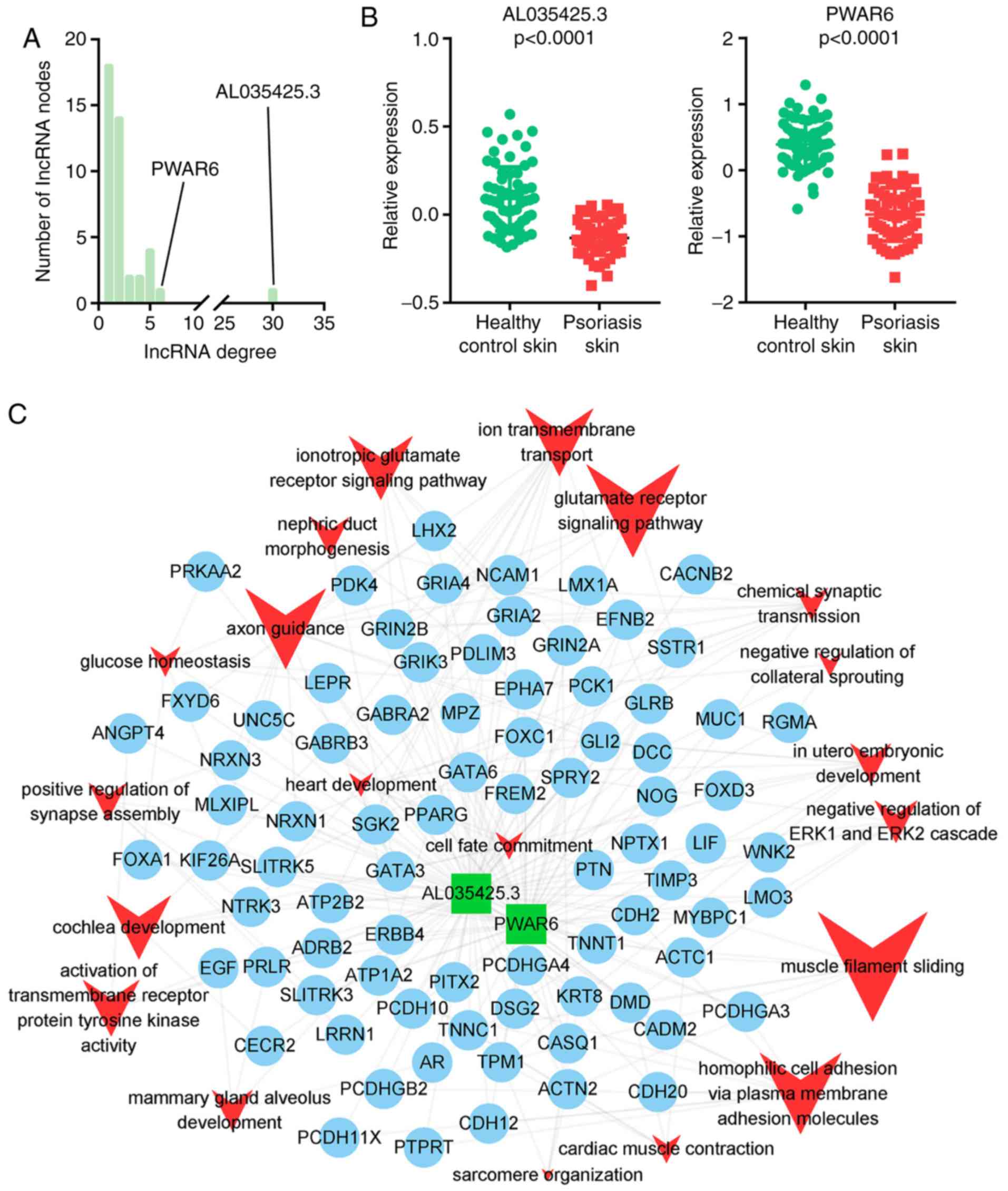
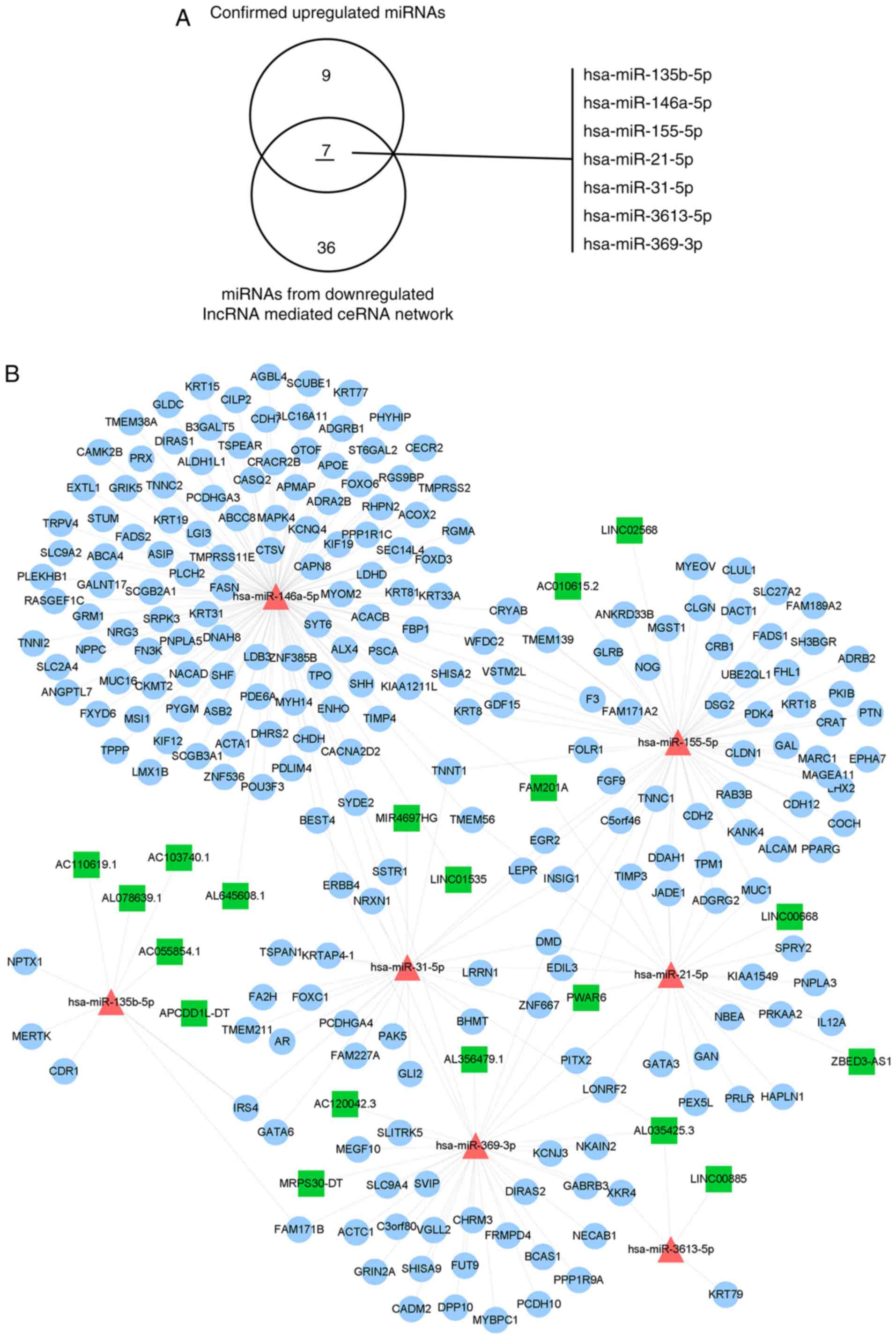
|
1
|
Nestle FO, Kaplan DH and Barker J:
Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 361:496–509. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Greb JE, Goldminz AM, Elder JT, Lebwohl
MG, Gladman DD, Wu JJ, Mehta NN, Finlay AY and Gottlieb AB:
Psoriasis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2:160822016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ogawa E, Sato Y, Minagawa A and Okuyama R:
Pathogenesis of psoriasis and development of treatment. J Dermatol.
45:264–272. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Di Cesare A, Di Meglio P and Nestle FO:
The IL-23/Th17 Axis in the Immunopathogenesis of Psoriasis. J
Invest Dermatol. 129:1339–1350. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
ENCODE Project Consortium, . An integrated
encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature.
489:57–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Szell M, Danis J, Bata-Csorgo Z and Kemeny
L: PRINS, a primate-specific long non-coding RNA, plays a role in
the keratinocyte stress response and psoriasis pathogenesis.
Pflugers Arch. 468:935–943. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Danis J, Goblos A, Bata-Csorgo Z, Kemeny L
and Szell M: PRINS Non-Coding RNA regulates nucleic acid-induced
innate immune responses of human keratinocytes. Front Immunol.
8:10532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szegedi K, Sonkoly E, Nagy N, Németh IB,
Bata-Csörgo Z, Kemény L, Dobozy A and Széll M: The anti-apoptotic
protein G1P3 is overexpressed in psoriasis and regulated by the
non-coding RNA, PRINS. Exp Dermatol. 19:269–278. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qiao M, Li R, Zhao X, Yan J and Sun Q:
Up-regulated lncRNA-MSX2P1 promotes the growth of IL-22-stimulated
keratinocytes by inhibiting miR-6731-5p and activating S100A7. Exp
Cell Res. 363:243–254. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L and
Pandolfi PP: A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA
language? Cell. 146:353–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bolger AM, Marc L and Bjoern U:
Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data.
Bioinformatics. 30:2114–2120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Daehwan K, Ben L and Salzberg SL: HISAT: A
fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods.
12:357–360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Simon A, Paul Theodor P and Wolfgang H:
HTSeq-a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing
data. Bioinformatics. 31:166–169. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shen L, Liu W, Cui J, Li J and Li C:
Analysis of long non-coding RNA expression profiles in ovarian
cancer. Oncol Lett. 14:1526–1530. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Friedl?Nder MR, Mackowiak SD, Na L, Wei C
and Nikolaus R: miRDeep2 accurately identifies known and hundreds
of novel microRNA genes in seven animal clades. Nucleic Acids Res.
40:37–52. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Karagkouni D, Paraskevopoulou MD,
Chatzopoulos S, Vlachos IS, Tastsoglou S, Kanellos I, Papadimitriou
D, Kavakiotis I, Maniou S, Skoufos G, et al: DIANA-TarBase v8: A
decade-long collection of experimentally supported miRNA-gene
interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D239–D245. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chou CH, Shrestha S, Yang CD, Chang NW,
Lin YL, Liao KW, Huang WC, Sun TH, Tu SJ, Lee WH, et al: miRTarBase
update 2018: A resource for experimentally validated
microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D296–d302.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42:D92–D97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paraskevopoulou MD, Vlachos IS, Karagkouni
D, Georgakilas G, Kanellos I, Vergoulis T, Zagganas K, Tsanakas P,
Floros E, Dalamagas T and Hatzigeorgiou AG: DIANA-LncBase v2:
Indexing microRNA targets on non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids
Res. 44:D231–D238. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tian L, Hu X, He Y, Wu Z, Li D and Zhang
H: Construction of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks reveals functional
lncRNAs in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Exp Ther Med. 16:3978–3986.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yan JJ, Qiao M, Li RH, Zhao XT, Wang XY
and Sun Q: Downregulation of miR-145-5p contributes to
hyperproliferation of keratinocytes and skin inflammation in
psoriasis. Br J Dermatol. 180:365–372. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sonkoly E, Wei T, Janson PC, Sääf A,
Lundeberg L, Tengvall-Linder M, Norstedt G, Alenius H, Homey B,
Scheynius A, et al: MicroRNAs: Novel regulators involved in the
pathogenesis of psoriasis? PLoS One. 2:e6102007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fu D, Yu W, Li M, Wang H, Liu D, Song X,
Li Z and Tian Z: MicroRNA-138 regulates the balance of Th1/Th2 via
targeting RUNX3 in psoriasis. Immunol Lett. 166:55–62. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Feng C, Bai M, Yu NZ, Wang XJ and Liu Z:
MicroRNA-181b negatively regulates the proliferation of human
epidermal keratinocytes in psoriasis through targeting TLR4. J Cell
Mol Med. 21:278–285. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu X, An J, Hua Y, Li Z, Yan N, Fan W and
Su C: MicroRNA-194 regulates keratinocyte proliferation and
differentiation by targeting Grainyhead-like 2 in psoriasis. Pathol
Res Pract. 213:89–97. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lerman G, Avivi C, Mardoukh C, Barzilai A,
Tessone A, Gradus B, Pavlotsky F, Barshack I, Polak-Charcon S,
Orenstein A, et al: MiRNA expression in psoriatic skin: Reciprocal
regulation of hsa-miR-99a and IGF-1R. PLoS One. 6:e209162011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li R, Qiao M, Zhao X, Yan J, Wang X and
Sun Q: MiR-20a-3p regulates TGF-β1/Survivin pathway to affect
keratinocytes proliferation and apoptosis by targeting SFMBT1 in
vitro. Cell Signal. 49:95–104. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu H, Hou L, Liu J and Li Z: MiR-217 is
down-regulated in psoriasis and promotes keratinocyte
differentiation via targeting GRHL2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
471:169–176. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Y, Yu X, Wang L, Ma W and Sun Q:
miR-320b is down-regulated in psoriasis and modulates keratinocyte
proliferation by targeting AKT3. Inflammation. 41:2160–2170. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ichihara A, Jinnin M, Yamane K, Fujisawa
A, Sakai K, Masuguchi S, Fukushima S, Maruo K and Ihn H:
microRNA-mediated keratinocyte hyperproliferation in psoriasis
vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 165:1003–1010. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chowdhari S, Sardana K and Saini N:
miR-4516, a microRNA downregulated in psoriasis inhibits
keratinocyte motility by targeting fibronectin/integrin α9
signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:3142–3152.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jiang M, Sun Z, Dang E, Li B, Fang H, Li
J, Gao L, Zhang K and Wang G: TGFβ/SMAD/microRNA-486-3p signaling
axis mediates keratin 17 expression and keratinocyte
hyperproliferation in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 137:2177–2186.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
A R, Yu P, Hao S and Li Y: MiR-876-5p
suppresses cell proliferation by targeting Angiopoietin-1 in the
psoriasis. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:1163–1169. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Joyce CE, Zhou X, Xia J, Ryan C, Thrash B,
Menter A, Zhang W and Bowcock AM: Deep sequencing of small RNAs
from human skin reveals major alterations in the psoriasis
miRNAome. Hum Mol Genet. 20:4025–4040. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jiang M, Ma W, Gao Y, Jia K, Zhang Y, Liu
H and Sun Q: IL-22-induced miR-122-5p promotes keratinocyte
proliferation by targeting Sprouty2. Exp Dermatol. 26:368–374.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Xiong Y, Chen H, Liu L, Wang Z, Tian F and
Zhao Y: microRNA-130a promotes human keratinocyte viability and
migration and inhibits apoptosis through direct regulation of
STK40-mediated NF-κB pathway and indirect regulation of
SOX9-meditated JNK/MAPK pathway: A potential role in psoriasis. DNA
Cell Biol. 36:219–226. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Hermann H, Runnel T, Aab A, Baurecht H,
Rodriguez E, Magilnick N, Urgard E, Šahmatova L, Prans E,
Maslovskaja J, et al: miR-146b probably assists miRNA-146a in the
suppression of keratinocyte proliferation and inflammatory
responses in psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 137:1945–1954. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Luo Q, Zeng J, Li W, Lin L, Zhou X, Tian
X, Liu W, Zhang L and Zhang X: Silencing of miR155 suppresses
inflammatory responses in psoriasis through inflammasome NLRP3
regulation. Int J Mol Med. 42:1086–1095. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zibert JR, Lovendorf MB, Litman T, Olsen
J, Kaczkowski B and Skov L: MicroRNAs and potential target
interactions in psoriasis. J Dermatol Sci. 58:177–185. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wu R, Zeng J, Yuan J, Deng X, Huang Y,
Chen L, Zhang P, Feng H, Liu Z, Wang Z, et al: MicroRNA-210
overexpression promotes psoriasis-like inflammation by inducing Th1
and Th17 cell differentiation. J Clin Invest. 128:2551–2568. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Guo S, Zhang W, Wei C, Wang L, Zhu G, Shi
Q, Li S, Ge R, Li K, Gao L, et al: Serum and skin levels of
miR-369-3p in patients with psoriasis and their correlation with
disease severity. Eur J Dermatol. 23:608–613. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang C, Zong J, Li Y, Wang X, Du W and Li
L: MiR-744-3p regulates keratinocyte proliferation and
differentiation via targeting KLLN in psoriasis. Exp Dermatol.
28:283–291. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rachakonda TD, Schupp CW and Armstrong AW:
Psoriasis prevalence among adults in the United States. J Am Acad
Dermatol. 70:512–516. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Baliwag J, Barnes DH and Johnston A:
Cytokines in psoriasis. Cytokine. 73:342–350. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Nograles KE and Krueger JG: Anti-cytokine
therapies for psoriasis. Exp Cell Res. 317:1293–1300. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu GC, Pan HF, Leng RX, Wang DG, Li XP, Li
XM and Ye DQ: Emerging role of long noncoding RNAs in autoimmune
diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 14:798–805. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tay Y, Rinn J and Pandolfi PP: The
multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature.
505:344–352. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li CX, Li HG, Huang LT, Kong YW, Chen FY,
Liang JY, Yu H and Yao ZR: H19 lncRNA regulates keratinocyte
differentiation by targeting miR-130b-3p. Cell Death Dis.
8:e31742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Akiyama M: Early-onset generalized
pustular psoriasis is representative of autoinflammatory
keratinization diseases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 143:809–810. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Deng Y, Chang C and Lu Q: The inflammatory
response in psoriasis: A Comprehensive review. Clin Rev Allergy
Immunol. 50:377–389. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Lin X, Jiang T, Bai J, Li J, Wang T, Xiao
J, Tian Y, Jin X, Shao T, Xu J, et al: Characterization of
transcriptome transition associates long noncoding RNAs with glioma
progression. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 13:620–632. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lei M, Mitsuhashi S, Miyake N, Ohta T,
Liang D, Wu L and Matsumoto N: Translocation breakpoint disrupting
the host SNHG14 gene but not coding genes or snoRNAs in typical
Prader-Willi syndrome. J Hum Genet. 64:647–652. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|