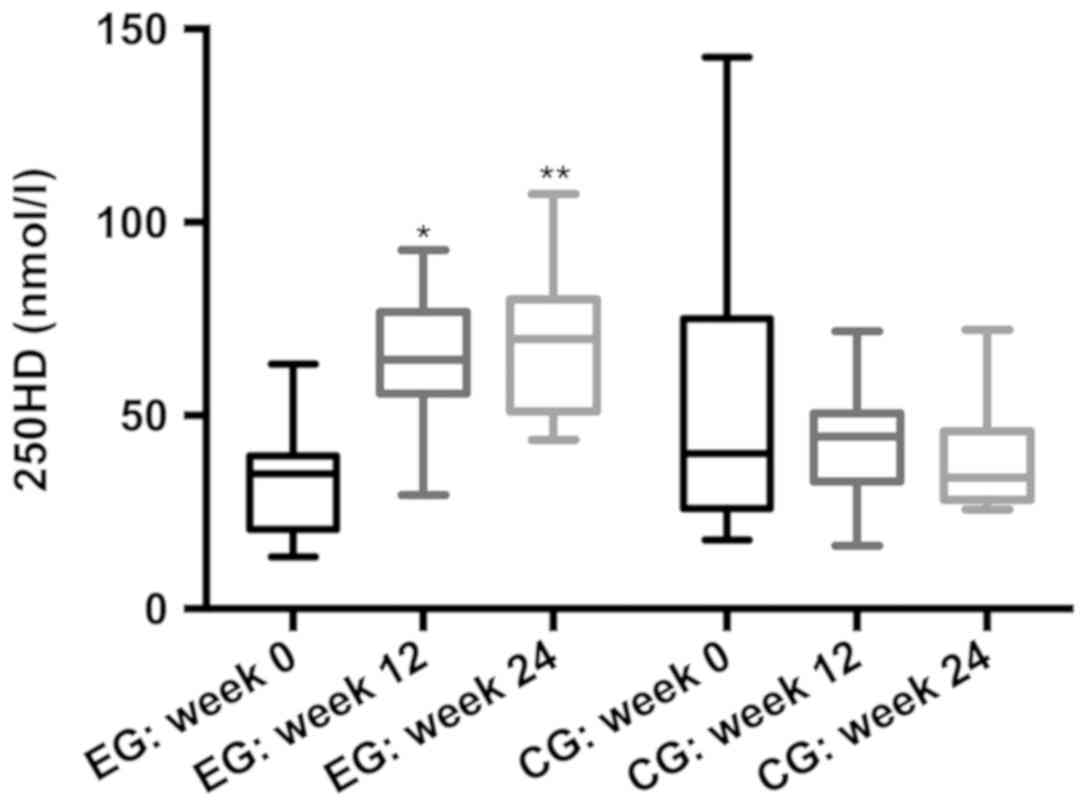
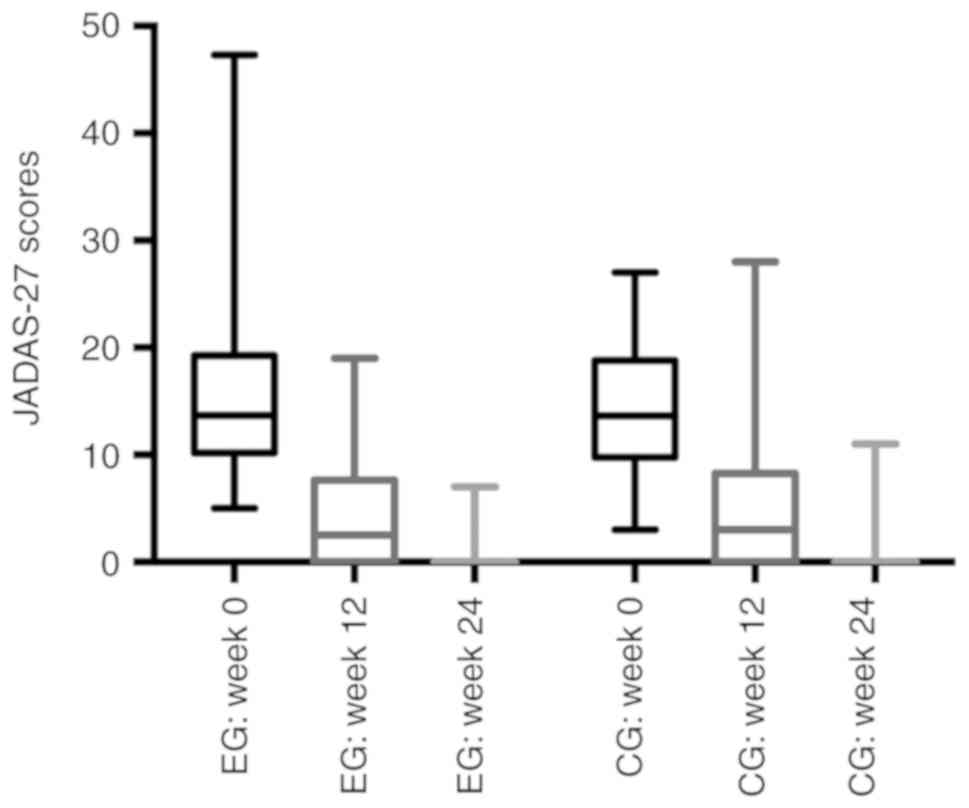
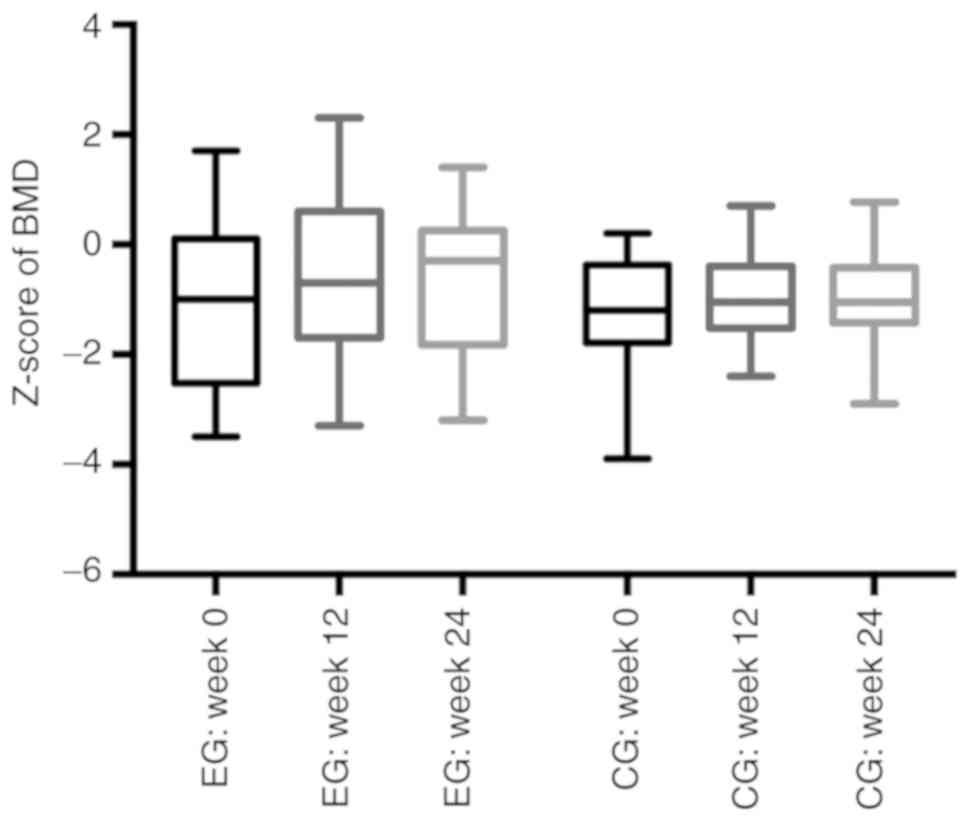
|
1
|
Prakken B, Albani S and Martini A:
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Lancet. 377:2138–2149. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Martini A and Lovell DJ: Juvenile
idiopathic arthritis: State of the art and future perspectives. Ann
Rheum Dis. 69:1260–1263. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bracaglia C, Prencipe G and Benedetti FD:
Macrophage Activation Syndrome: Different mechanisms leading to a
one clinical syndrome. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 15:52017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tappeiner C, Klotsche J, Sengler C, et al:
Risk factors and biomarkers for the occurrence of uveitis in JIA:
Data from the Inception Cohort of Newly diagnosed patients with
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (ICON-JIA) study. Arthritis
Rheumatol. 2018:[J]. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40544
|
|
5
|
DeLuca HF: Overview of general physiologic
features and functions of vitamin D. Am J Clin Nutr. 80
(Suppl):1689S–1696S. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
White JH: Vitamin D metabolism and
signaling in the immune system. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 13:21–29.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kamen DL and Tangpricha V: Vitamin D and
molecular actions on the immune system: Modulation of innate and
autoimmunity. J Mol Med (Berl). 88:441–450. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
White JH: Vitamin D metabolism and
signaling in the immune system. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 13:21–29.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Maddaloni E, Cavallari I, Napoli N and
Conte C: Vitamin D and diabetes mellitus. Front Horm Res.
50:161–176. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jeffery LE, Raza K and Hewison M: Vitamin
D in rheumatoid arthritis-towards clinical application. Rheumatol.
12:201–210. 2016.
|
|
11
|
Iruretagoyena M, Hirigoyen D, Naves R and
Burgos PI: Immune response modulation by vitamin D: Role in
systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. 6:5132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lima GL, Paupitz J, Aikawa NE, Takayama L,
Bonfa E and Pereira RM: Vitamin D supplementation in adolescents
and young adults with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus for
improvement in disease activity and fatigue scores: A randomized,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Care Res
(Hoboken). 68:91–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Finch SL, Rosenberg AM and Vatanparast H:
Vitamin D and juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Pediatr Rheumatol
Online J. 16:342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bouaddi I, Rostom S, El Badri D, Hassani
A, Chkirate B, Abouqal R, Amine B and Hajjaj-Hassouni N: Vitamin D
concentrations and disease activity in Moroccan children with
juvenile idiopathic arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.
15:1152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Çomak E, Doğan ÇS, Uslugökçeoğlu A, et al:
Association between vitamin D deficiency and disease activity in
juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Turk J Pediatr. 71 (Suppl 3):702.
2013.
|
|
16
|
Pelajo CF, Lopez-Benitez JM, Kent DM,
Price LL, Miller LC and Dawson-Hughes B: 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels
and juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Is there an association with
disease activity? Rheumatol Int. 32:3923–3929. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tang T, Tang X, Xu L, Huang Y, Zeng J and
Li Q: Evaluation of bone mass in children and young adults with
juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 33:758–764.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lima GL, Paupitz J, Aikawa NE, et al: A
randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of vitamin D
supplementation in adolescents and young adults with Juvenile-onset
SLE: Improvement in disease activity and fatigue scores. Arthritis
Care Res (Hoboken). 68:912015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ellis JA, Scurrah KJ, Li YR, Ponsonby AL,
Chavez RA, Pezic A, Dwyer T, Akikusa JD, Allen RC, Becker ML, et
al: Epistasis amongst PTPN2 and genes of the vitamin D pathway
contributes to risk of juvenile idiopathic arthritis. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 145:113–120. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Çomak E, Doǧan CS, Gökçeoglu AU, et al:
Evaluation of vitamin D levels in children with juvenile idiopathic
arthritis. Çocuk Sagligi Hastalik Derg. 55:191–196. 2012.
|
|
21
|
Zwerina K, Baum W, Axmann R, Heiland GR,
Distler JH, Smolen J, Hayer S, Zwerina J and Schett G: Vitamin D
receptor regulates TNF-mediated arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis.
70:1122–1129. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stagi S, Bertini F, Cavalli L,
Matucci-Cerinic M, Brandi ML and Falcini F: Determinants of vitamin
D levels in children, adolescents, and young adults with juvenile
idiopathic arthritis. J Rheumatol. 41:1884–1892. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P, Baum J,
Glass DN, Goldenberg J, He X, Maldonado-Cocco J, Orozco-Alcala J,
Prieur AM, et al International League of Associations for
Rheumatology, : International League of Associations for
Rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis:
Second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol. 31:390–392.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Consolaro A, Ruperto N, Bazso A, Pistorio
A, Magni-Manzoni S, Filocamo G, Malattia C, Viola S, Martini A and
Ravelli A; Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials
Organisation, : Development and validation of a composite disease
activity score for juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
61:658–666. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari
HA, Gordon CM, Hanley DA, Heaney RP, Murad MH and Weaver CM;
Endocrine Society, : Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of
vitamin D deficiency: An Endocrine Society clinical practice
guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:1911–1930. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ojaimi S, Skinner NA, Strauss BJ,
Sundararajan V, Woolley I and Visvanathan K: Vitamin D deficiency
impacts on expression of toll-like receptor-2 and cytokine profile:
A pilot study. J Transl Med. 11:1762013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jarvis JN, Jiang K, Frank MB, Knowlton N,
Aggarwal A, Wallace CA, McKee R, Chaser B, Tung C, Smith LB, et al:
Gene expression profiling in neutrophils from children with
polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
60:1488–1495. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gregorio A, Gambini C, Gerloni V,
Parafioriti A, Sormani MP, Gregorio S, De Marco G, Rossi F, Martini
A, et al: Lymphoid neogenesis in juvenile idiopathic arthritis
correlates with ANA positivity and plasma cells infiltration.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 46:308–313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chinese Nutrition Society. Dietary
nutrient intake for Chinese residents (M)(in Chinese). China light
industry press; 2010
|
|
30
|
John N: Hathcock. (3rd). Vitamin and
Mineral Safety. 33–36. 2014.
|
|
31
|
Heaney RP, Dowell MS, Hale CA and Bendich
A: Calcium absorption varies within the reference range for serum
25-hydroxyvitamin D. J Am Coll Nutr. 22:142–146. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Abrams SA, Hicks PD and Hawthorne KM:
Higher serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels in school-age children are
inconsistently associated with increased calcium absorption. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 94:2421–2427. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zerwekh JE: Blood biomarkers of vitamin D
status. Am J Clin Nutr. 87:1087S–1091S. 2008.[J]. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mellins ED, Macaubas C and Grom AA:
Pathogenesis of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: Some
answers, more questions. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 7:416–426. 2011.[J].
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ursin K, Lydersen S, Skomsvoll JF and
Wallenius M: Disease Activity of Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
during and after Pregnancy: A Prospective Multicenter Study. J
Rheumatol. 45:257–265. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|