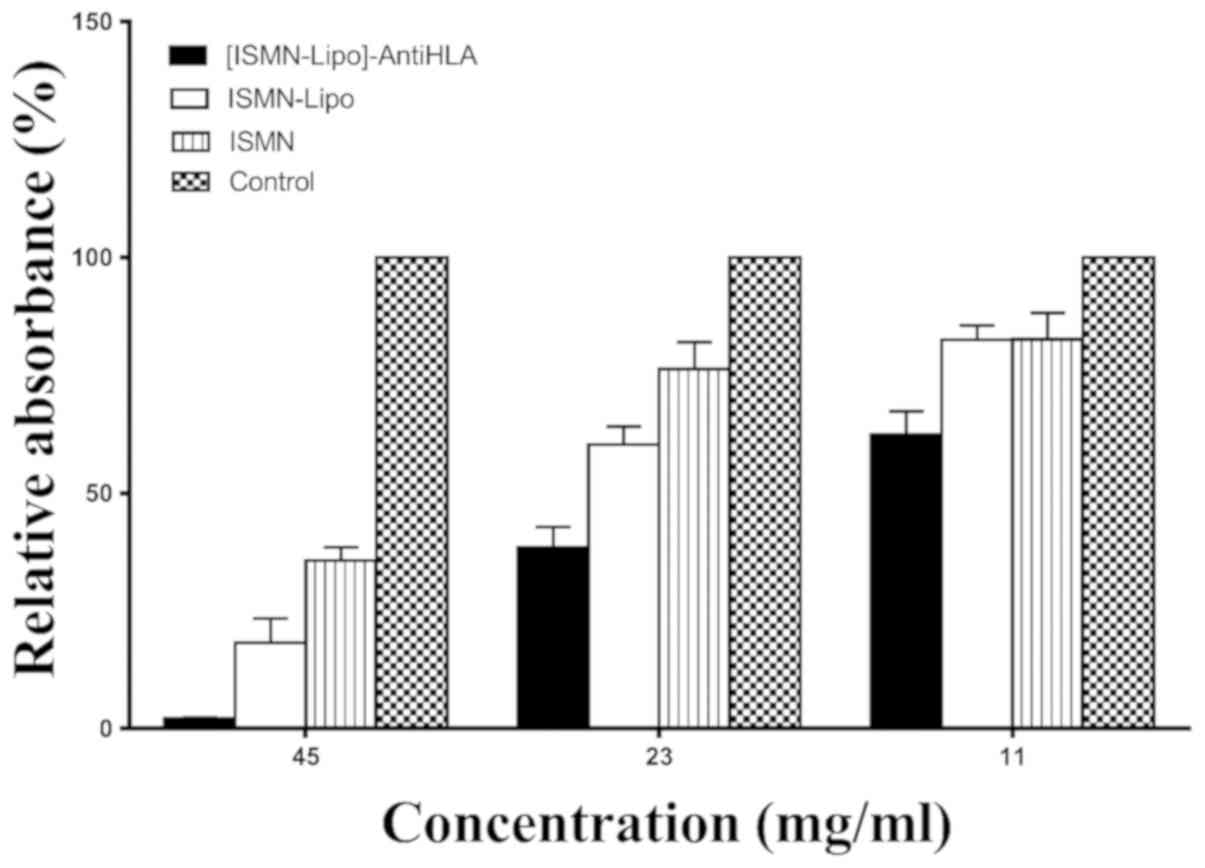
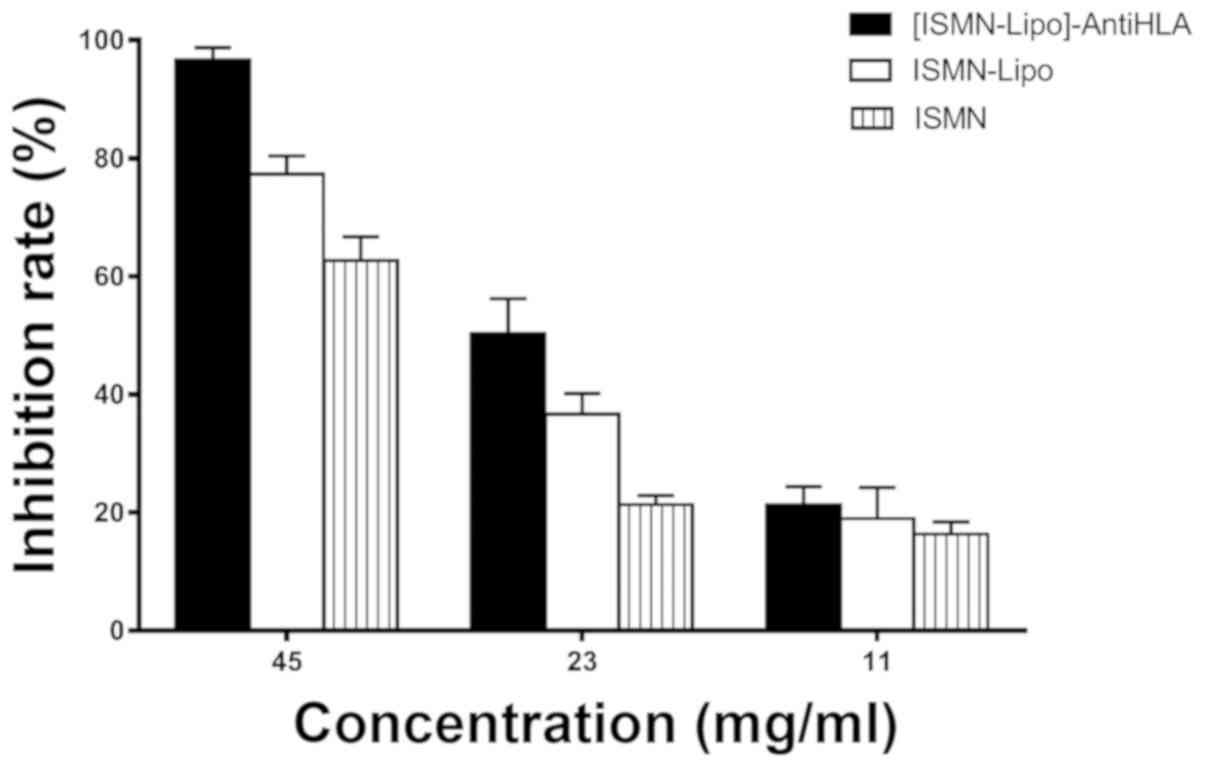
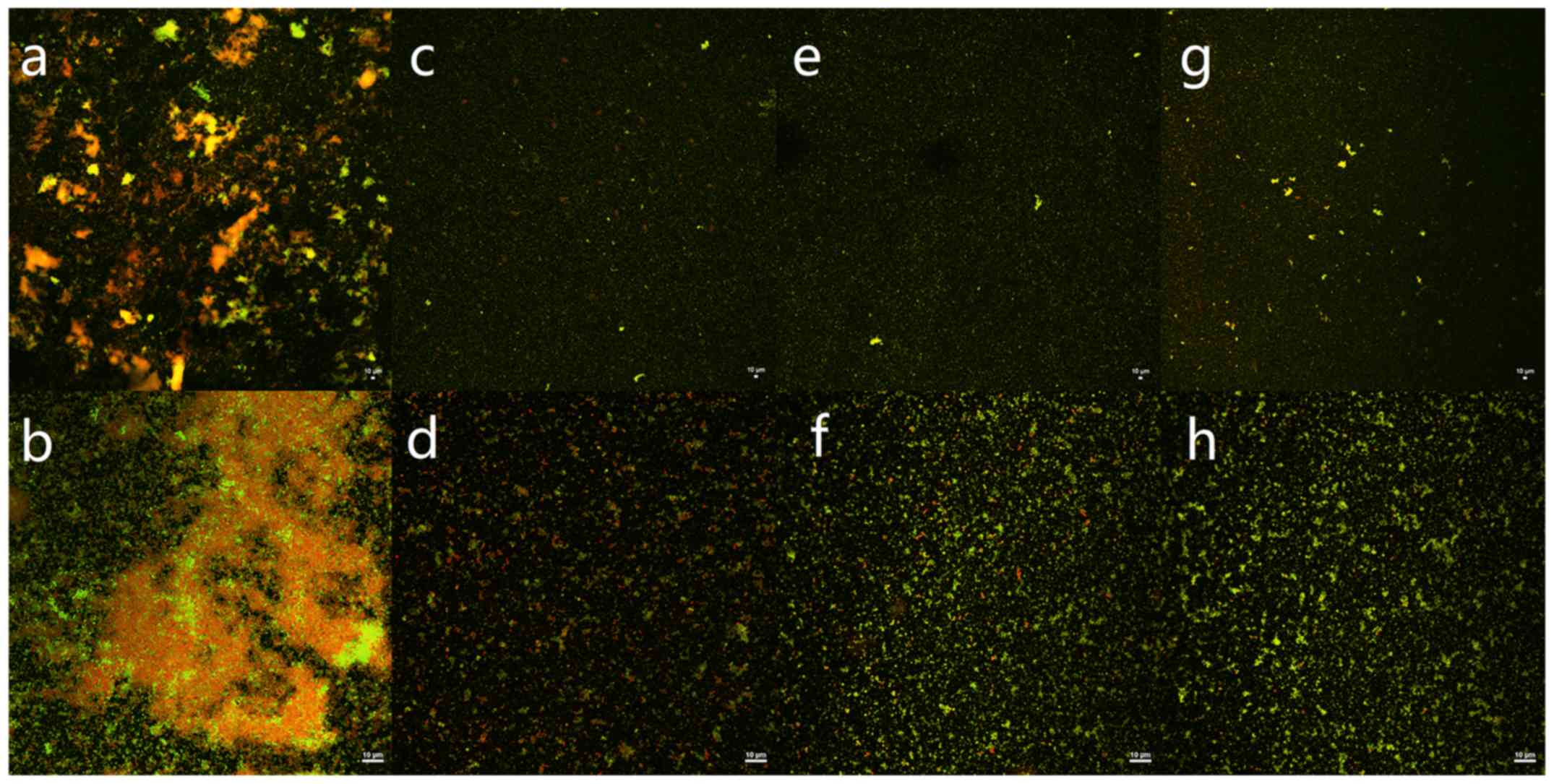
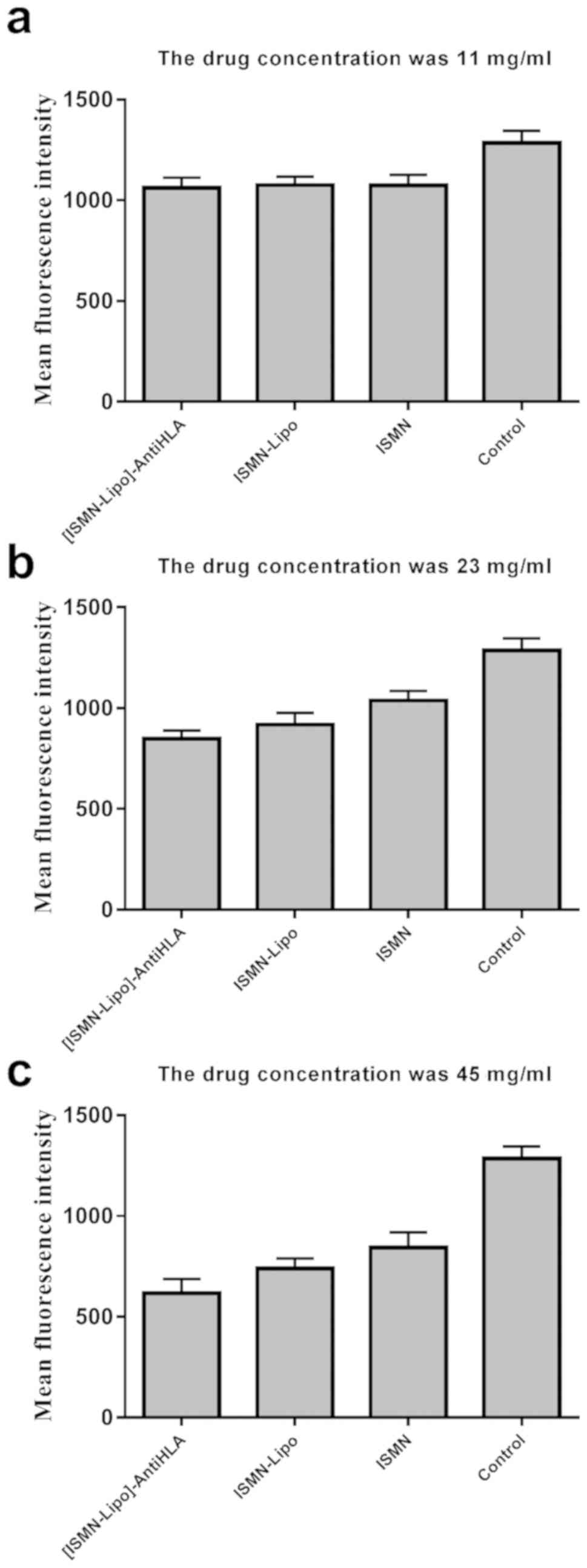
|
1
|
Boase S, Foreman A, Cleland E, Tan L,
Melton-Kreft R, Pant H, Hu FZ, Ehrlich GD and Wormald PJ: The
microbiome of chronic rhinosinusitis: Culture, molecular
diagnostics and biofilm detection. BMC Infect Dis. 13:2102013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ha KR, Psaltis AJ, Butcher AR, Wormald PJ
and Tan LW: In vitro activity of mupirocin on clinical isolates of
Staphylococcus aureus and its potential implications in
chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope. 118:535–540. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jardeleza C, Rao S, Thierry B, Gajjar P,
Vreugde S, Prestidge CA and Wormald PJ: Liposome-encapsulated ISMN:
A novel nitric oxide-based therapeutic agent against
Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. PLoS One. 9:e921172014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abuzeid WM, Girish VM, Fastenberg JH,
Draganski AR, Lee AY, Nosanchuk JD and Friedman JM: Nitric
oxide-releasing microparticles as a potent antimicrobial
therapeutic against chronic rhinosinusitis bacterial isolates. Int
Forum Allergy Rhinol. 8:1190–1198. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Barraud N, Hassett DJ, Hwang SH, Rice SA,
Kjelleberg S and Webb JS: Involvement of nitric oxide in biofilm
dispersal of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol.
188:7344–7353. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Workman AD, Carey RM, Kohanski MA, Kennedy
DW, Palmer JN, Adappa ND and Cohen NA: Relative susceptibility of
airway organisms to antimicrobial effects of nitric oxide. Int
Forum Allergy Rhinol. 7:770–776. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hariri BM, McMahon DB, Chen B, Freund JR,
Mansfield CJ, Doghramji LJ, Adappa ND, Palmer JN, Kennedy DW, Reed
DR, et al: Flavones modulate respiratory epithelial innate
immunity: Anti-inflammatory effects and activation of the T2R14
receptor. J Biol Chem. 292:8484–8497. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kishikawa H, Ebberyd A, Römling U, Brauner
A, Lüthje P, Lundberg JO and Weitzberg E: Control of pathogen
growth and biofilm formation using a urinary catheter that releases
antimicrobial nitrogen oxides. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:1257–1264.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Slomberg DL, Lu Y, Broadnax AD, Hunter RA,
Carpenter AW and Schoenfisch MH: Role of size and shape on biofilm
eradication for nitric oxide-releasing silica nanoparticles. ACS
Appl Mater Interfaces. 5:9322–9329. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Oelze M, Knorr M, Kröller-Schön S,
Kossmann S, Gottschlich A, Rümmler R, Schuff A, Daub S, Doppler C,
Kleinert H, et al: Chronic therapy with isosorbide-5-mononitrate
causes endothelial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and a marked
increase in vascular endothelin-1 expression. Eur Heart J.
34:3206–3216. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Müller S, König I, Meyer W and Kojda G:
Inhibition of vascular oxidative stress in hypercholesterolemia by
eccentric isosorbide mononitrate. J Am Coll Cardiol. 44:624–631.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yaari Z, da Silva D, Zinger A, Goldman E,
Kajal A, Tshuva R, Barak E, Dahan N, Hershkovitz D, Goldfeder M, et
al: Theranostic barcoded nanoparticles for personalized cancer
medicine. Nat Commun. 7:133252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anaya-Ruiz M, Bandala C, Landeta G,
Martínez-Morales P, Zumaquero-Rios JL, Sarracent-Pérez J and
Pérez-Santos M: Nanostructured systems in advanced drug targeting
for the cancer treatment: Recent patents. Recent Patents Anticancer
Drug Discov. 14:85–94. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zheng Y, Tang L, Mabardi L, Kumari S and
Irvine DJ: Enhancing adoptive cell therapy of cancer through
targeted delivery of small-molecule immunomodulators to
internalizing or noninternalizing receptors. ACS Nano.
11:3089–3100. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dong D, Thomas N, Thierry B, Vreugde S,
Prestidge CA and Wormald PJ: Distribution and inhibition of
liposomes on Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas
aeruginosa biofilm. PLoS One. 10:e01318062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ahmed K, Gribbon PN and Jones MN: The
application of confocal microscopy to the study of liposome
adsorption onto bacterial biofilms. J Liposome Res. 12:285–300.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tan Y, Ma S, Leonhard M, Moser D,
Haselmann GM, Wang J, Eder D and Schneider-Stickler B: Enhancing
antibiofilm activity with functional chitosan nanoparticles
targeting biofilm cells and biofilm matrix. Carbohydr Polym.
200:35–42. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Akanda ZZ, Taha M and Abdelbary H: Current
review - The rise of bacteriophage as a unique therapeutic platform
in treating peri-prosthetic joint infections. J Orthop Res.
36:1051–1060. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ivanova K, Fernandes MM, Francesko A,
Mendoza E, Guezguez J, Burnet M and Tzanov T: Quorum-quenching and
matrix-degrading enzymes in multilayer coatings synergistically
prevent bacterial biofilm formation on urinary catheters. ACS Appl
Mater Interfaces. 7:27066–27077. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pires DP, Melo L, Vilas Boas D,
Sillankorva S and Azeredo J: Phage therapy as an alternative or
complementary strategy to prevent and control biofilm-related
infections. Curr Opin Microbiol. 39:48–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Figueiredo AMS, Ferreira FA, Beltrame CO
and Côrtes MF: The role of biofilms in persistent infections and
factors involved in ica-independent biofilm development and gene
regulation in Staphylococcus aureus. Crit Rev Microbiol.
43:602–620. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Forier K, Raemdonck K, De Smedt SC,
Demeester J, Coenye T and Braeckmans K: Lipid and polymer
nanoparticles for drug delivery to bacterial biofilms. J Control
Release. 190:607–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Martins M, McCusker MP, McCabe EM, O'Leary
D, Duffy G and Fanning S: Evidence of metabolic switching and
implications for food safety from the phenome(s) of Salmonella
enterica serovar Typhimurium DT104 cultured at selected points
across the pork production food chain. Appl Environ Microbiol.
79:5437–5449. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Fauvart M, De Groote VN and Michiels J:
Role of persister cells in chronic infections: Clinical relevance
and perspectives on anti-persister therapies. J Med Microbiol.
60:699–709. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang G and Yin B: Therapeutic effects of
long-circulating miR-135a-containing cationic immunoliposomes
against gallbladder carcinoma. Sci Rep. 7:59822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Marques J, Valle-Delgado JJ, Urbán P, Baró
E, Prohens R, Mayor A, Cisteró P, Delves M, Sinden RE, Grandfils C,
et al: Adaptation of targeted nanocarriers to changing requirements
in antimalarial drug delivery. Nanomedicine (Lond). 13:515–525.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Moles E, Moll K, Ch'ng JH, Parini P,
Wahlgren M and Fernàndez-Busquets X: Development of drug-loaded
immunoliposomes for the selective targeting and elimination of
rosetting Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells. J Control
Release. 241:57–67. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ertem E, Gutt B, Zuber F, Allegri S, Le
Ouay B, Mefti S, Formentin K, Stellacci F and Ren Q: Core-shell
silver nanoparticles in endodontic disinfection solutions enable
long-term antimicrobial effect on oral biofilms. ACS Appl Mater
Interfaces. 9:34762–34772. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|