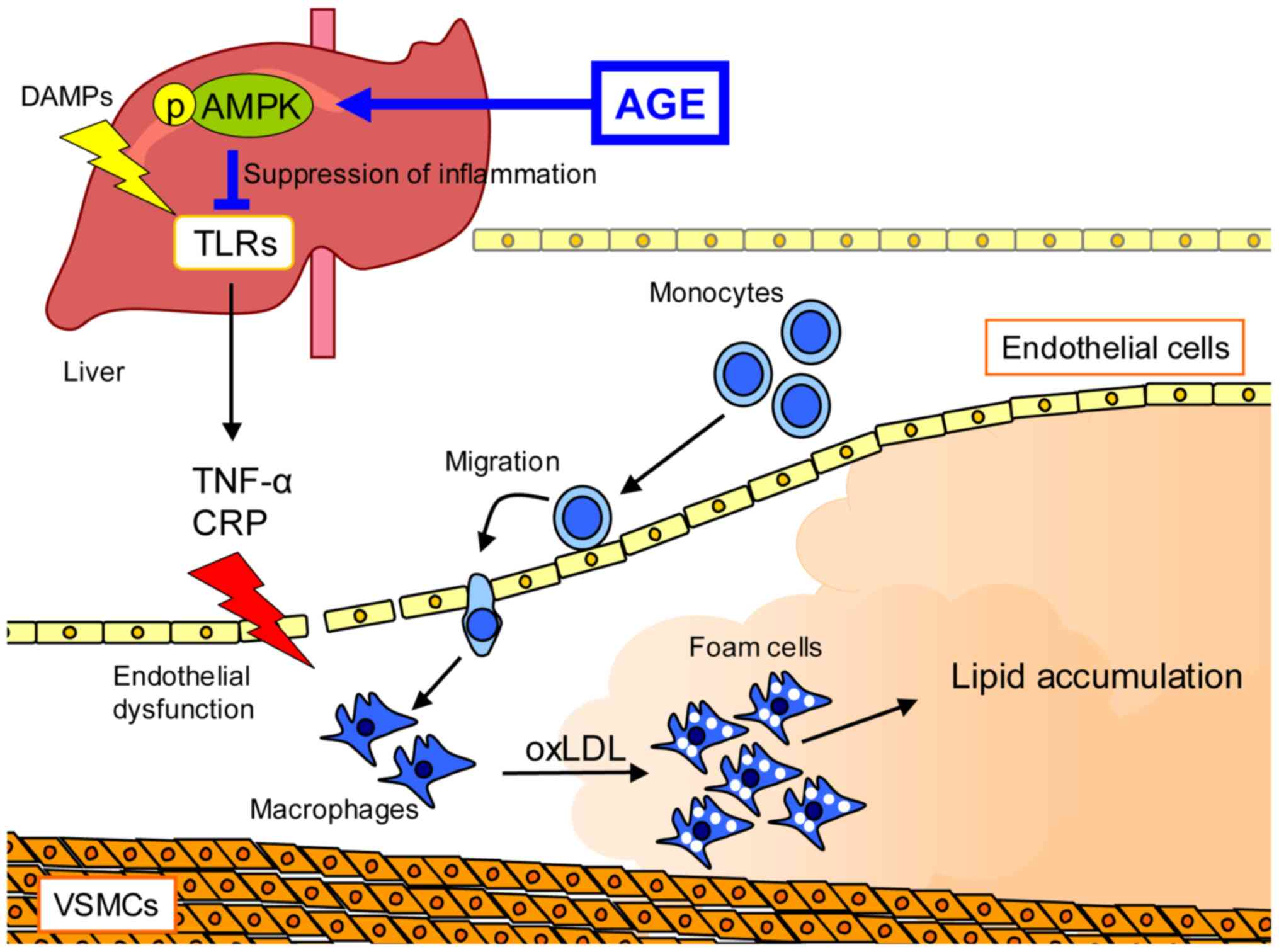
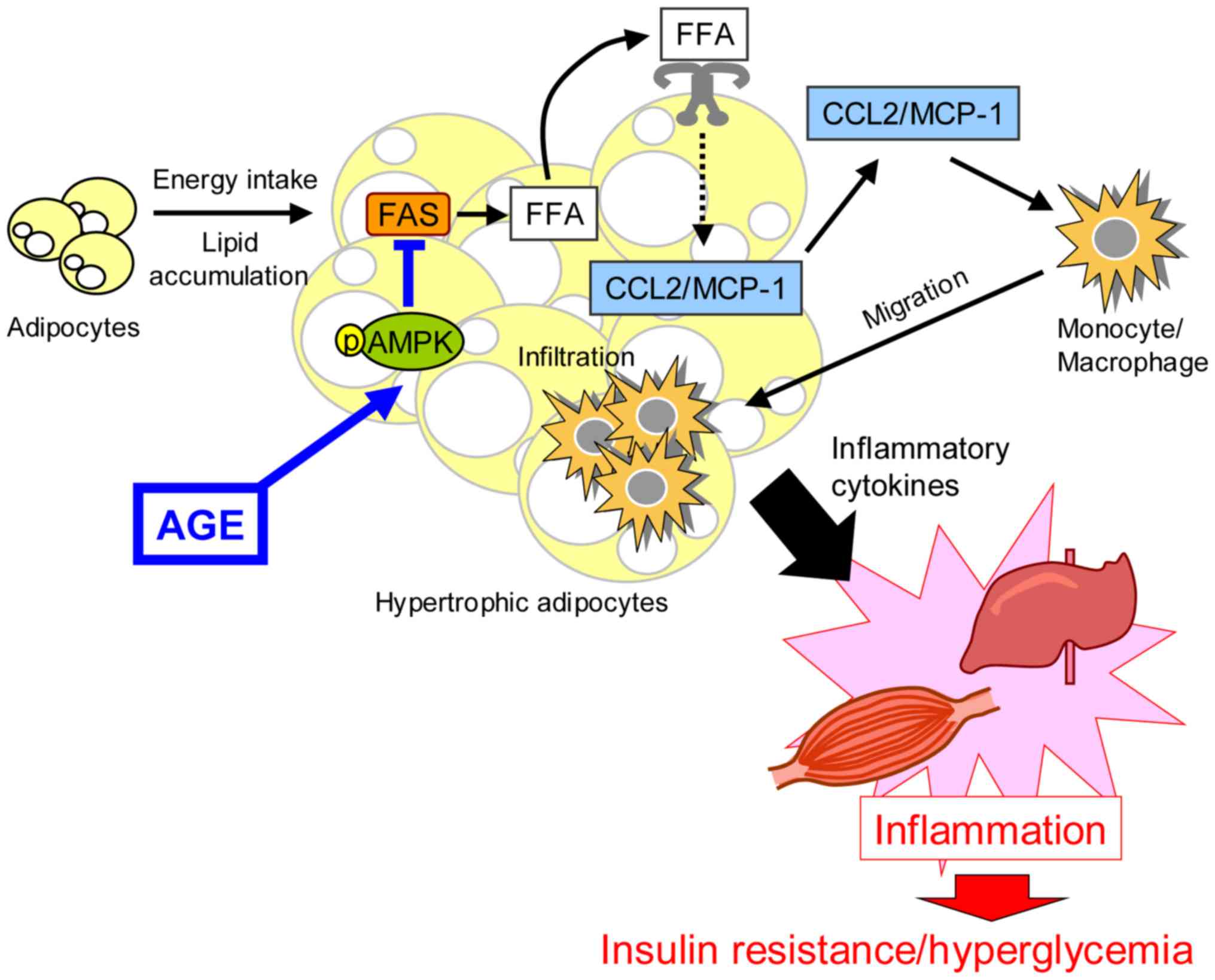
|
1
|
Hardie DG, Ross FA and Hawley SA: AMPK: A
nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:251–262. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mihaylova MM and Shaw RJ: The AMPK
signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and
metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1016–1023. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Garcia D and Shaw RJ: AMPK: Mechanisms of
Cellular Energy Sensing and Restoration of Metabolic Balance. Mol
Cell. 66:789–800. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bai A, Ma AG, Yong M, Weiss CR, Ma Y, Guan
Q, Bernstein CN and Peng Z: AMPK agonist downregulates innate and
adaptive immune responses in TNBS-induced murine acute and
relapsing colitis. Biochem Pharmacol. 80:1708–1717. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nath N, Giri S, Prasad R, Salem ML, Singh
AK and Singh I: 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleoside: A
novel immunomodulator with therapeutic efficacy in experimental
autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 175:566–574. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao X, Zmijewski JW, Lorne E, Liu G, Park
YJ, Tsuruta Y and Abraham E: Activation of AMPK attenuates
neutrophil proinflammatory activity and decreases the severity of
acute lung injury. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
295:L497–L504. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lorenzatti AJ and Servato ML: New evidence
on the role of inflammation in CVD risk. Curr Opin Cardiol.
34:418–423. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Geovanini GR and Libby P: Atherosclerosis
and inflammation: Overview and updates. Clin Sci (Lond).
132:1243–1252. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu CH, Abrams ND, Carrick DM, Chander P,
Dwyer J, Hamlet MRJ, Macchiarini F, PrabhuDas M, Shen GL, Tandon P,
et al: Biomarkers of chronic inflammation in disease development
and prevention: Challenges and opportunities. Nat Immunol.
18:1175–1180. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arulselvan P, Fard MT, Tan WS, Gothai S,
Fakurazi S, Norhaizan ME and Kumar SS: Role of Antioxidants and
Natural Products in Inflammation. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:52761302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Conti P and Shaik-Dasthagirisaeb Y:
Atherosclerosis: A chronic inflammatory disease mediated by mast
cells. Cent Eur J Immunol. 40:380–386. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Piccinini AM and Midwood KS: DAMPening
inflammation by modulating TLR signalling. Mediators Inflamm.
2010:6723952010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vénéreau E, Ceriotti C and Bianchi ME:
DAMPs from Cell Death to New Life. Front Immunol. 6:4222015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Patel S: Danger-Associated Molecular
Patterns (DAMPs): The Derivatives and Triggers of Inflammation.
Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 18:632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matsutomo T and Kodera Y: Development of
an Analytic Method for Sulfur Compounds in Aged Garlic Extract with
the Use of a Postcolumn High Performance Liquid Chromatography
Method with Sulfur-Specific Detection. J Nutr. 146:450S–455S. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kodera Y, Ushijima M, Amano H, Suzuki JI
and Matsutomo T: Chemical and biological properties of
S−1-propenyl-l-cysteine in aged garlic extract. Molecules.
22:E5702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nantz MP, Rowe CA, Muller CE, Creasy RA,
Stanilka JM and Percival SS: Supplementation with aged garlic
extract improves both NK and γδ-T cell function and reduces the
severity of cold and flu symptoms: A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled nutrition intervention. Clin Nutr. 31:337–344.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu C, Mathews AE, Rodrigues C, Eudy BJ,
Rowe CA, O'Donoughue A and Percival SS: Aged garlic extract
supplementation modifies inflammation and immunity of adults with
obesity: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical
trial. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 24:148–155. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Suzuki JI, Kodera Y, Miki S, Ushijima M,
Takashima M, Matsutomo T and Morihara N: Anti-inflammatory action
of cysteine derivative S−1-propenylcysteine by inducing
MyD88 degradation. Sci Rep. 8:141482018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kyo E, Uda N, Kasuga S and Itakura Y:
Immunomodulatory effects of aged garlic extract. J Nutr. 131((3s)):
1075S–1079S. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morihara N, Ide N and Weiss N: Aged garlic
extract inhibits CD36 expression in human macrophages via
modulation of the PPARgamma pathway. Phytother Res. 24:602–608.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morihara N, Hino A, Yamaguchi T and Suzuki
J: Aged garlic extract suppresses the development of
atherosclerosis apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. J Nutr.
146:460S–463S. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Morihara N, Hino A, Miki S, Takashima M
and Suzuki JI: Aged garlic extract suppresses inflammation in
apolipoprotein E-knockout mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 61:17003082017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Matsumoto S, Nakanishi R, Li D, Alani A,
Rezaeian P, Prabhu S, Abraham J, Fahmy MA, Dailing C, Flores F, et
al: Aged Garlic Extract Reduces Low Attenuation Plaque in Coronary
Arteries of Patients with Metabolic Syndrome in a Prospective
Randomized Double-Blind Study. J Nutr. 146:427S–432S. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Budoff M: Aged garlic extract retards
progression of coronary artery calcification. J Nutr. 136
(Suppl):741S–744S. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ried K, Frank OR and Stocks NP: Aged
garlic extract reduces blood pressure in hypertensives: A
dose-response trial. Eur J Clin Nutr. 67:64–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Matsutomo T, Ushijima M, Kodera Y,
Nakamoto M, Takashima M, Morihara N and Tamura K: Metabolomic study
on the antihypertensive effect of S−1-propenylcysteine in
spontaneously hypertensive rats using liquid chromatography coupled
with quadrupole-Orbitrap mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt
Technol Biomed Life Sci. 1046:147–155. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ried K, Travica N and Sali A: The effect
of aged garlic extract on blood pressure and other cardiovascular
risk factors in uncontrolled hypertensives: The AGE at Heart trial.
Integr Blood Press Control. 9:9–21. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ried K, Travica N and Sali A: The Effect
of Kyolic Aged Garlic Extract on Gut Microbiota, Inflammation, and
Cardiovascular Markers in Hypertensives: The GarGIC Trial. Front
Nutr. 5:1222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hiramatsu K, Tsuneyoshi T, Ogawa T and
Morihara N: Aged garlic extract enhances heme oxygenase-1 and
glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit expression via the
nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2-antioxidant response
element signaling pathway in human endothelial cells. Nutr Res.
36:143–149. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tsuneyoshi T, Kunimura K and Morihara N:
S−1-Propenylcysteine augments BACH1 degradation and heme
oxygenase 1 expression in a nitric oxide-dependent manner in
endothelial cells. Nitric Oxide. 84:22–29. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Thomson M, Al-Qattan KK, Js D and Ali M:
Anti-diabetic and anti-oxidant potential of aged garlic extract
(AGE) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. BMC Complement
Altern Med. 16:172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ushijima M, Takashima M, Kunimura K,
Kodera Y, Morihara N and Tamura K: Effects of
S−1-propenylcysteine, a sulfur compound in aged garlic
extract, on blood pressure and peripheral circulation in
spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 70:559–565.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Miki S, Inokuma KI, Takashima M, Nishida
M, Sasaki Y, Ushijima M, Suzuki JI and Morihara N: Aged garlic
extract suppresses the increase of plasma glycated albumin level
and enhances the AMP-activated protein kinase in adipose tissue in
TSOD mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 61:16007972017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hwang YP, Kim HG, Choi JH, Do MT, Chung
YC, Jeong TC and Jeong HG: S-allylcysteine attenuates free
fatty acid-induced lipogenesis in human HepG2 cells through
activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. J
Nutr Biochem. 24:1469–1478. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu L, Di W, Dong X, Li Z, Xue X, Zhang J,
Wang Q, Xiao X, Han J, Yang Y, et al: Diallyl trisulfide exerts
cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in
diabetic state, role of AMPK-mediated AKT/GSK-3β/HIF-1α activation.
Oncotarget. 8:74791–74805. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xiao J, Guo R, Fung ML, Liong EC, Chang
RC, Ching YP and Tipoe GL: Garlic-Derived
S-Allylmercaptocysteine Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver
Disease in a Rat Model through Inhibition of Apoptosis and
Enhancing Autophagy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013:6429202013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kim J, Yang G, Kim Y, Kim J and Ha J: AMPK
activators: Mechanisms of action and physiological activities. Exp
Mol Med. 48:e2242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Coughlan KA, Valentine RJ, Ruderman NB and
Saha AK: AMPK activation: A therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes?
Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 7:241–253. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bäck M, Yurdagul A Jr, Tabas I, Öörni K
and Kovanen PT: Inflammation and its resolution in atherosclerosis:
Mediators and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cardiol.
16:389–406. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Salminen A, Hyttinen JM and Kaarniranta K:
AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits NF-κB signaling and
inflammation: Impact on healthspan and lifespan. J Mol Med (Berl).
89:667–676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Salminen A and Kaarniranta K:
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) controls the aging process via
an integrated signaling network. Ageing Res Rev. 11:230–241. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ou H, Liu C, Feng W, Xiao X, Tang S and Mo
Z: Role of AMPK in atherosclerosis via autophagy regulation. Sci
China Life Sci. 61:1212–1221. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu-Bryan R: Inflammation and
intracellular metabolism: New targets in OA. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 23:1835–1842. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li Y, Xu S, Mihaylova MM, Zheng B, Hou X,
Jiang B, Park O, Luo Z, Lefai E, Shyy JY, et al: AMPK
phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic
steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant
mice. Cell Metab. 13:376–388. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Doddapattar P, Radović B, Patankar JV,
Obrowsky S, Jandl K, Nusshold C, Kolb D, Vujić N, Doshi L, Chandak
PG, et al: Xanthohumol ameliorates atherosclerotic plaque
formation, hypercholesterolemia, and hepatic steatosis in
ApoE-deficient mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 57:1718–1728.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang Q, Zhang M, Liang B, Shirwany N, Zhu
Y and Zou MH: Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase is
required for berberine-induced reduction of atherosclerosis in
mice: The role of uncoupling protein 2. PLoS One. 6:e254362011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Van Gaal LF, Mertens IL and De Block CE:
Mechanisms linking obesity with cardiovascular disease. Nature.
444:875–880. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shoelson SE, Lee J and Goldfine AB:
Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 116:1793–1801.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rameshrad M, Maleki-Dizaji N, Soraya H,
Toutounchi NS, Barzegari A and Garjani A: Effect of A-769662, a
direct AMPK activator, on Tlr-4 expression and activity in mice
heart tissue. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 19:1308–1317. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Mancini SJ, White AD, Bijland S,
Rutherford C, Graham D, Richter EA, Viollet B, Touyz RM, Palmer TM
and Salt IP: Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase rapidly
suppresses multiple pro-inflammatory pathways in adipocytes
including IL-1 receptor-associated kinase-4 phosphorylation. Mol
Cell Endocrinol. 440:44–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Malekpour-Dehkordi Z, Javadi E, Doosti M,
Paknejad M, Nourbakhsh M, Yassa N, Gerayesh-Nejad S and Heshmat R:
S-Allylcysteine, a garlic compound, increases ABCA1
expression in human THP-1 macrophages. Phytother Res. 27:357–361.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kemmerer M, Wittig I, Richter F, Brüne B
and Namgaladze D: AMPK activates LXRα and ABCA1 expression in human
macrophages. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 78:1–9. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Olokoba AB, Obateru OA and Olokoba LB:
Type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review of current trends. Oman Med J.
27:269–273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kahn SE, Cooper ME and Del Prato S:
Pathophysiology and treatment of type 2 diabetes: Perspectives on
the past, present, and future. Lancet. 383:1068–1083. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
DeFronzo RA, Ferrannini E, Groop L, Henry
RR, Herman WH, Holst JJ, Hu FB, Kahn CR, Raz I, Shulman GI, et al:
Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 1:150192015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
de Luca C and Olefsky JM: Inflammation and
insulin resistance. FEBS Lett. 582:97–105. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Mancuso P: The role of adipokines in
chronic inflammation. ImmunoTargets Ther. 5:47–56. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
McArdle MA, Finucane OM, Connaughton RM,
McMorrow AM and Roche HM: Mechanisms of obesity-induced
inflammation and insulin resistance: Insights into the emerging
role of nutritional strategies. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
4:522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
León-Pedroza JI, González-Tapia LA, del
Olmo-Gil E, Castellanos-Rodríguez D, Escobedo G and González-Chávez
A: Low-grade systemic inflammation and the development of metabolic
diseases: From the molecular evidence to the clinical practice. Cir
Cir. 83:543–551. 2015.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lumeng CN and Saltiel AR: Inflammatory
links between obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest.
121:2111–2117. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Rehman K and Akash MS: Mechanisms of
inflammatory responses and development of insulin resistance: How
are they interlinked? J Biomed Sci. 23:872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhang BB, Zhou G and Li C: AMPK: An
emerging drug target for diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell
Metab. 9:407–416. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hardie DG: AMPK: A target for drugs and
natural products with effects on both diabetes and cancer.
Diabetes. 62:2164–2172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Rena G, Hardie DG and Pearson ER: The
mechanisms of action of metformin. Diabetologia. 60:1577–1585.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Rojas LB and Gomes MB: Metformin: An old
but still the best treatment for type 2 diabetes. Diabetol Metab
Syndr. 5:62013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Setter SM, Iltz JL, Thams J and Campbell
RK: Metformin hydrochloride in the treatment of type 2 diabetes
mellitus: A clinical review with a focus on dual therapy. Clin
Ther. 25:2991–3026. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Lagouge M, Argmann C, Gerhart-Hines Z,
Meziane H, Lerin C, Daussin F, Messadeq N, Milne J, Lambert P,
Elliott P, et al: Resveratrol improves mitochondrial function and
protects against metabolic disease by activating SIRT1 and
PGC-1alpha. Cell. 127:1109–1122. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Price NL, Gomes AP, Ling AJ, Duarte FV,
Martin-Montalvo A, North BJ, Agarwal B, Ye L, Ramadori G, Teodoro
JS, et al: SIRT1 is required for AMPK activation and the beneficial
effects of resveratrol on mitochondrial function. Cell Metab.
15:675–690. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhu X, Wu C, Qiu S, Yuan X and Li L:
Effects of resveratrol on glucose control and insulin sensitivity
in subjects with type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. Nutr Metab (Lond). 14:602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liang Y, Xu X, Yin M, Zhang Y, Huang L,
Chen R and Ni J: Effects of berberine on blood glucose in patients
with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic literature review and a
meta-analysis. Endocr J. 66:51–63. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lee YS, Kim WS, Kim KH, Yoon MJ, Cho HJ,
Shen Y, Ye JM, Lee CH, Oh WK, Kim CT, et al: Berberine, a natural
plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase with
beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin-resistant
states. Diabetes. 55:2256–2264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Welsh KJ, Kirkman MS and Sacks DB: Role of
Glycated Proteins in the Diagnosis and Management of Diabetes:
Research Gaps and Future Directions. Diabetes Care. 39:1299–1306.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Anguizola J, Matsuda R, Barnaby OS, Hoy
KS, Wa C, DeBolt E, Koke M and Hage DS: Review: Glycation of human
serum albumin. Clin Chim Acta. 425:64–76. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Leto D and Saltiel AR: Regulation of
glucose transport by insulin: Traffic control of GLUT4. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 13:383–396. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Huang S and Czech MP: The GLUT4 glucose
transporter. Cell Metab. 5:237–252. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Bijland S, Mancini SJ and Salt IP: Role of
AMP-activated protein kinase in adipose tissue metabolism and
inflammation. Clin Sci (Lond). 124:491–507. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|