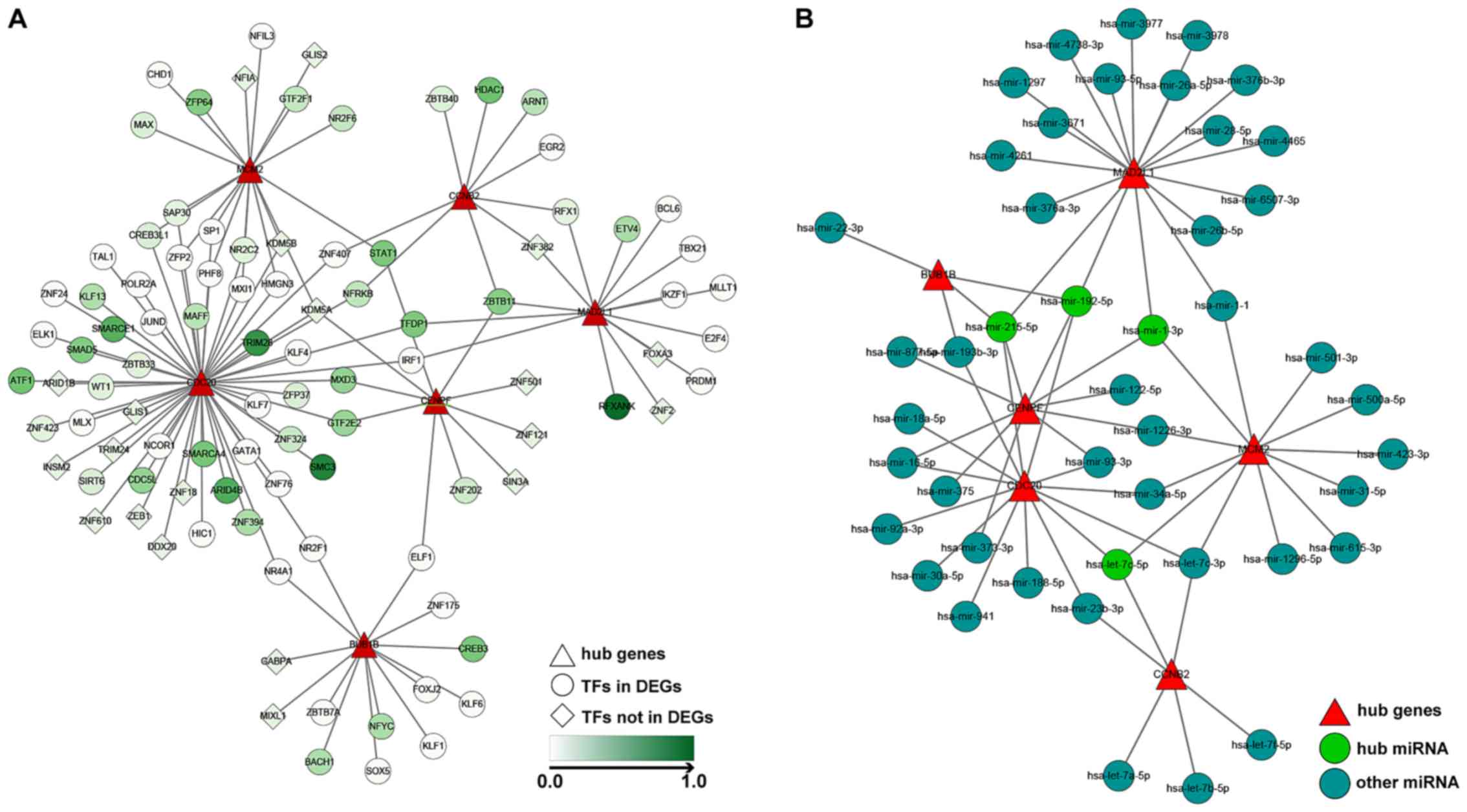
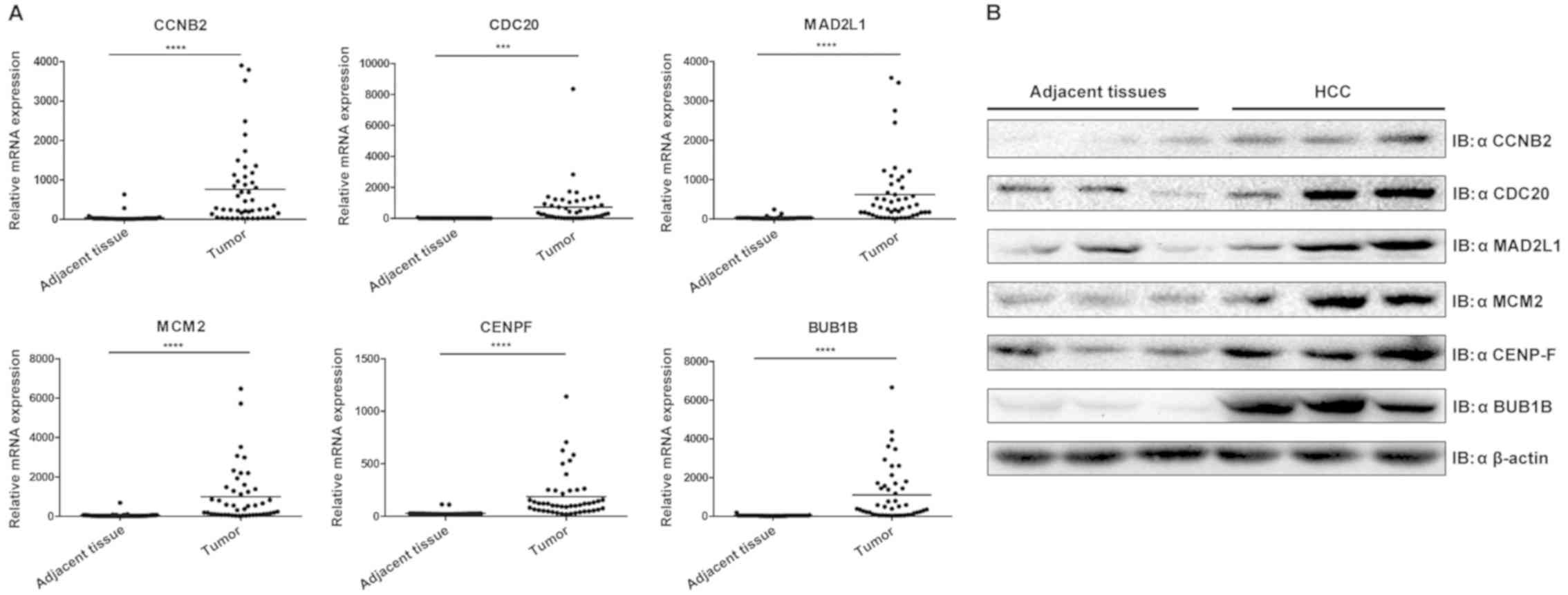
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mittal S and El-Serag HB: Epidemiology of
hepatocellular carcinoma: Consider the population. J Clin
Gastroenterol. 47 (Suppl):S2–S6. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma: An
epidemiologic view. J Clin Gastroenterol. 35 (Suppl 2):S72–S78.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang JD and Roberts LR: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: A global view. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:448–458.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ho DW, Kai AK and Ng IO: TCGA
whole-transcriptome sequencing data reveals significantly
dysregulated genes and signaling pathways in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Front Med. 9:322–330. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ho DW, Yang ZF, Yi K, Lam CT, Ng MN, Yu
WC, Lau J, Wan T, Wang X, Yan Z, et al: Gene expression profiling
of liver cancer stem cells by RNA-sequencing. PLos One.
7:e371592012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mazzola A, Costantino A, Petta S,
Bartolotta TV, Raineri M, Sacco R, Brancatelli G, Cammà C and
Cabibbo G: Recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver
transplantation: An update. Future Oncol. 11:2923–2936. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Regalia E, Fassati LR, Valente U,
Pulvirenti A, Damilano I, Dardano G, Montalto F, Coppa J and
Mazzaferro V: Pattern and management of recurrent hepatocellular
carcinoma after liver transplantation. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat
Surg. 5:29–34. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun B, Lin G, Ji D, Li S, Chi G and Jin X:
Dysfunction of sister chromatids separation promotes progression of
hepatocellular carcinoma according to analysis of gene expression
profiling. Front Physiol. 9:10192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chaisaingmongkol J, Budhu A, Dang H,
Rabibhadana S, Pupacdi B, Kwon SM, Forgues M, Pomyen Y,
Bhudhisawasdi V, Lertprasertsuke N, et al: Common molecular
subtypes among asian hepatocellular carcinoma and
cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Cell. 32:57–70.e3. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin KT, Shann YJ, Chau GY, Hsu CN and
Huang CY: Identification of latent biomarkers in hepatocellular
carcinoma by ultra-deep whole-transcriptome sequencing. Oncogene.
33:4786–4794. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mas VR, Maluf DG, Archer KJ, Yanek K, Kong
X, Kulik L, Freise CE, Olthoff KM, Ghobrial RM, McIver P and Fisher
R: Genes involved in viral carcinogenesis and tumor initiation in
hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med.
15:85–94. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Roessler S, Jia HL, Budhu A, Forgues M, Ye
QH, Lee JS, Thorgeirsson SS, Sun Z, Tang ZY, Qin LX and Wang XW: A
unique metastasis gene signature enables prediction of tumor
relapse in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer
Res. 70:10202–10212. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Edgar R, Domrachev M and Lash AE: Gene
Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array
data repository. Nucleic Acids Res. 30:207–210. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Archer KJ, Mas VR, David K, Maluf DG,
Bornstein K and Fisher RA: Identifying genes for establishing a
multigenic test for hepatocellular carcinoma surveillance in
hepatitis C virus-positive cirrhotic patients. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 18:2929–2932. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wilson C and Miller C: Simpleaffy: A
BioConductor package for Affymetrix quality control and data
analysis. Bioinformatics. 21:3683–3685. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene
Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
The Gene Ontology Consortium: The Gene
Ontology Resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids
Res. 47:D330–D338. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi
M and Tanabe M: KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein
annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:D457–D462. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Walter W, Sánchez-Cabo F and Ricote M:
GOplot: An R package for visually combining expression data with
functional analysis. Bioinformatics. 31:2912–2914. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Subramanian A, Kuehn H, Gould J, Tamayo P
and Mesirov JP: GSEA-P: A desktop application for Gene Set
Enrichment Analysis. Bioinformatics. 23:3251–3253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43((Database Issue)): D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Langfelder P, Zhang B and Horvath S:
Defining clusters from a hierarchical cluster tree: The Dynamic
Tree Cut package for R. Bioinformatics. 24:719–720. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ravasz E, Somera AL, Mongru DA, Oltvai ZN
and Barabasi AL: Hierarchical organization of modularity in
metabolic networks. Science. 297:1551–1555. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Colaprico A, Silva TC, Olsen C, Garofano
L, Cava C, Garolini D, Sabedot TS, Malta TM, Pagnotta SM,
Castiglioni I, et al: TCGAbiolinks: An R/Bioconductor package for
integrative analysis of TCGA data. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:e712016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou G, Soufan O, Ewald J, Hancock REW,
Basu N and Xia J: NetworkAnalyst 3.0: A visual analytics platform
for comprehensive gene expression profiling and meta-analysis.
Nucleic Acids Res. 47:W234–W241. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Davis CA, Hitz BC, Sloan CA, Chan ET,
Davidson JM, Gabdank I, Hilton JA, Jain K, Baymuradov UK, Narayanan
AK, et al: The Encyclopedia of DNA elements (ENCODE): Data portal
update. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D794–D801. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sticht C, De La Torre C, Parveen A and
Gretz N: miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA
binding sites. PLoS One. 13:e02062392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS Biol.
2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miranda KC, Huynh T, Tay Y, Ang YS, Tam
WL, Thomson AM, Lim B and Rigoutsos I: A pattern-based method for
the identification of MicroRNA binding sites and their
corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell. 126:1203–1217. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Johnson WE, Li C and Rabinovic A:
Adjusting batch effects in microarray expression data using
empirical Bayes methods. Biostatistics. 8:118–127. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Blum HE: Treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 19:129–145. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Raza A and Sood GK: Hepatocellular
carcinoma review: Current treatment, and evidence-based medicine.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:4115–4127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Oishi N, Kumar MR, Roessler S, Ji J,
Forgues M, Budhu A, Zhao X, Andersen JB, Ye QH, Jia HL, et al:
Transcriptomic profiling reveals hepatic stem-like gene signatures
and interplay of miR-200c and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 56:1792–1803. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yin L, Chang C and Xu C: G2/M checkpoint
plays a vital role at the early stage of HCC by analysis of key
pathways and genes. Oncotarget. 8:76305–76317. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tanaka M, Masaki Y, Tanaka K, Miyazaki M,
Kato M, Sugimoto R, Nakamura K, Aishima S, Shirabe K, Nakamuta M,
et al: Reduction of fatty acid oxidation and responses to hypoxia
correlate with the progression of de-differentiation in HCC. Mol
Med Rep. 7:365–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jinawath N, Chamgramol Y, Furukawa Y,
Obama K, Tsunoda T, Sripa B, Pairojkul C and Nakamura Y: Comparison
of gene expression profiles between Opisthorchis viverrini
and non-Opisthorchis viverrini associated human intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology. 44:1025–1038. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shi Q, Wang W, Jia Z, Chen P, Ma K and
Zhou C: ISL1, a novel regulator of CCNB1, CCNB2 and c-MYC genes,
promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and tumor growth.
Oncotarget. 7:36489–36500. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhang X, Teng Y, Yang F, Wang M, Hong X,
Ye LG, Gao YN and Chen GY: MCM2 is a therapeutic target of
lovastatin in human non-small cell lung carcinomas. Oncol Rep.
33:2599–2605. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shi YX, Zhu T, Zou T, Zhuo W, Chen YX,
Huang MS, Zheng W, Wang CJ, Li X, Mao XY, et al: Prognostic and
predictive values of CDK1 and MAD2L1 in lung adenocarcinoma.
Oncotarget. 7:85235–85243. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jin B, Wang W, Du G, Huang GZ, Han LT,
Tang ZY, Fan DG, Li J and Zhang SZ: Identifying hub genes and
dysregulated pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 19:592–601. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hanna MO, Zayed NA, Darwish H and Girgis
SI: Asynchronous DNA replication and aneuploidy in lymphocytes of
hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Cancer Genetics. 205:636–643.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Qian X, Song X, He Y, Yang Z, Sun T, Wang
J, Zhu G, Xing W and You C: CCNB2 overexpression is a poor
prognostic biomarker in Chinese NSCLC patients. Biomed
Pharmacother. 74:222–227. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lei CY, Wang W, Zhu YT, Fang WY and Tan
WL: The decrease of cyclin B2 expression inhibits invasion and
metastasis of bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 34:237.e1–e10. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Mo ML, Chen Z, Li J, Li HL, Sheng Q, Ma
HY, Zhang FX, Hua YW, Zhang X, Sun DQ, et al: Use of serum
circulating CCNB2 in cancer surveillance. Int J Biol Markers.
25:236–242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Shubbar E, Kovács A, Hajizadeh S, Parris
TZ, Nemes S, Gunnarsdóttir K, Einbeigi Z, Karlsson P and Helou K:
Elevated cyclin B2 expression in invasive breast carcinoma is
associated with unfavorable clinical outcome. BMC Cancer. 13:12013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li R, Jiang X, Zhang Y, Wang S, Chen X, Yu
X, Ma J and Huang X: Cyclin B2 overexpression in human
hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with poor prognosis. Arch
Med Res. 50:10–17. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang L, Zhang J, Wan L, Zhou X, Wang Z and
Wei W: Targeting Cdc20 as a novel cancer therapeutic strategy.
Pharmacol Ther. 151:141–151. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yuan B, Xu Y, Woo JH, Wang Y, Bae YK, Yoon
DS, Wersto RP, Tully E, Wilsbach K and Gabrielson E: Increased
expression of mitotic checkpoint genes in breast cancer cells with
chromosomal instability. Clin Cancer Res. 12:405–410. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wu WJ, Hu KS, Wang DS, Zeng ZL, Zhang DS,
Chen DL, Bai L and Xu RH: CDC20 overexpression predicts a poor
prognosis for patients with colorectal cancer. J Transl Med.
11:1422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chang DZ, Ma Y, Ji B, Liu Y, Hwu P,
Abbruzzese JL, Logsdon C and Wang H: Increased CDC20 expression is
associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma differentiation
and progression. J Hematol Oncol. 5:152012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Taniguchi K, Momiyama N, Ueda M, Matsuyama
R, Mori R, Fujii Y, Ichikawa Y, Endo I, Togo S and Shimada H:
Targeting of CDC20 via small interfering RNA causes enhancement of
the cytotoxicity of chemoradiation. Anticancer Res. 28:1559–1563.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Li J, Gao JZ, Du JL, Huang ZX and Wei LX:
Increased CDC20 expression is associated with development and
progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 45:1547–1555.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zeng X, Sigoillot F, Gaur S, Choi S, Pfaff
KL, Oh DC, Hathaway N, Dimova N, Cuny GD and King RW: Pharmacologic
inhibition of the anaphase-promoting complex induces a spindle
checkpoint-dependent mitotic arrest in the absence of spindle
damage. Cancer Cell. 18:382–395. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Das T, Roy KS, Chakrabarti T, Mukhopadhyay
S and Roychoudhury S: Withaferin A modulates the Spindle assembly
checkpoint by degradation of Mad2-Cdc20 complex in colorectal
cancer cell lines. Biochem Pharmacol. 91:31–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Jiang J, Thyagarajan-Sahu A, Krchňák V,
Jedinak A, Sandusky GE and Sliva D: NAHA, a novel hydroxamic
acid-derivative, inhibits growth and angiogenesis of breast cancer
in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 7:e342832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Regenbrecht CR, Jung M, Lehrach H and
Adjaye J: The molecular basis of genistein-induced mitotic arrest
and exit of self-renewal in embryonal carcinoma and primary cancer
cell lines. BMC Med Genomics. 1:492008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Nasr T, Bondock S and Youns M: Anticancer
activity of new coumarin substituted hydrazide-hydrazone
derivatives. Eur J Med Chem. 76:539–548. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Golubnitschaja O and Flammer J: What are
the biomarkers for glaucoma? Survey Ophthalmol. 52
(Suppl):S155–S161. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|