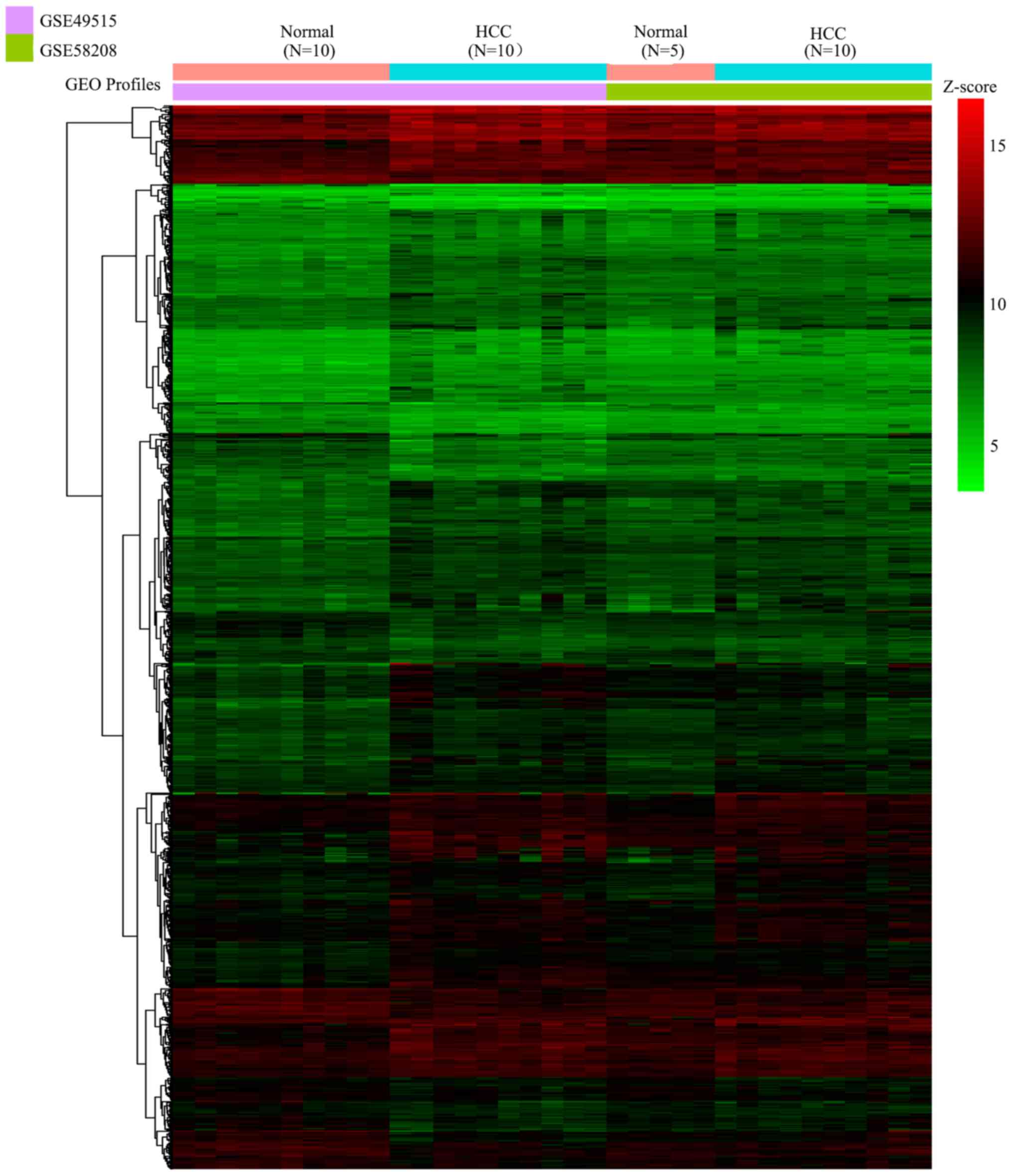
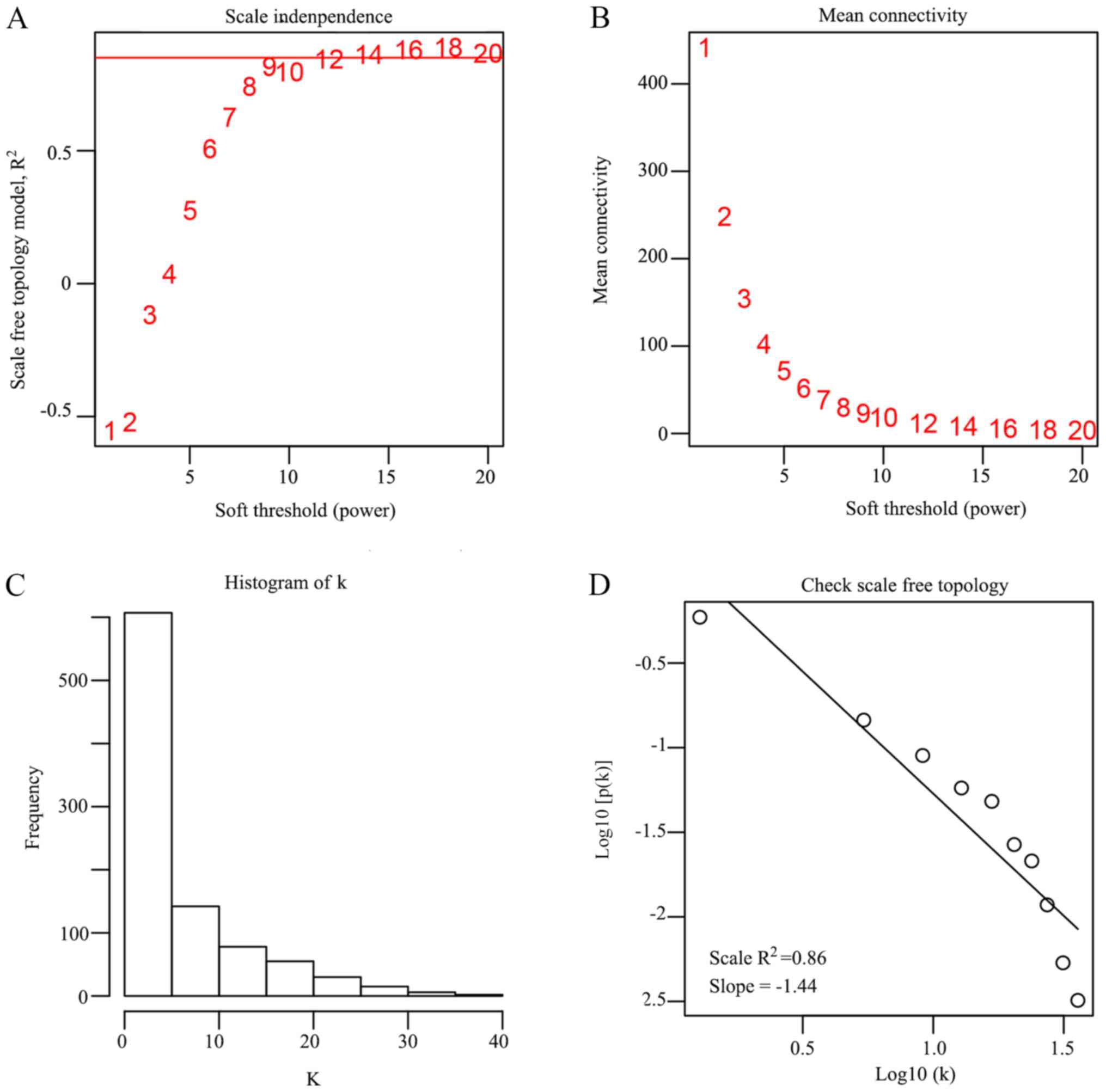
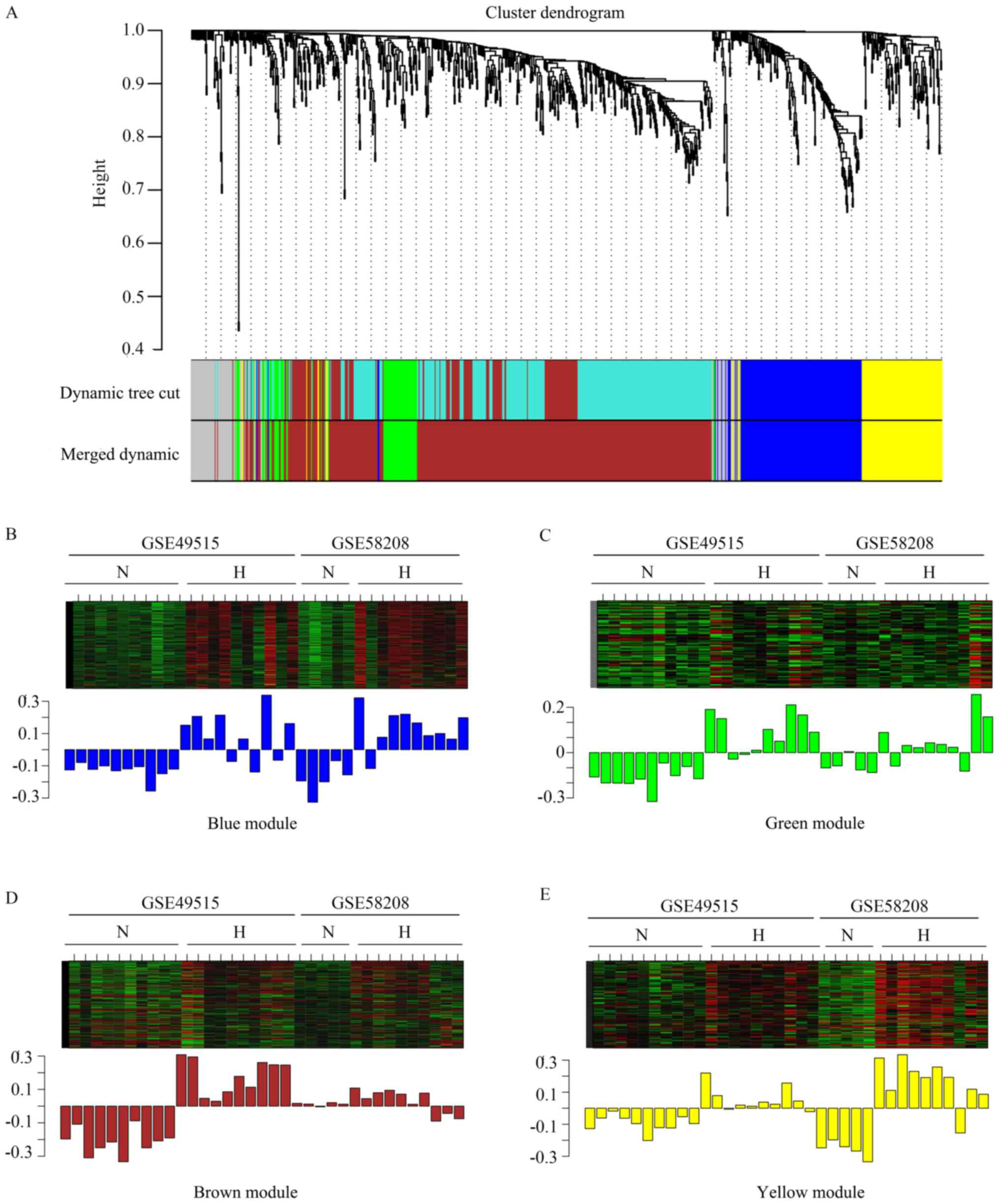
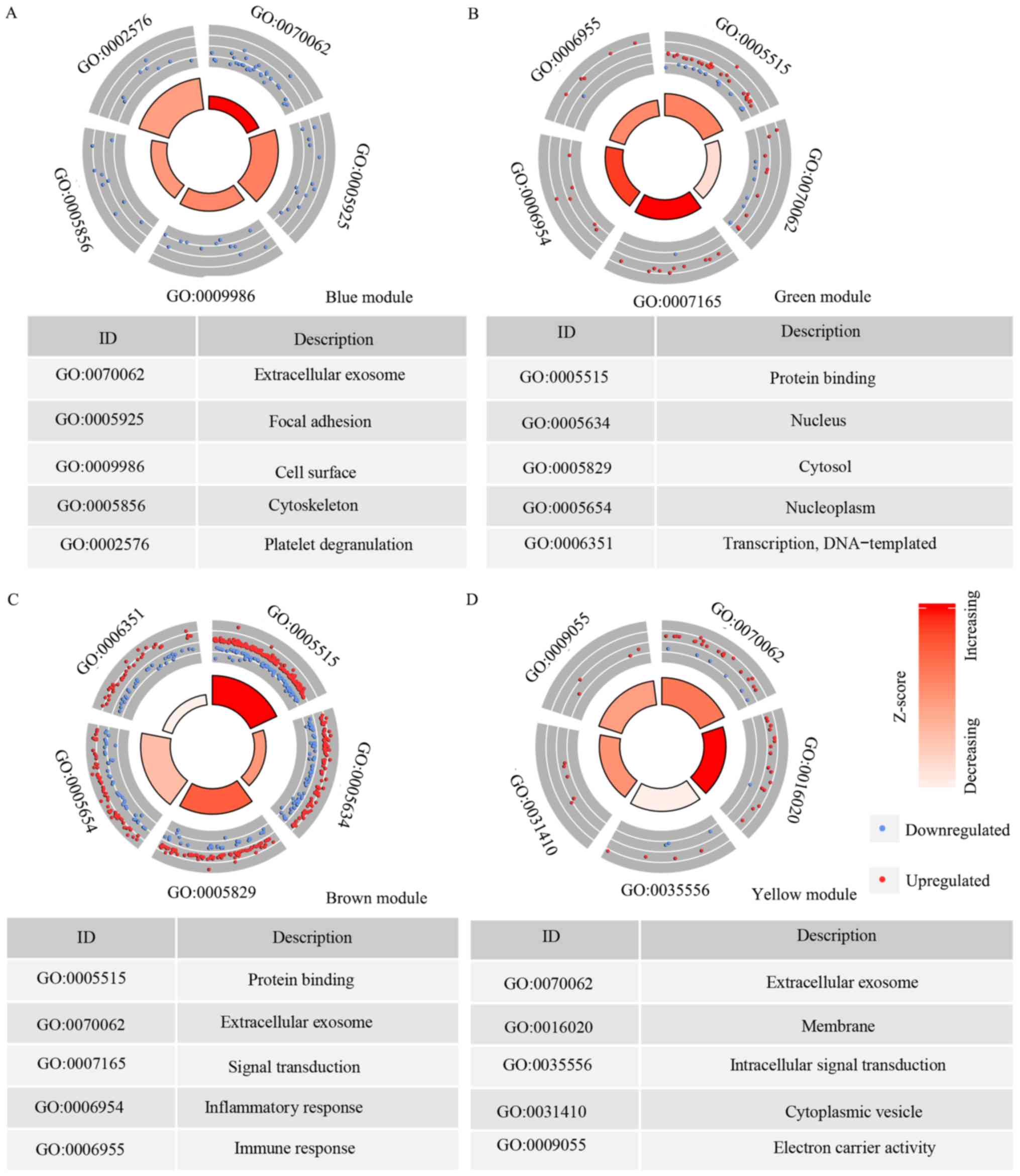
|
1
|
Raoul JL, Raimbourg J, Hiret S, Adhoute X
and Senellart H: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Increase in incidence or
future plague? Bull Cancer. 105:502–507. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In French).
|
|
2
|
Gupta M, Gabriel H and Miller FH: Role of
imaging in surveillance and diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 47:585–602. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sparchez Z and Mocan T: Contemporary role
of liver biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol.
10:452–461. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lok AS, Sterling RK, Everhart JE, Wright
EC, Hoefs JC, Di Bisceglie AM, Morgan TR, Kim HY, Lee WM, Bonkovsky
HL, et al: Des-gamma-carboxy prothrombin and alpha-fetoprotein as
biomarkers for the early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 138:493–502. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Marrero JA, Feng Z, Wang Y, Nguyen MH,
Befeler AS, Roberts LR, Reddy KR, Harnois D, Llovet JM, Normolle D,
et al: Alpha-fetoprotein, des-gamma carboxyprothrombin, and
lectin-bound alpha-fetoprotein in early hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 137:110–118. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jiang JX, Yu C, Li ZP, Xiao J, Zhang H,
Chen MY and Sun CY: Insights into significant pathways and gene
interaction networks in peripheral blood mononuclear cells for
early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Ther.
12:981–989. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li H, Mao Y, Xiong Y, Zhao HH, Shen F, Gao
X, Yang P, Liu X and Fu D: A comprehensive proteome analysis of
peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) to identify candidate
biomarkers of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Genomics Proteomics.
16:81–89. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Papageorgiou SG, Kontos CK, Diamantopoulos
MA, Bouchla A, Glezou E, Bazani E, Pappa V and Scorilas A:
MicroRNA-155-5p overexpression in peripheral blood mononuclear
cells of chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients is a novel,
independent molecular biomarker of poor prognosis. Dis Markers.
2017(2046545)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ciarloni L, Ehrensberger SH, Imaizumi N,
Monnier-Benoit S, Nichita C, Myung SJ, Kim JS, Song SY, Kim TI, van
der Weg B, et al: Development and clinical validation of a blood
test based on 29-gene expression for early detection of colorectal
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:4604–4611. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Baine MJ, Chakraborty S, Smith LM, Mallya
K, Sasson AR, Brand RE and Batra SK: Transcriptional profiling of
peripheral blood mononuclear cells in pancreatic cancer patients
identifies novel genes with potential diagnostic utility. PLoS One.
6(e17014)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Baine MJ, Menning M, Smith LM, Mallya K,
Kaur S, Rachagani S, Chakraborty S, Sasson AR, Brand RE and Batra
SK: Differential gene expression analysis of peripheral blood
mononuclear cells reveals novel test for early detection of
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Biomark. 11:1–14. 2011-2012.
|
|
12
|
Mishra S, Srivastava AK, Suman S, Kumar V
and Shukla Y: Circulating miRNAs revealed as surrogate molecular
signatures for the early detection of breast cancer. Cancer Lett.
369:67–75. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Leek JT: Svaseq: Removing batch effects
and other unwanted noise from sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res
42: 2014.
|
|
14
|
R Core Team. R: A language and environment
for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing,
Vienna, Austria. 2013; ISBN 3-900051-07-0.
|
|
15
|
Zhao W, Langfelder P, Fuller T, Dong J, Li
A and Hovarth S: Weighted gene coexpression network analysis: State
of the art. J Biopharm Stat. 20:281–300. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vaz J, Ansari D, Sasor A and Andersson R:
SPARC: A potential prognostic and therapeutic target in pancreatic
cancer. Pancreas. 44:1024–1035. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Arqueros C, Salazar J, Arranz MJ, Sebio A,
Mora J, Sullivan I, Tobeña M, Martín-Richard M, Barnadas A, Baiget
M and Páez D: SPARC gene variants predict clinical outcome in
locally advanced and metastatic pancreatic cancer patients. Med
Oncol. 34(136)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jing Y, Jin Y, Wang Y, Chen S, Zhang X,
Song Y, Wang Z, Pu Y, Ni Y and Hu Q: SPARC promotes the
proliferation and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma by
PI3K/AKT/PDGFB/PDGFRβ axis. J Cell Physiol 2019 (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
20
|
Zhang Q, Huang D, Zhang Z, Feng Y, Fu M,
Wei M, Zhou J, Huang Y, Liu S and Shi R: High expression of TMEM40
contributes to progressive features of tongue squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 41:154–164. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang ZF, Zhang HR, Zhang QY, Lai SY, Feng
YZ, Zhou Y, Zheng SR, Shi R and Zhou JY: High expression of TMEM40
is associated with the malignant behavior and tumorigenesis in
bladder cancer. J Transl Med. 16(9)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Alessi MC, Cenac N, Si-Tahar M and Riteau
B: FPR2: A novel promising target for the treatment of influenza.
Front Microbiol. 8(1719)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hou XL, Ji CD, Tang J, Wang YX, Xiang DF,
Li HQ, Liu WW, Wang JX, Yan HZ, Wang Y, et al: FPR2 promotes
invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells and predicts the
prognosis of patients. Sci Rep. 7(3153)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xiang Y, Yao X, Chen K, Wang X, Zhou J,
Gong W, Yoshimura T, Huang J, Wang R, Wu Y, et al: The G-protein
coupled chemoattractant receptor FPR2 promotes malignant phenotype
of human colon cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res. 6:2599–2610.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lan J, Lu H, Samanta D, Salman S, Lu Y and
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-dependent expression of
adenosine receptor 2B promotes breast cancer stem cell enrichment.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 115:E9640–E9648. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wen J, Hu Y, Liu Q, Ling Y, Zhang S, Luo
K, Xie X, Fu J and Yang H: miR-424 coordinates multilayered
regulation of cell cycle progression to promote esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma cell proliferation. EBioMedicine. 37:110–124.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yue L, Guo S, Zhang Y, Liu L, Wang Q, Wang
X, Shen D, Wang L, Sun L, Wang J, et al: The modulation of
phosphatase expression impacts the proliferation efficiency of
HSV-1 in infected astrocytes. PLoS One. 8(e79648)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|