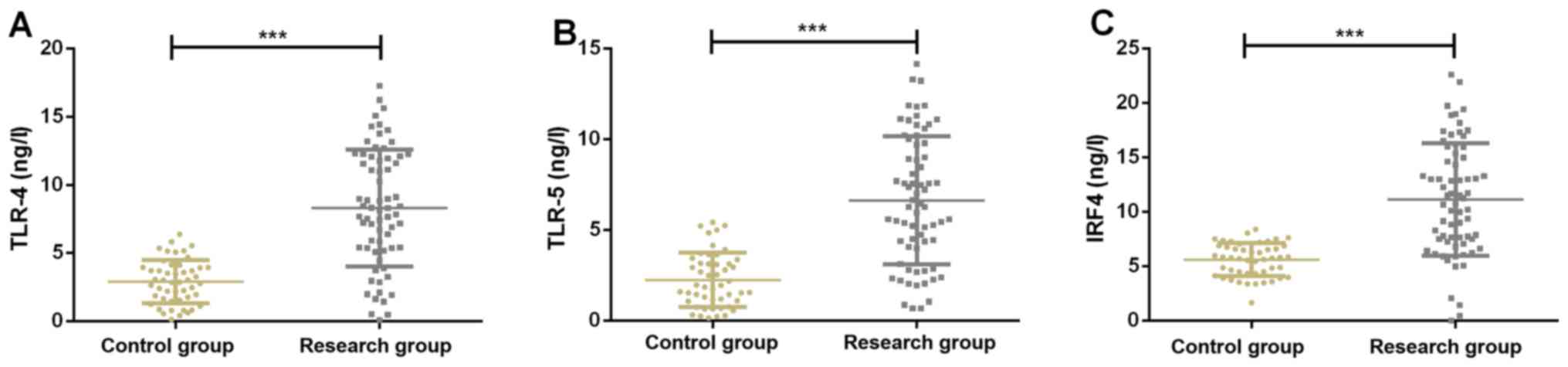
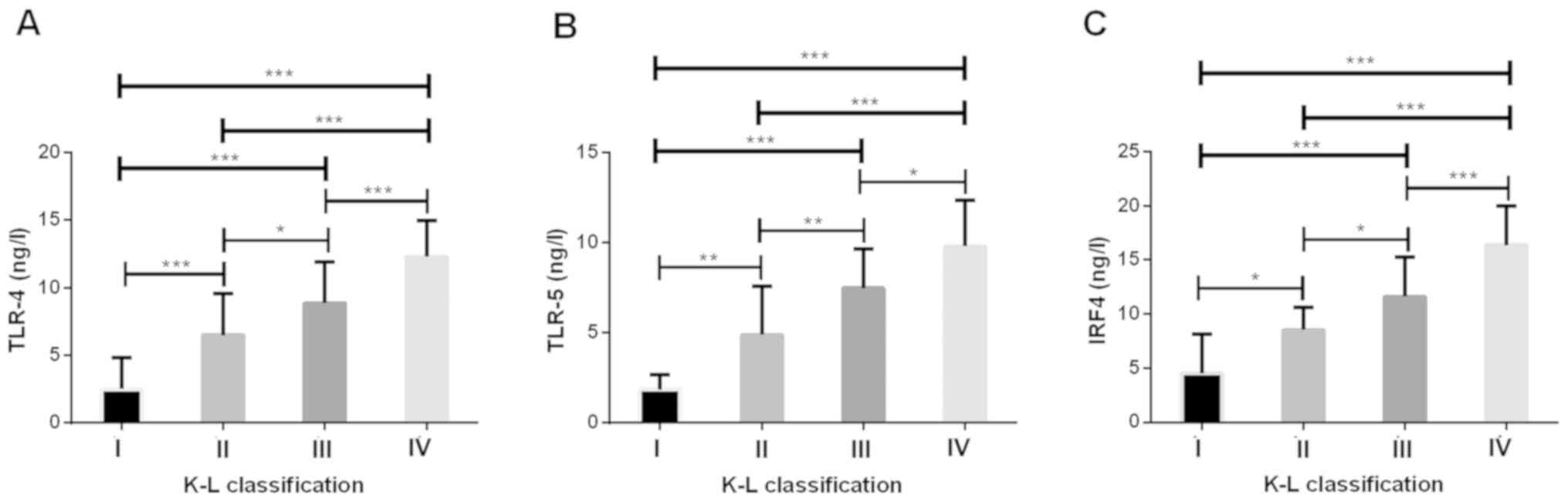
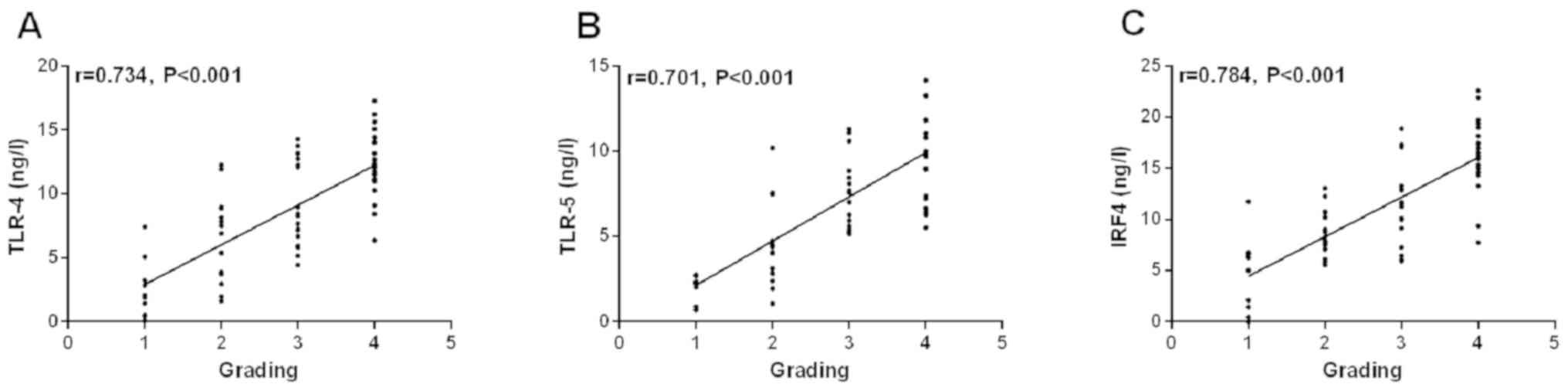
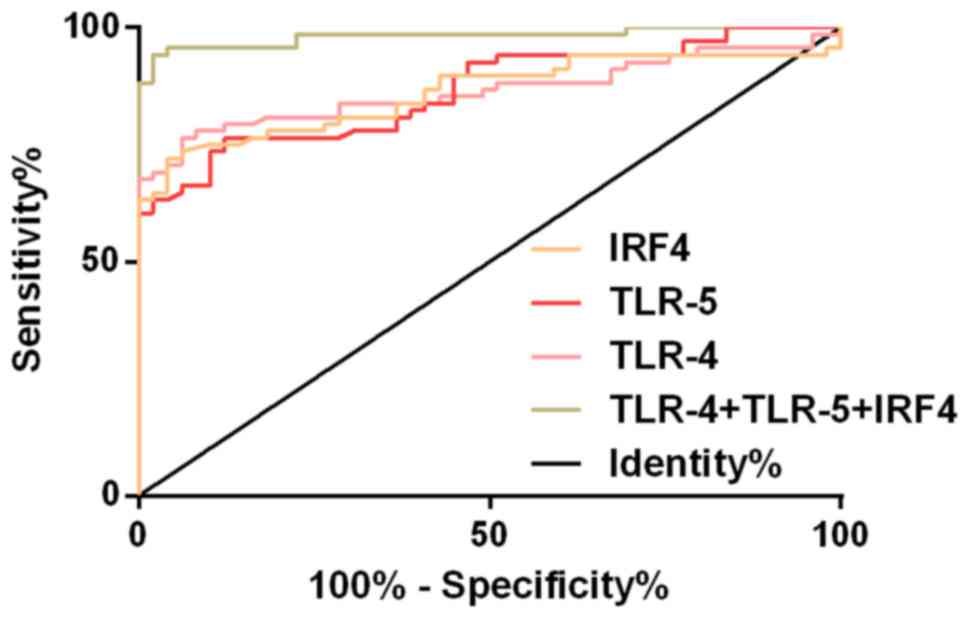
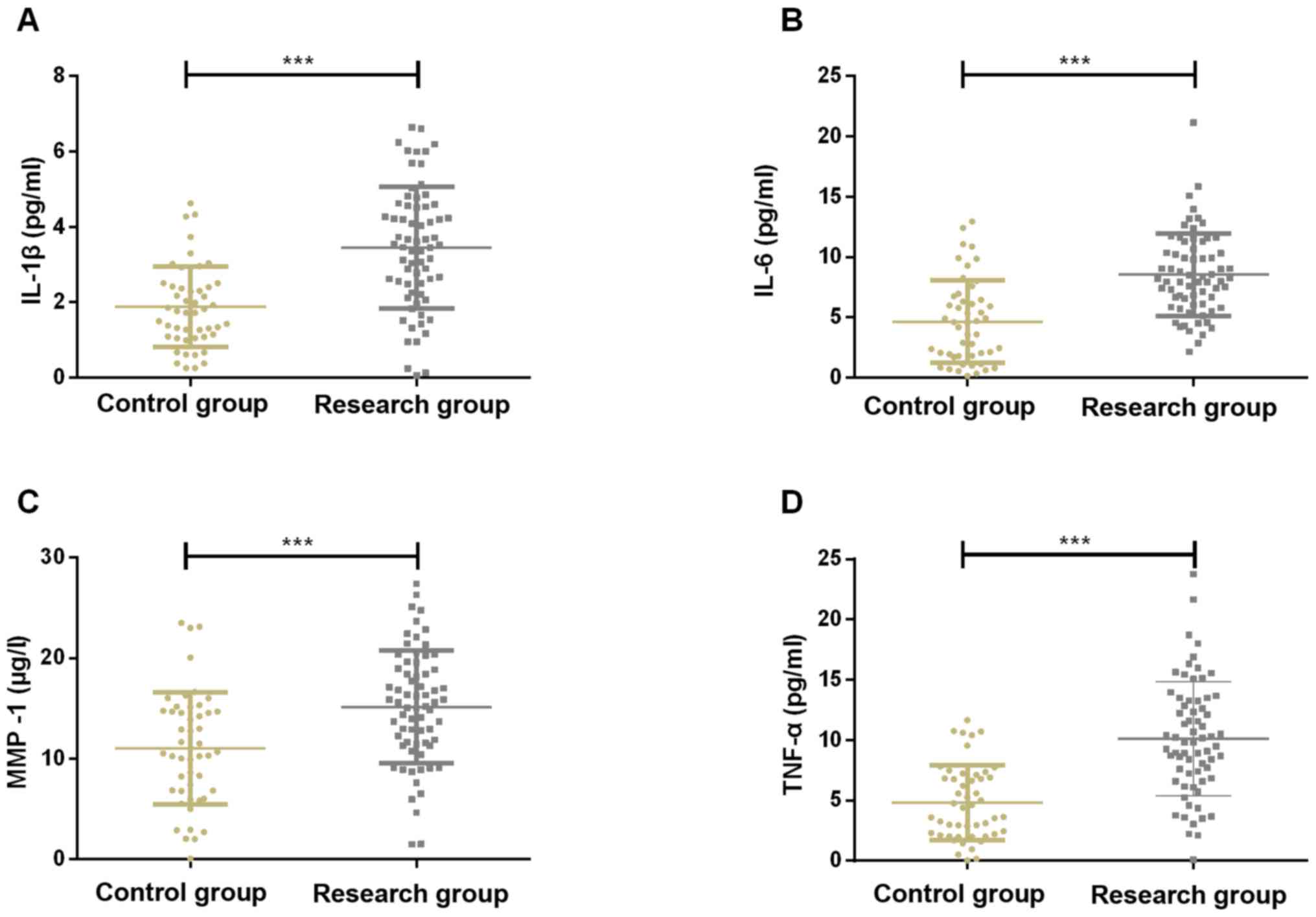
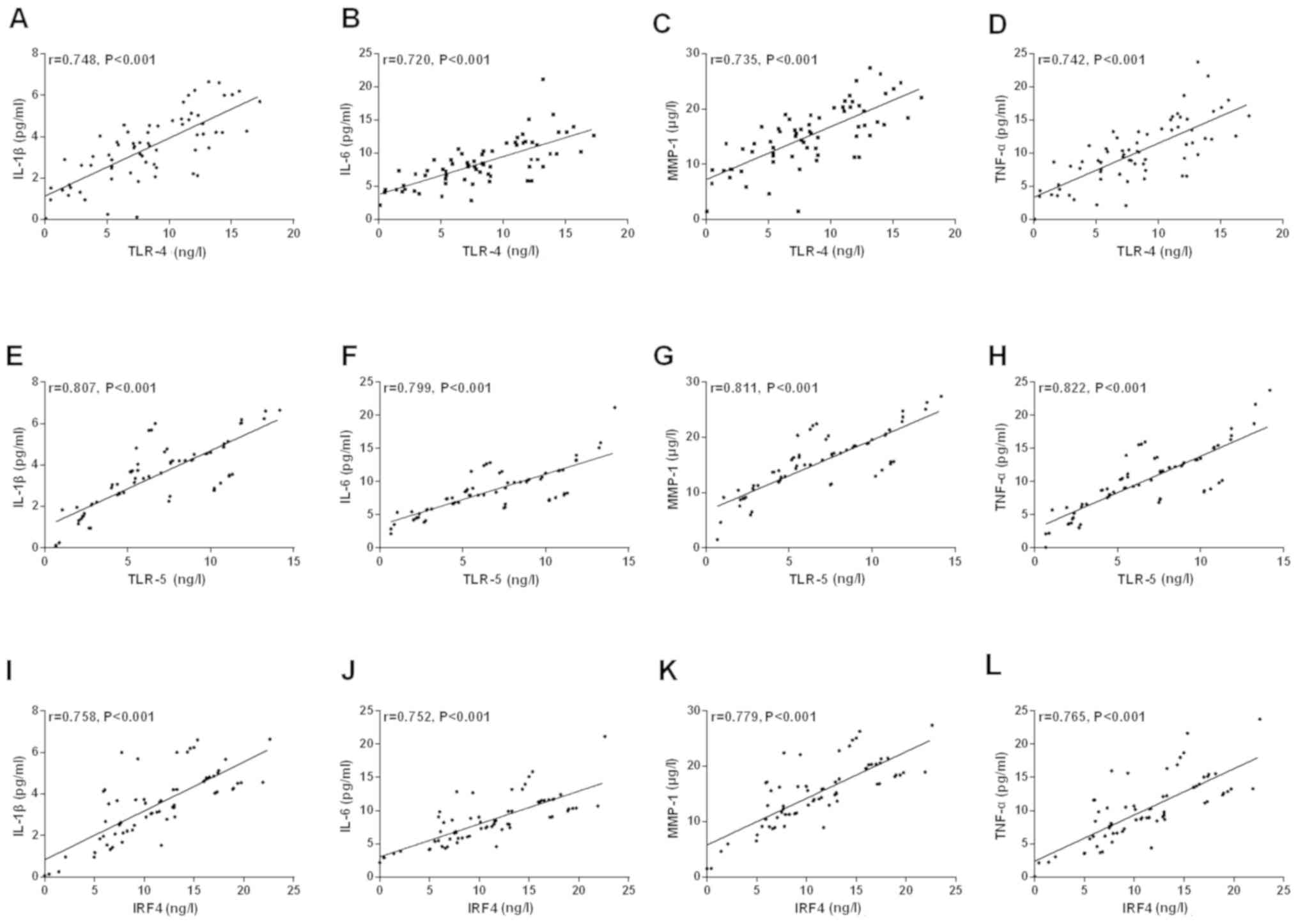
|
1
|
Chen H, Zheng X, Huang H, Liu C, Wan Q and
Shang S: The effects of a home-based exercise intervention on
elderly patients with knee osteoarthritis: A quasi-experimental
study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 20(160)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Peixoto JG, de Souza Moreira B, Diz JBM,
Timoteo EF, Kirkwood RN and Teixeira-Salmela LF: Analysis of
symmetry between lower limbs during gait of older women with
bilateral knee osteoarthritis. Aging Clin Exp Res. 31:67–73.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gigis I, Fotiadis E, Nenopoulos A, Tsitas
K and Hatzokos I: Comparison of two different molecular weight
intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid for the treatment of
knee osteoarthritis. Hippokratia. 20:26–31. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clynes MA, Jameson KA, Edwards MH, Cooper
C and Dennison EM: Impact of osteoarthritis on activities of daily
living: Does joint site matter? Aging Clin Exp Res. 31:1049–1056.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Paik J, Duggan ST and Keam SJ: Correction
to: Triamcinolone aceonide extended-release: A review in
osteoarthritis pain of the knee. Drugs. 79(691)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Akintayo RO, Yerima A, Olaosebikan HB,
Uhunmwangho C and Akpabio AA: How much gloom is in groans?
Depression and its determinants in Nigerian patients with knee
osteoarthritis: A multi-center cross-sectional study. Clin
Rheumatol. 38:1971–1978. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Camacho Encina M, Calamia V, Picchi
Figueira F, Van Duine J, Qiu J, Ruiz Romero C, LaBaer J and Blanco
F: Discovery of an autoantibody profile for the early diagnosis of
knee osteoarthritis using NAPPA: Data from the osteoarthritis
initiative. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 26:S39–S40. 2018.
|
|
8
|
Ryan MD, Roulston C, de Felipe P, Odon V,
Tilsner J and Luke GA: The potential consequences for cell
signaling by a class of NOD-like receptor proteins (NLRs) bearing
an N-terminal signal sequence. J Cell Signal. 2(148)2017.
|
|
9
|
Kandahari AM, Yang X, Dighe AS, Pan D and
Cui Q: Recognition of immune response for the early diagnosis and
treatment of osteoarthritis. J Immunol Res.
2015(192415)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xu WD, Pan HF, Ye DQ and Xu Y: Targeting
IRF4 in autoimmune diseases. Autoimmun Rev. 11:918–924.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Schoenemeyer A, Barnes BJ, Mancl ME, Latz
E, Goutagny N, Pitha PM, Fitzgerald KA and Golenbock DT: The
interferon regulatory factor, IRF5, is a central mediator of
toll-like receptor 7 signaling. J Biol Chem. 280:17005–17012.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Petrasek J, Dolganiuc A, Csak T,
Kurt-Jones EA and Szabo G: Type I interferons protect from
Toll-like receptor 9-associated liver injury and regulate IL-1
receptor antagonist in mice. Gastroenterology. 140:697–708.e4.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mullen LM, Chamberlain G and Sacre S:
Pattern recognition receptors as potential therapeutic targets in
inflammatory rheumatic disease. Arthritis Res Ther.
17(122)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jiang W, Wang H, Li YS and Luo W: Role of
vasoactive intestinal peptide in osteoarthritis. J Biomed Sci.
23(63)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nair A, Kanda V, Bush-Joseph C, Verma N,
Chubinskaya S, Mikecz K, Glant TT, Malfait AM, Crow MK, Spear GT,
et al: Synovial fluid from patients with early osteoarthritis
modulates fibroblast-like synoviocyte responses to toll-like
receptor 4 and toll-like receptor 2 ligands via soluble CD14.
Arthritis Rheum. 64:2268–2277. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chamberlain ND, Vila OM, Volin MV, Volkov
S, Pope RM, Swedler W, Mandelin AM II and Shahrara S: TLR5, a novel
and unidentified inflammatory mediator in rheumatoid arthritis that
correlates with disease activity score and joint TNF-α levels. J
Immunol. 189:475–483. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yang C, He D, Yin C and Tan J: Inhibition
of interferon regulatory factor 4 suppresses Th1 and Th17 cell
differentiation and ameliorates experimental autoimmune
encephalomyelitis. Scand J Immunol. 82:345–351. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chang MW, Cook AD, Nutt SL, Hamilton JA
and Lacey DC: Interferon regulatory factor 4 and inflammation.
Cytokine. 70(33)2014.
|
|
19
|
Lana JF, Macedo A, Ingrao ILG, Huber SC,
Santos GS and Santana MHA: Leukocyte-rich PRP for knee
osteoarthritis: Current concepts. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 10 (Suppl
1):S179–S182. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Rogoveanu OC, Calina D, Cucu MG, Burada F,
Docea AO, Sosoi S, Stefan E, Ioana M and Burada E: Association of
cytokine gene polymorphisms with osteoarthritis susceptibility. Exp
Ther Med. 16:2659–2664. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang R, Yang X, Wang J, Han L, Yang A,
Zhang J, Zhang D, Li B, Li Z and Xiong Y: Identification of
potential biomarkers for differential diagnosis between rheumatoid
arthritis and osteoarthritis via integrative genome-wide gene
expression profiling analysis. Mol Med Rep. 19:30–40.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Trachana V, Mourmoura E, Papathanasiou I
and Tsezou A: Understanding the role of chondrocytes in
osteoarthritis: Utilizing proteomics. Expert Rev Proteomics.
16:201–213. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Hochberg MC, Altman RD, Brandt KD, Clark
BM, Dieppe PA, Griffin MR, Moskowitz RW and Schnitzer TJ: American
College of Rheumatology: Guidelines for the medical management of
osteoarthritis. Part I. Osteoarthritis of the hip. Arthritis Rheum.
38:1535–1540. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kraus VB, Catterall J, Soderblom E,
Moseley MA and Suchindran S: Development of a serum biomarker panel
highly predictive of knee osteoarthritis progression.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 24(S20)2016.
|
|
25
|
Brandt KD, Fife RS, Braunstein EM and Katz
B: Radiographic grading of the severity of knee osteoarthritis:
Relation of the Kellgren and Lawrence grade to a grade based on
joint space narrowing, and correlation with arthroscopic evidence
of articular cartilage degeneration. Arthritis Rheum. 34:1381–1386.
1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Norman B, Pedoia V, Noworolski A, Link TM
and Majumdar S: Applying densely connected convolutional neural
networks for staging osteoarthritis severity from plain
radiographs. J Digit Imaging. 32:471–477. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ahmed U, Anwar A, Savage RS, Thornalley PJ
and Rabbani N: Protein oxidation, nitration and glycation
biomarkers for early-stage diagnosis of osteoarthritis of the knee
and typing and progression of arthritic disease. Arthritis Res
Ther. 18(250)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chen D, Shen J, Zhao W, Wang T, Han L,
Hamilton JL and Im HJ: Osteoarthritis: Toward a comprehensive
understanding of pathological mechanism. Bone Res.
5(16044)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liang H, Wang H, Luo L, Fan S, Zhou L, Liu
Z, Yao S, Zhang X, Zhong K, Zhao H and Zha Z: Toll-like receptor 4
promotes high glucose-induced catabolic and inflammatory responses
in chondrocytes in an NF-κB-dependent manner. Life Sci.
228:258–265. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jin J, Yu X, Hu Z, Tang S, Zhong X, Xu J,
Shang P, Huang Y and Liu H: Isofraxidin targets the TLR4/MD-2 axis
to prevent osteoarthritis development. Food Funct. 9:5641–5652.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Mudter J, Yu J, Zufferey C, Brüstle A,
Wirtz S, Weigmann B, Hoffman A, Schenk M, Galle PR, Lehr HA, et al:
IRF4 regulates IL-17A promoter activity and controls RORγ
t-dependent Th17 colitis in vivo. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 17:1343–1358.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Brüstle A, Heink S, Huber M, Rosenplänter
C, Stadelmann C, Yu P, Arpaia E, Mak TW, Kamradt T and Lohoff M:
The development of inflammatory T(H)-17 cells requires
interferon-regulatory factor 4. Nat Immunol. 8:958–966.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lim R, Barker G and Lappas M: The TLR2
ligand FSL-1 and the TLR5 ligand Flagellin mediate pro-inflammatory
and pro-labour response via MyD88/TRAF6/NF-κB-dependent signalling.
Am J Reprod Immunol. 71:401–417. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kwa MQ, Nguyen T, Huynh J, Ramnath D, De
Nardo D, Lam PY, Reynolds EC, Hamilton JA, Sweet MJ and Scholz GM:
Interferon regulatory factor 6 differentially regulates Toll-like
receptor 2-dependent chemokine gene expression in epithelial cells.
J Biol Chem. 289:19758–19768. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Miller RE, Scanzello CR and Malfait AM: An
emerging role for Toll-like receptors at the neuroimmune interface
in osteoarthritis. Semin Immunopathol. 41:583–594. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ospelt C, Brentano F, Rengel Y, Stanczyk
J, Kolling C, Tak PP, Gay RE, Gay S and Kyburz D: Overexpression of
toll-like receptors 3 and 4 in synovial tissue from patients with
early rheumatoid arthritis: Toll-like receptor expression in early
and longstanding arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 58:3684–3692.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lee MC, Saleh R, Achuthan A, Fleetwood AJ,
Förster I, Hamilton JA and Cook AD: CCL17 blockade as a therapy for
osteoarthritis pain and disease. Arthritis Res Ther.
20(62)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ding L, Hong X, Sun B, Huang Q, Wang X,
Liu X, Li L, Huang Z and Liu D: IL-37 is associated with
osteoarthritis disease activity and suppresses proinflammatory
cytokines production in synovial cells. Sci Rep.
7(11601)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Haseeb A, Ansari MY and Haqqi TM:
Harpagoside suppresses IL-6 expression in primary human
osteoarthritis chondrocytes. J Orthop Res. 35:311–320.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang C, Wang P, Jiang P, Lv Y, Dong C,
Dai X, Tan L and Wang Z: Upregulation of lncRNA HOTAIR contributes
to IL-1β-induced MMP overexpression and chondrocytes apoptosis in
temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Gene. 586:248–253.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Li ZC, Han N, Li X, Li G, Liu YZ, Sun GX,
Wang Y, Chen GT and Li GF: Decreased expression of microRNA-130a
correlates with TNF-α in the development of osteoarthritis. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:2555–2564. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zheng W, Zhang H, Jin Y, Wang Q, Chen L,
Feng Z, Chen H and Wu Y: Butein inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory
response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and slows the
progression of osteoarthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol.
42:1–10. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zeng GQ, Chen AB, Li W, Song JH and Gao
CY: High MMP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-9 protein levels in osteoarthritis.
Genet Mol Res. 14:14811–14822. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Stannus O, Jones G, Cicuttini F,
Parameswaran V, Quinn S, Burgess J and Ding C: Circulating levels
of IL-6 and TNF-α are associated with knee radiographic
osteoarthritis and knee cartilage loss in older adults.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18:1441–1447. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|