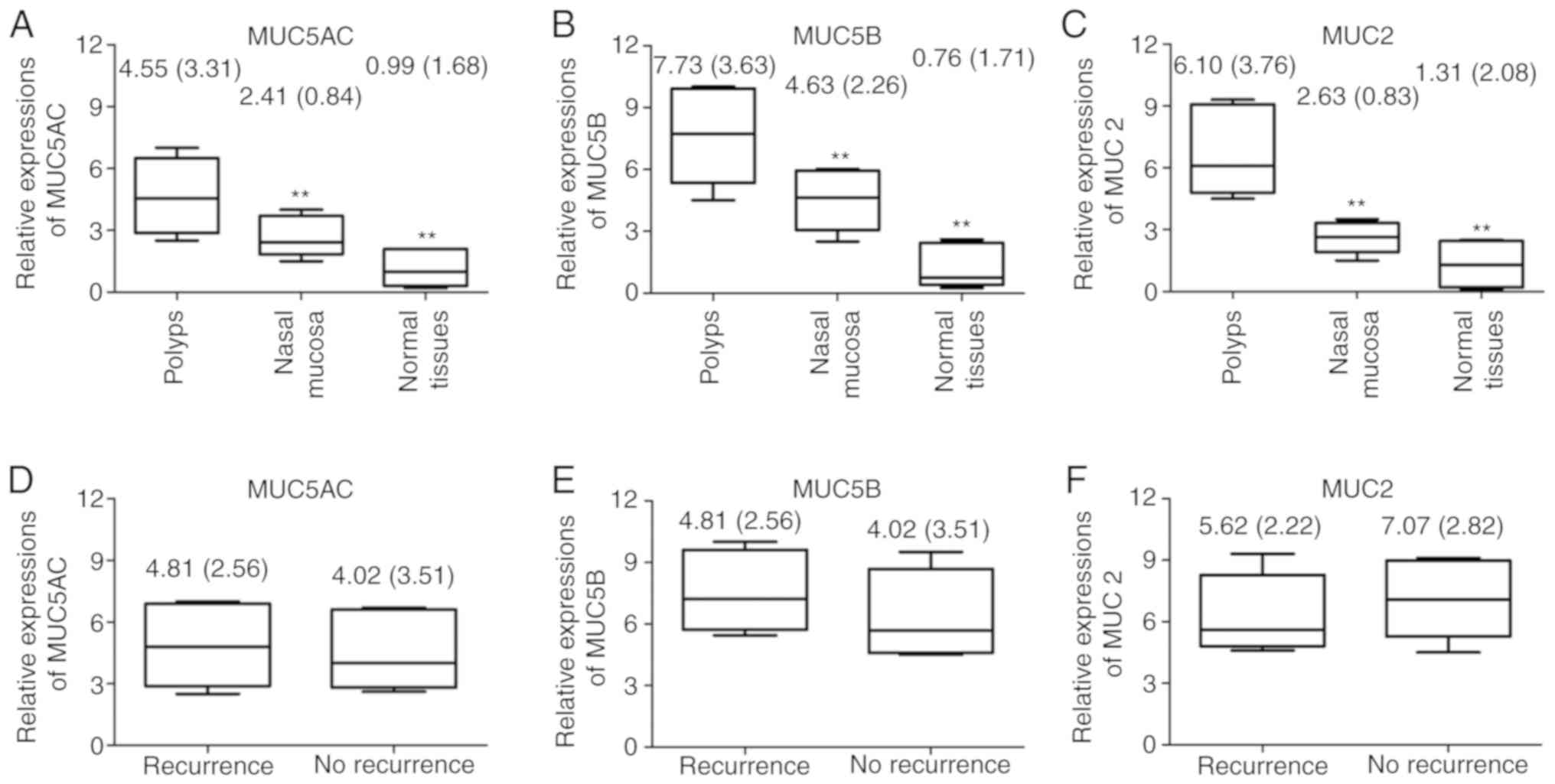
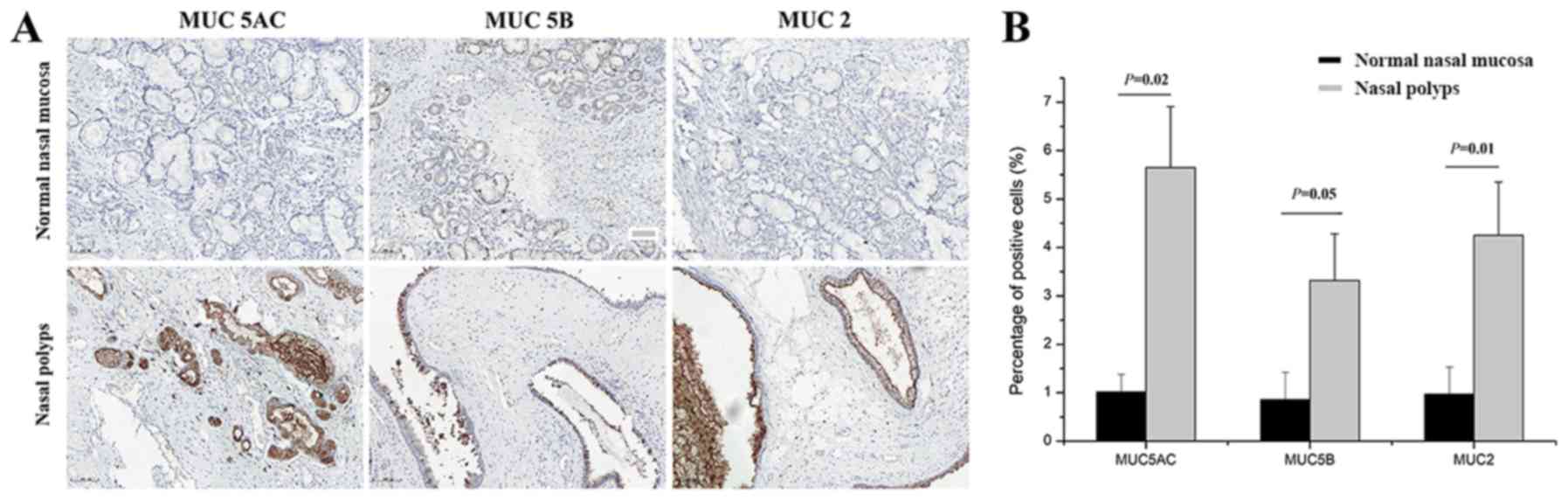
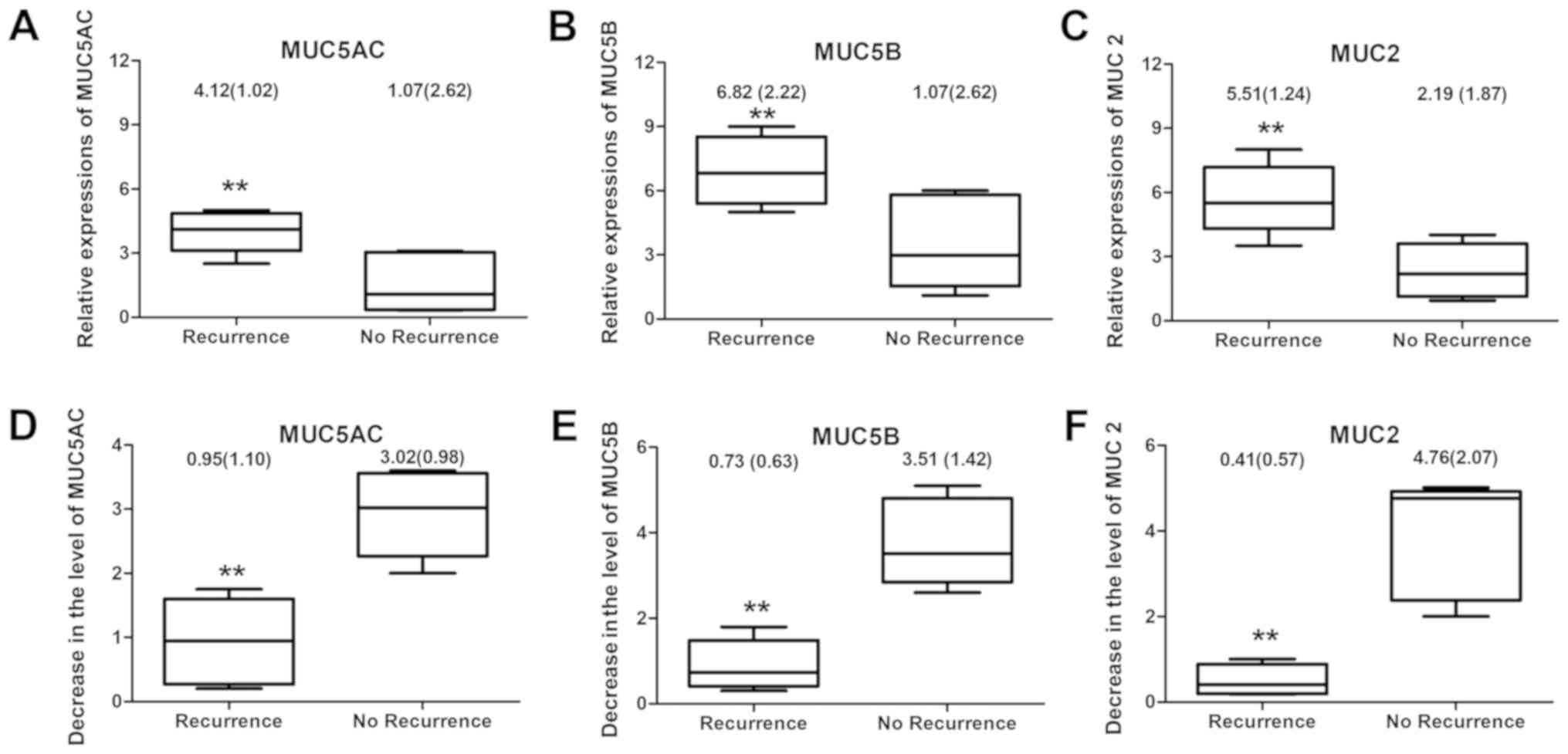
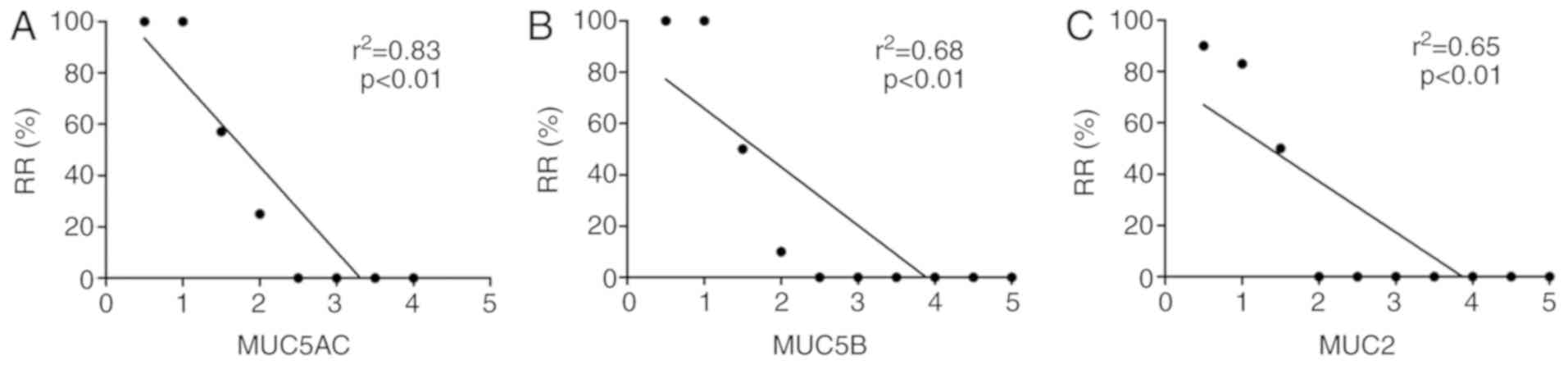
|
1
|
Pawliczak R, Lewandowska-Polak A and
Kowalski ML: Pathogenesis of nasal polyps: An update. Curr Allergy
Asthma Rep. 5:463–471. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Deal RT and Kountakis SE: Significance of
nasal polyps in chronic rhinosinusitis: Symptoms and surgical
outcomes. Laryngoscope. 114:1932–1935. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bequignon E, Dupuy L, Zerah-Lancner F,
Bassinet L, Honoré I, Legendre M, Devars du Mayne M, Escabasse V,
Crestani B, Maître B, et al: Critical evaluation of sinonasal
disease in 64 adults with primary ciliary dyskinesia. J Clin Med.
8(619)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Crystal RG, Randell SH, Engelhardt JF,
Voynow J and Sunday ME: Airway epithelial cells: Current concepts
and challenges. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 5:772–777. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Perrais M, Pigny P, Copin MC, Aubert JP
and Van Seuningen I: Induction of MUC2 and MUC5AC mucins by factors
of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) family is mediated by EGF
receptor/Ras/Raf/extracellular signal-regulated kinase cascade and
Sp1. J Biol Chem. 277:32258–32267. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Henke MO, John G, Germann M, Lindemann H
and Rubin BK: MUC5AC and MUC5B mucins increase in cystic fibrosis
airway secretions during pulmonary exacerbation. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 175:816–821. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ali MS, Wilson J and Pearson JP: Mixed
nasal mucus as a model for sinus mucin gene expression studies.
Laryngoscope. 112:326–331. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Milara J, Peiró T, Armengot M, Frias S,
Morell A, Serrano A and Cortijio J: Mucin 1 downregulation
associates with corticosteroid resistance in chronic rhinosinusitis
with nasal polyps. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 135:470–476.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ding GQ and Zheng CQ: The expression of
MUC5AC and MUC5B mucin genes in the mucosa of chronic
rhinosinusitis and nasal polyposis. Am J Rhinol. 21:359–366.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mao YJ, Chen HH, Wang B, Liu X and Xiong
GY: Increased expression of MUC5AC and MUC5B promoting bacterial
biofilm formation in chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Auris Nasus
Larynx. 42:294–298. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Xue-Kun H, Yuan L, Jin Y, Peng L and Hong
L: Expression of MUC2 and MUC5B in ethmoid sinus mucosa of patients
with chronic rhinosinusitis. Sci Res Essays. 5:1690–1696. 2010.
|
|
12
|
Lund VJ and Kennedy DW: Staging for
rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 117 (Suppl):S35–S40.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lund WJ and Kennedy DW: Quantification for
staging. The Staging and Therapy Group. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol.
167 (Suppl):S17–S21. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kennedy DW: Functional endoscopic sinus
surgery Technique. Arch Otolaryngol. 111:643–649. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2-(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ali MS, Wilson JA, Bennett M and Pearson
JP: Mucin gene expression in nasal polyps. Acta Otolaryngol.
125:618–624. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chang JH, Song KJ, Kim HJ, Kim JH, Kim NH
and Kim KS: Dietary polyphenols affect MUC5AC expression and
ciliary movement in respiratory cells and nasal mucosa. Am J Rhinol
Allergy. 24:e59–e62. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
İlhan Ö, Han Ü, Önal B and Çelık SY:
Prognostic significance of MUC1, MUC2 and MUC5AC expressions in
gastric carcinoma. Turk J Gastroenterol. 21:345–352.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Saieg A, Brown KJ, Pena MT, Rose MC and
Preciado D: Proteomic analysis of pediatric sinonasal secretions
shows increased MUC5B mucin in CRS. Pediatr Res. 77:356–362.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kim DH, Chu HS, Lee JY, Hwang SJ, Lee SH
and Lee HM: Up-regulation of MUC5AC and MUC5B mucin genes in
chronic rhinosinusitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 130:747–752.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Poachanukoon O, Koontongkaew S,
Monthanapisut P and Pattanacharoenchai N: Mometasone furoate
suppresses PMA-Induced MUC-5AC and MUC-2 production in human airway
epithelial cells. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 80:60–68.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Radhakrishnan P, Halagowder D and Devaraj
SN: Altered expression of MUC2 and MUC5AC in response to Shigella
infection, an in vivo study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1770:884–889.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tos M and Mogensen C: Pathogenesis of
nasal polyps. Rhinology. 15:87–95. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|