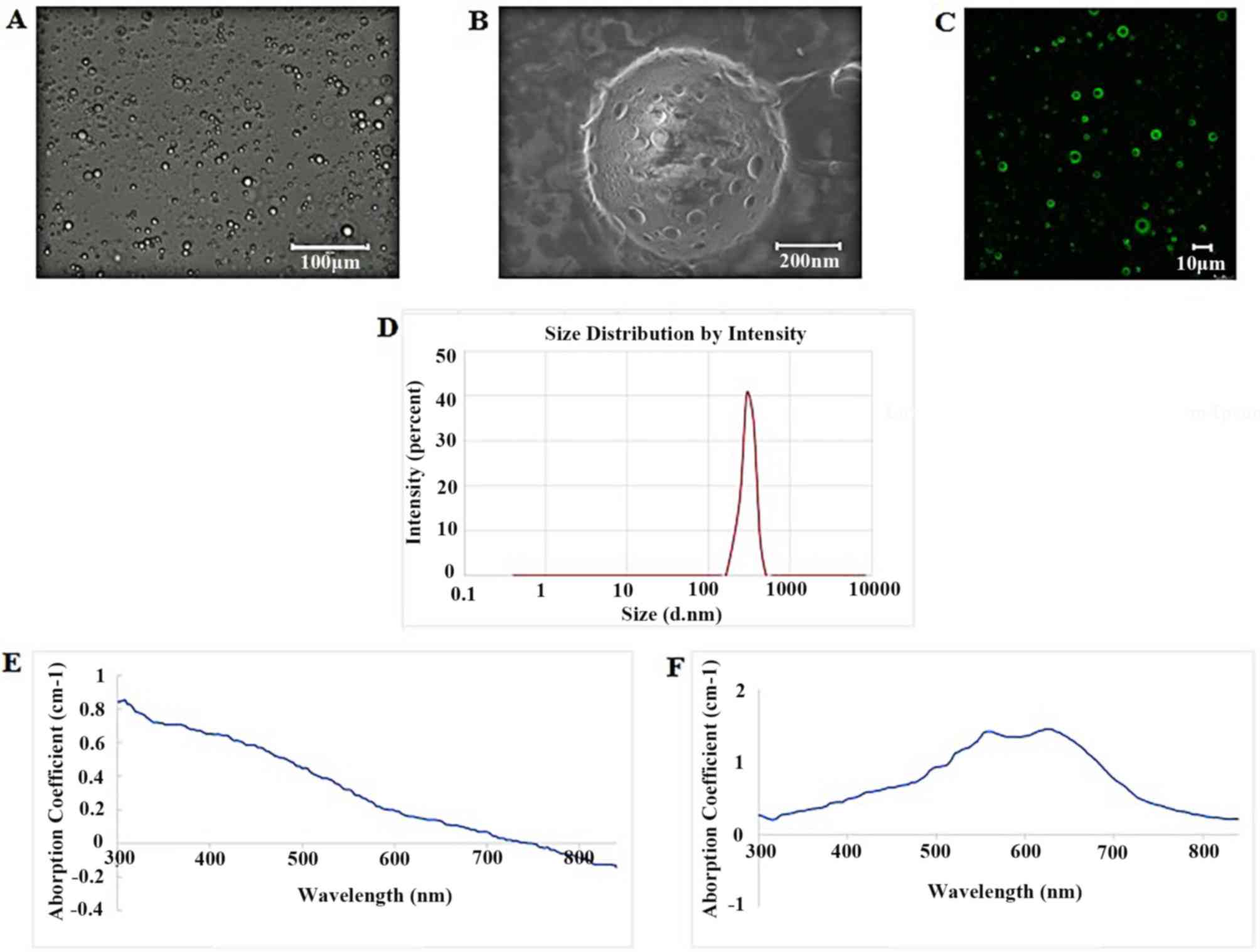
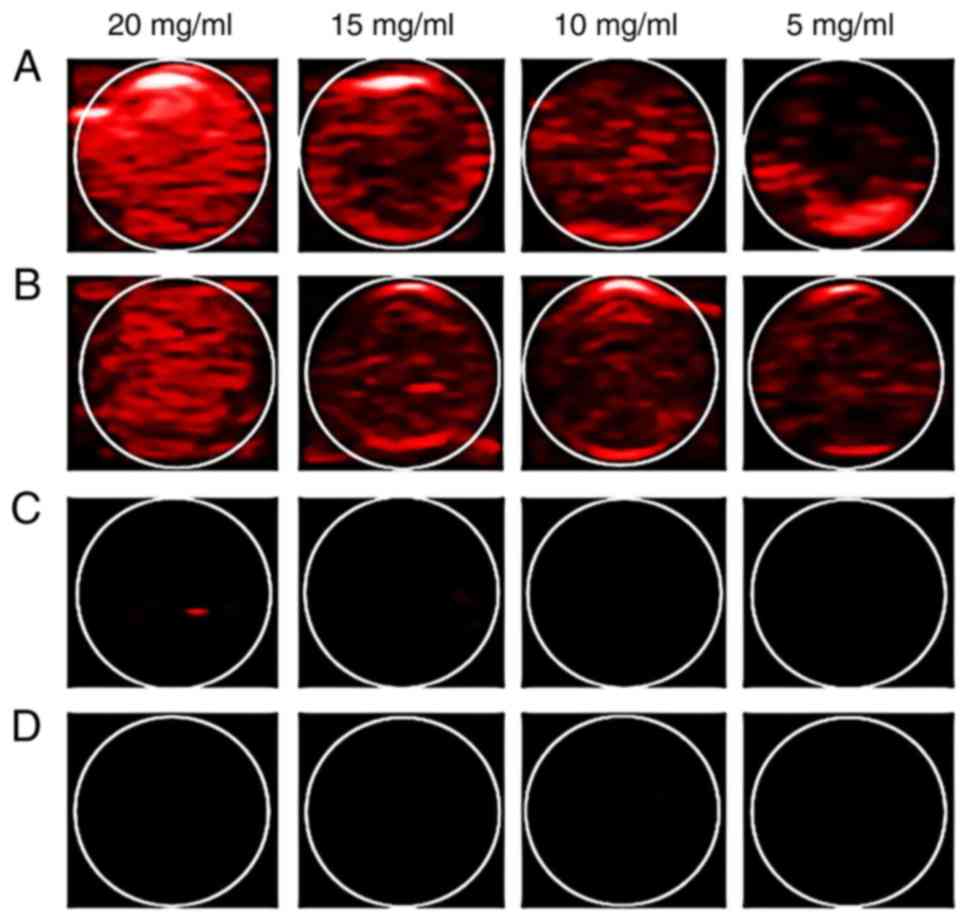
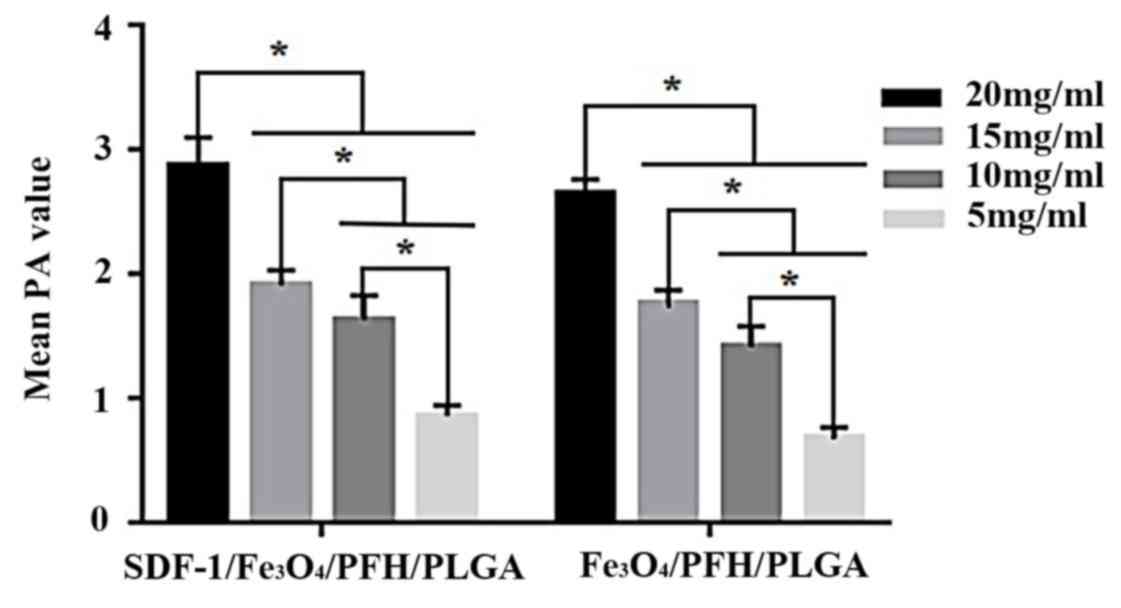
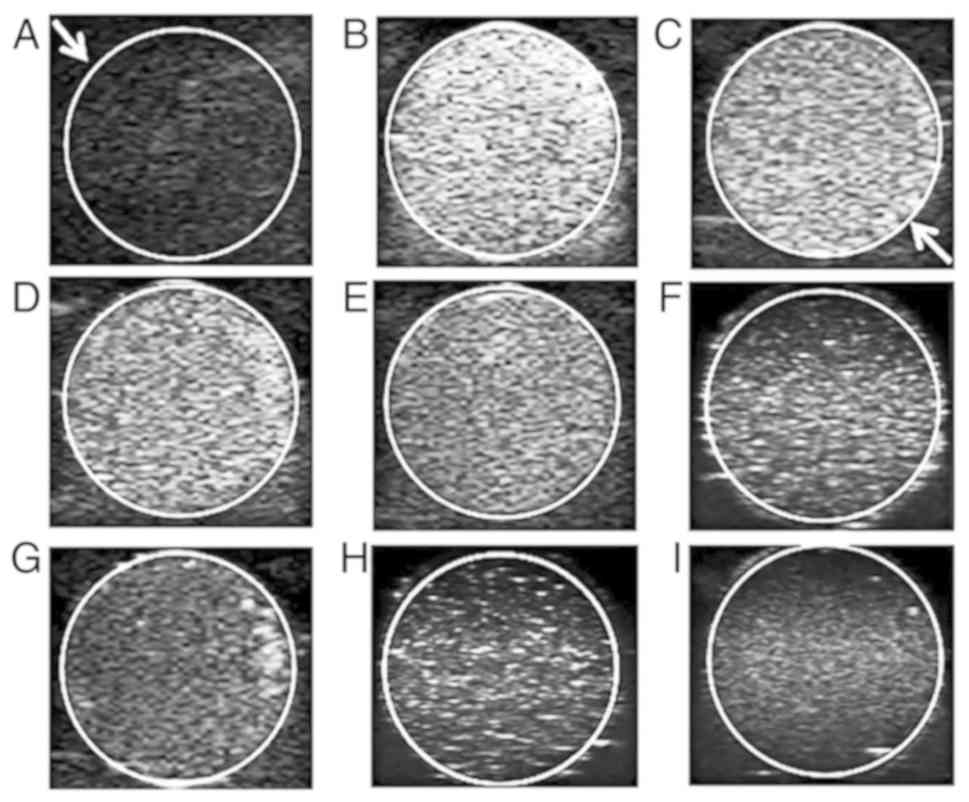
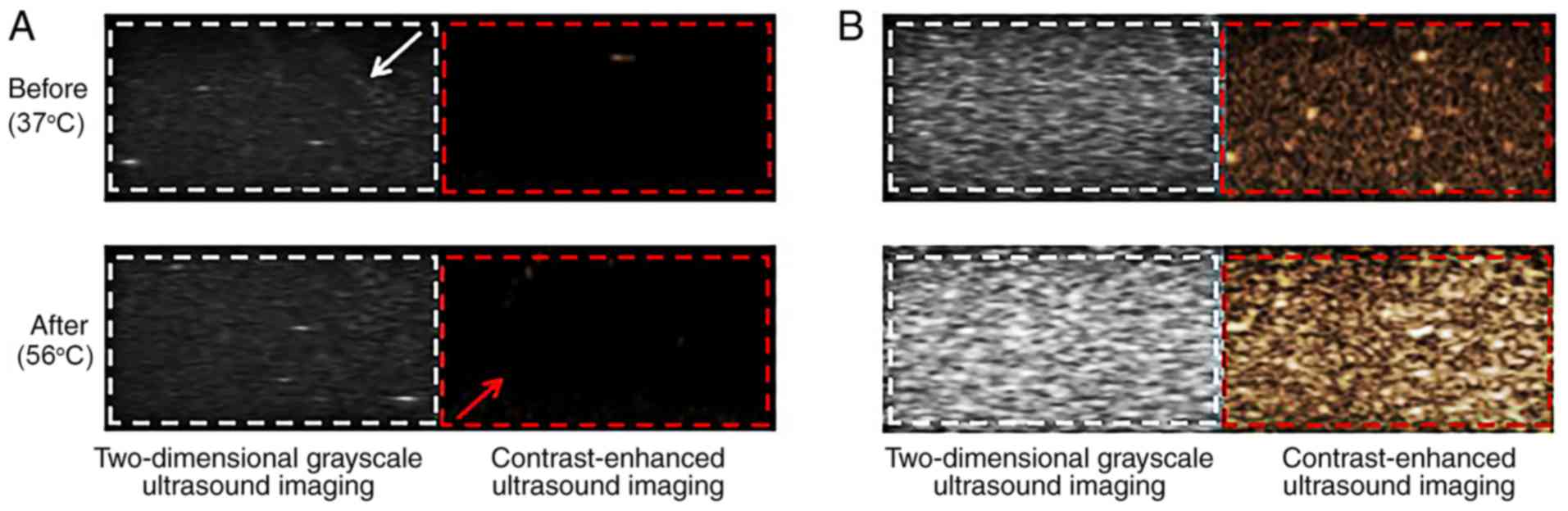
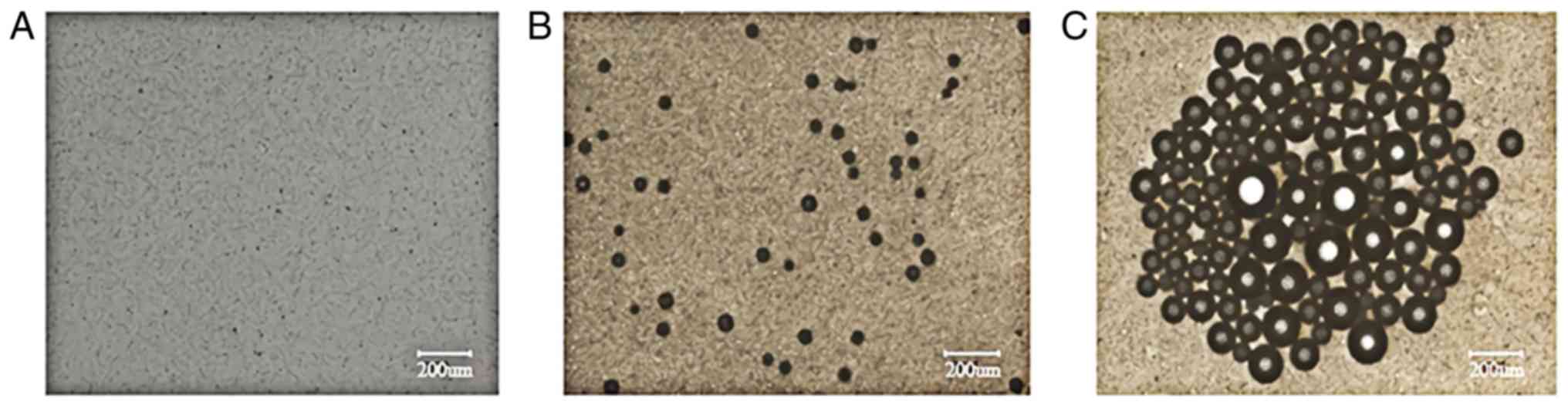
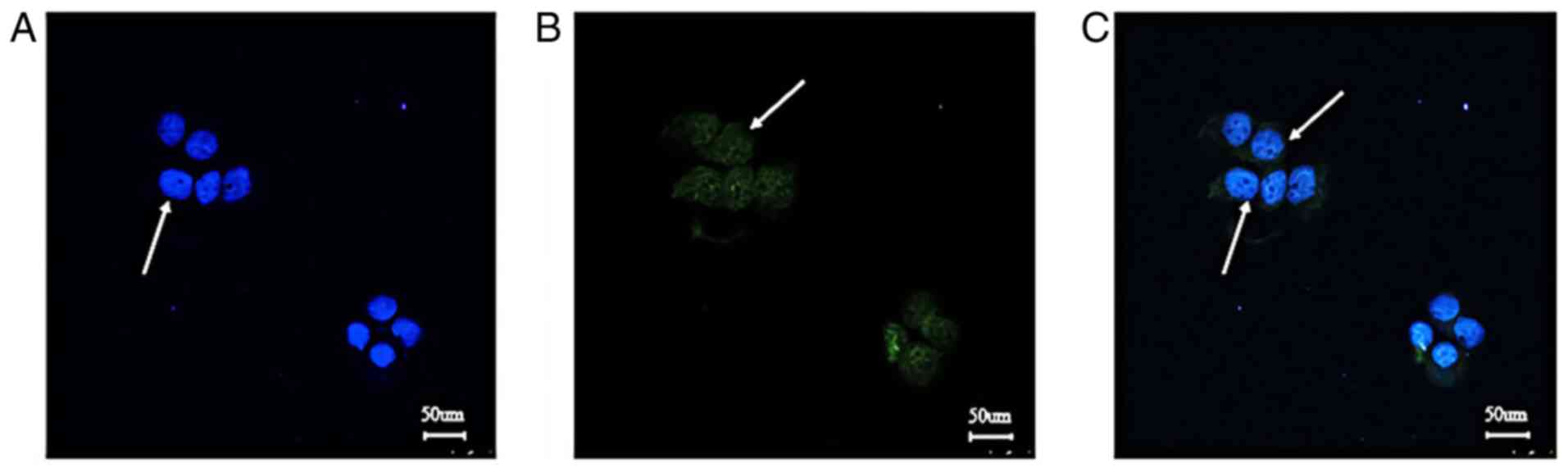
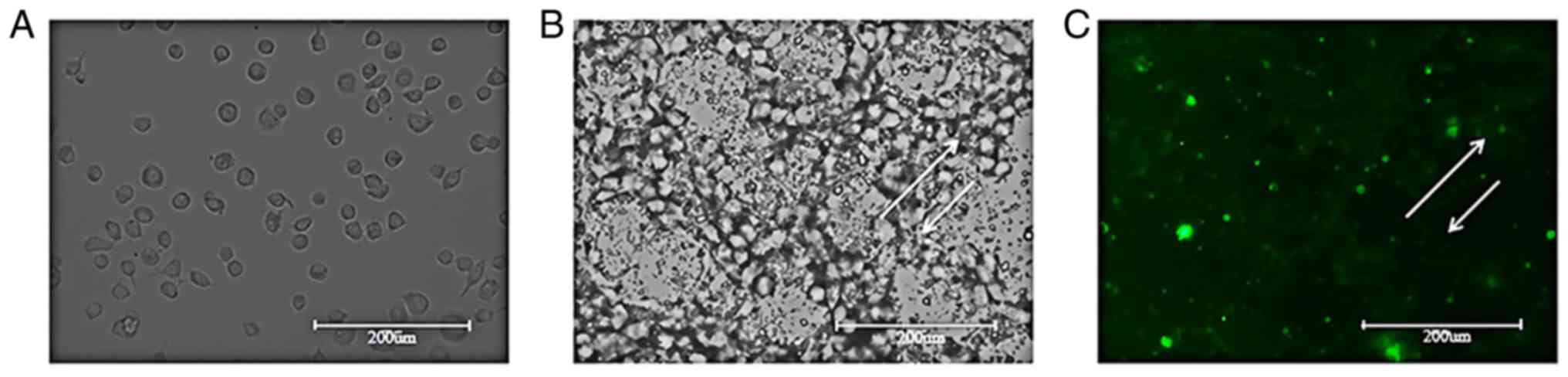
|
1
|
Chen X, Xu WH, Zhou J and Wang YL: Current
situation of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Stomatology. 37:462–465.
2017.
|
|
2
|
Chen F, Yan L, Lin L, Liu F, Qiu Y, Wang
J, Wu J, Liu F, Huang J, Cai L, et al: Dietary score and the risk
of oral cancer: A case-control study in southeast China.
Oncotarget. 8:34610–34616. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Deshpande N, Needles A and Willmann JK:
Molecular ultrasound imaging: Current status and future directions.
Clin Radiol. 65:567–581. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Riemann M, Knipfer C, Rohde M, Alder W,
Schuster M, Noeth E, Oetter N, Shams N, Neukam FW and Stelzlle F:
Oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: Prospective and
objective speech evaluation of patients undergoing surgical
therapy. Head Neck. 38:993–1001. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chang CC, Yang YJ, Li YJ, Chen ST, Lin BR,
Wu TS, Lin SK, Kuo MY and Tan CT: Corrigendum to ‘MicroRNA-17/20a
functions to inhibit cell migration and can be used a prognostic
marker in oral squamous cell carcinoma’ [Oral Oncol. 49(9) (2013)
923-931]. Oral Oncol. 72:202–203. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Xiong J, Feng J, Qiu L, Gao Z, Li P, Pang
L and Zhang Z: SDF-1-loaded PLGA nanoparticles for the targeted
photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy of metastatic lymph
nodes in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Pharm. 554:93–104.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hwang-Bo J, Bae MG, Park JH and Chung IS:
3-O-Acetyloleanolic acid inhibits VEGF-A-induced lymphangiogenesis
and lymph node metastasis in an oral cancer sentinel lymph node
animal model. BMC Cancer. 18(714)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang X, Zhang L, Tan X, Lin Y, Han X,
Wang H, Ming H, Li Q, Liu K and Feng G: Systematic analysis of
genes involved in oral cancer metastasis to lymph nodes. Cell Mol
Biol Lett. 23(53)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Szaniszlo P, Fennewald SM, Qiu S, Kantara
C, Shilagard T, Vargas G and Resto VA: Temporal characterization of
lymphatic metastasis in an orthotopic mouse model of oral cancer.
Head Neck. 36:1638–1647. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wei W, Jiang D, Rosenkrans ZT, Barnhart
TE, Engle JW, Luo Q and Cai W: HER2-targeted multimodal imaging of
anaplastic thyroid cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 9:2413–2427.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xue LY, Jiang ZY, Fu TT, Wang QM, Zhu YL,
Dai M, Wang WP, Yu JH and Ding H: Transfer learning radiomics based
on multimodal ultrasound imaging for staging liver fibrosis. Eur
Radiol. 30:2973–2983. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rapoport N, Christensen DA, Kennedy AM and
Nam KH: Cavitation properties of block copolymer stabilized
phase-shift nanoemulsions used as drug carriers. Ultrasound Med
Biol. 36:419–429. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Niu C, Wang Z, Lu G, Krupka TM, Sun Y, You
Y, Song W, Ran H, Li P and Zheng Y: Doxorubicin loaded
superparamagnetic PLGA-iron oxide multifunctional microbubbles for
dual-mode US/MR imaging and therapy of metastasis in lymph nodes.
Biomaterials. 34:2307–2317. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li A, Zheng Y, Yu J, Wang Z, Yang Y, Wu W,
Guo D and Ran H: Superparamagnetic perfluorooctylbromide
nanoparticles as a multimodal contrast agent for US, MR, and CT
imaging. Acta Radiol. 54:278–283. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jain RA: The manufacturing techniques of
various drug loaded biodegradable poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA)
devices. Biomaterials. 21:2475–2490. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li P, Zheng Y, Ran H, Tan J, Lin Y, Zhang
Q, Ren J and Wang Z: Ultrasound triggered drug release from
10-hydroxycamptothecin-loaded phospholipid microbubbles for
targeted tumor therapy in mice. J Control Release. 162:349–354.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ao M, Wang Z, Ran H, Guo D, Yu J, Li A,
Chen W, Wu W and Zheng Y: Gd-DTPA-loaded PLGA microbubbles as both
ultrasound contrast agent and MRI contrast agent-a feasibility
research. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 93:551–556.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lowe KC: Engineering blood: Synthetic
substitutes from fluorinated compounds. Tissue Eng. 9:389–399.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Cyrus T, Winter PM, Caruthers SD, Wickline
SA and Lanza GM: Magnetic resonance nanoparticles for
cardiovascular molecular imaging and therapy. Expert Rev Cardiovasc
Ther. 3:705–715. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tural B, Ozenbaş M, Atalay S and Volkan M:
Rapid synthesis and characterization of maghemite nanoparticles. J
Nanosci Nanotechnol. 8:861–866. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sun Y, Zheng Y, Ran H, Zhou Y, Shen H,
Chen Y, Chen H, Krupka TM, Li A, Li P, et al: Superparamagnetic
PLGA-iron oxide microcapsules for dual-modality US/MR imaging and
high intensity focused US breast cancer ablation. Biomaterials.
33:5854–5864. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Qiao RR, Yang CH and Gao MY:
Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: From preparations to in
vivo MRI applications. J Mater Chem. 19:6274–6293. 2009.
|
|
23
|
Mu X, Zhang F, Kong C, Zhang H, Zhang W,
Ge R, Liu Y and Jiang J: EGFR-targeted delivery of DOX-loaded
Fe3O4@ polydopamine multifunctional
nanocomposites for MRI and antitumor chemo-photothermal therapy.
Int J Nanomedicine. 12:2899–2911. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Liu ZY, Wang Y, Liang CH, Li XH, Wang GY,
Liu HJ and Li Y: In vitro labeling of mesenchymal stem cells with
superparamagnetic iron oxide by means of microbubble-enhanced US
exposure: Initial experience. Radiology. 253:153–159.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Degen CL, Poggio M, Mamin HJ, Rettner CT
and Rugar D: Nanoscale magnetic resonance imaging. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:1313–1317. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jun YW, Lee JH and Cheon J: Chemical
design of nanoparticle probes for high-performance magnetic
resonance imaging. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 47:5122–5135.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Norton SJ and Vo-Dinh T: Imaging the
distribution of magnetic nanoparticles with ultrasound. IEEE Trans
Med Imaging. 26:660–665. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chen ZJ, Yang SH and Xing D: In vivo
detection of hemoglobin oxygen saturation and carboxyhemoglobin
saturation with multiwavelength photoacoustic microscopy. Opt Lett.
37:3414–3416. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ermilov SA, Khamapirad T, Conjusteau A,
Leonard MH, Lacewell R, Mehta K, Miller T and Oraevsky AA: Laser
optoacoustic imaging system for detection of breast cancer. J
Biomed Opt. 14(024007)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Li C and Wang LV: Photoacoustic tomography
and sensing in biomedicine. Phys Med Biol. 54:R59–R97.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Grootendorst DJ, Jose J, Fratila RM,
Visscher M, Velders AH, Ten Haken B, Van Leeuwen TG, Steenbergen W,
Manohar S and Ruers TJ: Evaluation of superparamagnetic iron oxide
nanoparticles (Endorem®) as a photoacoustic contrast
agent for intra-operative nodal staging. Contrast Media Mol
Imaging. 8:83–91. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Strohm E, Rui M, Gorelikov I, Matsuura N
and Kolios M: Vaporization of perfluorocarbon droplets using
optical irradiation. Biomed Opt Express. 2:1432–1442.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Balkwill F: The significance of cancer
cell expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Semin Cancer Biol.
14:171–179. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Delilbasi CB, Okura M, Iida S and Kogo M:
Investigation of CXCR4 in squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue.
Oral Oncol. 40:154–157. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lee DJ, Lyshchik A, Huamani J, Hallahan DE
and Fleischer AC: Relationship between retention of a vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 2 (VEGFR2)-targeted
ultrasonographic contrast agent and the level of VEGFR2 expression
in an in vivo breast cancer model. J Ultrasound Med. 27:855–866.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mei L, Liu Y, Zhang Q, Gao HL, Zhang Z and
He Q: Enhanced antitumor and anti-metastasis efficiency via
combined treatment with CXCR4 antagonist and liposomal doxorubicin.
J Control Release. 196:324–331. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Iyer AK, Khaled G, Fang J and Maeda H:
Exploiting the enhanced permeability and retention effect for tumor
targeting. Drug Discov Today. 11:812–818. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ke H, Yue X, Wang J, Xing S, Zhang Q, Dai
Z, Tian J, Wang S and Jin Y: Gold nanoshelled liquid
perfluorocarbon nanocapsules for combined dual modal ultrasound/CT
imaging and photothermal therapy of cancer. Small. 10:1220–1227.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhigang W, Zhiyu L, Haitao R, Hong R,
Qunxia Z, Ailong H, Qi L, Chunjing Z, Hailin T, Lin G, et al:
Ultrasound-mediated microbubble destruction enhances VEGF gene
delivery to the infarcted myocardium in rats. Clin Imaging.
28:395–398. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kuhl CK, Strobel K, Bieling H, Leutner C,
Schild HH and Schrading S: Supplemental breast MR imaging screening
of women with average risk of breast cancer. Radiology.
283:361–370. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ell PJ: PET/CT in oncology: A major
technology for cancer care. Chang Gung Med J. 28:274–283.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Razansky D, Buehler A and Ntziachristos V:
Volumetric real-time multispectral optoacoustic tomography of
biomarkers. Nat Protoc. 6:1121–1129. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Liu Z, Lammers T, Ehling J, Fokong S,
Bornemann J, Kiessling F and Gätjens J: Iron oxide
nanoparticle-containing microbubble composites as contrast agents
for MR and ultrasound dual-modality imaging. Biomaterials.
32:6155–6163. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kim J, Park S, Lee JE, Jin SM, Lee JH, Lee
IS, Yang I, Kim JS, Kim SK, Cho MH and Hyeon T: Designed
fabrication of multifunctional magnetic gold nanoshells and their
application to magnetic resonance imaging and photothermal therapy.
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 45:7754–7758. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Tian Q, Hu J, Zhu Y, Zou R, Chen Z, Yang
S, Li R, Su Q, Han Y and Liu X: Sub-10 nm Fe3O4@Cu(2-x)S core-shell
nanoparticles for dual-modal imaging and photothermal therapy. J Am
Chem Soc. 135:8571–8577. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ling Y, Wei K, Luo Y, Gao X and Zhong S:
Dual docetaxel/superparamagnetic iron oxide loaded nanoparticles
for both targeting magnetic resonance imaging and cancer therapy.
Biomaterials. 32:7139–7150. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Duguet E, Vasseur S, Mornet S and
Devoisselle JM: Magnetic nanoparticles and their applications in
medicine. Nanomedicine (Lond). 1:157–168. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Chen YL, Liu FQ, Guo Y, Cheng J, Yang L,
Lu M, Li P, Xu J, Yu T, Wang ZG, et al: PA/US dual-modality imaging
to guide VEGFR-2 targeted photothermal therapy using
ZnPc-/PFH-loaded polymeric nanoparticles. Biomater Sci.
6:2130–2143. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Huang JW, Xu JS, Schmidt C and Xu RX: Heat
sensitive microbubbles for intraoperative assessment of cancer
ablation margin. Multimodal biomedical imaging VII. Int Soc Opt
Photonics. 8216(821604)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhou Y, Wang Z, Chen Y, Shen H, Luo Z, Li
A, Wang Q, Ran H, Li P, Song W, et al: Microbubbles from
gas-generating perfluorohexane nanoemulsions for targeted
temperature-sensitive ultrasonography and synergistic HIFU ablation
of tumors. Adv Mater. 25:4123–4130. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Xu S, Zong Y, Li W, Zhang S and Wan M:
Bubble size distribution in acoustic droplet vaporization via
dissolution using an ultrasound wide-beam method. Ultrason
Sonochem. 21:975–983. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Chu M, Shao Y, Peng J, Dai X, Li H, Wu Q
and Shi D: Near-infrared laser light mediated cancer therapy by
photothermal effect of Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles. Biomaterials.
34:4078–4088. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Sano D and Myers JN: Metastasis of
squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
26:645–662. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Oliveira-Neto HH, Silva ET, Leles CR,
Mendonca EF, Alencar Rde C, Silva TA and Batista AC: Involvement of
CXCL12 and CXCR4 in lymph node metastases and development of oral
squamous cell carcinomas. Tumour Biol. 29:262–271. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Almofti A, Uchida D, Begum NM, Tomizuka Y,
Iga H, Yoshida H and Sato M: The clinicopathological significance
of the expression of CXCR4 protein in oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Int J Oncol. 25:65–71. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Teicher BA and Fricker SP: CXCL12
(SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:2927–2931.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Rave-Fränk M, Tehrany N, Kitz J, Leu M,
Weber HE, Burfeind P, Schliephake H, Canis M, Beissbarth T,
Reichardt HM and Wolff HA: Prognostic value of CXCL12 and CXCR4 in
inoperable head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Strahlenther
Onkol. 192:47–54. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Meng W, Xue S and Chen Y: The role of
CXCL12 in tumor microenvironment. Gene. 641:105–110.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|