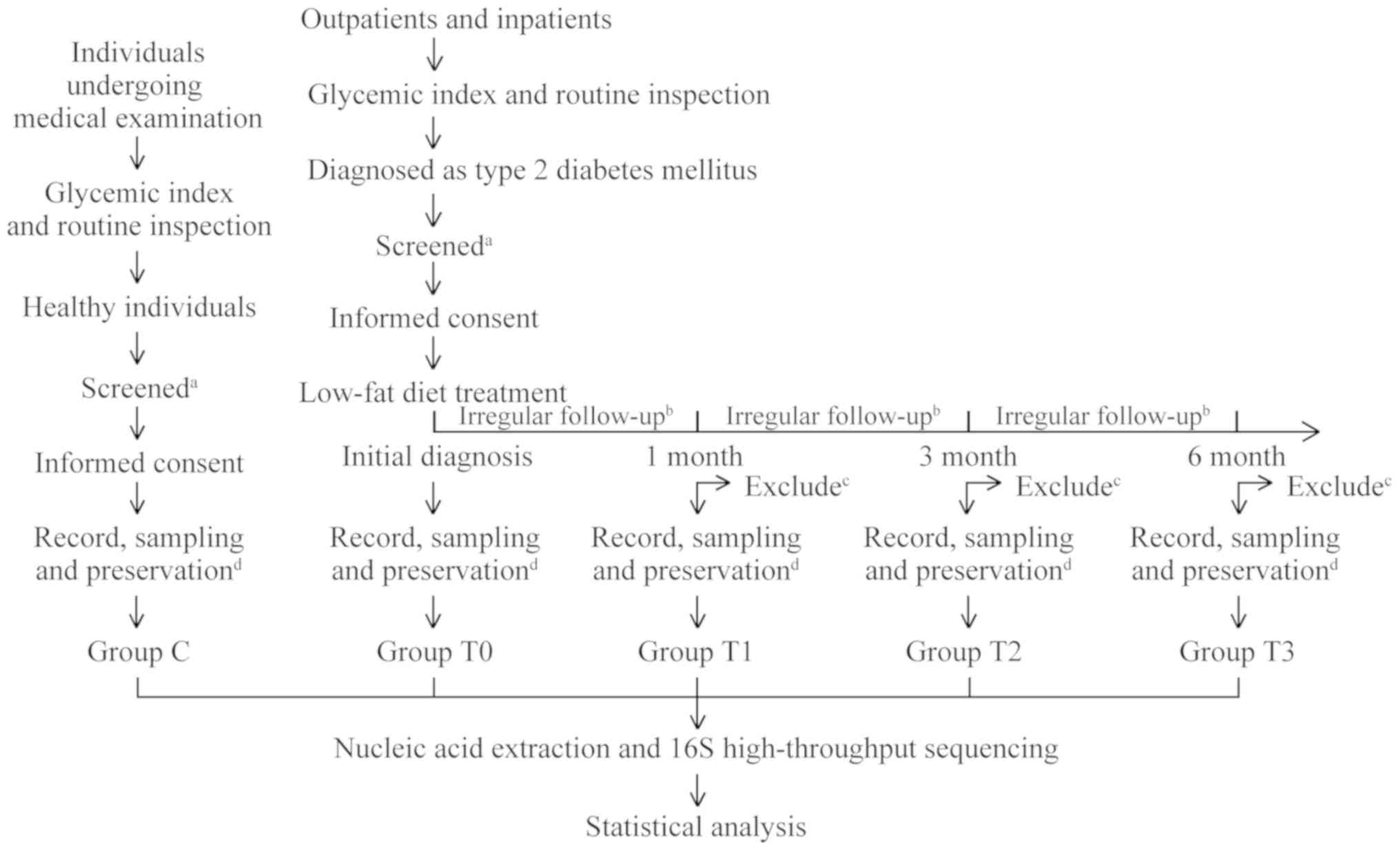
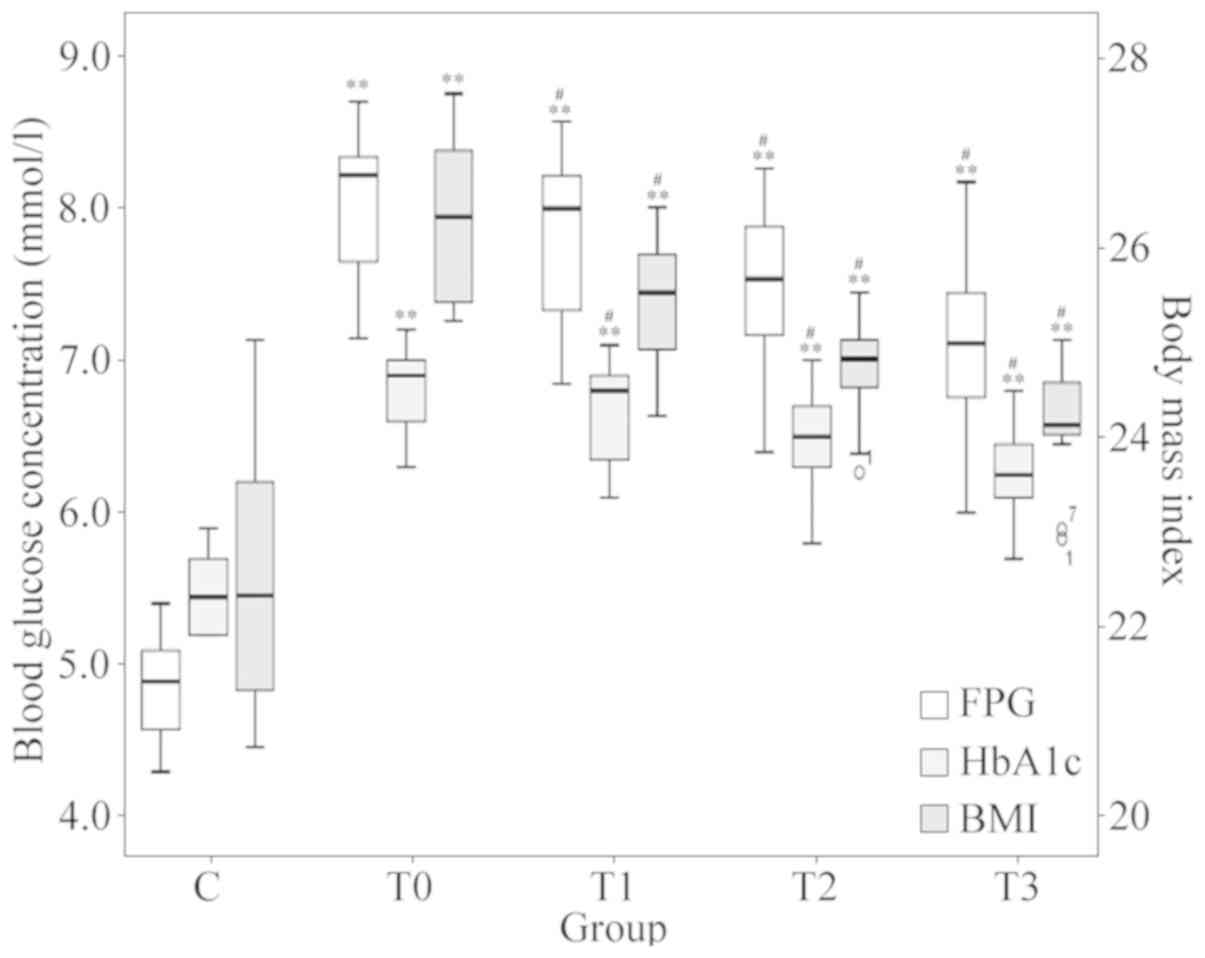
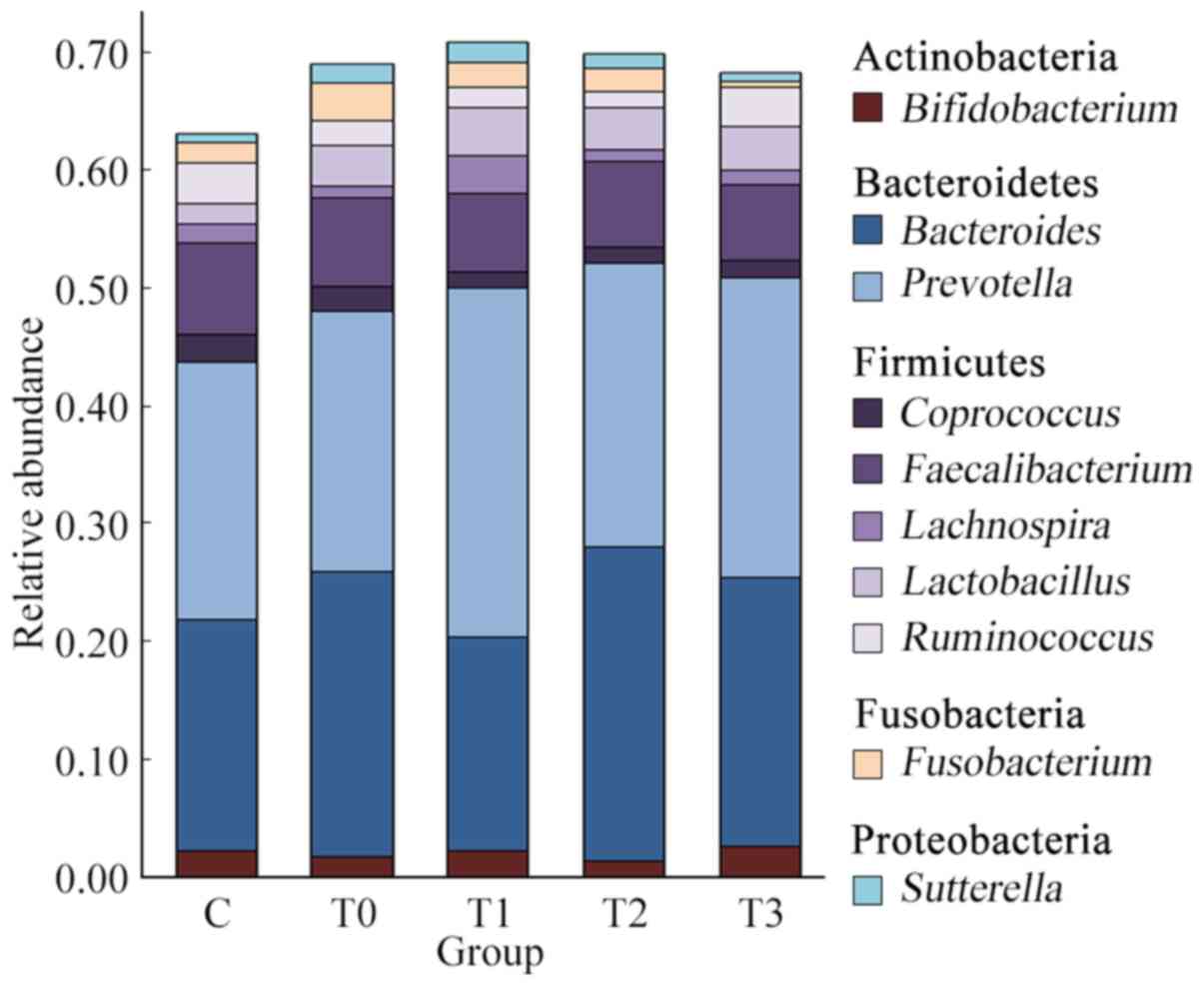
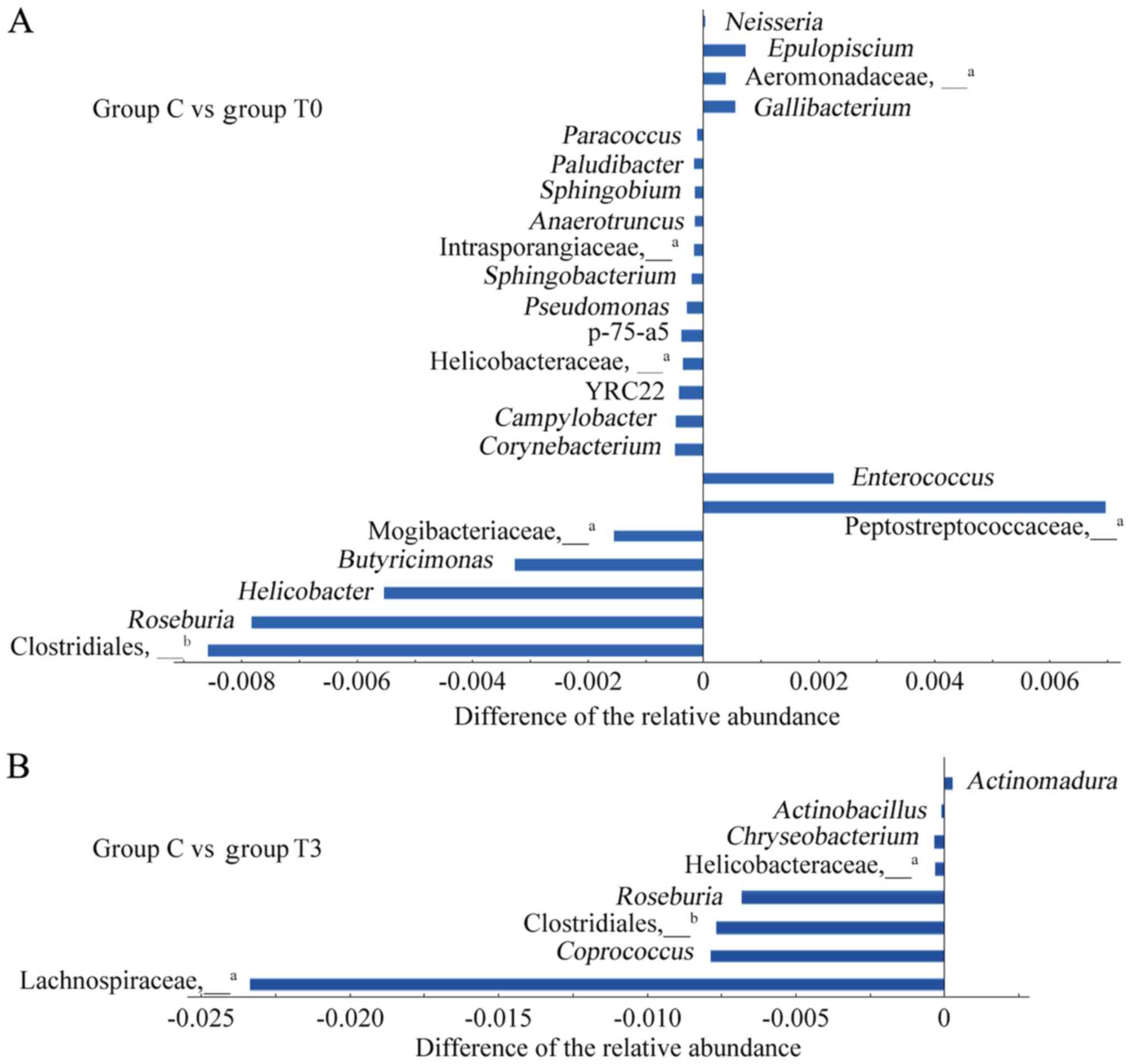
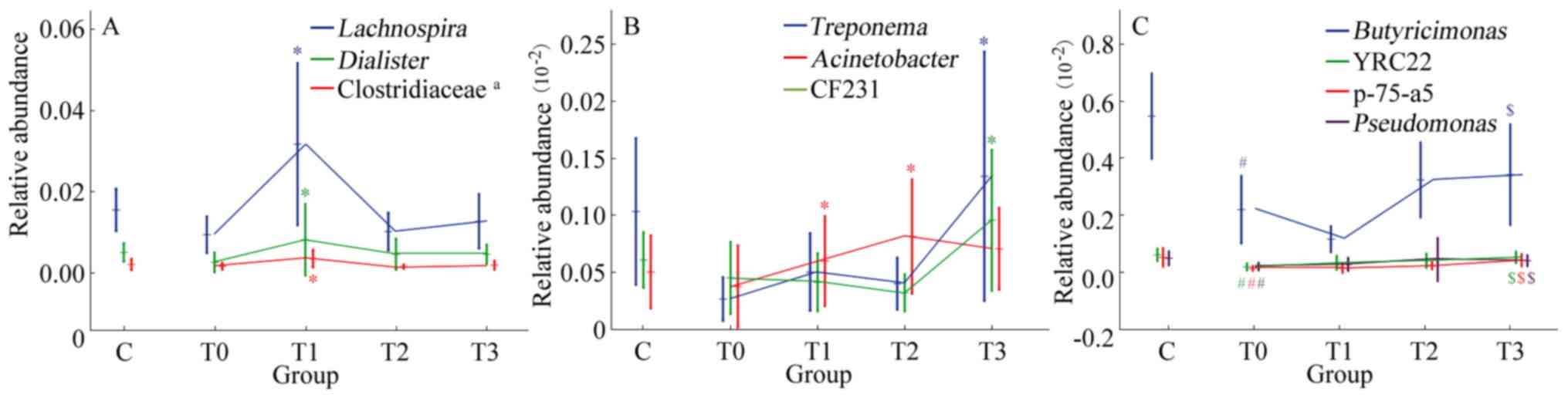
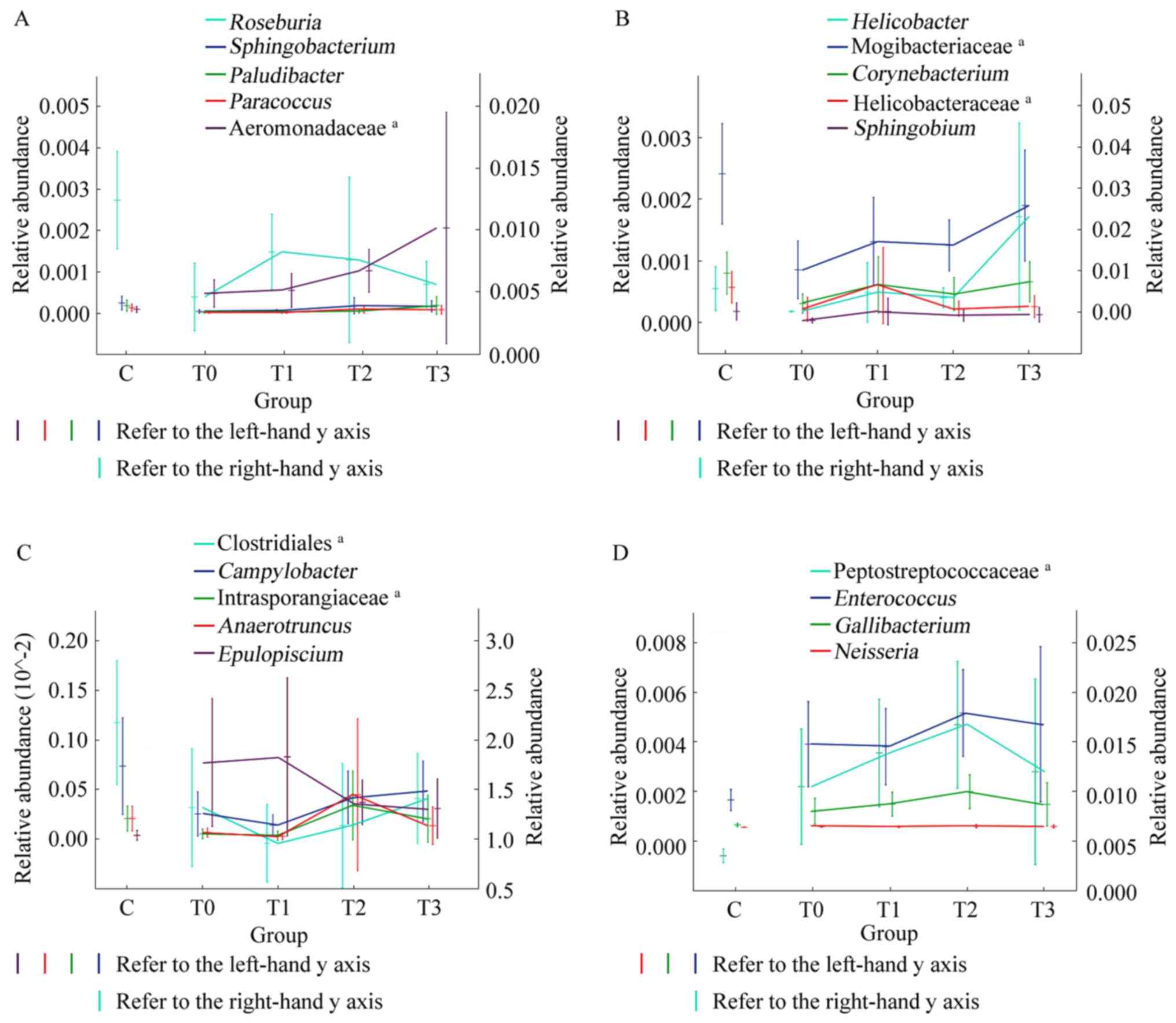
|
1
|
American Diabetes Association. The
prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 25:742–749.
2002.
|
|
2
|
Wang L, Gao P, Zhang M, Huang Z, Zhang D,
Deng Q, Li Y, Zhao Z, Qin X, Jin D, et al: Prevalence and ethnic
pattern of diabetes and prediabetes in china in 2013. JAMA.
317:2515–2523. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li H, Gan W, Lu L, Dong X, Han X, Hu C,
Yang Z, Sun L, Bao W, Li P, et al: A genome-wide association study
identifies GRK5 and RASGRP1 as type 2 diabetes loci in Chinese
Hans. Diabetes. 62:291–298. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sami W, Ansari T, Butt NS and Hamid MRA:
Effect of diet on type 2 diabetes mellitus: A review. Int J Health
Sci (Qassim). 11:65–71. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lee MS: ED 05-2 Interaction of gut
dysbiosis and innate immune dysfunction in the development of
metabolic syndrome. J Hypertension. 34(e187)2016.
|
|
6
|
Soare A, Khazrai YM, Del Toro R, Roncella
E, Fontana L, Fallucca S, Angeletti S, Formisano V, Capata F, Ruiz
V, et al: The effect of the macrobiotic Ma-Pi 2 diet vs the
recommended diet in the management of type 2 diabetes: The
randomized controlled MADIAB trial. Nutr Metab (Lond).
25(39)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Victoria JV, Valentine RJ, Wilund KR,
Antao N, Baynard T and Woods JA: Effects of exercise and low-fat
diet on adipose tissue inflammation and metabolic complications in
obese mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 296:E1164–E1171.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhao L: The gut microbiota and obesity:
From correlation to causality. Nat Rev Microbiol. 11:639–647.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pedersen HK, Gudmundsdottir V, Nielsen HB,
Hyotylainen T, Nielsen T, Jensen BA, Forslund K, Hildebrand F,
Prifti E, Falony G, et al: Human gut microbes impact host serum
metabolome and insulin sensitivity. Nature. 535(376)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Karlsson FH, Tremaroli V, Nookaew I,
Bergström G, Behre CJ, Fagerberg B, Nielsen J and Bäckhed F: Gut
metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic
glucose control. Nature. 498:99–103. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S and Gordon
JI: Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity.
Nature. 444:1022–1023. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wirth R, Bódi N, Maróti G, Bagyánszki M,
Talapka P, Fekete É, Bagi Z and Kovács KL: Regionally distinct
alterations in the composition of the gut microbiota in rats with
streptozotocin-induced diabete. PLoS One. 9(e110440)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Heinritz SN, Weiss E, Eklund M, Aumiller
T, Louis S, Rings A, Messner S, Camarinha-Silva A, Seifert J,
Bischoff SC and Mosenthin R: Intestinal Microbiota and microbial
metabolites are changed in a pig model fed a High-Fat/Low-Fiber or
a Low-Fat/High-Fiber diet. PLoS One. 11(e0154329)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhao LP, Zhang F, Ding XY, Wu GJ, Lam YY,
Wang XJ, Fu HQ, Xue XH, Lu CH, Ma JL, et al: Gut bacteria
selectively promoted by dietary fibers alleviate type 2 diabetes.
Sience. 359:1151–1156. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
World Health Organization: Definition and
diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycemia:
Report of a WHO/IDF consultation, 2006.
|
|
16
|
Yan Z, Tao ZH and Xiang F: Diabetics diets
and their nutritional analyses. J Res Dietet Sci Culture. 32:51–53.
2015.
|
|
17
|
Cheng YY: Brief Introduction of the 2013
revision of ‘Reference Intake of Dietary Nutrients of Chinese
Residents’. Acta Nutrimenta Sinia. 36:313–317. 2014.
|
|
18
|
Ismaiel M, Yang H and Min C: Dietary fiber
role in type 2 diabetes prevention. Br Food J. 118:961–975.
2016.
|
|
19
|
Lin L, Wen ZB, Lin DJ, Dong JT, Jin J and
Meng F: Correlations between microbial communities in stool and
clinical indicators in patients with metabolic syndrome. World J
Clin Cases. 6:54–63. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Edgar RC: Search and clustering orders of
magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics. 26:2460–2461.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Qin JJ, Li YR, Cai ZM, Li SH, Zhu JF,
Zhang F, Liang SS, Zhang WW, Guan YL, Shen DQ, et al: A
metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2
diabetes. Nature. 490:55–60. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cann I, Bernardi RC and Mackie RI:
Cellulose degradation in the human gut: Ruminococcus
champanellensis expands the cellulosome paradigm. Environ
Microbiol. 18:307–310. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jones N: Gut study divides people into
three types. Nature: 20 April, 2011 doi: 10.1038/news.2011.249.
|
|
24
|
Cherdyntseva TA, Kotova IB and Netrusov
AI: Gut study divides people into three types. Adv Exp Med Biol.
897:103–111. 2015.
|
|
25
|
Sedighi M, Razavi S, Navab-Moghadam F,
Khamseh ME, Alaei-Shahmiri F, Mehrtash A and Amirmozafari N:
Comparison of gut microbiota in adult patients with type 2 diabetes
and healthy individuals. Microb Pathog. 111:362–369.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Morrison DJ, Mackay WG, Edwards CA,
Morrison DJ, Mackay WG, Edwards CA, Preston T and Weaver LT:
Butyrate production from oligofructose fermentation by the human
faecal flora: What is the contribution of extracellular acetate and
lactate? Br J Nutr. 96:570–577. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Patterson E, Marques TM, O'Sullivan O,
Fitzgerald P, Fitzgerald GF, Cotter PD, Dinan TG, Cryan JF, Stanton
C and Ross RP: Streptozotocin-induced type-1-diabetes disease onset
in Sprague-Dawley rats is associated with an altered intestinal
microbiota composition and decreased diversity. Microbiology.
161:182–193. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Polansky O, Sekelova Z, Faldynova M,
Sebkova A, Sisak F and Rychlik I: Important metabolic pathways and
biological processes expressed by chicken Cecal microbiota. Appl
Environ Microbiol. 82:1569–1576. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ijaz MU, Ahmed MI, Zou X, Hussain M, Zhang
M, Zhao F, Xu X, Zhou G and Li C: Beef, casein, and soy proteins
differentially affect lipid metabolism, triglycerides accumulation
and gut microbiota of high-fat Diet-Fed C57BL/6J Mice. Front
Microbiol. 9(2200)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Louis P and Flint HJ: Diversity,
metabolism and microbial ecology of butyrate-producing bacteria
from the human large intestine. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 294:1–8.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Devillard E, McIntosh FM, Duncan SH and
Wallace RJ: Metabolism of linoleic acid by human gut bacteria:
Different routes for biosynthesis of conjugated linoleic acid. J
Bacteriol. 189:2566–2570. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Haro C, Montes-Borrego M, Rangel-Zúñiga
OA, Alcalá-Díaz JF, Gómez-Delgado F, Pérez-Martínez P,
Delgado-Lista J, Quintana-Navarro GM, Tinahones FJ, Landa BB, et
al: Two healthy diets modulate gut microbial community improving
insulin sensitivity in a human obese population. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 101:233–242. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cantu-Jungles TM, Ruthes AC, El-Hindawy M,
Moreno RB, Zhang X, Cordeiro LMC, Hamaker BR and Iacomini M: In
vitro fermentation of Cookeina speciosa glucans stimulates the
growth of the butyrogenic Clostridium cluster XIVa in a targeted
way. Carbohydr Polym. 183:219–229. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|