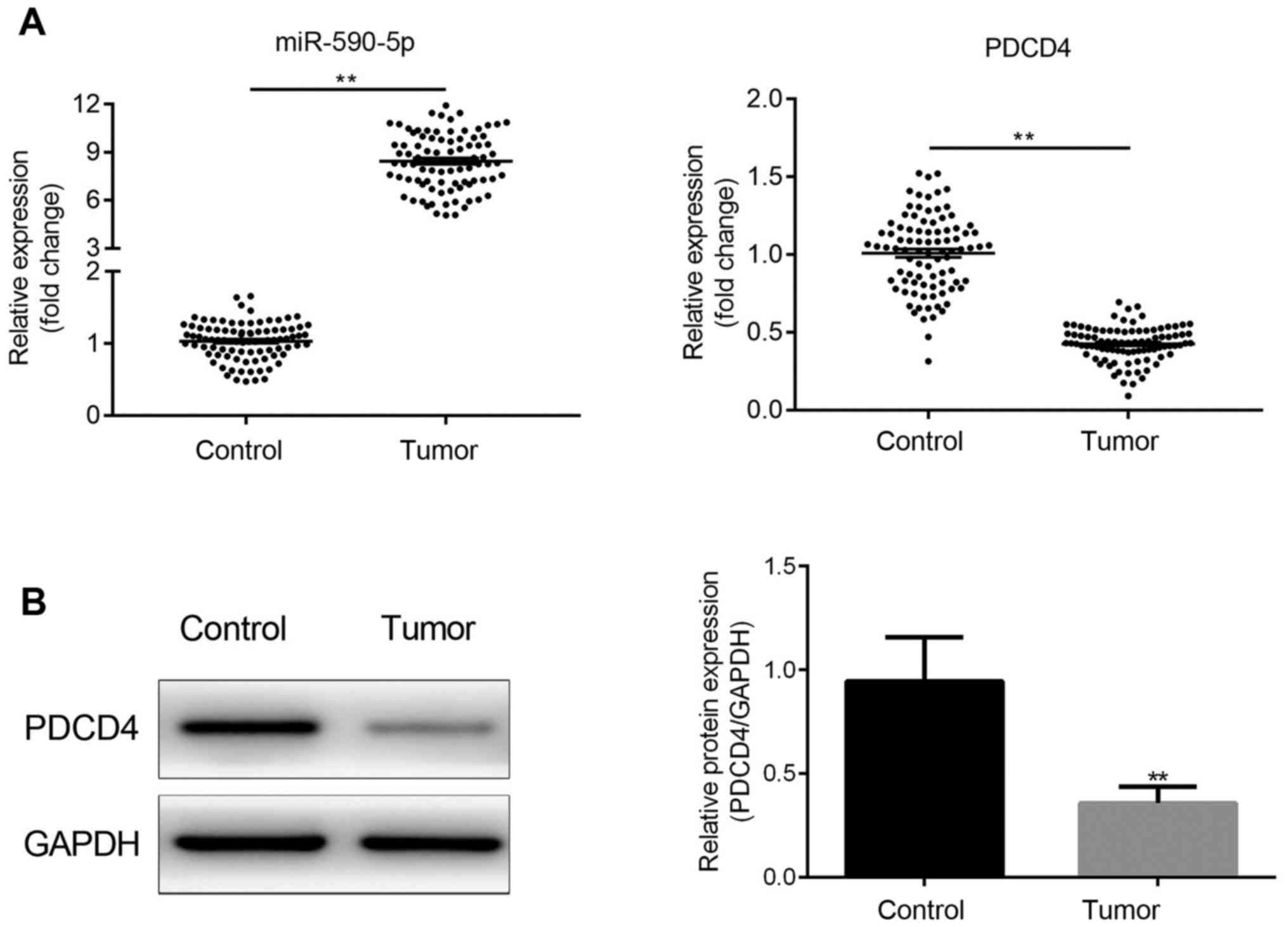
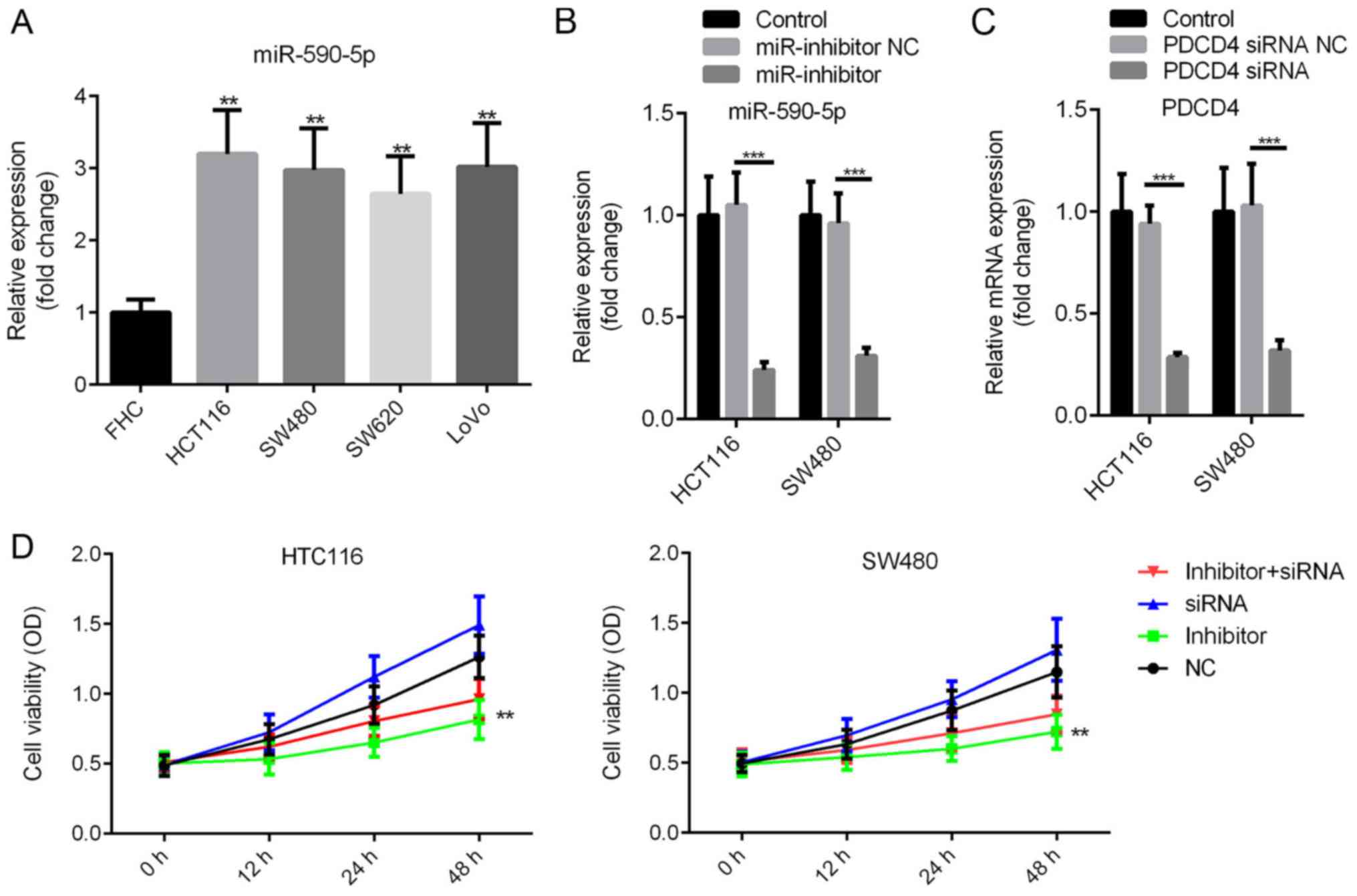
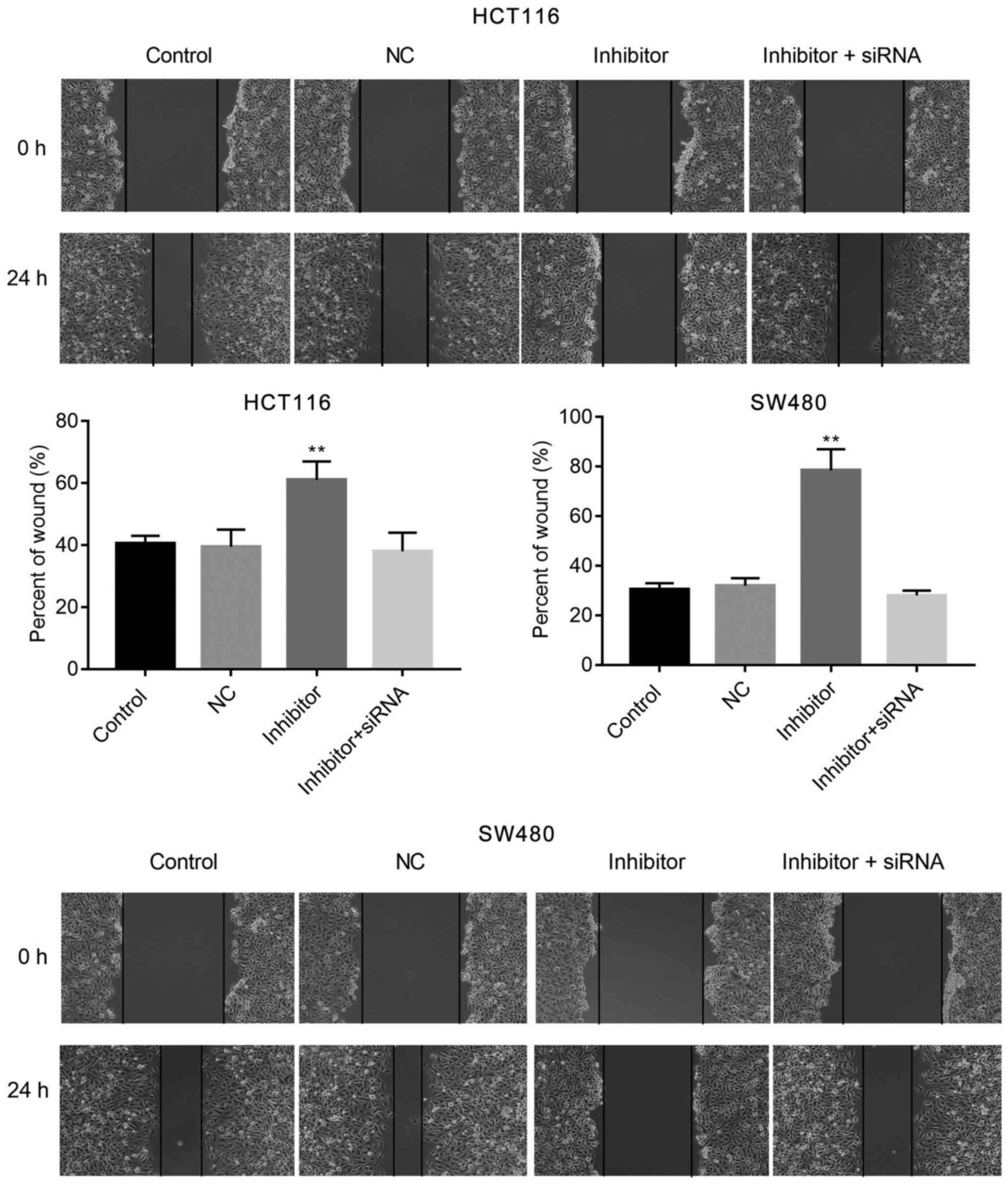
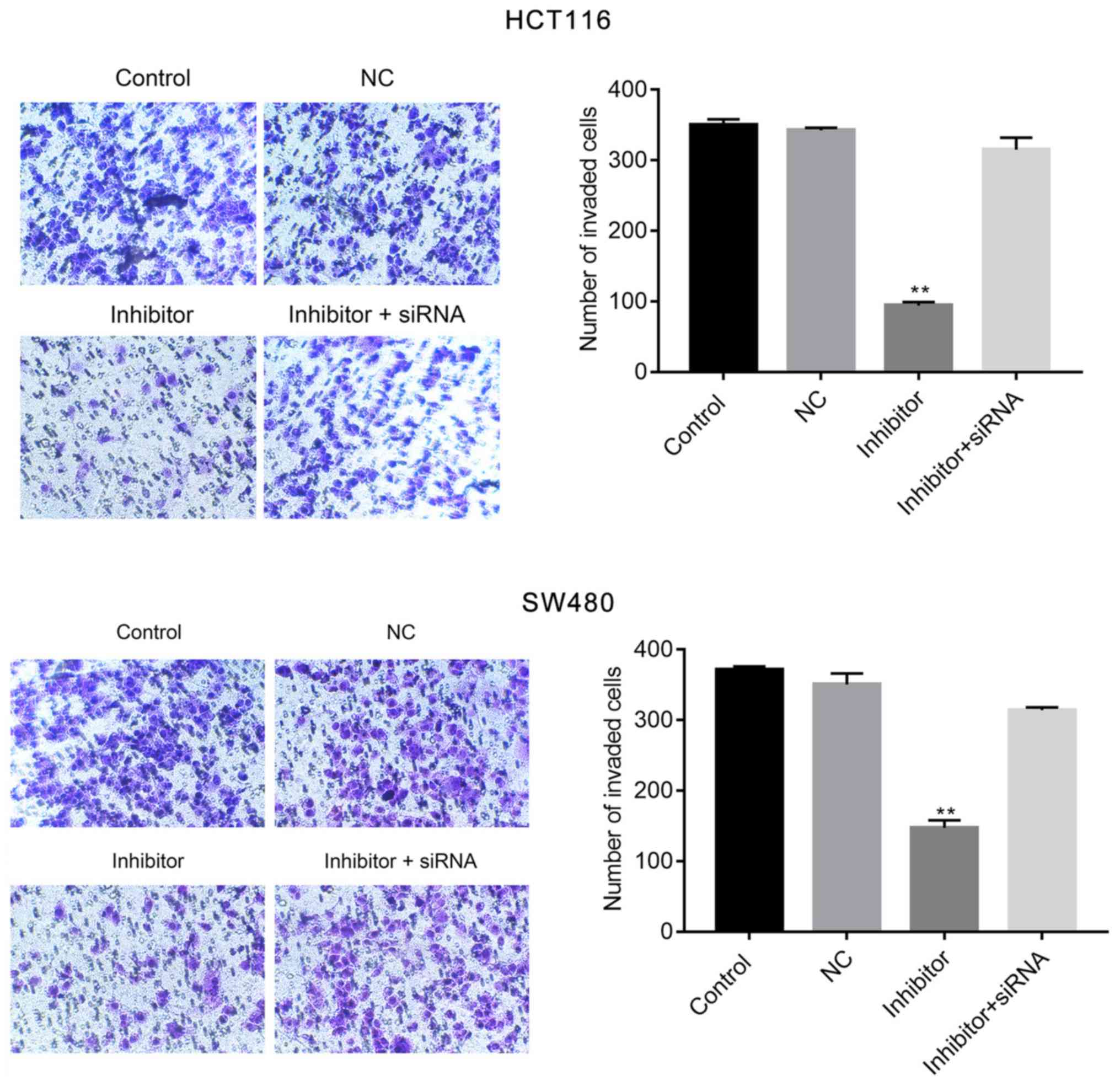
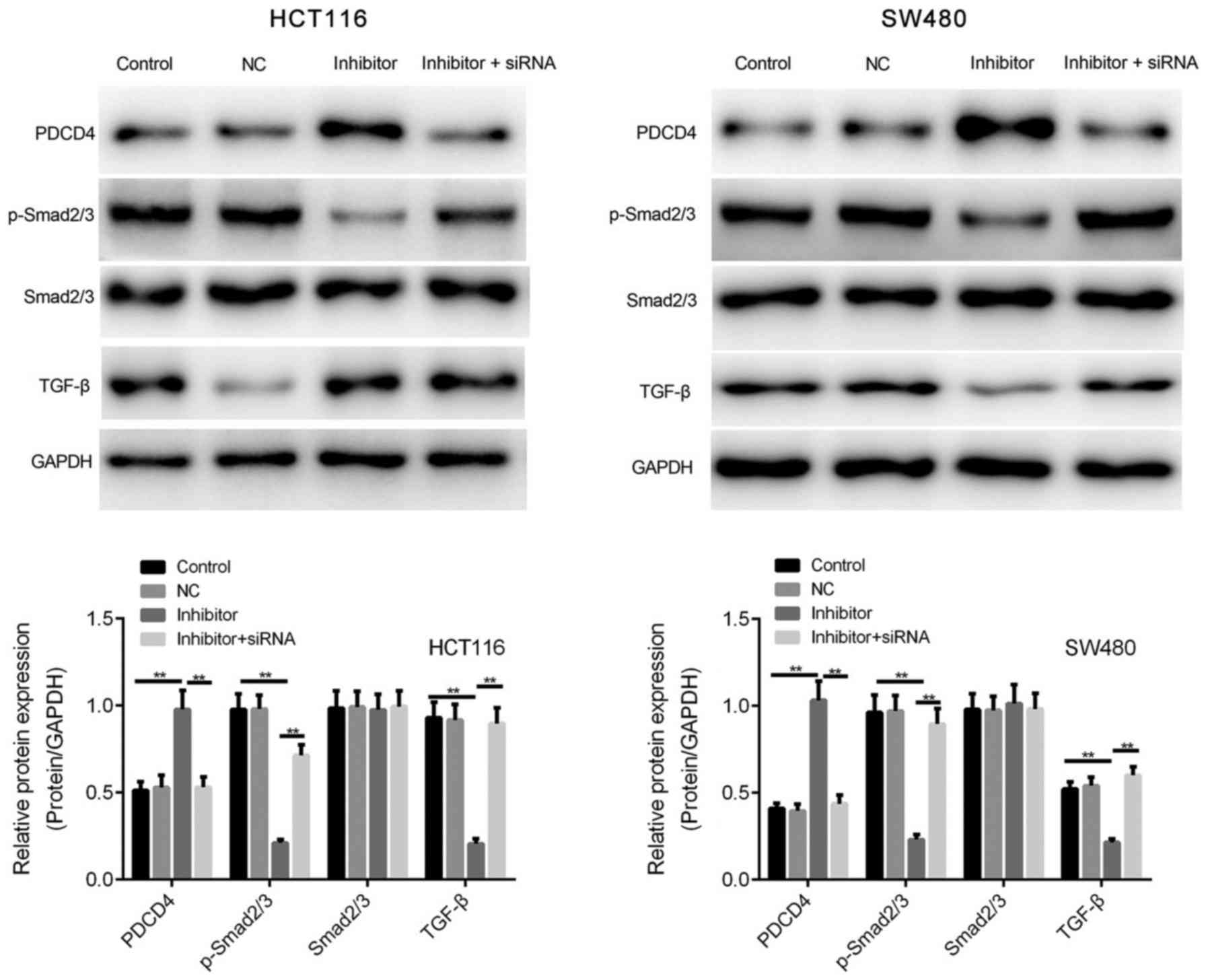
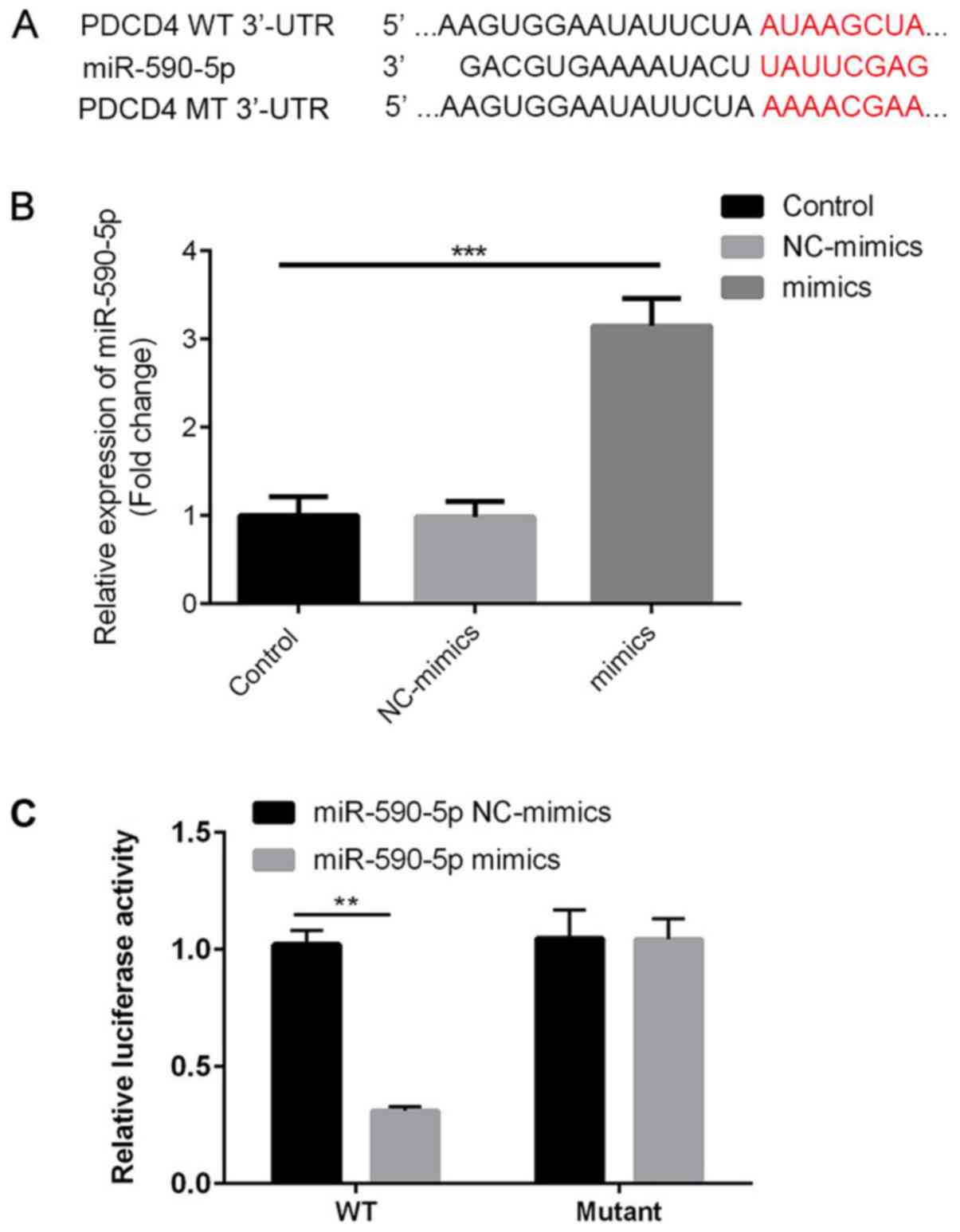
|
1
|
Jacobsen F, Kraft J, Schroeder C,
Hube-Magg C, Kluth M, Lang DS, Simon R, Sauter G, Izbicki JR,
Clauditz TS, et al: Up-regulation of biglycan is associated with
poor prognosis and PTEN deletion in patients with prostate cancer.
Neoplasia. 19:707–715. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Anderson JC and Levine JB: Age and crc
risk in the serrated pathway. J Clin Gastroenterol. 52:465–467.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang G, Fu Y, Hu F, Lan J, Xu F, Yang X,
Luo X, Wang J and Hu J: Loss of BRG1 induces CRC cell senescence by
regulating p53/p21 pathway. Cell Death Dis. 8(e2607)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Orang AV and Barzegari A: MicroRNAs in
colorectal cancer: From diagnosis to targeted therapy. Asian Pac J
Cancer Prev. 15:6989–6999. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sun ZQ, Shi K, Zhou QB, Zeng XY, Liu J,
Yang SX, Wang QS, Li Z, Wang GX, Song JM, et al: MiR-590-3p
promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer via
Hippo pathway. Oncotarget. 8:58061–58071. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chen M, Li D, Gong N, Wu H, Su C, Xie C,
Xiang H, Lin C and Li X: miR-133b down-regulates ABCC1 and enhances
the sensitivity of CRC to anti-tumor drugs. Oncotarget.
8:52983–52994. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Guglielmo A, Staropoli N, Giancotti M and
Mauro M: Personalized medicine in colorectal cancer diagnosis and
treatment: A systematic review of health economic evaluations. Cost
Eff Resour Alloc. 16(2)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Dekker E and IJspeert JEG: Serrated
pathway: A paradigm shift in CRC prevention. Gut. 67:1751–1752.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Park YR, Lee ST, Kim SL, Zhu SM, Lee MR,
Kim SH, Kim IH, Lee SO, Seo SY and Kim SW: Down-regulation of miR-9
promotes epithelial mesenchymal transition via regulating
anoctamin-1 (ANO1) in CRC cells. Cancer Genet. 231-232:22–31.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang Z, Li J, Huang Y, Peng W, Qian W, Gu
J, Wang Q, Hu T, Ji D, Ji B, et al: Upregulated miR-1258 regulates
cell cycle and inhibits cell proliferation by directly targeting
E2F8 in CRC. Cell Prolif. 51(e12505)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tong F, Ying Y, Pan H, Zhao W, Li H and
Zhan X: MicroRNA-466 (miR-466) functions as a tumor suppressor and
prognostic factor in colorectal cancer (CRC). Bosn J Basic Med Sci.
18:252–259. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu X and Cui M: MiRNA-98-5p inhibits the
progression of osteosarcoma by regulating cell cycle via targeting
CDC25A expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:9793–9802.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ling Z, Guan H, You Z, Wang C, Hu L, Zhang
L, Wang Y, Chen S, Xu B and Chen M: Aloperine executes antitumor
effects through the induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in
prostate cancer in vitro and in vivo. Onco Targets Ther.
11:2735–2743. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Shi J, Niu Z, Wang J and Zhang W:
MiR-216a-3p regulates the proliferation, apoptosis, migration, and
invasion of lung cancer cells via targeting COPB2. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem: Jul 3, 2020 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
15
|
Gao ZY, Liu H and Zhang Z: miR-144-3p
increases radiosensibility of gastric cancer cells by targeting
inhibition of ZEB1. Clin Transl Oncol: Jul 1, 2020 (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
16
|
Chen S, Wang Y, Xu M, Zhang L, Su Y, Wang
B and Zhang X: miR-1184 regulates the proliferation and apoptosis
of colon cancer cells via targeting CSNK2A1. Mol Cell Probes.
101625:2020.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhou Q, Zhu Y, Wei X, Zhou J, Chang L, Sui
H, Han Y, Piao D, Sha R and Bai Y: MiR-590-5p inhibits colorectal
cancer angiogenesis and metastasis by regulating nuclear factor
90/vascular endothelial growth factor A axis. Cell Death Dis.
7(e2413)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu Q, Yang W, Luo Y, Hu S and Zhu L:
Correlation between miR-21 and miR-145 and the incidence and
prognosis of colorectal cancer. J BUON. 23:29–35. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu JL, He GY, Lan XL, Zeng ZC, Guan J,
Ding Y, Qian XL, Liao WT, Ding YQ and Liang L: Inhibition of
ATG12-mediated autophagy by miR-214 enhances radiosensitivity in
colorectal cancer. Oncogenesis. 7(16)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liao D, Li T, Ye C, Zeng L, Li H, Pu X,
Ding C, He Z and Huang GL: miR-221 inhibits autophagy and targets
TP53INP1 in colorectal cancer cells. Exp Ther Med. 15:1712–1717.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ou C, Sun Z, Li X, Li X, Ren W, Qin Z,
Zhang X, Yuan W, Wang J, Yu W, et al: MiR-590-5p, a
density-sensitive microRNA, inhibits tumorigenesis by targeting
YAP1 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 399:53–63. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang X, Lai Q, He J, Li Q, Ding J, Lan Z,
Gu C, Yan Q, Fang Y, Zhao X and Liu S: LncRNA SNHG6 promotes
proliferation, invasion and migration in colorectal cancer cells by
activating TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway via targeting UPF1 and
inducing EMT via regulation of ZEB1. Int J Med Sci. 16:51–59.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Peng H, Wang L, Su Q, Yi K, Du J and Wang
Z: MiR-31-5p promotes the cell growth, migration and invasion of
colorectal cancer cells by targeting NUMB. Biomed Pharmacother.
109:208–216. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jiang Z, Cao Q, Dai G, Wang J, Liu C, Lv L
and Pan J: Celastrol inhibits colorectal cancer through
TGF-beta1/Smad signaling. Onco Targets Ther. 12:509–518.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jin Y, Chen W, Yang H, Yan Z, Lai Z, Feng
J, Peng J and Lin J: Scutellaria barbata D. Don inhibits migration
and invasion of colorectal cancer cells via suppression of PI3K/AKT
and TGF-β/Smad signaling pathways. Exp Ther Med. 14:5527–5534.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu Y, Uzair-Ur-Rehman Guo Y, Liang H,
Cheng R, Yang F, Hong Y, Zhao C, Liu M, Yu M, et al: miR-181b
functions as an oncomiR in colorectal cancer by targeting PDCD4.
Protein Cell. 7:722–734. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lee YR, Chen SH, Lin CY, Chao WY, Lim YP,
Yu HI and Lu CH: In vitro antitumor activity of aloperine on human
thyroid cancer cells through caspase-dependent apoptosis. Int J Mol
Sci. 19(312)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang L, Zhao M, Guo C, Wang G, Zhu F, Wang
J, Wang X, Wang Q, Zhao W, Shi Y, et al: PDCD4 deficiency
aggravated colitis and Colitis-associated colorectal cancer via
promoting IL-6/STAT3 pathway in mice. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
22:1107–1118. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lim SC and Hong R: Programmed cell death 4
(Pdcd4) expression in colorectal adenocarcinoma: Association with
clinical stage. Oncol Lett. 2:1053–1057. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|