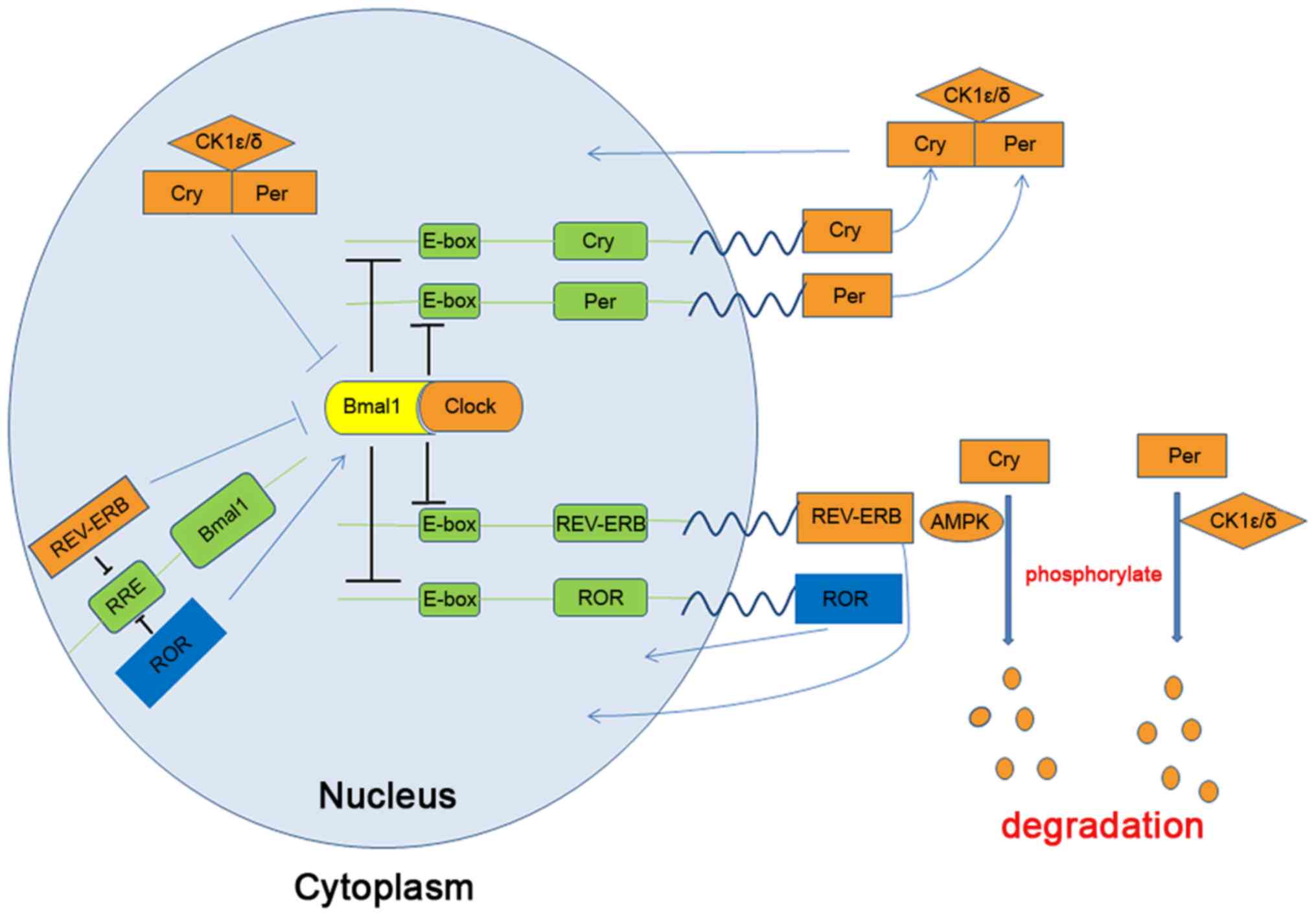
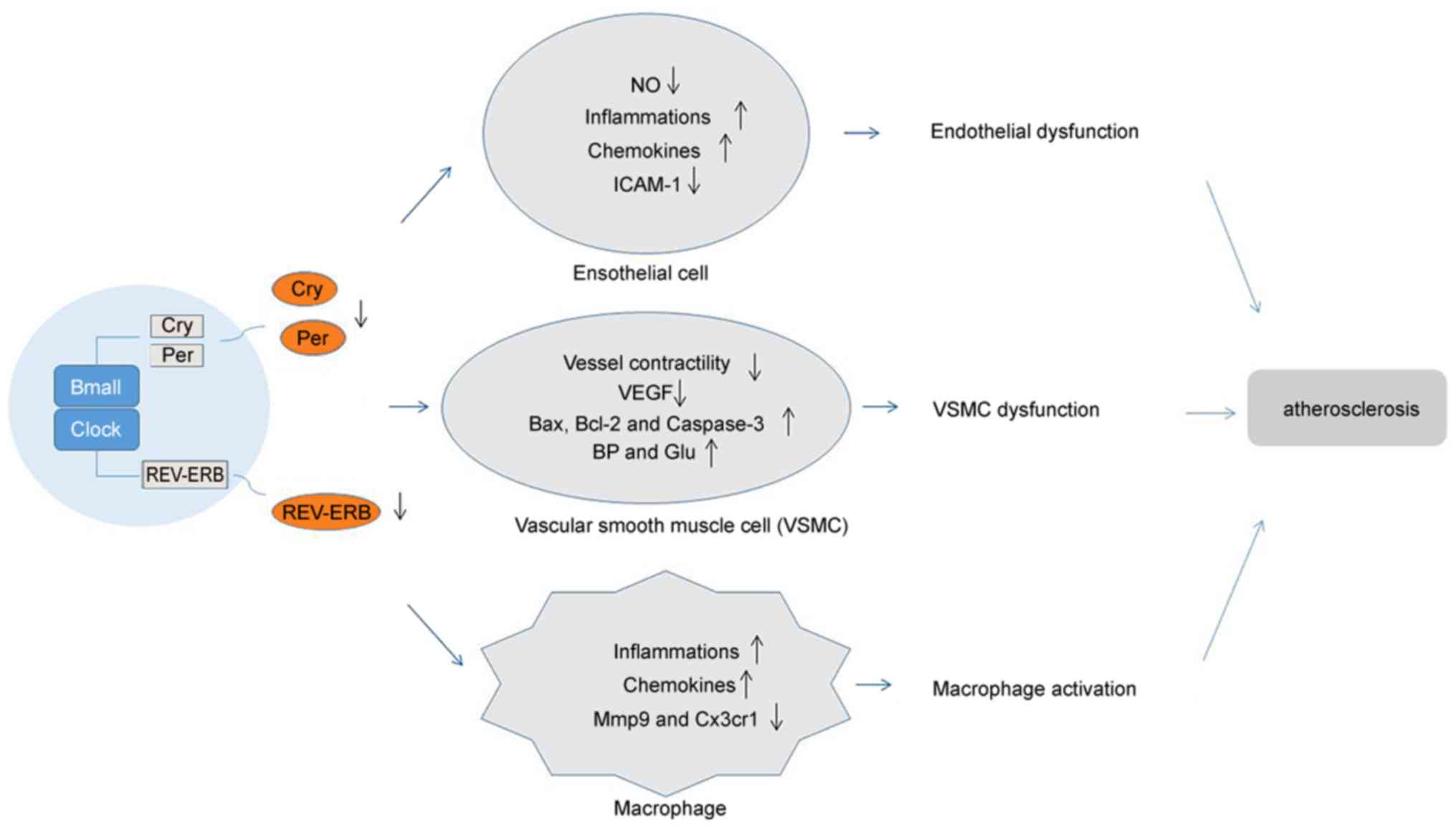
|
1
|
Shah MS and Brownlee M: Molecular and
cellular mechanisms of cardiovascular disorders in diabetes. Circ
Res. 118:1808–1829. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nguyen KD, Fentress SJ, Qiu Y, Yun K, Cox
JS and Chawla A: Circadian gene Bmal1 regulates diurnal
oscillations of Ly6C(hi) inflammatory monocytes. Science.
341:1483–1488. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Scheiermann C, Kunisaki Y and Frenette PS:
Circadian control of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol.
13:190–198. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Steffens S, Winter C, Schloss MJ, Hidalgo
A, Weber C and Soehnlein O: Circadian control of inflammatory
processes in atherosclerosis and its complications. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 37:1022–1028. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mohawk JA, Green CB and Takahashi JS:
Central and peripheral circadian clocks in mammals. Annu Rev
Neurosci. 35:445–462. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lowrey PL, Shimomura K, Antoch MP,
Yamazaki S, Zemenides PD, Ralph MR, Menaker M and Takahashi JS:
Positional syntenic cloning and functional characterization of the
mammalian circadian mutation tau. Science. 288:483–492.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Shirogane T, Jin J, Ang XL and Harper JW:
SCFbeta-TRCP controls clock-dependent transcription via casein
kinase 1-dependent degradation of the mammalian period-1 (Per1)
protein. J Biol Chem. 280:26863–26872. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lamia KA, Sachdeva UM, DiTacchio L,
Williams EC, Alvarez JG, Egan DF, Vasquez DS, Juguilon H, Panda S,
Shaw RJ, et al: AMPK regulates the circadian clock by cryptochrome
phosphorylation and degradation. Science. 326:437–440.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Buhr ED and Takahashi JS: Molecular
components of the Mammalian circadian clock. Handb Exp Pharmacol.
217:3–27. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Bugge A, Feng D, Everett LJ, Briggs ER,
Mullican SE, Wang F, Jager J and Lazar MA: Rev-erbα and Rev-erbβ
coordinately protect the circadian clock and normal metabolic
function. Genes Dev. 26:657–667. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Solt LA, Wang Y, Banerjee S, Hughes T,
Kojetin DJ, Lundasen T, Shin Y, Liu J, Cameron MD, Noel R, et al:
Regulation of circadian behaviour and metabolism by synthetic
REV-ERB agonists. Nature. 485:62–68. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Crumbley C and Burris TP: Direct
regulation of CLOCK expression by REV-ERB. PLoS One.
6(e17290)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Skogstad M, Mamen A, Lunde LK, Ulvestad B,
Matre D, Aass H, Øvstebø R, Nielsen P, Samuelsen KN, Skare Ø and
Sirnes PA: Shift work including night work and long working hours
in industrial plants increases the risk of atherosclerosis. Int J
Environ Res Public Health. 16(521)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Laermans J and Depoortere I: Chronobesity:
Role of the circadian system in the obesity epidemic. Obes Rev.
17:108–125. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
O'Keeffe SM, Beynon AL, Davies JS, Moynagh
PN and Coogan AN: NF-κB signalling is involved in
immune-modulation, but not basal functioning, of the mouse
suprachiasmatic circadian clock. Eur J Neurosci. 45:1111–1123.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pan X, Jiang XC and Hussain MM: Impaired
cholesterol metabolism and enhanced atherosclerosis in clock mutant
mice. Circulation. 128:1758–1769. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yang L, Chu Y, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhao X, He
W, Zhang P, Yang X, Liu X, Tian L, et al: Overexpression of CRY1
protects against the development of atherosclerosis via the
TLR/NF-κB pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 28:525–530. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sitaula S, Billon C, Kamenecka TM, Solt LA
and Burris TP: Suppression of atherosclerosis by synthetic REV-ERB
agonist. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 460:566–571. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kalsbeek A, la Fleur S and Fliers E:
Circadian control of glucose metabolism. Mol Metab. 3:372–383.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Buxton OM, Cain SW, O'Connor SP, Porter
JH, Duffy JF, Wang W, Czeisler CA and Shea SA: Adverse metabolic
consequences in humans of prolonged sleep restriction combined with
circadian disruption. Sci Transl Med. 4(129ra43)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Morris CJ, Yang JN, Garcia JI, Myers S,
Bozzi I, Wang W, Buxton OM, Shea SA and Scheer FA: Endogenous
circadian system and circadian misalignment impact glucose
tolerance via separate mechanisms in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 112:E2225–E2234. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Polonsky KS, Given BD, Hirsch LJ, Tillil
H, Shapiro ET, Beebe C, Frank BH, Galloway JA and Van Cauter E:
Abnormal patterns of insulin secretion in non-insulin-dependent
diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 318:1231–1239. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Panda S, Antoch MP, Miller BH, Su AI,
Schook AB, Straume M, Schultz PG, Kay SA, Takahashi JS and
Hogenesch JB: Coordinated transcription of key pathways in the
mouse by the circadian clock. Cell. 109:307–320. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yang X, Downes M, Yu RT, Bookout AL, He W,
Straume M, Mangelsdorf DJ and Evans RM: Nuclear receptor expression
links the circadian clock to metabolism. Cell. 126:801–810.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
McCarthy JJ, Andrews JL, McDearmon EL,
Campbell KS, Barber BK, Miller BH, Walker JR, Hogenesch JB,
Takahashi JS and Esser KA: Identification of the circadian
transcriptome in adult mouse skeletal muscle. Physiol Genomics.
31:86–95. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shi SQ, Ansari TS, McGuinness OP,
Wasserman DH and Johnson CH: Circadian disruption leads to insulin
resistance and obesity. Curr Biol. 23:372–381. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee J, Moulik M, Fang Z, Saha P, Zou F, Xu
Y, Nelson DL, Ma K, Moore DD and Yechoor VK: Bmal1 and β-cell clock
are required for adaptation to circadian disruption, and their loss
of function leads to oxidative stress-induced β-cell failure in
mice. Mol Cell Biol. 33:2327–2338. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Coomans CP, van den Berg SA, Lucassen EA,
Houben T, Pronk AC, van der Spek RD, Kalsbeek A, Biermasz NR,
Willems van Dijk K, Romijn JA and Meijer JH: The suprachiasmatic
nucleus controls circadian energy metabolism and hepatic insulin
sensitivity. Diabetes. 62:1102–1108. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Turek FW, Joshu C, Kohsaka A, Lin E,
Ivanova G, McDearmon E, Laposky A, Losee-Olson S, Easton A, Jensen
DR, et al: Obesity and metabolic syndrome in circadian Clock mutant
mice. Science. 308:1043–1045. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Rudic RD, McNamara P, Curtis AM, Boston
RC, Panda S, Hogenesch JB and Fitzgerald GA: BMAL1 and CLOCK, two
essential components of the circadian clock, are involved in
glucose homeostasis. PLoS Biol. 2(e377)2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Doi R, Oishi K and Ishida N: CLOCK
regulates circadian rhythms of hepatic glycogen synthesis through
transcriptional activation of Gys2. J Biol Chem. 285:22114–22121.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zani F, Breasson L, Becattini B, Vukolic
A, Montani JP, Albrecht U, Provenzani A, Ripperger JA and Solinas
G: PER2 promotes glucose storage to liver glycogen during feeding
and acute fasting by inducing Gys2 PTG and G L expression. Mol
Metab. 2:292–305. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lamia KA, Papp SJ, Yu RT, Barish GD,
Uhlenhaut NH, Jonker JW, Downes M and Evans RM: Cryptochromes
mediate rhythmic repression of the glucocorticoid receptor. Nature.
480:552–556. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Delezie J, Dumont S, Dardente H, Oudart H,
Gréchez-Cassiau A, Klosen P, Teboul M, Delaunay F, Pévet P and
Challet E: The nuclear receptor REV-ERBα is required for the daily
balance of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. FASEB J.
26:3321–3335. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Tao H, Li X, Qiu JF, Cui WZ, Sima YH and
Xu SQ: Inhibition of expression of the circadian clock gene Period
causes metabolic abnormalities including repression of
glycometabolism in Bombyx mori cells. Sci Rep.
7(46258)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chua EC, Shui G, Lee IT, Lau P, Tan LC,
Yeo SC, Lam BD, Bulchand S, Summers SA, Puvanendran K, et al:
Extensive diversity in circadian regulation of plasma lipids and
evidence for different circadian metabolic phenotypes in humans.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:14468–14473. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Adamovich Y, Rousso-Noori L, Zwighaft Z,
Neufeld-Cohen A, Golik M, Kraut-Cohen J, Wang M, Han X and Asher G:
Circadian clocks and feeding time regulate the oscillations and
levels of hepatic triglycerides. Cell Metab. 19:319–330.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Spiegel K, Tasali E, Leproult R and Van
Cauter E: Effects of poor and short sleep on glucose metabolism and
obesity risk. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 5:253–261. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Lumeng JC, Somashekar D, Appugliese D,
Kaciroti N, Corwyn RF and Bradley RH: Shorter sleep duration is
associated with increased risk for being overweight at ages 9 to 12
years. Pediatrics. 120:1020–1029. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Vieira E, Eg R, Figueroa AL, Aranda G,
Momblan D, Carmona F, Gomis R, Vidal J and Hanzu FA: Altered clock
gene expression in obese visceral adipose tissue is associated with
metabolic syndrome. PLoS One. 9(e111678)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Pan X, Bradfield CA and Hussain MM: Global
and hepatocyte-specific ablation of Bmal1 induces hyperlipidaemia
and enhances atherosclerosis. Nat Commun. 7(13011)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Takaguri A, Sasano J, Akihiro O and Satoh
K: The role of circadian clock gene BMAL1 in vascular
proliferation. Eur J Pharmacol. 872(172924)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Jacobi D, Liu S, Burkewitz K, Kory N,
Knudsen NH, Alexander RK, Unluturk U, Li X, Kong X, Hyde AL, et al:
Hepatic Bmal1 regulates rhythmic mitochondrial dynamics and
promotes metabolic Fitness. Cell Metab. 22:709–720. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Grimaldi B, Bellet MM, Katada S, Astarita
G, Hirayama J, Amin RH, Granneman JG, Piomelli D, Leff T and
Sassone-Corsi P: PER2 controls lipid metabolism by direct
regulation of PPARγ. Cell Metab. 12:509–520. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Le Martelot G, Claudel T, Gatfield D,
Schaad O, Kornmann B, Lo Sasso G, Moschetta A and Schibler U:
REV-ERBalpha participates in circadian SREBP signaling and bile
acid homeostasis. PLoS Biol. 7(e1000181)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
McAlpine CS and Swirski FK: Circadian
influence on metabolism and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Circ
Res. 119:131–141. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Davidson AJ, London B, Block GD and
Menaker M: Cardiovascular tissues contain independent circadian
clocks. Clin Exp Hypertens. 27:307–311. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Tang H, Zhu M, Zhao G, Fu W, Shi Z, Ding
Y, Tang X and Guo D: Loss of CLOCK under high glucose upregulates
ROCK1-mediated endothelial to mesenchymal transition and aggravates
plaque vulnerability. Atherosclerosis. 275:58–67. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Takeda N, Maemura K, Horie S, Oishi K,
Imai Y, Harada T, Saito T, Shiga T, Amiya E, Manabe I, et al:
Thrombomodulin is a clock-controlled gene in vascular endothelial
cells. J Biol Chem. 282:32561–32567. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Viswambharan H, Carvas JM, Antic V,
Marecic A, Jud C, Zaugg CE, Ming XF, Montani JP, Albrecht U and
Yang Z: Mutation of the circadian clock gene Per2 alters vascular
endothelial function. Circulation. 115:2188–2195. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Bellet MM, Deriu E, Liu JZ, Grimaldi B,
Blaschitz C, Zeller M, Edwards RA, Sahar S, Dandekar S, Baldi P, et
al: Circadian clock regulates the host response to
Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:9897–9902.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Early JO, Menon D, Wyse CA,
Cervantes-Silva MP, Zaslona Z, Carroll RG, Palsson-McDermott EM,
Angiari S, Ryan DG, Corcoran SE, et al: Circadian clock protein
BMAL1 regulates IL-1β in macrophages via NRF2. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 115:E8460–E8468. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Pourcet B, Zecchin M, Ferri L, Beauchamp
J, Sitaula S, Billon C, Delhaye S, Vanhoutte J, Mayeuf-Louchart A,
Thorel Q, et al: Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 Group D Member 1
regulates circadian activity of NLRP3 inflammasome to reduce the
severity of fulminant hepatitis in mice. Gastroenterology.
154:1449–1464.e20. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Chen L, Wu X, Zeb F, Huang Y, An J, Jiang
P, Chen A, Xu C and Feng Q: Acrolein-induced apoptosis of smooth
muscle cells through NEAT1-Bmal1/Clock pathway and a protection
from asparagus extract. Environ Pollut. 258(113735)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Migita H, Morser J and Kawai K:
Rev-Erbalpha upregulates NF-kappaB-responsive genes in vascular
smooth muscle cells. FEBS Lett. 561:69–74. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Rodrigo GC and Herbert KE: Regulation of
vascular function and blood pressure by circadian variation in
redox signalling. Free Radic Biol Med. 119:115–120. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Yang Z and Ming XF: Recent advances in
understanding endothelial dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Clin Med
Res. 4:53–65. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Maruo T, Nakatani S, Kanzaki H, Kakuchi H,
Yamagishi M, Kitakaze M, Ohe T and Miyatake K: Circadian variation
of endothelial function in idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Am J
Cardiol. 97:699–702. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Gibbs J, Ince L, Matthews L, Mei J, Bell
T, Yang N, Saer B, Begley N, Poolman T, Pariollaud M, et al: An
epithelial circadian clock controls pulmonary inflammation and
glucocorticoid action. Nat Med. 20:919–926. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Bhatwadekar AD, Beli E, Diao Y, Chen J,
Luo Q, Alex A, Caballero S, Dominguez JM, Salazar TE, Busik JV, et
al: Conditional deletion of Bmal1 accentuates microvascular and
macrovascular injury. Am J Pathol. 187:1426–1435. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Gao Y, Meng D, Sun N, Zhu Z, Zhao R, Lu C,
Chen S, Hua L and Qian R: Clock upregulates intercellular adhesion
molecule-1 expression and promotes mononuclear cells adhesion to
endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 443:586–591.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Carvas JM, Vukolic A, Yepuri G, Xiong Y,
Popp K, Schmutz I, Chappuis S, Albrecht U, Ming XF, Montani JP and
Yang Z: Period2 gene mutant mice show compromised insulin-mediated
endothelial nitric oxide release and altered glucose homeostasis.
Front Physiol. 3(337)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Qin B and Deng Y: Overexpression of
circadian clock protein cryptochrome (CRY) 1 alleviates sleep
deprivation-induced vascular inflammation in a mouse model. Immunol
Lett. 163:76–83. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Savalli G, Diao W, Schulz S, Todtova K and
Pollak DD: Diurnal oscillation of amygdala clock gene expression
and loss of synchrony in a mouse model of depression. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 18(pyu095)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Lacolley P, Regnault V, Segers P and
Laurent S: Vascular smooth muscle cells and arterial stiffening:
Relevance in development, aging, and disease. Physiol Rev.
97:1555–1617. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Feil S, Hofmann F and Feil R: SM22alpha
modulates vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype during
atherogenesis. Circ Res. 94:863–865. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Rudolph V and Freeman BA: Cardiovascular
consequences when nitric oxide and lipid signaling converge. Circ
Res. 105:511–522. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Wang L, Zheng J, Bai X, Liu B, Liu CJ, Xu
Q, Zhu Y, Wang N, Kong W and Wang X: ADAMTS-7 mediates vascular
smooth muscle cell migration and neointima formation in
balloon-injured rat arteries. Circ Res. 104:688–698.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Xie Z, Su W, Liu S, Zhao G, Esser K,
Schroder EA, Lefta M, Stauss HM, Guo Z and Gong MC: Smooth-muscle
BMAL1 participates in blood pressure circadian rhythm regulation. J
Clin Invest. 125:324–336. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Suyama K, Silagi ES, Choi H, Sakabe K,
Mochida J, Shapiro IM and Risbud MV: Circadian factors BMAL1 and
RORα control HIF-1α transcriptional activity in nucleus pulposus
cells: Implications in maintenance of intervertebral disc health.
Oncotarget. 7:23056–23071. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Lin C, Tang X, Zhu Z, Liao X, Zhao R, Fu
W, Chen B, Jiang J, Qian R and Guo D: The rhythmic expression of
clock genes attenuated in human plaque-derived vascular smooth
muscle cells. Lipids Health Dis. 13(14)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Su W, Xie Z, Guo Z, Duncan MJ, Lutshumba J
and Gong MC: Altered clock gene expression and vascular smooth
muscle diurnal contractile variations in type 2 diabetic db/db
mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 302:H621–H633.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Chen S, Ding Y, Zhang Z, Wang H and Liu C:
Hyperlipidaemia impairs the circadian clock and physiological
homeostasis of vascular smooth muscle cells via the suppression of
Smarcd1. J Pathol. 233:159–169. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Keller M, Mazuch J, Abraham U, Eom GD,
Herzog ED, Volk HD, Kramer A and Maier B: A circadian clock in
macrophages controls inflammatory immune responses. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 106:21407–21412. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Gibbs JE, Blaikley J, Beesley S, Matthews
L, Simpson KD, Boyce SH, Farrow SN, Else KJ, Singh D, Ray DW, et
al: The nuclear receptor REV-ERBα mediates circadian regulation of
innate immunity through selective regulation of inflammatory
cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:582–587. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Hayashi M, Shimba S and Tezuka M:
Characterization of the molecular clock in mouse peritoneal
macrophages. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:621–626. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Huo M, Huang Y, Qu D, Zhang H, Wong WT,
Chawla A, Huang Y and Tian XY: Myeloid Bmal1 deletion increases
monocyte recruitment and worsens atherosclerosis. FASEB J.
31:1097–1106. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Lam MT, Cho H, Lesch HP, Gosselin D, Heinz
S, Tanaka-Oishi Y, Benner C, Kaikkonen MU, Kim AS, Kosaka M, et al:
Rev-Erbs repress macrophage gene expression by inhibiting
enhancer-directed transcription. Nature. 498:511–515.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Sato S, Sakurai T, Ogasawara J, Takahashi
M, Izawa T, Imaizumi K, Taniguchi N, Ohno H and Kizaki T: A
circadian clock gene, Rev-erbα, modulates the inflammatory function
of macrophages through the negative regulation of Ccl2 expression.
J Immunol. 192:407–417. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Xie M, Tang Q, Nie J, Zhang C, Zhou X, Yu
S, Sun J, Cheng X, Dong N, Hu Y and Chen L: BMAL1-downregulation
aggravates Porphyromonas gingivalis-induced atherosclerosis
by encouraging oxidative stress. Circ Res. 126:e15–e29.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Lucassen EA, Coomans CP, van Putten M, de
Kreij SR, van Genugten JH, Sutorius RP, de Rooij KE, van der Velde
M, Verhoeve SL, Smit JW, et al: Environmental 24-hr cycles are
essential for health. Curr Biol. 26:1843–1853. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
McAlpine CS, Kiss MG, Rattik S, He S,
Vassalli A, Valet C, Anzai A, Chan CT, Mindur JE, Kahles F, et al:
Sleep modulates haematopoiesis and protects against
atherosclerosis. Nature. 566:383–387. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Schilperoort M, van den Berg R, Bosmans
LA, van Os BW, Dollé M, Smits N, Guichelaar T, van Baarle D,
Koemans L, Berbée J, et al: Disruption of circadian rhythm by
alternating light-dark cycles aggravates atherosclerosis
development in APOE*3-Leiden.CETP mice. J Pineal Res.
68(e12614)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Arjona A and Sarkar DK: The circadian gene
mPer2 regulates the daily rhythm of IFN-gamma. J Interferon
Cytokine Res. 26:645–649. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Hashiramoto A, Yamane T, Tsumiyama K,
Yoshida K, Komai K, Yamada H, Yamazaki F, Doi M, Okamura H and
Shiozawa S: Mammalian clock gene Cryptochrome regulates arthritis
via proinflammatory cytokine TNF-alpha. J Immunol. 184:1560–1565.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Raffatellu M, George MD, Akiyama Y,
Hornsby MJ, Nuccio SP, Paixao TA, Butler BP, Chu H, Santos RL,
Berger T, et al: Lipocalin-2 resistance confers an advantage to
Salmonella enterica serotype Typhimurium for growth and
survival in the inflamed intestine. Cell Host Microbe. 5:476–486.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Yu X, Rollins D, Ruhn KA, Stubblefield JJ,
Green CB, Kashiwada M, Rothman PB, Takahashi JS and Hooper LV: TH17
cell differentiation is regulated by the circadian clock. Science.
342:727–730. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|