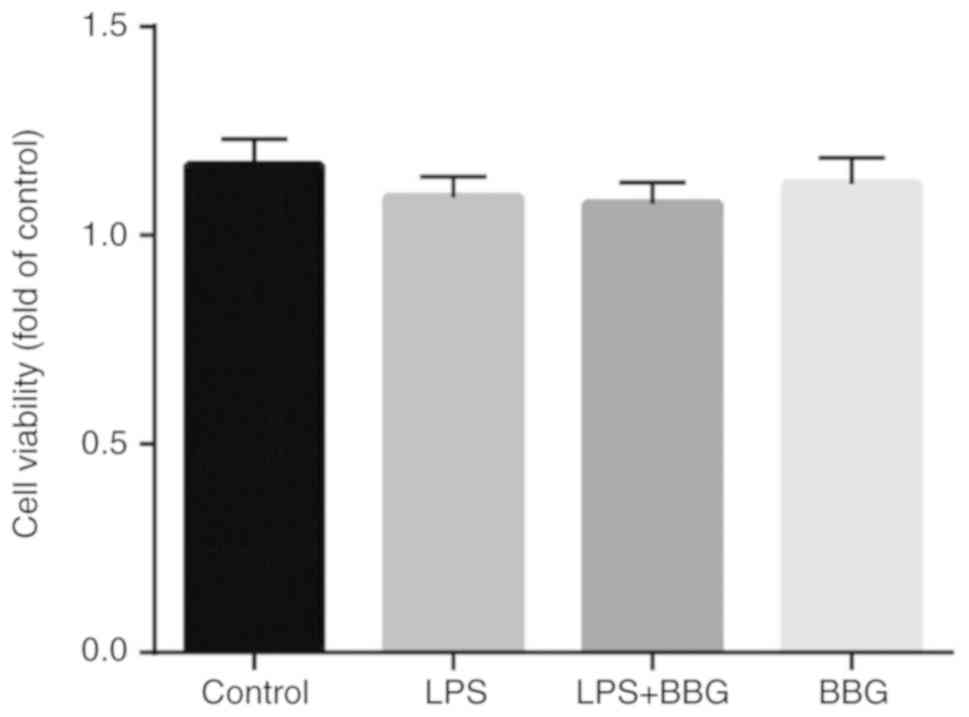
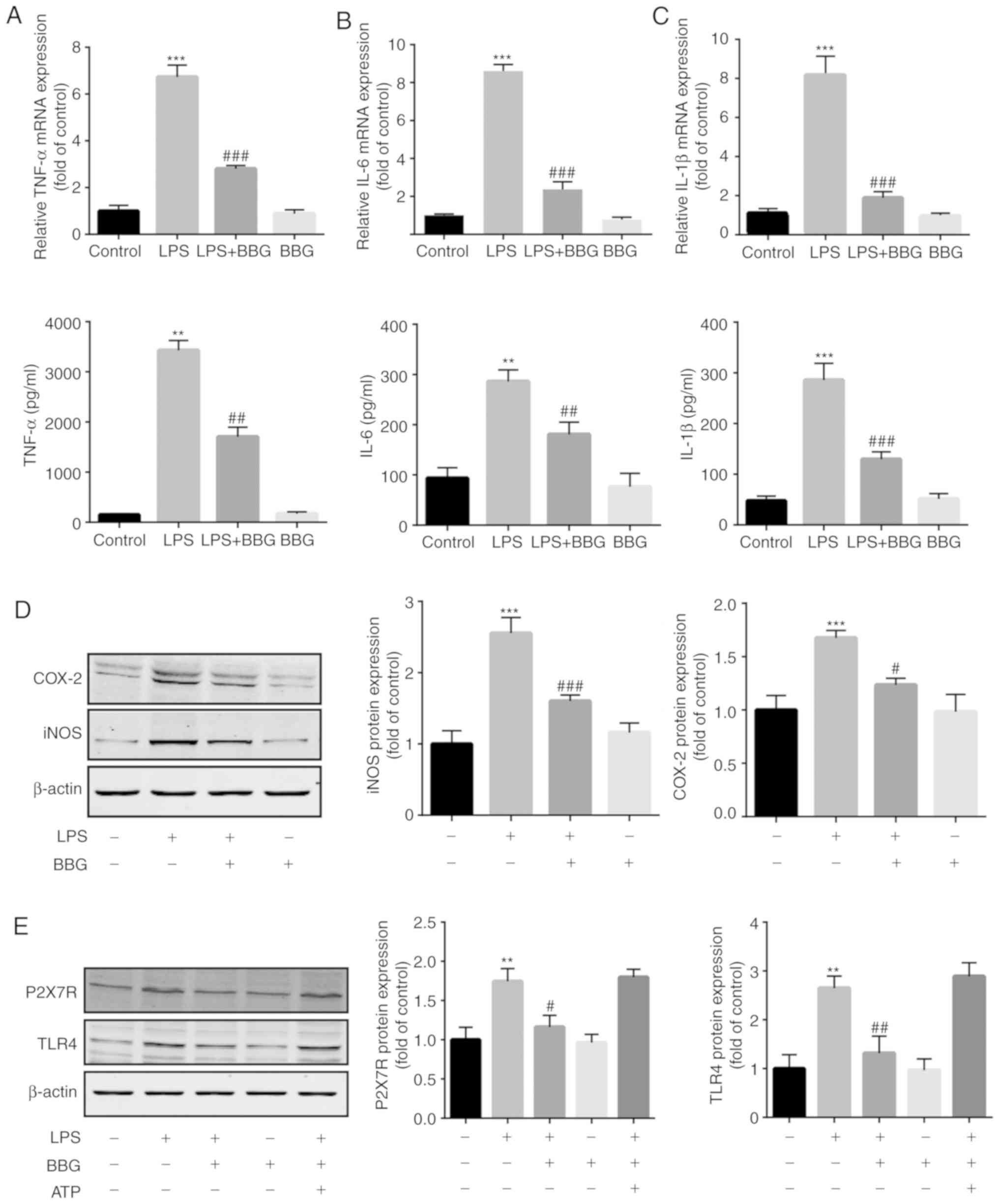
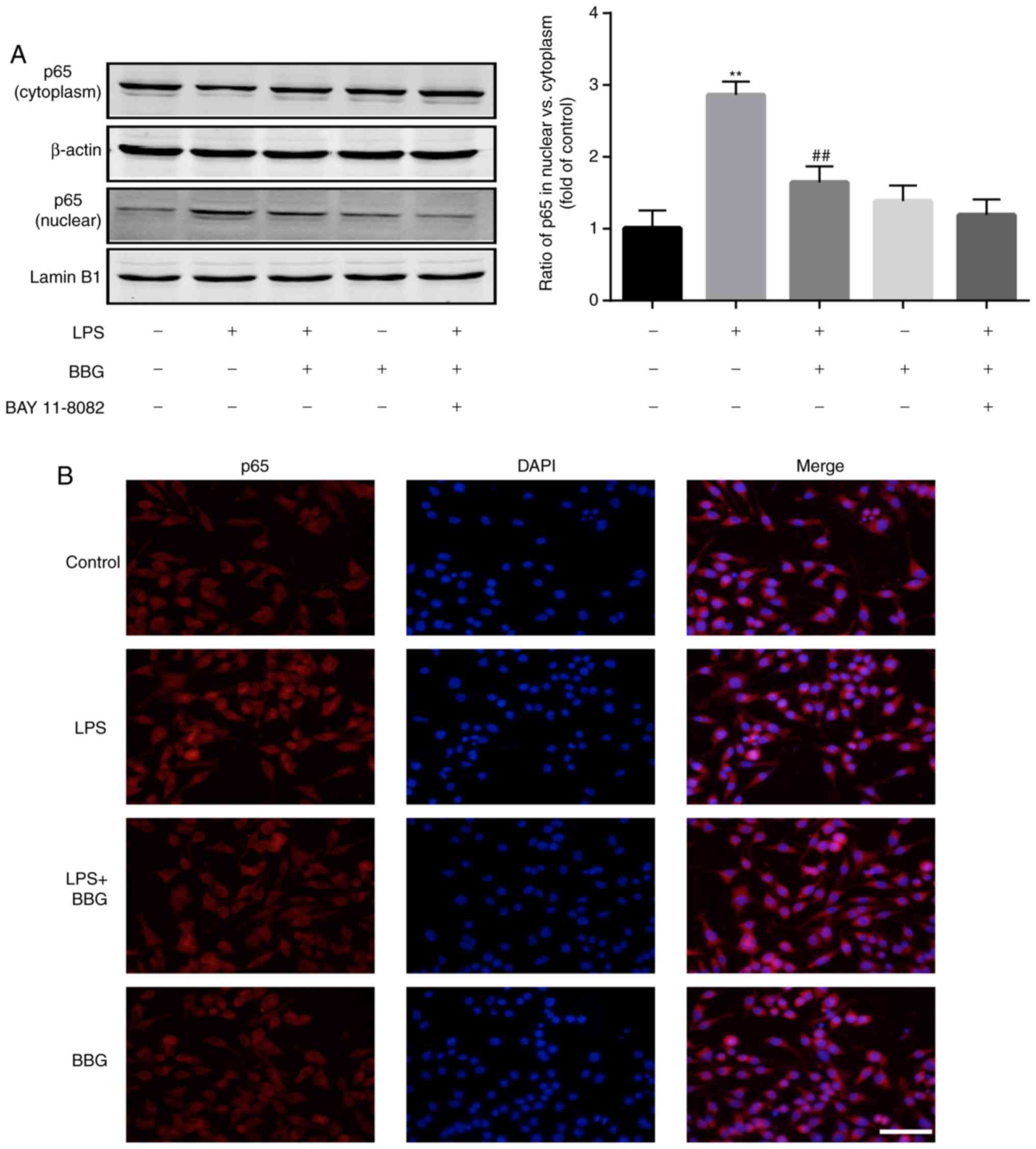
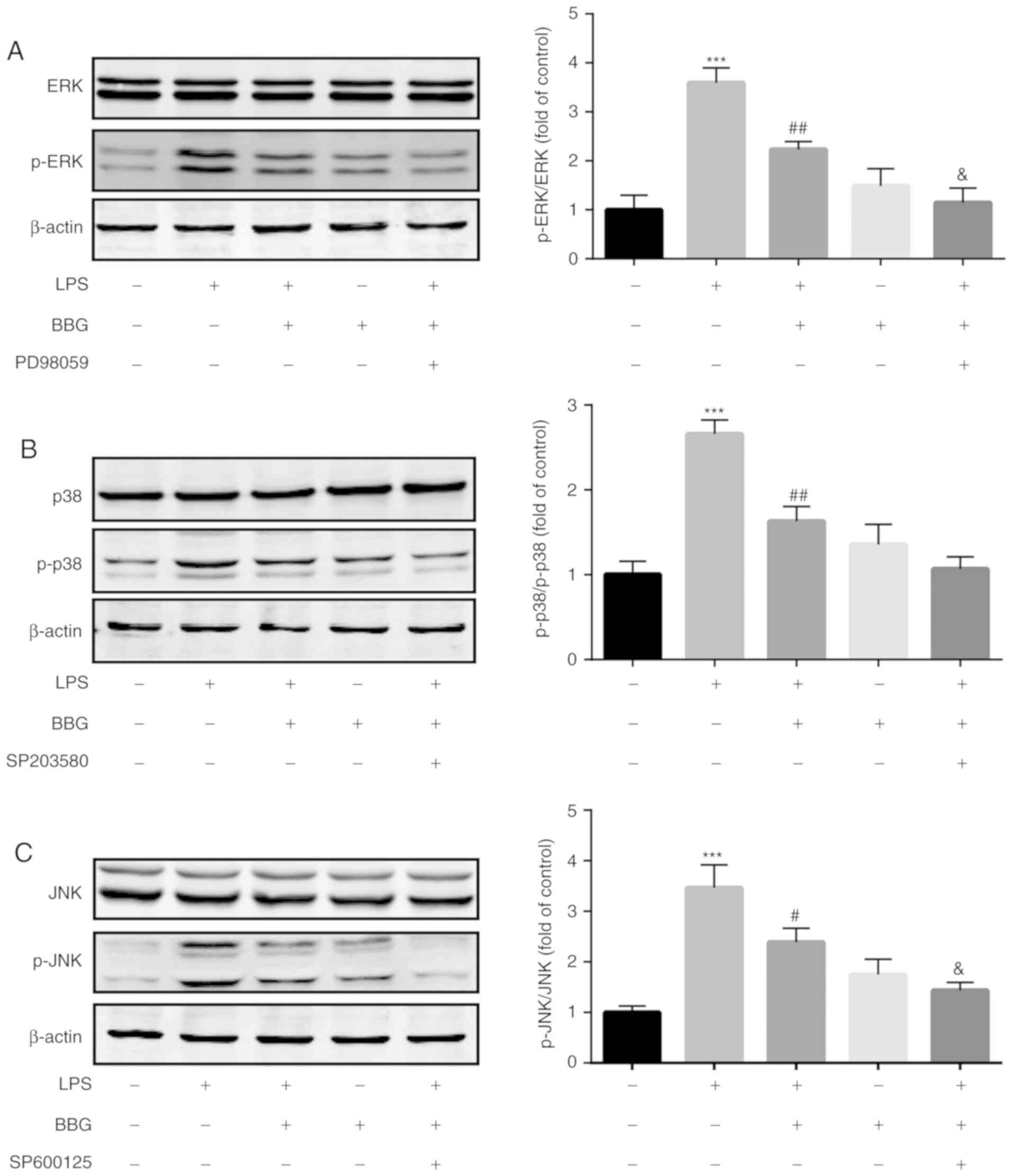
|
1
|
Hanamsagar R and Bilbo SD: Sex differences
in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders: Focus on
microglial function and neuroinflammation during development. J
Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 160:127–133. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J,
Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL, Jacobs AH, Wyss-Coray T,
Vitorica J, Ransohoff RM, et al: Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's
disease. Lancet Neurol. 14:388–405. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Colonna M and Butovsky O: Microglia
function in the central nervous system during health and
neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Immunol. 35:441–468. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Biber K, Moller T, Boddeke E and Prinz M:
Central nervous system myeloid cells as drug targets: current
status and translational challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
15:110–124. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liu RP, Zou M, Wang JY, Zhu JJ, Lai JM,
Zhou LL, Chen SF, Zhang X and Zhu JH: Paroxetine ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced microglia activation via differential
regulation of MAPK signaling. J Neuroinflammation.
11(47)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yoshida Y, Yoshimi R, Yoshii H, Kim D, Dey
A, Xiong H, Munasinghe J, Yazawa I, O’Donovan MJ, Maximova OA, et
al: The transcription factor IRF8 activates integrin-mediated TGF-β
signaling and promotes neuroinflammation. Immunity. 40:187–198.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wilms H, Sievers J, Rickert U,
Rostami-Yazdi M, Mrowietz U and Lucius R: Dimethylfumarate inhibits
microglial and astrocytic inflammation by suppressing the synthesis
of nitric oxide, IL-1beta, TNF-alpha and IL-6 in an in-vitro model
of brain inflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 7(30)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sarkar FH, Li Y, Wang Z and Kong D:
NF-kappaB signaling pathway and its therapeutic implications in
human diseases. Int Rev Immunol. 27:293–319. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lai JL, Liu YH, Liu C, Qi MP, Liu RN, Zhu
XF, Zhou QG, Chen YY, Guo AZ and Hu CM: Indirubin inhibits
LPS-induced inflammation via TLR4 abrogation mediated by the NF-κB
and MAPK signaling pathways. Inflammation. 40:1–12. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chew J, Biswas S, Shreeram S, Humaidi M,
Wong ET, Dhillion MK, Teo H, Hazra A, Fang CC, López-Collazo E, et
al: WIP1 phosphatase is a negative regulator of NF-kappaB
signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 11:659–666. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhao H, Wang SL, Qian L, Jin JL, Li H, Xu
Y and Zhu XL: Diammonium glycyrrhizinate attenuates
Aβ(1-42)-induced neuroinflammation and regulates MAPK and NF-κB
pathways in vitro and in vivo. CNS Neurosci Ther. 19:117–124.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Leyns CEG, Ulrich JD, Finn MB, Stewart FR,
Koscal LJ, Serrano JR, Robinson GO, Anderson E, Colonna M and
Holtzman DM: TREM2 deficiency attenuates neuroinflammation and
protects against neurodegeneration in a mouse model of tauopathy.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:11524–11529. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Volonte C, Apolloni S, Skaper SD and
Burnstock G: P2X7 receptors: channels, pores and more. CNS Neurol
Disord Drug Targets. 11:705–721. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chen S, Ma Q, Krafft PR, Chen Y, Tang J,
Zhang J and Zhang JH: P2X7 receptor antagonism inhibits p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase activation and ameliorates
neuronal apoptosis after subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. Crit Care
Med. 41:e466–e474. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Skaper SD, Debetto P and Giusti P: The
P2X7 purinergic receptor: from physiology to neurological
disorders. FASEB J. 24:337–345. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhao H, Pan P, Yang Y, Ge H, Chen W, Qu J,
Shi J, Cui G, Liu X, Feng H and Chen Y: Endogenous hydrogen
sulphide attenuates NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated neuroinflammation
by suppressing the P2X7 receptor after intracerebral haemorrhage in
rats. J Neuroinflammation. 14(163)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang XH, Xie X, Luo XG, Shang H and He ZY:
Inhibiting purinergic P2X7 receptors with the antagonist brilliant
blue G is neuroprotective in an intranigral lipopolysaccharide
animal model of Parkinson's disease. Mol Med Rep. 15:768–776.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rahimifard M, Maqbool F, Moeini-Nodeh S,
Niaz K, Abdollahi M, Braidy N, Nabavi SM and Nabavi SF: Targeting
the TLR4 signaling pathway by polyphenols: A novel therapeutic
strategy for neuroinflammation. Ageing Res Rev. 36:11–19.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Baima ET, Guzova JA, Mathialagan S, Nagiec
EE, Hardy MM, Song LR, Bonar SL, Weinberg RA, Selness SR, Woodard
SS, et al: Novel insights into the cellular mechanisms of the
anti-inflammatory effects of NF-kappaB essential modulator binding
domain peptides. J Biol Chem. 285:13498–13506. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Le W, Rowe D, Xie W, Ortiz I, He Y and
Appel SH: Microglial activation and dopaminergic cell injury: An in
vitro model relevant to Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci.
21:8447–8455. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, Marchetto MC
and Gage FH: Mechanisms underlying inflammation in
neurodegeneration. Cell. 140:918–934. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yu Q, Guo Z, Liu X, Ouyang Q, He C,
Burnstock G, Yuan H and Xiang Z: Block of P2X7 receptors could
partly reverse the delayed neuronal death in area CA1 of the
hippocampus after transient global cerebral ischemia. Purinergic
Signal. 9:663–675. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Petes C, Wynick C, Guzzo C, Mehta D, Logan
S, Banfield BW, Basta S, Cooper A and Gee K: IL-27 enhances
LPS-induced IL-1β in human monocytes and murine macrophages. J
Leukoc Biol. 102:83–94. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cesario A, Rocca B and Rutella S: The
interplay between indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO1) and
cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 in chronic inflammation and cancer. Curr Med
Chem. 18:2263–2271. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cai B, Seong KJ, Bae SW, Chun C, Kim WJ
and Jung JY: A synthetic diosgenin primary amine derivative
attenuates LPS-stimulated inflammation via inhibition of NF-kappaB
and JNK MAPK signaling in microglial BV2 cells. Int
Immunopharmacol. 61:204–214. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Stokes JA, Cheung J, Eddinger K, Corr M
and Yaksh TL: Toll-like receptor signaling adapter proteins govern
spread of neuropathic pain and recovery following nerve injury in
male mice. J Neuroinflammation. 10(148)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mattson MP, Culmsee C, Yu Z and Camandola
S: Roles of nuclear factor kappaB in neuronal survival and
plasticity. J Neurochem. 74:443–456. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wan P, Liu X, Xiong Y, Ren Y, Chen J, Lu
N, Guo Y and Bai A: Extracellular ATP mediates inflammatory
responses in colitis via P2 x7 receptor signaling. Sci Rep.
6(19108)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hu H, Yang B, Li Y, Zhang S and Li Z:
Blocking of the P2X7 receptor inhibits the activation of the MMP-13
and NF-kappaB pathways in the cartilage tissue of rats with
osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 38:1922–1932. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Pathological roles of
MAPK signaling pathways in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1802:396–405. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chu K, Yin B, Wang J, Peng G, Liang H, Xu
Z, Du Y, Fang M, Xia Q and Luo B: Inhibition of P2X7 receptor
ameliorates transient global cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
via modulating inflammatory responses in the rat hippocampus. J
Neuroinflammation. 9(69)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Papp L, Vizi ES and Sperlagh B: P2X7
receptor mediated phosphorylation of p38MAP kinase in the
hippocampus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 355:568–574.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wen Z, Mei B, Li H, Dou Y, Tian X, Shen M
and Chen G: P2X7 participates in intracerebral hemorrhage-induced
secondary brain injury in rats via MAPKs signaling pathways.
Neurochem Res. 42:2372–2383. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kumar S, Mishra A and Krishnamurthy S:
Purinergic antagonism prevents mitochondrial dysfunction and
behavioral deficits associated with dopaminergic toxicity induced
by 6-OHDA in rats. Neurochem Res. 42:3414–3430. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wu F, Wang Z, Gu JH, Ge JB, Liang ZQ and
Qin ZH: p38(MAPK)/p53-Mediated Bax induction contributes to neurons
degeneration in rotenone-induced cellular and rat models of
Parkinson's disease. Neurochem Int. 63:133–140. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|