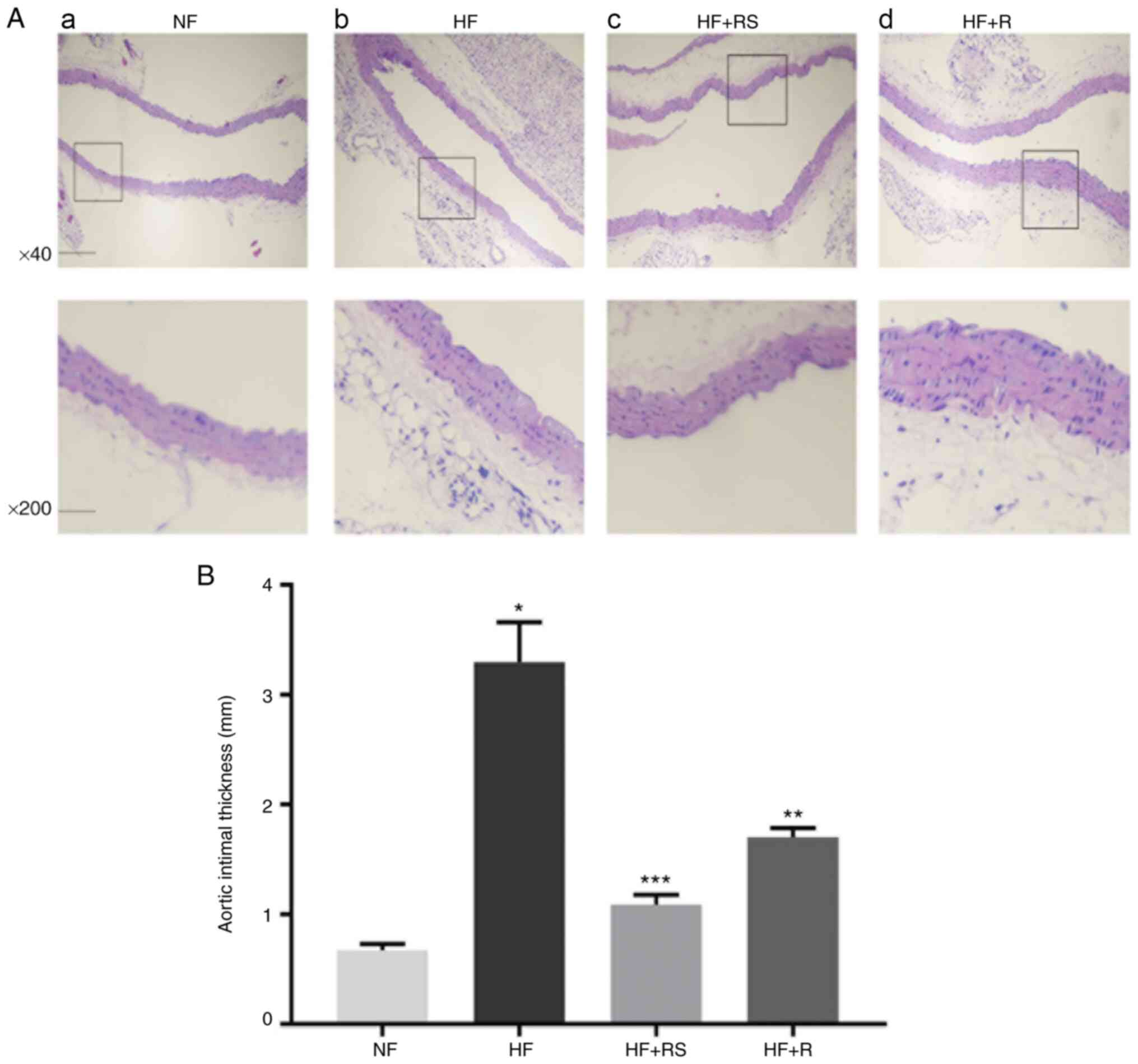
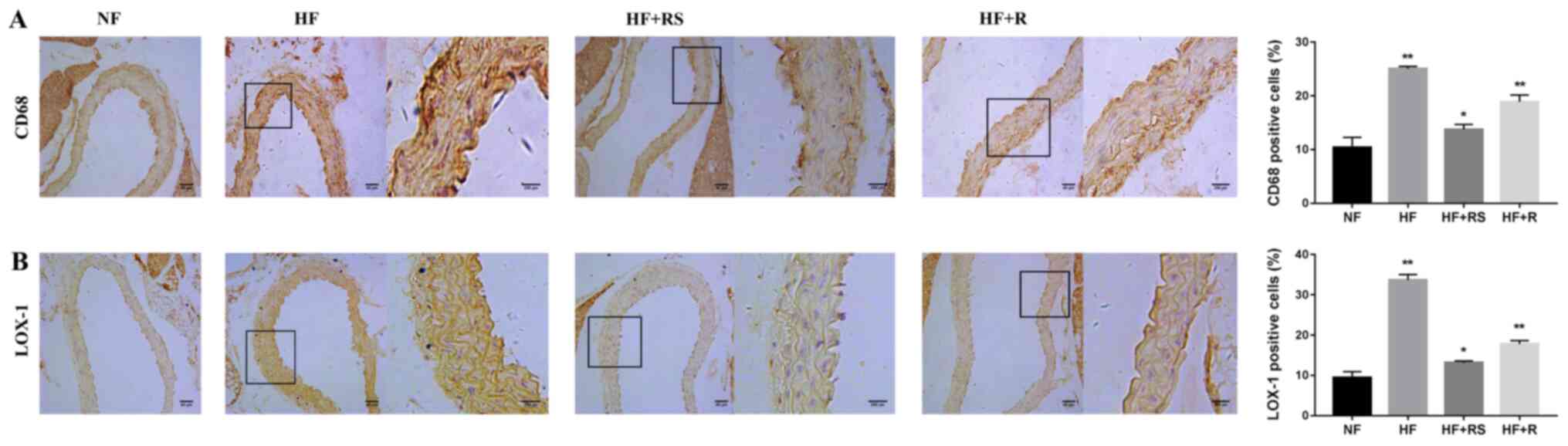
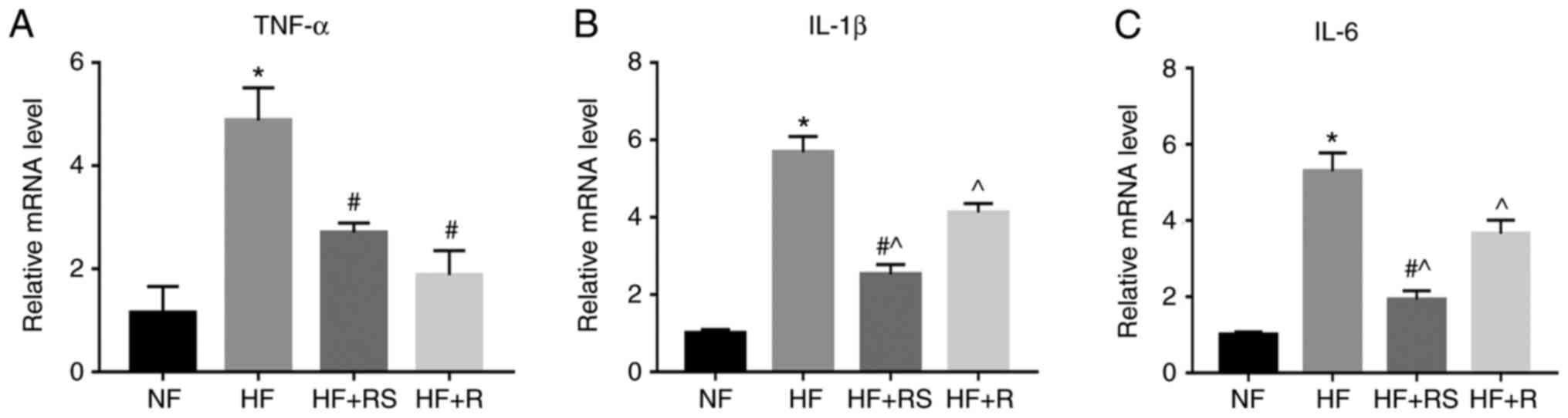
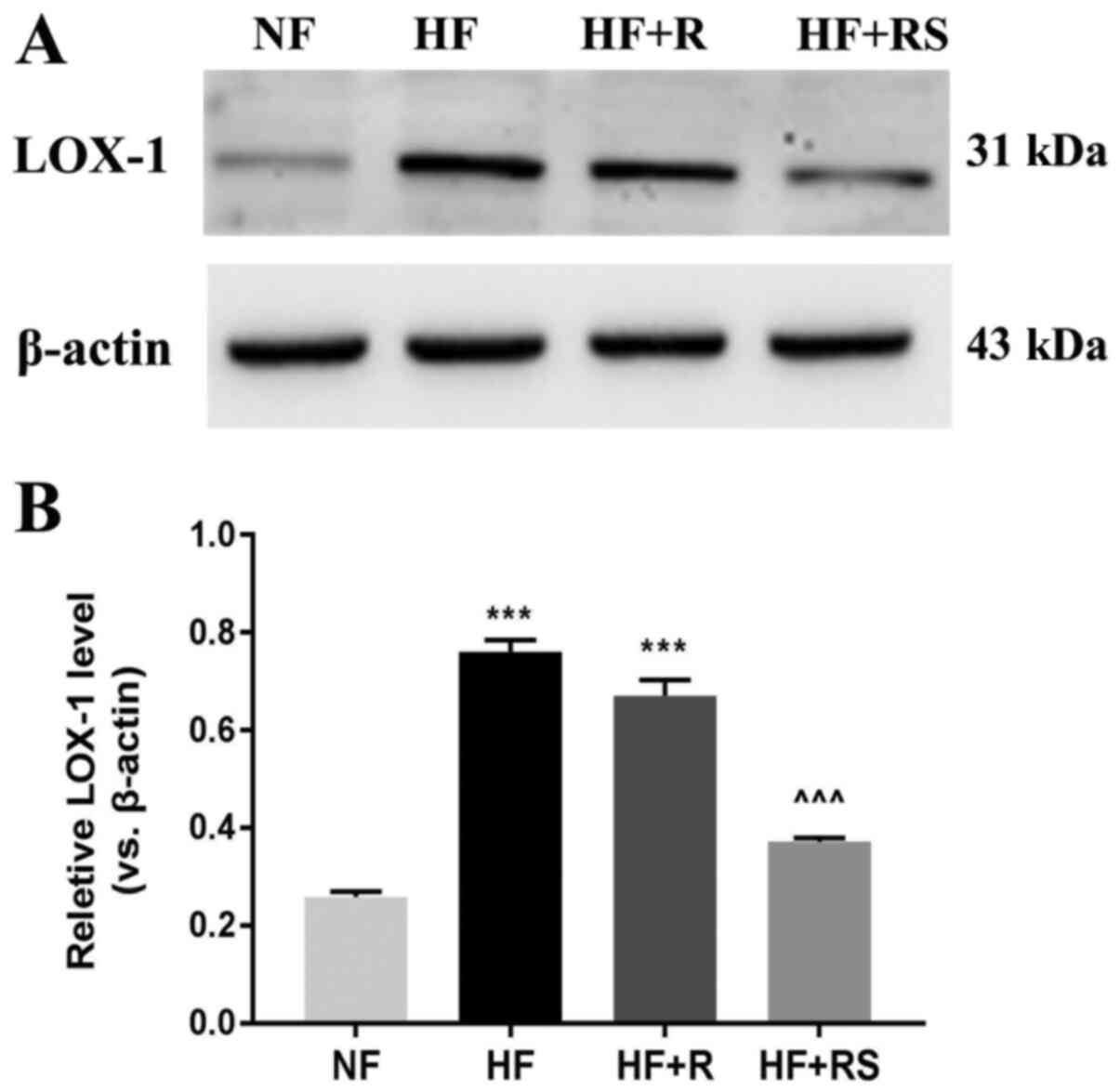
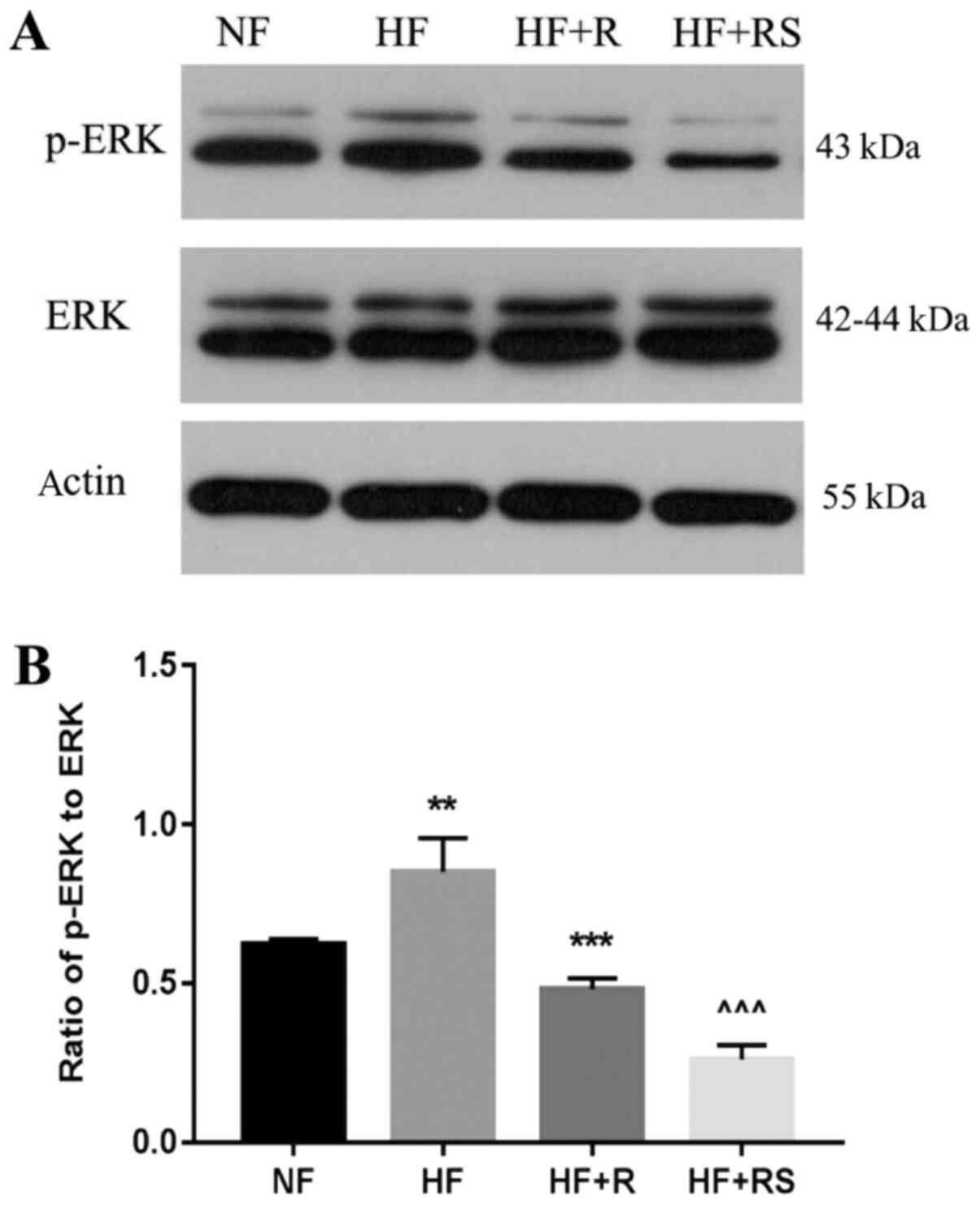
|
1
|
Wijeysundera DN, Duncan D, Nkonde-Price C,
Virani SS, Washam JB, Fleischmann KE and Fleisher LA: Perioperative
beta blockade in noncardiac surgery: A systematic review for the
2014 ACC/AHA guideline on perioperative cardiovascular evaluation
and management of patients undergoing noncardiac surgery: A report
of the; American college of cardiology American heart association
task force on practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 64:2406–2425.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Arsenault BJ, Kritikou EA and Tardif JC:
Regression of atherosclerosis. Curr Cardiol Rep. 14:443–449.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Karshovska E, Zhao Z, Blanchet X, Schmitt
MM, Bidzhekov K, Soehnlein O, von Hundelshausen P, Mattheij NJ,
Cosemans JM, Megens RT, et al: Hyperreactivity of junctional
adhesion molecule A-deficient platelets accelerates atherosclerosis
in hyperlipidemic mice. Circ Res. 116:587–599. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Pei Z, Okura T, Nagao T, Enomoto D, Kukida
M, Tanino A, Miyoshi K, Kurata M and Higaki J: Osteopontin
deficiency reduces kidney damage from hyperlipidemia in
Apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Sci Rep. 6(28882)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Collins R, Reith C, Emberson J, Armitage
J, Baigent C, Blackwell L, Blumenthal R, Danesh J, Smith GD, DeMets
D, et al: Interpretation of the evidence for the efficacy and safey
of statin therapy. Lancet. 388:2532–2561. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Prospective Studies Collaboration.
Lewington S, Whitlock G, Clarke R, Sherliker P, Emberson J, Halsey
J, Qizilbash N, Peto R and Collins R. Blood cholesterol and
vascular mortality by age, sex, and blood pressure. A meta analysis
of individual data from 61 prospective studies with 55000 vascular
deaths. Lancet. 370:1829–1839. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rosenson RS: Rosuvastatin: A new inhibitor
of HMG-coA reductase for the treatment of dyslipidemia. Expert Rev
Cardiovasc Ther. 1:495–505. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Alqahtani SA and Sanchez W: Statins are
safe for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia in patients with
chronic liver disease. Gastroenterology. 135:702–704.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Phillips PS, Haas RH, Bannykh S, Hathaway
S, Gray NL, Kimura BJ, Vladutiu GD and England JD: Scripps Mercy
Clinical Research Center. Statin-associated myopathy with normal
creatine kinase levels. Ann Intern Med. 137:581–585.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chogtu B, Magazine R and Bairy KL: Statin
use and risk of diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes. 6:352–357.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ahn CH and Choi SH: New drugs for treating
dyslipidemia: Beyond statins. Diabetes Metab J. 39:87–94.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fruchart JC, Davignon J, Hermans MP,
Al-Rubeaan K, Amarenco P, Assmann G, Barter P, Betteridge J,
Bruckert E, Cuevas A, et al: Residual macrovascular risk in 2013:
What have we learned? Cardiovasc Diabetol. 13(26)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nordestgaard BG: Triglyceride-rich
lipoproteins atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: New insights
from epidemiology, genetics, and biology. Circ Res. 118:547–563.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Saini HK, Takeda N, Goyal RK, Kumamoto H,
Arneja AS and Dhalla NS: Therapeutic potentials of sarpogrelate in
cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Drug Rev. 22:27–54.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Suguro T, Watanabe T, Kanome T, Kodate S,
Hirano T, Miyazaki A and Adachi M: Serotonin acts as an
up-regulator of acyl-coenzyme A: Cholesterol acyltransferase-1 in
human monocyte-macrophages. Atherosclerosis. 186:275–281.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xu YJ, Zhang M, Ji L, Elimban V, Chen L
and Dhalla NS: Suppression of high lipid diet induced by
atherosclerosis sarpogrelate. J Cell Mol Med. 16:2394–2400.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hayashi T, Sumi D, Matsui-Hirai H, Fukatsu
A, Arockia Rani PJ, Kano H, Tsunekawa T and Iguchi A: Sarpogrelate
HCl, a selective 5-HT2A antagonist, retards the progression of
atherosclerosis through a novel mechanism. Atherosclerosis.
168:23–31. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yamakawa J, Takahashi T, Saegusa S, Moriya
J, Itoh T, Kusaka K, Kawaura K, Wang XQ and Kanda T: Effect of the
serotonin blocker sarpogrelate on circulating interleukin-18 levels
in patients with diabetes and arteriosclerosis obliterans. J Int
Med Res. 32:166–169. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Takahara M, Kaneto H, Katakami N, Iida O,
Matsuoka TA and Shimomura I: Effect of sarpogrelate treatment on
the prognosis after endovascular therapy for critical limb
ischemia. Heart Vessels. 29:563–567. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Miyazaki M, Higashi Y, Goto C, Chayama K,
Yoshizumi M, Sanada H, Orihashi K and Sueda T: Sarpogrelate
hydrochloride, a selective 5-HT2A antagonist, improves vascular
function in patients with peripheral arterial disease. J Cardiovasc
Pharmacol. 49:221–227. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Carbone L: Pain management standards in
the eighth edition of the guide for the care and use of laboratory
animals. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 51:322–328. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shinohara Y, Nishimaru K, Sawada T,
Terashi A, Handa S, Hirai S, Hayashi K, Tohgi H, Fukuuchi Y,
Uchiyama S, et al: Sarpogrelate-aspirin comparative clinical study
for efficacy and safety in secondary prevention of cerebral
infarction (S-ACCESS): A randomized, double-blind,
aspirin-controlled trial. Stroke. 39:1827–1833. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yang HY, Bian YF, Zhang HP, Gao F, Xiao
CS, Liang B, Li J, Zhang NN and Yang ZM: LOX 1 is implicated in
oxidized low density lipoprotein induced oxidative stress of
macrophages in atherosclerosis. Mol Med Rep. 12:5335–5341.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang X, Ding Z, Lin J, Guo Z and Mehta JL:
LOX-1 in macrophage migration in response to ox-LDL and the
involvement of calpains. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 467:135–139.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yu XH, Fu YC, Zhang DW, Yin K and Tang CK:
Foam cells in atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta. 424:245–252.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Graeves DR and Gordon S: The macrophage
scavenger receptor at 30 years of age: Current knowledge and future
challenges. J Lipid Res. 50 (Suppl):S282–S286. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ramprasad MP, Terpstra V, Kondratenko N,
Quehenberger O and Steinberg D: Cell surface expression of mouse
macrosialin and human CD68 and their role as macrophage receptors
for oxidized low density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
93:14833–14838. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang Z, Zhang M, Li Y, Liu S, Ping S,
Wang J, Ning F, Xie F and Li C: Simvastatin inhibits the additive
activation of ERK1/2 and proliferation of rat vascular smooth
muscle cells induced by combined mechanical stress and oxLDL
through LOX-1 pathway. Cell Signal. 25:332–340. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Fujita M, Mizuno K, Ho M, Tsukahara R,
Miyamoto A, Miki O, Ishii K and Miwa K: Sarpogrelate treatment
reduces restenosis after coronary stenting. Am Heart J.
145(E16)2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kajiwara I, Soejima H, Miyamoto S and
Ogawa H: Effects of additional treatment of sarpogrelate to aspirin
therapy on platelet aggregation and plasma plasminogen activator
inhibitor activity in patients with stable effort angina. Thromb
Res. 128:547–551. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Katsiki N, Athyros VG and Karagiannis A:
Exploring the management of statin intolerant patients: 2016 and
beyond. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 14:523–533. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Aviram M, Fuhrman B, Maor I and Brook GJ:
Serotonin increases macrophage uptake of oxidized low density
lipoprotein. Eur J Clin Chem Clin Biochem. 30:55–61.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tannock LR: Advances in the management of
hyperlipidemia-induced atherosclerosis. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther.
6:369–383. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Siasos G, Tousoulis D, Oikonomou E,
Zaromitidou M, Stefanadis C and Papavassiliou AG: Inflammatory
markers in hyperlipidemia: From experimental models to clinical
practice. Curr Pharm Des. 17:4132–4146. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lee ES, Lee MY, Kwon MH, Kim HM, Kang JS,
Kim YM, Lee EY and Chung CH: Sarpogrelate hydrochloride ameliorates
diabetic nephropathy associated with inhibition of macrophage
activity and inflammatory reaction in db/db mice. PLoS One.
12(e0179221)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Metha JL, Chen J, Hermonat PL, Romeo F and
Novelli G: Lectin-like, oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1
(LOX-1): A critical player in the development of atherosclerosis
and related disorders. Cardiovasc Res. 69:36–45. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Morawietz H: LOX-1 and atherosclerosis:
Proof of concept in LOX-1-knockout mice. Circ Res. 100:1534–1536.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Moriwaki H, Kume N, Kataoka H, Murase T,
Nishi E, Sawamura T, Masaki T and Kita T: Expression of lectin-like
oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor-1 in human and murine
macrophages: Upregulated expression by TNF-alpha. FEBS Lett.
440:29–32. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Li D and Mehta JL: Antisense to LOX-1
inhibits oxidized LDL-mediated upregulation of monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 and monocyte adhesion to human coronary
artery endothelial cells. Circulation. 101:2889–2895.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Xu S, Ogura S, Chen J, Little PJ, Moss J
and Liu P: LOX-1 in atherosclerosis: Biological functions and
pharmacological modifiers. Cell Mol Life Sci. 70:2859–2872.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lu J, Mitra S, Wang X, Khaidakov M and
Methta JL: Oxidative stress and lectin-like ox-LDL-receptor LOX-1
in atherogenesis and tumorigenesis. Antioxid Redox Signal.
15:2301–2333. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zamani A and Qu Z: Serotonin activates
angiogenic phosphorylation signaling in human endothelial cells.
FEBS Lett. 586:2360–2365. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Li L, Sawamura T and Renier G: Glucose
enhances human macrophage LOX-1 expression: Role for LOX-1 in
glucose-induced macrophage foam cell formation. Circ Res.
94:892–901. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Chang PY, Pai JH, Lai YS and Lu SC:
Electronegative LDL from rabbits fed with atherogenic diet is
highly proinflammatory. Mediators Inflamm.
2019(6163130)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yang TC, Chang PY, Kuo TL and Lu SC:
Electronegative L5-LDL induces the production of G-CSF and GM-CSF
in human macrophages through LOX-1 involving NF-κB and ERK2
activation. Atherosclerosis. 267:1–9. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ran X, Zhao W, Li W, Shi J and Chen X:
Cryptotanshinone inhibits TNF-α-induced LOX-1 expression by
suppressing reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation in endothelial
cells. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 20:347–355. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Su X and Peng D: The exchangeable
apolipoproteins in lipid metabolism and obesity. Clin Chim Acta.
503:128–135. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|