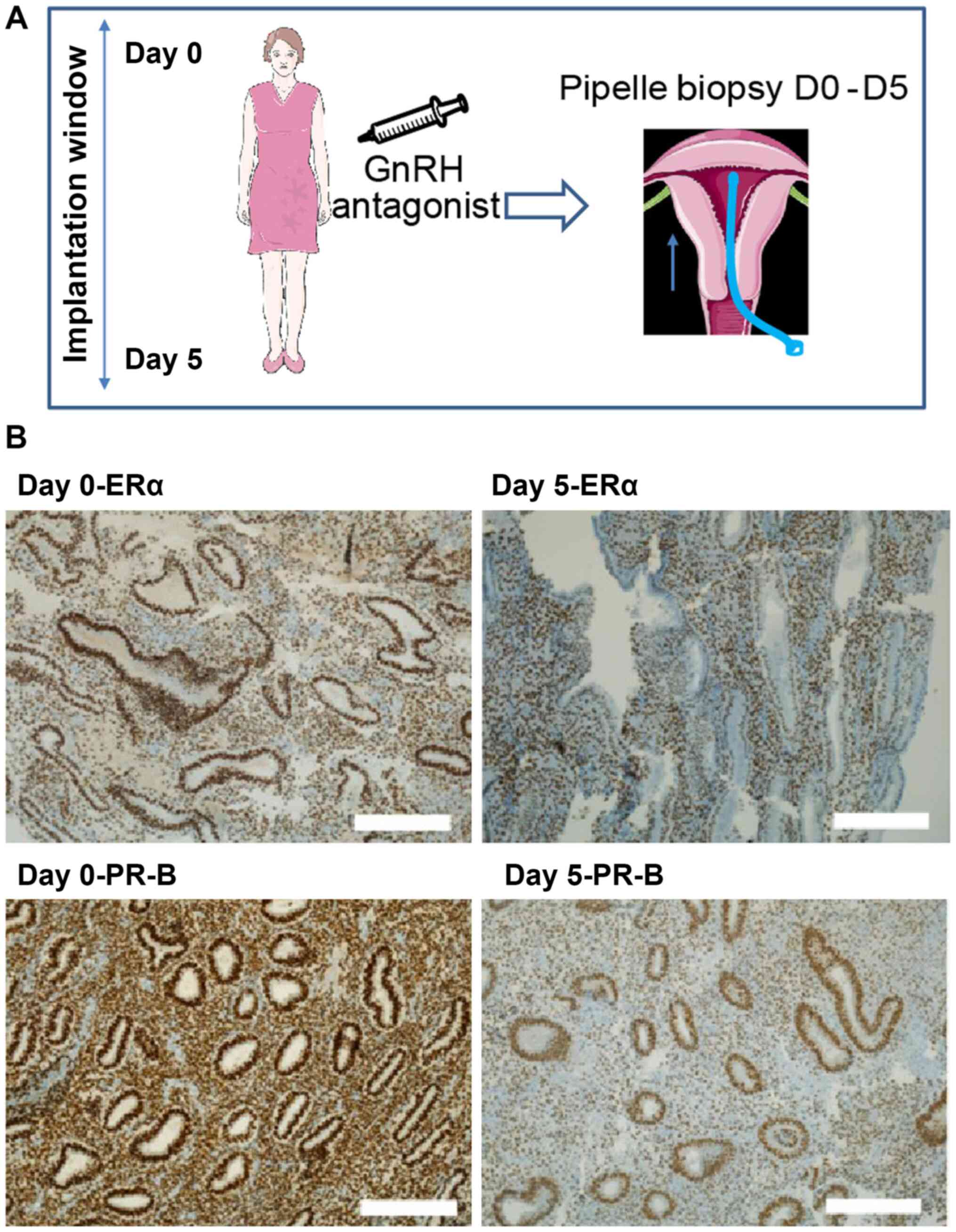
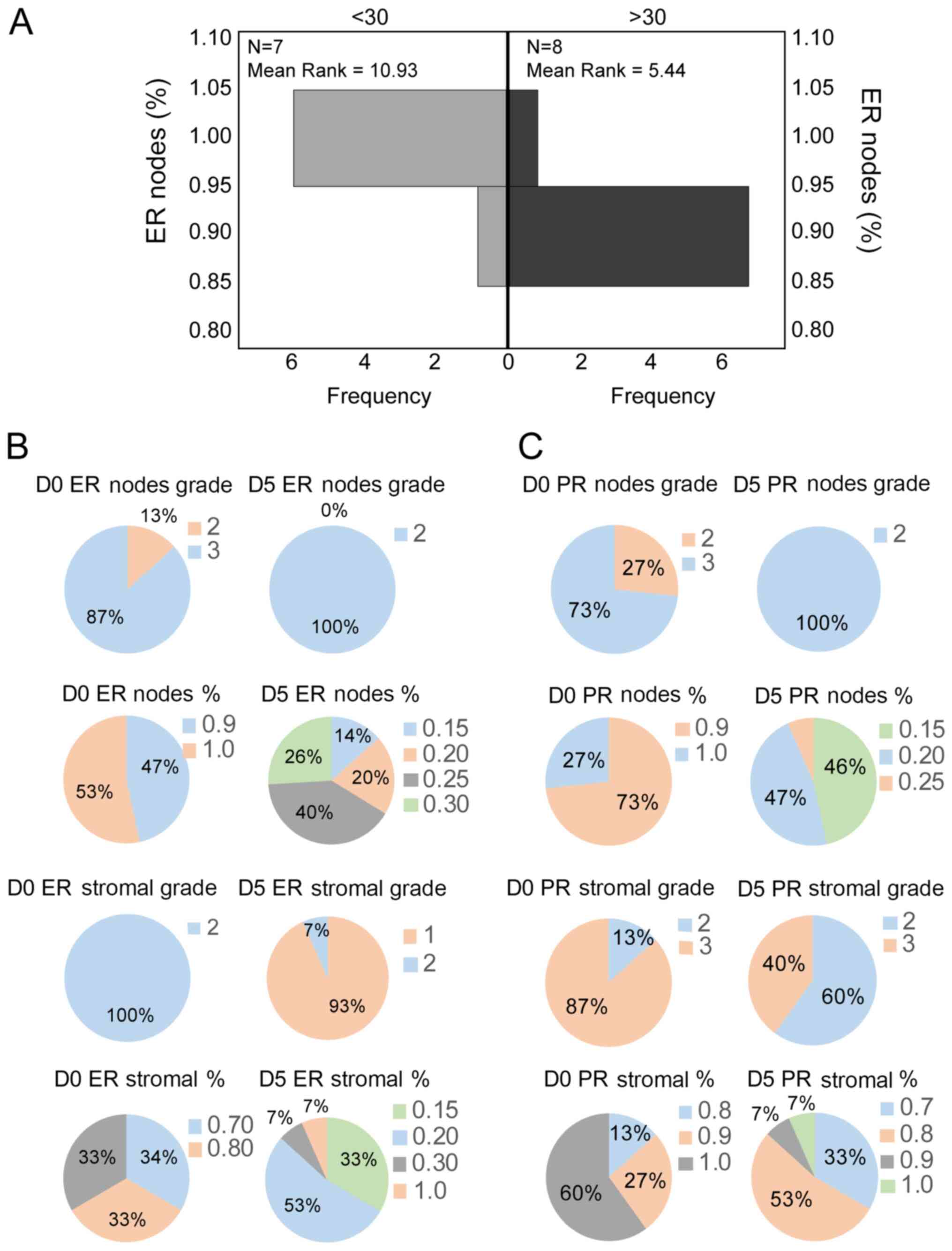
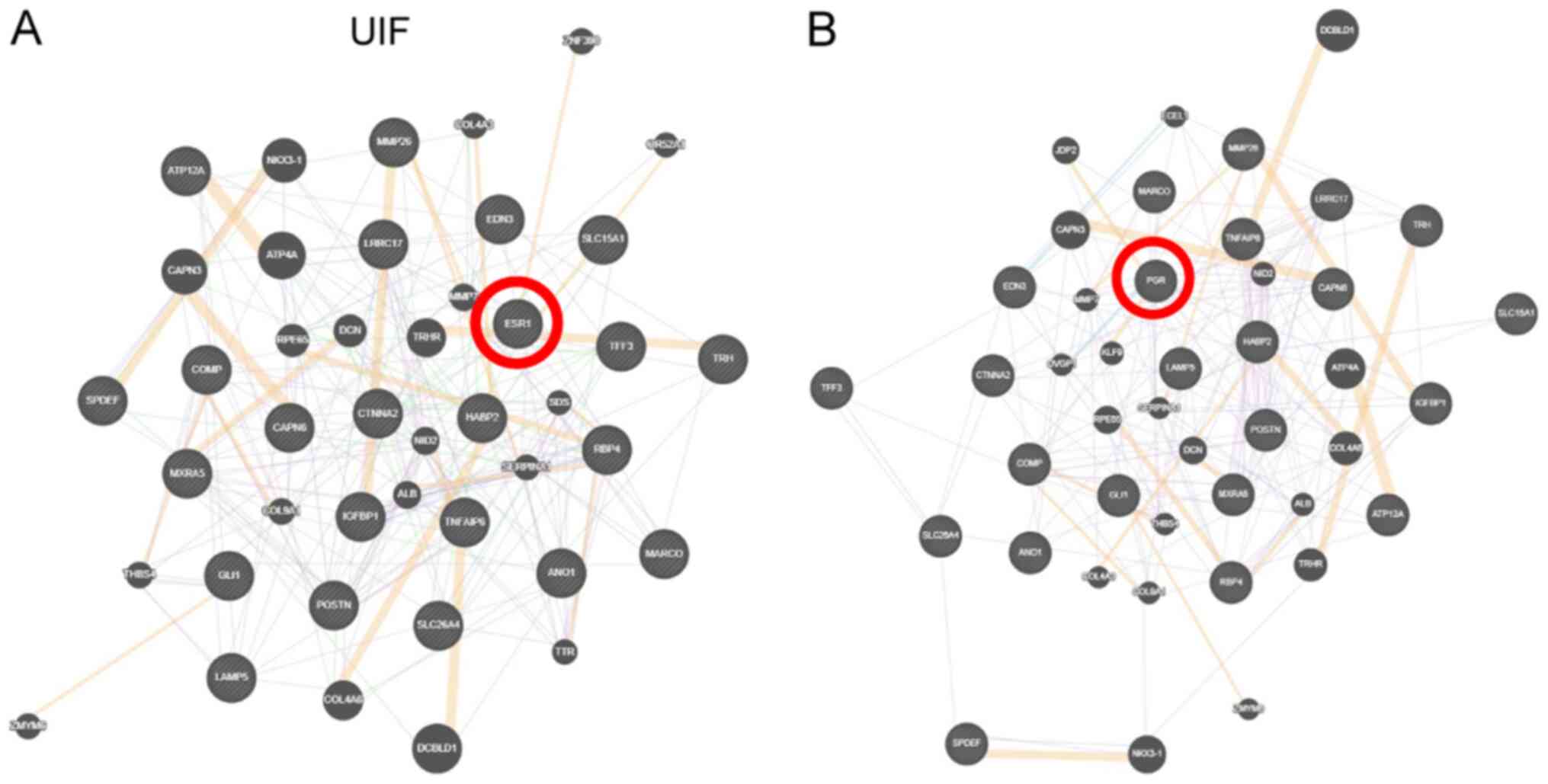
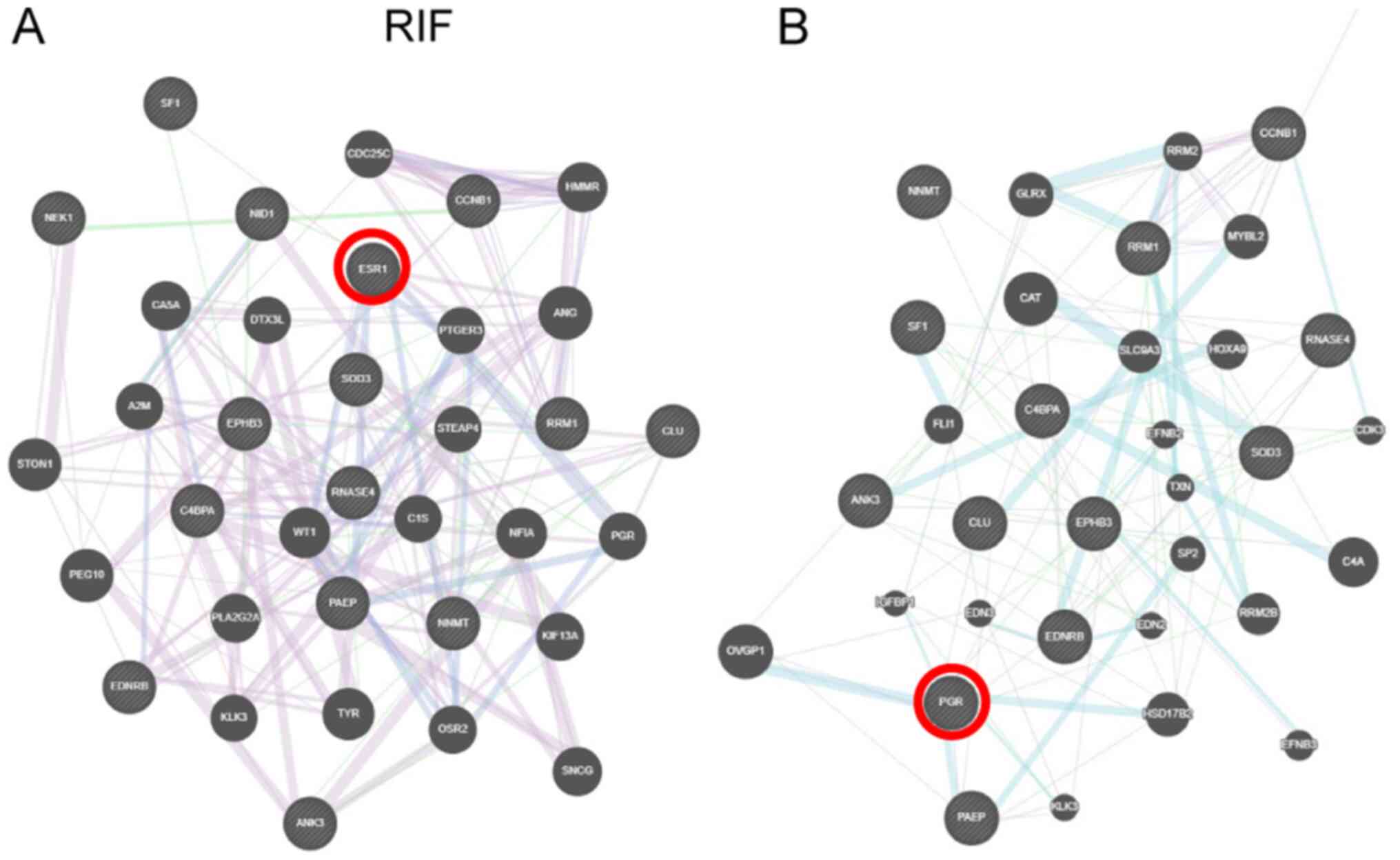
|
1
|
Krüssel JS, Bielfeld P, Polan ML and Simón
C: Regulation of embryonic implantation. Eur J Obstet Gynecol
Reprod Biol. 110 (Suppl 1):S2–S9. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Teh WT, McBain J and Rogers P: What is the
contribution of embryo-endometrial asynchrony to implantation
failure? J Assist Reprod Genet. 33:1419–1430. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sharma A and Kumar P: Understanding
implantation window, a crucial phenomenon. J Hum Reprod Sci. 5:2–6.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fox C and Lessey BA: Signaling between
embryo and endometrium: Normal implantation. In: Recurrent
Implantation Failure: Etiologies and Clinical Management, pp1-19,
2018.
|
|
5
|
Young SL: Oestrogen and progesterone
action on endometrium: A translational approach to understanding
endometrial receptivity. Reprod Biomed Online. 27:497–505.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kumar R, Zakharov MN, Khan SH, Miki R,
Jang H, Toraldo G, Singh R, Bhasin S and Jasuja R: The dynamic
structure of the estrogen receptor. J Amino Acids.
2011(812540)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sharkey AM and Smith SK: The endometrium
as a cause of implantation failure. Best Pract Res Clin Obstet
Gynaecol. 17:289–307. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Schwartz MA: Integrins and extracellular
matrix in mechanotransduction. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
2(a005066)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Arnaout MA, Goodman SL and Xiong JP:
Structure and mechanics of integrin-based cell adhesion. Curr Opin
Cell Biol. 19:495–507. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang J and Armant DR: Integrin-mediated
adhesion and signaling during blastocyst implantation. Cells
Tissues Organs. 172:190–201. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Basak S, Dhar R and Das C: Steroids
modulate the expression of alpha4 integrin in mouse blastocysts and
uterus during implantation. Biol Reprod. 66:1784–1789.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Stemmler MP: Cadherins in development and
cancer. Mol Biosyst. 4:835–850. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gumbiner BM: Cell adhesion: the molecular
basis of tissue architecture and morphogenesis. Cell. 84:345–357.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Poncelet C, Leblanc M, Walker-Combrouze F,
Soriano D, Feldmann G, Madelenat P, Scoazec JY and Daraï E:
Expression of cadherins and CD44 isoforms in human endometrium and
peritoneal endometriosis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 81:195–203.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jha RK, Titus S, Saxena D, Kumar PG and
Laloraya M: Profiling of E-cadherin, beta-catenin and Ca(2+) in
embryo-uterine interactions at implantation. FEBS Lett.
580:5653–5660. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lessey BA, Killam AP, Metzger DA, Haney
AF, Greene GL and McCarty KS Jr: Immunohistochemical analysis of
human uterine estrogen and progesterone receptors throughout the
menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 67:334–340.
1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gregory CW, Wilson EM, Apparao KB,
Lininger RA, Meyer WR, Kowalik A, Fritz MA and Lessey BA: Steroid
receptor coactivator expression throughout the menstrual cycle in
normal and abnormal endometrium. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
87:2960–2966. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Papanikolaou EG, Bourgain C, Kolibianakis
E, Tournaye H and Devroey P: Steroid receptor expression in late
follicular phase endometrium in GnRH antagonist IVF cycles is
already altered, indicating initiation of early luteal phase
transformation in the absence of secretory changes. Hum Reprod.
20:1541–1547. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Papanikolaou EG, D'haeseleer E, Verheyen
G, Van de Velde H, Camus M, Van Steirteghem A, Devroey P and
Tournaye H: Live birth rate is significantly higher after
blastocyst transfer than after cleavage-stage embryo transfer when
at least four embryos are available on day 3 of embryo culture. A
randomized prospective study. Hum Reprod. 20:3198–3203.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Noyes RW, Hertig AT and Rock J: Dating the
endometrial biopsy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 122:262–263.
1975.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Herington JL, Guo Y, Reese J and Paria BC:
Gene profiling the window of implantation: Microarray analyses from
human and rodent models. J Reprod Heal Med. 2 (Suppl 2):S19–S25.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fox C, Morin S, Jeong JW, Scott RT Jr and
Lessey BA: Local and systemic factors and implantation: What is the
evidence? Fertil Steril. 105:873–884. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Carpenter KD and Korach KS: Potential
biological functions emerging from the different estrogen
receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1092:361–373. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kodaman PH and Taylor HS: Hormonal
regulation of implantation. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am.
31:745–66, ix. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dunn CL, Kelly RW and Critchley HO:
Decidualization of the human endometrial stromal cell: An enigmatic
transformation. Reprod Biomed Online. 7:151–161. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Detti L, Saed GM, Fletcher NM, Kruger ML,
Brossoit M and Diamond MP: Endometrial morphology and modulation of
hormone receptors during ovarian stimulation for assisted
reproductive technology cycles. Fertil Steril. 95:1037–1041.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zachariades E, Foster H, Goumenou A,
Thomas P, Rand-Weaver M and Karteris E: Expression of membrane and
nuclear progesterone receptors in two human placental
choriocarcinoma cell lines (JEG-3 and BeWo): Effects of
syncytialization. Int J Mol Med. 27:767–774. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Foster H, Reynolds A, Stenbeck G, Dong J,
Thomas P and Karteris E: Internalisation of membrane progesterone
receptor-alpha after treatment with progesterone: Potential
involvement of a clathrin-dependent pathway. Mol Med Rep. 3:27–35.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Karteris E, Zervou S, Pang Y, Dong J,
Hillhouse EW, Randeva HS and Thomas P: Progesterone signaling in
human myometrium through two novel membrane G protein-coupled
receptors: Potential role in functional progesterone withdrawal at
term. Mol Endocrinol. 20:1519–1534. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sosa LD, Gutiérrez S, Petiti JP, Palmeri
CM, Mascanfroni ID, Soaje M, De Paul AL and Torres AI:
17β-Estradiol modulates the prolactin secretion induced by TRH
through membrane estrogen receptors via PI3K/Akt in female rat
anterior pituitary cell culture. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
302:E1189–E1197. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Uribe RM, Zacarias M, Corkidi G, Cisneros
M, Charli JL and Joseph-Bravo P: 17β-Oestradiol indirectly inhibits
thyrotrophin-releasing hormone expression in the hypothalamic
paraventricular nucleus of female rats and blunts thyroid axis
response to cold exposure. J Neuroendocrinol. 21:439–448.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hulchiy M, Zhang H, Cline JM, Hirschberg
AL and Sahlin L: Receptors for thyrotropin-releasing hormone,
thyroid-stimulating hormone, and thyroid hormones in the macaque
uterus: Effects of long-term sex hormone treatment. Menopause.
19:1253–1259. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ding L, Zhao Y, Warren CL, Sullivan R,
Eliceiri KW and Shull JD: Association of cellular and molecular
responses in the rat mammary gland to 17β-estradiol with
susceptibility to mammary cancer. BMC Cancer.
13(573)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Filant J, Zhou H and Spencer T:
Progesterone inhibits uterine gland development in the neonatal
mouse uterus. Biol Reprod. 86: 146:1–9. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Attar E, Tokunaga H, Imir G, Yilmaz MB,
Redwine D, Putman M, Gurates B, Attar R, Yaegashi N, Hales DB and
Bulun SE: Prostaglandin E2 via steroidogenic factor-1 coordinately
regulates transcription of steroidogenic genes necessary for
estrogen synthesis in endometriosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
94:623–631. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Slayden OD, Friason FKE, Bond KR and
Mishler EC: Hormonal regulation of oviductal glycoprotein 1 (OVGP1;
MUC9) in the rhesus macaque cervix. J Med Primatol. 47:362–370.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Cheng YH, Imir A, Suzuki T, Fenkci V,
Yilmaz B, Sasano H and Bulun SE: SP1 and SP3 mediate
progesterone-dependent induction of the 17beta hydroxysteroid
dehydrogenase type 2 gene in human endometrium. Biol Reprod.
75:605–614. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|