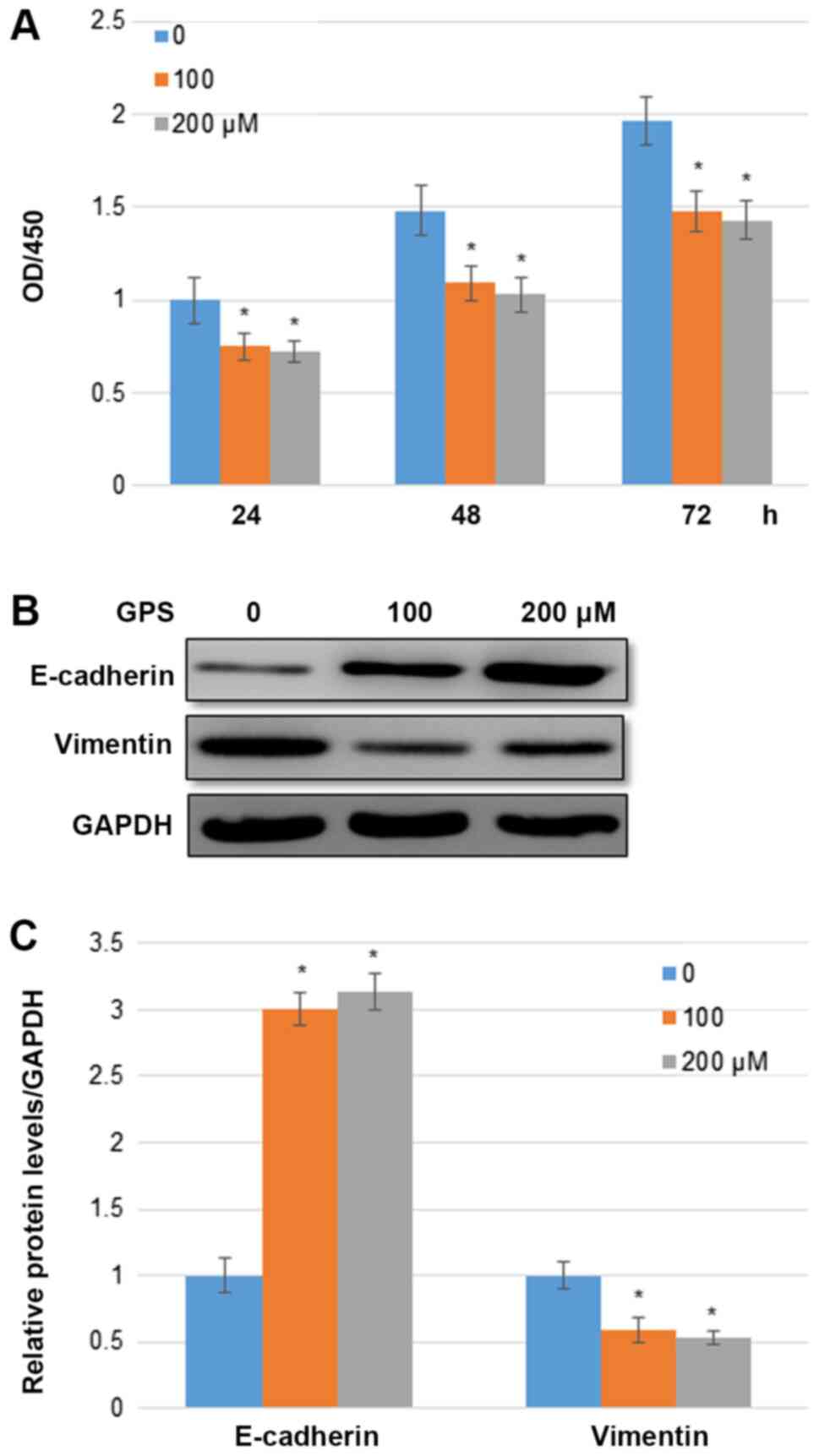
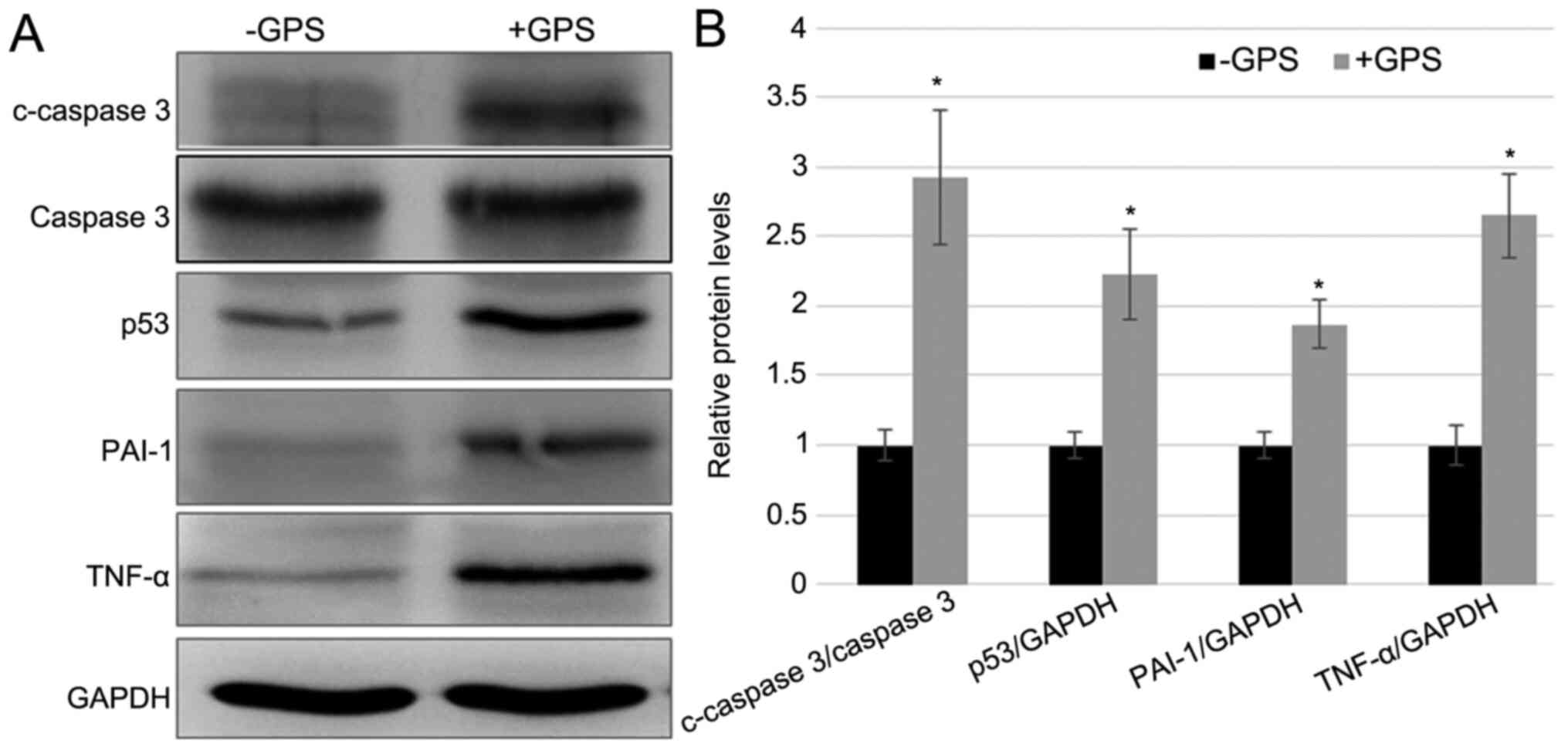
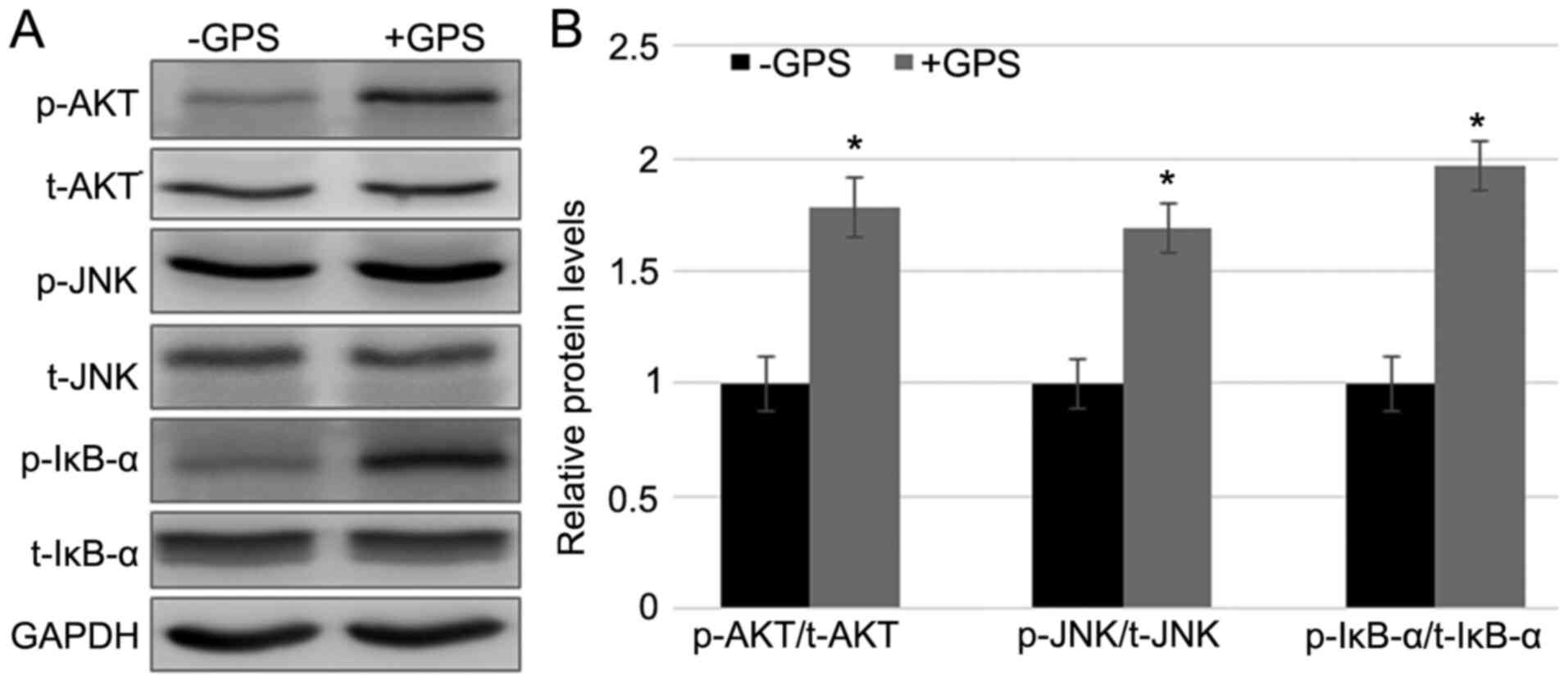
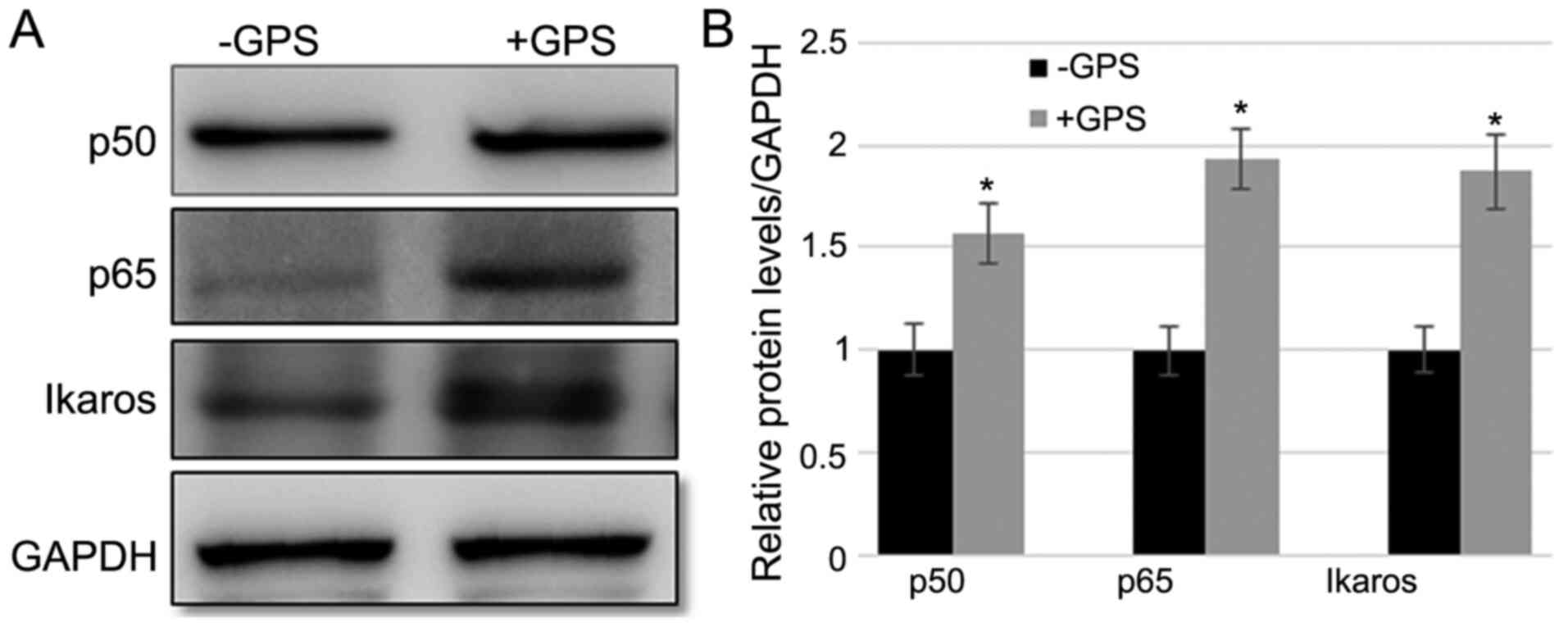
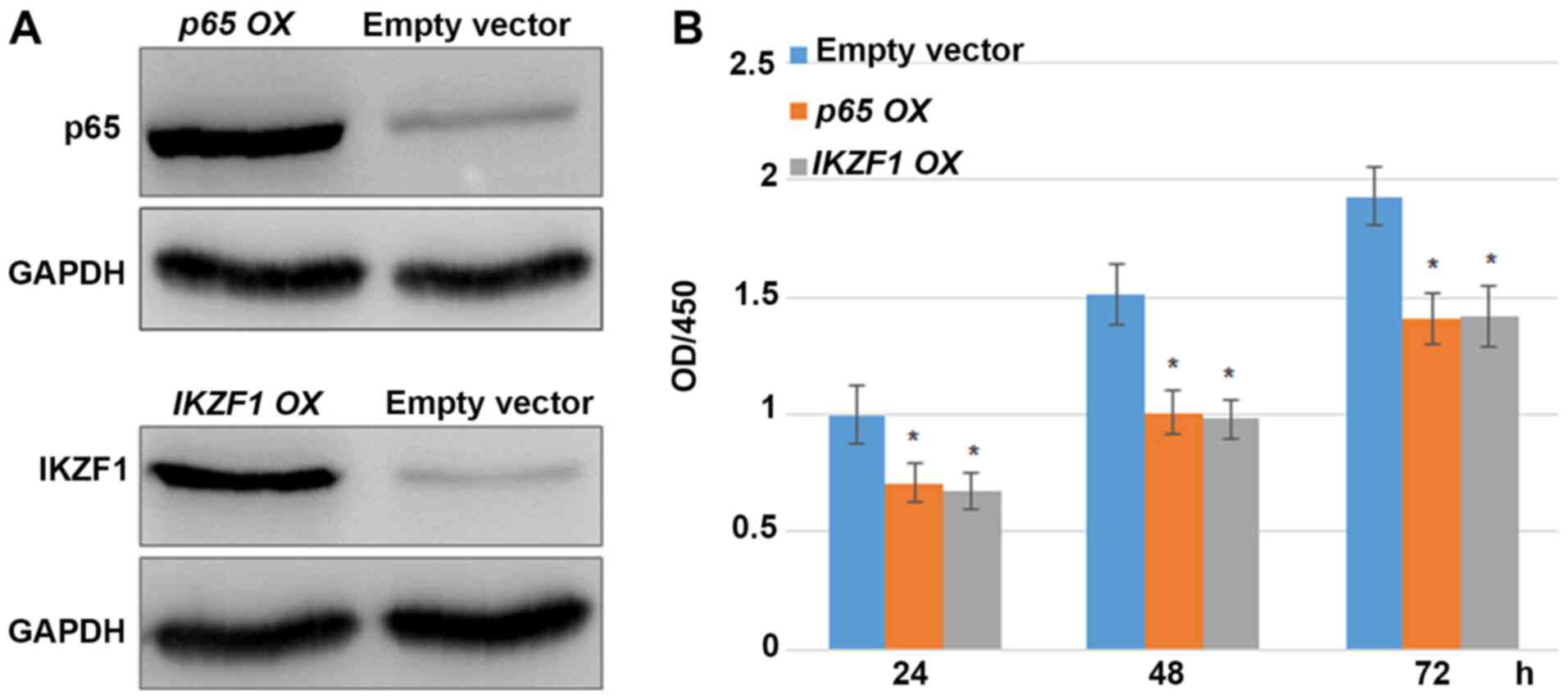
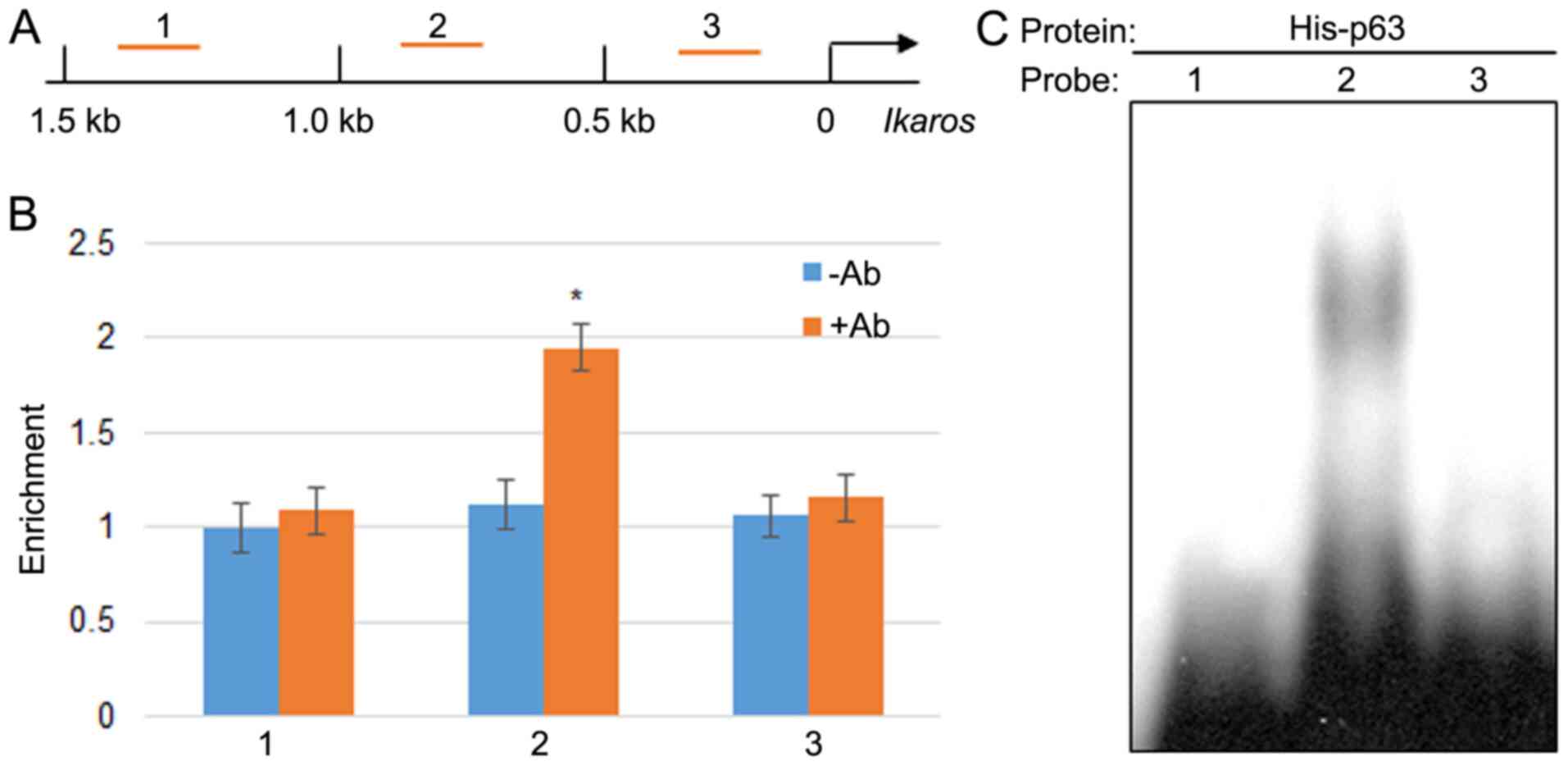
|
1
|
National Cancer Institute: Cancer topics:
Breast cancer, 2014. Accessed 5 Jan 2015. 2015:1-1.
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide:
IARC Cancer Base no. 10. GLOBOCAN 2008. Lyon: International Agency
for Research on Cancer, 2010.
|
|
3
|
Han Z, Wei B, Zheng Y, Yin Y, Li K and Li
S: Breast cancer multi-classification from histopathological images
with structured deep learning model. Sci Rep.
7(4172)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Prat A, Pineda E, Adamo B, Galván P,
Fernández A, Gaba L, Díez M, Viladot M, Arance A and Muñoz M:
Clinical implications of the intrinsic molecular subtypes of breast
cancer. Breast. 24 (Suppl 2):S26–S35. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sørlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R, Aas T,
Geisler S, Johnsen H, Hastie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey
SS, et al: Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas
distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 98:10869–10874. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wilson S and Chia SK: Treatment algorithms
for hormone receptor positive advanced breast cancer: Applying the
results from recent clinical trials into daily practice-insights,
limitations, and moving forward. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book.
33(e20)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Saxton RA and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth, 379 metabolism, and disease. Cell. 168:960–976.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Dickler MN, Tolaney SM, Rugo HS, Cortés J,
Diéras V, Patt D, Wildiers H, Frenzel M, Koustenis A and Baselga J:
MONARCH 1: Results from phase II study of abemaciclib, a CDK4 and
CDK6 inhibitor, as monotherpay, in patients with HR+/HER2- breast
cancer, after chemotherapy for advanced disease. J Clin Oncol.
34(510)2016.
|
|
9
|
Di Cristofano A, Pesce B, Cordon-Cardo C
and Pandolfi PP: PTEN is essential for embryonic development and
tumour suppression. Nature Genetics. 19:348–355. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Garcia-Cao I, Song MS, Hobbs RM, Laurent
G, Giorgi C, de Boer VC, Anastasiou D, Ito K, Sasaki AT, Rameh L,
et al: Pandolfi systemic elevation of PTEN induces a
tumor-suppressive metabolic state. Cell. 149:49–62. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Song MS, Salmena L and Pandolfi PP: The
functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 13:283–296. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ma X and Blenis J: Molecular mechanisms of
mTOR-mediated translational control. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
10:307–318. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Huang J and Manning BD: A complex
interplay between Akt, TSC2 and the two mTOR complexes. Biochem Soc
Trans. 37:217–222. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Inoki K, Li Y, Zhu T, Wu J and Guan KL:
TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR
signaling. Nat Cell Biol. 4:648–657. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shaw RJ, Bardeesy N, Manning BD, Lopez L,
Kosmatka M, DePinho RA and Cantley LC: The LKB1 tumor suppressor
negatively regulates mTOR signaling. Cancer Cell. 6:91–99.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wilkinson KD and Hochstrasser M:
Deubiquitinating enzymes. In: Ubiquitin and Biology of the Cell.
Peters JM, Finley D and Harris JR (eds). Plenum Press, New York,
NY, pp99-120, 1998.
|
|
17
|
Everett RD, Meredith M, Orr A, Cross A,
Kathoria M and Parkinson J: A novel ubiquitin-specific protease is
dynamically associated with the PML nuclear domain and binds to a
herpesvirus regulatory protein. EMBO J. 16:566–577. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Amerik AY and Hochstrasser M: Mechanism
and function of deubiquitinating enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1695:189–207. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang J, Zhang P, Wei Y, Piao HL, Wang W,
Maddika S, Wang M, Chen D, Sun Y, Hung MC, et al: Deubiquitylation
and stabilization of PTEN by USP13. Nat Cell Biol. 15:1486–1494.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hussain S, Zhang Y and Galardy PJ: DUBs
and cancer: The role of deubiquitinating enzymes as oncogenes,
non-oncogenes and tumor suppressors. Cell Cycle. 8:1688–1697.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang M, Hu C, Tong D, Xiang S, Williams
K, Bai W, Li GM, Bepler G and Zhang X: Ubiquitin-specific peptidase
10 (USP10) deubiquitinates and stabilizes MutS Homolog 2 (MSH2) to
regulate cellular sensitivity to DNA damage. J Biol Chem.
291:10783–10791. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lin Z, Yang H, Tan C, Li J, Liu Z, Quan Q,
Kong S, Ye J, Gao B and Fang D: USP10 antagonizes c-Myc
transcriptional activation through SIRT6 stabilization to suppress
tumor formation. Cell Rep. 5:1639–1649. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sun J, Li T, Zhao Y, Huang L, Sun H, Wu H
and Jiang X: USP10 inhibits lung cancer cell growth and invasion by
upregulating PTEN. Mol Cell Biochem. 41:1–7. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lu C, Ning Z, Wang A, Chen D, Liu X, Xia
T, Tekcham DS, Wang W, Li T, Liu X, et al: USP10 suppresses tumor
progression by inhibiting mTOR activation in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 436:139–148. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chung HY, Cesari M, Anton S, Marzetti E,
Giovannini S, Seo AY, Carter C, Yu BP and Leeuwenburgh C: Molecular
inflammation: Underpinnings of aging and age-related diseases.
Ageing Res Rev. 8:18–30. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Douglas EV, Rahul R, Sadiya SK, Mesut E
and Asish KG: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is a marker and a
mediator of senescence. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
37:1446–1452. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shin SG, Koh SH, Woo CH and Lim JH: PAI-1
inhibits development of chronic otitis media and tympanosclerosis
in a mouse model of otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol. 134:1231–1238.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wei X, Li S, He J, Du H, Liu Y, Yu W, Hu
H, Han L, Wang C, Li H, et al: Tumor-secreted PAI-1 promotes breast
cancer metastasis via the induction of adipocyte-derived collagen
remodeling. Cell Commun Signal. 17(58)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bhatelia K, Singh K and Singh R: TLRs:
Linking inflammation and breast cancer. Cell Signal. 26:2350–2357.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jiang X and Shapiro DJ: The immune system
and inflammation in breast cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
382:673–682. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Harris RE, Casto BC and Harris ZM:
Cyclooxygenase-2 and the inflammogenesis of breast cancer. World J
Clin Oncol. 5:677–692. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Erler JT, Bennewith KL, Nicolau M,
Dornhöfer N, Kong C, Le QT, Chi JT, Jeffrey SS and Giaccia AJ:
Lysyl oxidase is essential for hypoxia-induced metastasis. Nature.
440:1222–1226. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kirschmann DA, Seftor EA, Fong SFT, Nieva
DR, Sullivan CM, Edwards EM, Sommer P, Csiszar K and Hendrix MJ: A
molecular role for lysyl oxidase in breast cancer invasion. Cancer
Res. 62:4478–4483. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Basudhar D, Glynn SA, Greer M,
Somasundaram V, No JH, Scheiblin DA, Garrido P, Heinz WF, Ryan AE,
Weiss JM, et al: Coexpression of NOS2 and COX2 accelerates tumor
growth and reduces survival in estrogen receptor-negative breast
cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:13030–13035. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Noguchi M, Rose DP, Earashi M and Miyazaki
I: The role of fatty acids and eicosanoid inhibitors in breast
carcinoma. Oncology. 52:265–271. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ma YV, Lam C, Dalmia S, Gao P, Young J,
Middleton K, Liu C, Xu H and You L: Mechanical regulation of breast
cancer migration and apoptosis via direct and indirect osteocyte
signaling. J Cell Biochem. 119:5665–5675. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Breunig C, Pahl J, Küblbeck M, Miller M,
Antonelli D, Erdem N, Wirth C, Will R, Bott A, Cerwenka A and
Wiemann S: MicroRNA-519a-3p mediates apoptosis resistance in breast
cancer cells and their escape from recognition by natural killer
cells. Cell Death Dis. 8(e2973)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yu B, Gao W, Zhou H, Miao X, Chang Y, Wang
L, Xu M and Ni G: Propofol induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells
by downregulation of miR-24 signal pathway. Cancer Biomark.
21:513–519. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yin N, Yi L, Khalid S, Ozbey U,
Sabitaliyevich UY and Farooqi AA: TRAIL mediated signaling in
breast cancer: Awakening guardian angel to induce apoptosis and
overcome drug resistance. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1152:243–252.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Li Y, Li H, Chen W and Liu W:
Clostridium difficile toxin B recombinant protein inhibits tumor
growth and induces apoptosis through inhibiting Bcl-2 expression,
triggering inflammatory responses and activating C-erbB-2 and Cox-2
expression in breast cancer mouse model. Biomed Pharmacother.
101:391–398. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Luo J, Hu YL and Wang H: Ursolic acid
inhibits breast cancer growth by inhibiting proliferation, inducing
autophagy and apoptosis, and suppressing inflammatory responses via
the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways in vitro. Exp Ther Med.
14:3623–3631. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Burstein E and Ducket CS: Dying for
NF-kappaB? Control of cell death by transcriptional regulation of
the apoptotic machinery. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 15:732–737.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Helms S: Cancer prevention and
therapeutics: Panax ginseng. Altern Med Rev. 9:259–274.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Davydov M and Krikorian AD:
Eleutherococcus senticosus (Rupr & Maxim.) Maxim. (Araliaceae)
as an adaptogen: A closer look. J Ethnopharmacol. 72:345–393.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Lee S, Shin DS, Oh KB and Skin KH:
Antibacterial compounds from leaves of Acanthopanax senticosus.
Arch Pharm Res. 26:40–42. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Hasegawa H, Suzuki R, Nagaoka T, Tezuka Y,
Kadota S and Saiki I: Prevention of growth and metastasis of murine
melanoma through enhanced natural-killercytotoxicity by fatty acid
conjugate of protopanaxatriol. Biol Pharm Bull. 25:861–866.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kiyohara H, Hirano M, Wen XG, Matsumoto T,
Sun XB and Yamada H: Characterization of an antiulcer pectic
polysaccharide from leaves of Panaxginseng C.A. Meyer. Carbohydr
Res. 263:89–101. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Schepetkin IA and Quinn MT: Botanical
polysaccharides: Macrophage immunomodulation and therapeutic
potential. Int Immunopharmacol. 6:317–333. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yoon TJ, Yoo YC, Kang TB, Baek YJ, Huh CS,
Song SK, Lee KH, Azuma I and Kim JB: Prophylactic effect of Korean
mistletoe (Viscum album coloratum) extract on tumor metastasis is
mediated by enhancement of NK cell activity. Int J Immunopharmacol.
20:163–172. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Shin MS, Lee H, Hong HD and Shin KS:
Characterization of immunostimulatory pectic polysaccharide
isolated from the leaves of Diospyros kaki Tumb (Persimmon). J
Funct Foods. 26:319–329. 2016.
|
|
52
|
Park JY, Shin MS, Kim SN, Kim HY, Kim KH,
Shin KS and Kang KS: Polysaccharides from Korean Citrus hallabong
peels inhibit angiogenesis andbreast cancer cell migration. Int J
Biol Macromol. 85:522–529. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Lee EH, Park HR, Shin MS, Cho SY, Choi HJ
and Shin KS: Antitumor metastasis activity of pectic polysaccharide
purified from the peels of Korean Citrus Hallabong. Carbohydr
Polym. 111:72–79. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Xuan YH, Huang BB, Tian HS, Chi LS, Duan
YM, Wang X, Zhu ZX, Cai WH, Zhu YT, Wei TM, et al: High-glucose
inhibits human fibroblast cell migration in wound healing via
repression of bFGF-regulating JNK phosphorylation. PLoS One.
9(e108182)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Keum YS, Han SS, Chun KS, Park KK, Park
JH, Lee SK and Surh YJ: Inhibitory effects of the ginsenoside Rg3
on phorbol ester-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression, NF-kappaB
activation and tumor promotion. Mutat Res. 523-524:75–85.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Ip YT and Davis RJ: Signal transduction by
the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-from inflammation to development.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 10:205–219. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Liu YY, Ge C, Tian H, Jiang JY, Zhao FY,
Li H, Chen TY, Yao M and Li JJ: The transcription factor Ikaros
inhibits cell proliferation by downregulating ANXA4 expression in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Cancer Res. 7:1285–1297.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Baeuerle PA and Baltimore D: NF-kappa B:
Ten years after. Cell. 87:13–20. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Ahn JY, Choi IS, Shim JY, Yun EK, Yun YS,
Jeong G and Song JY: The immunomodulator ginsan induces resistance
to experimental sepsis by inhibiting Toll-like receptor-mediated
inflammatory signals. Eur J Immunol. 36:37–45. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Kashii-Magaribuchi K, Takeuchi R, Haisa Y,
Sakamoto A, Itoh A, Izawa Y, Isa M, Fukuzawa M, Murakami M and
Takahashi R: Induced expression of cancer stem cell markers ALDH1A3
and Sox-2 in hierarchical reconstitution of apoptosis-resistant
human breast cancer cells. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 49:149–158.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Wallach D, Varfolomeev EE, Malinin NL,
Goltsev YV, Kovalenko AV and Boldin M: Tumor necrosis factor
receptor and Fas signaling mechanisms. Ann Rev Immunol. 17:331–367.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Ehrhardt H, Fulda S, Schmid I, Hiscott J,
Debatin KM and Jeremias I: TRAIL induced survival and proliferation
in cancer cells resistant towards TRAIL-induced apoptosis mediated
by NF-kappaB. Oncogene. 22:3842–3852. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Trauzold A, Siegmund D, Schniewind B,
Sipos B, Egberts J, Zorenkov D, Emme D, Röder C, Kalthoff H and
Wajant H: TRAIL promotes metastasis of human pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 25:7434–7439. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|