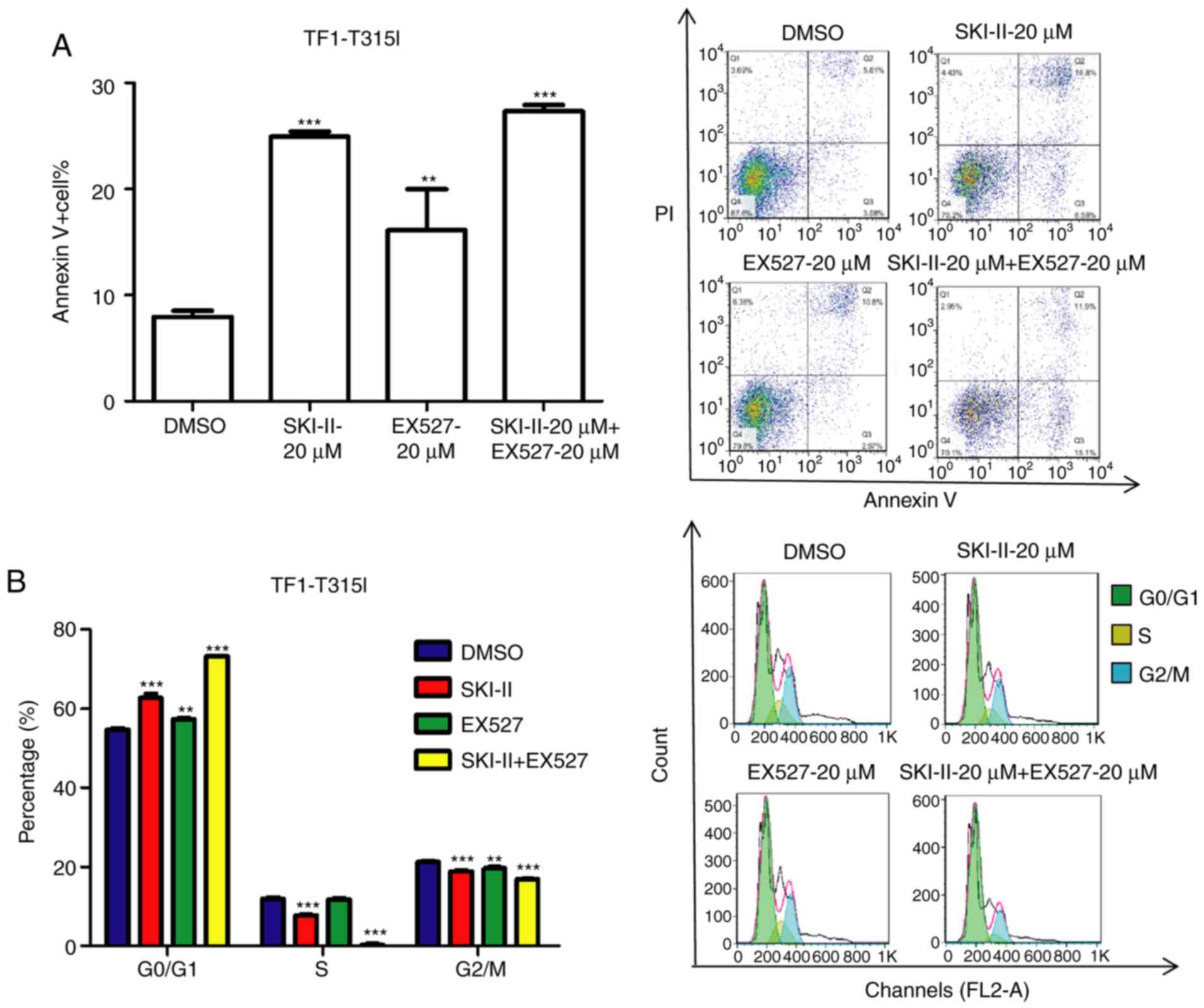
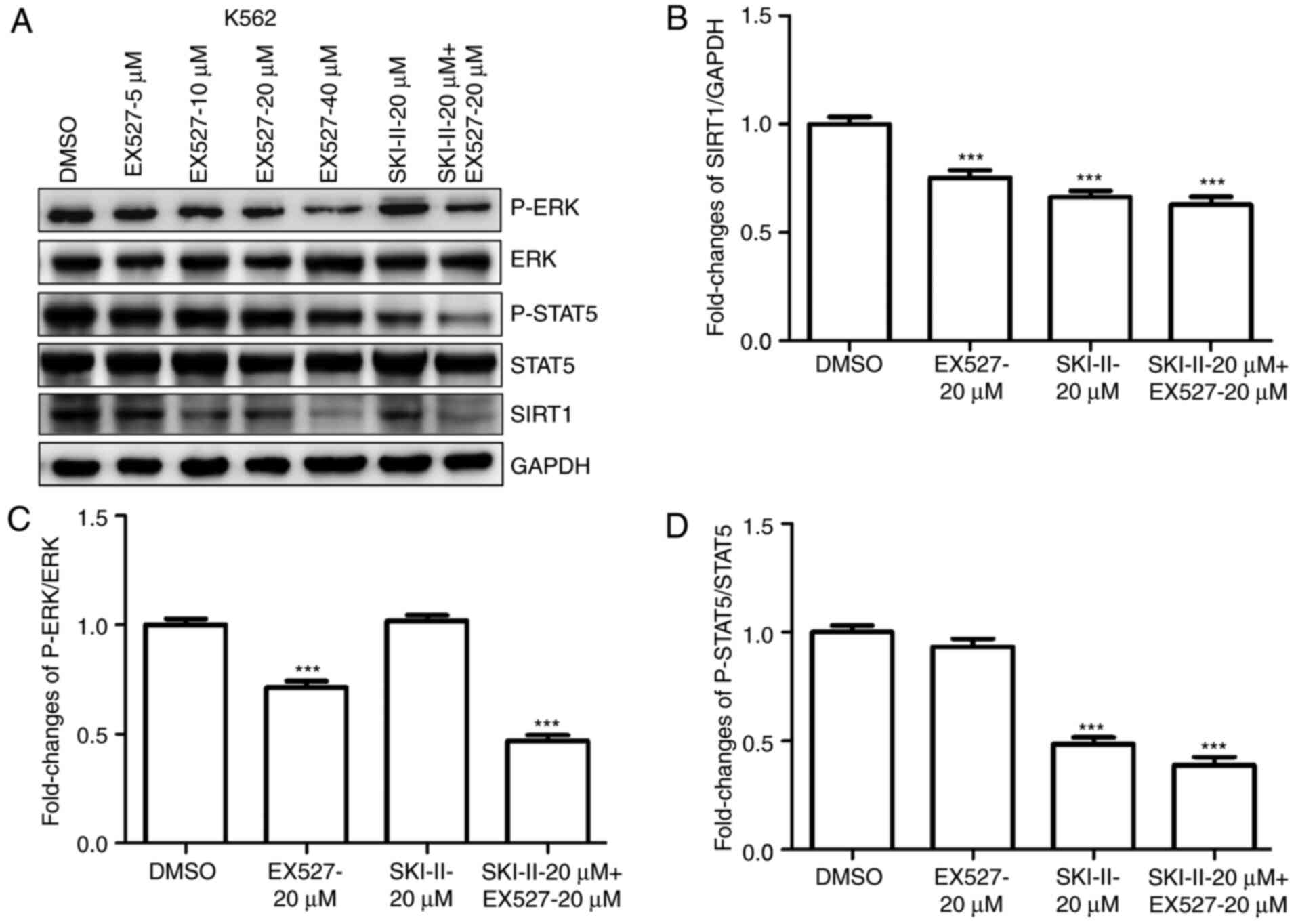
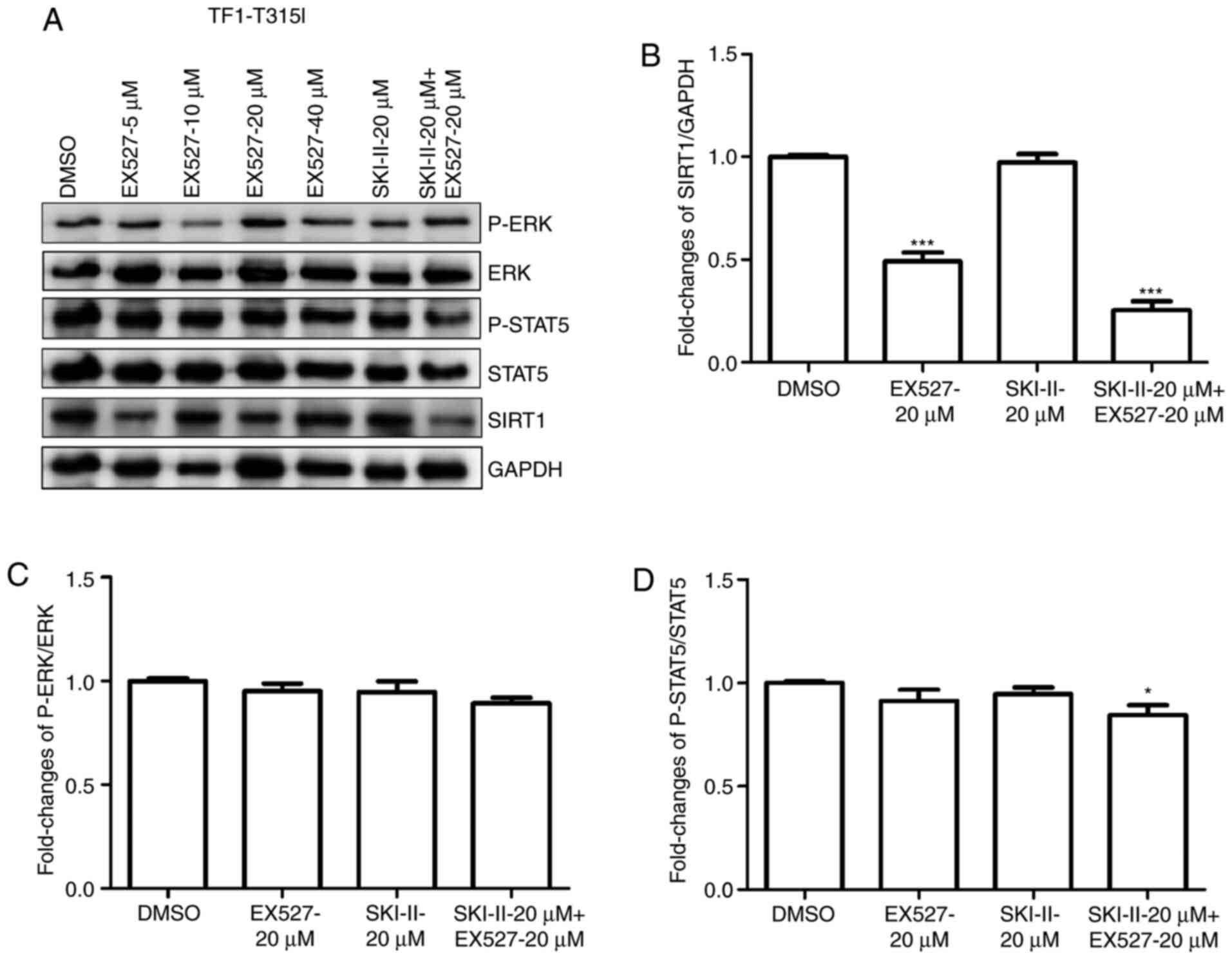
|
1
|
Kumari A, Brendel C, Hochhaus A, Neubauer
A and Burchert A: Low BCR-ABL expression levels in hematopoietic
precursor cells enable persistence of chronic myeloid leukemia
under imatinib. Blood. 119:530–539. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
O'Hare T, Deininger MW, Eide CA, Clackson
T and Druker BJ: Targeting the BCR-ABL signaling pathway in
therapy-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:212–221. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Corbin AS, Agarwal A, Loriaux M, Cortes J,
Deininger MW and Druker BJ: Human chronic myeloid leukemia stem
cells are insensitive to imatinib despite inhibition of BCR-ABL
activity. J Clin Invest. 121:396–409. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cilloni D and Saglio G: Molecular
pathways: BCR-ABL. Clin Cancer Res. 18:930–937. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sattler M and Griffin JD: Molecular
mechanisms of transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene. Semin
Hematol. 40 (Suppl 2):S4–S10. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sinclair A, Latif AL and Holyoake TL:
Targeting survival pathways in chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells.
Br J Pharmacol. 169:1693–1707. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu Q, Luo Q, Halim A and Song G:
Targeting lipid metabolism of cancer cells: A promising therapeutic
strategy for cancer. Cancer Lett. 401:39–45. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tang X, Benesch MG and Brindley DN: Lipid
phosphate phosphatases and their roles in mammalian physiology and
pathology. J Lipid Res. 56:2048–2060. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Patmanathan SN, Wang W, Yap LF, Herr DR
and Paterson IC: Mechanisms of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor
signalling in cancer. Cell Signal. 34:66–75. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Tabasinezhad M, Samadi N, Ghanbari P,
Mohseni M, Saei AA, Sharifi S, Saeedi N and Pourhassan A:
Sphingosin 1-phosphate contributes in tumor progression. J Cancer
Res Ther. 9:556–563. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nagahashi M, Takabe K, Terracina KP, Soma
D, Hirose Y, Kobayashi T, Matsuda Y and Wakai T:
Sphingosine-1-phosphate transporters as targets for cancer therapy.
Biomed Res Int. 2014(651727)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mendelson K, Evans T and Hla T:
Sphingosine 1-phosphate signalling. Development. 141:5–9.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gao Z, Wang H, Xiao FJ, Shi XF, Zhang YK,
Xu QQ, Zhang XY, Ha XQ and Wang LS: SIRT1 mediates
Sphk1/S1P-induced proliferation and migration of endothelial cells.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 74:152–160. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li QF, Wu CT, Guo Q, Wang H and Wang LS:
Sphingosine 1-phosphate induces Mcl-1 upregulation and protects
multiple myeloma cells against apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 371:159–162. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Evangelisti C, Evangelisti C, Buontempo F,
Lonetti A, Orsini E, Chiarini F, Barata JT, Pyne S, Pyne NJ and
Martelli AM: Therapeutic potential of targeting sphingosine kinases
and sphingosine 1-phosphate in hematological malignancies.
Leukemia. 30:2142–2151. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li QF, Huang WR, Duan HF, Wang H, Wu CT
and Wang LS: Sphingosine kinase-1 mediates BCR/ABL-induced
upregulation of Mcl-1 in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Oncogene.
26:7904–7908. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Salas A, Ponnusamy S, Senkal CE,
Meyers-Needham M, Selvam SP, Saddoughi SA, Apohan E, Sentelle RD,
Smith C, Gault CR, et al: Sphingosine kinase-1 and sphingosine
1-phosphate receptor 2 mediate Bcr-Abl1 stability and drug
resistance by modulation of protein phosphatase 2A. Blood.
117:5941–5952. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Baran Y, Salas A, Senkal CE, Gunduz U,
Bielawski J, Obeid LM and Ogretmen B: Alterations of
ceramide/sphingosine 1-phosphate rheostat involved in the
regulation of resistance to imatinib-induced apoptosis in K562
human chronic myeloid leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 282:10922–10934.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ricci C, Onida F, Servida F, Radaelli F,
Saporiti G, Todoerti K, Deliliers GL and Ghidoni R: In vitro
anti-leukaemia activity of sphingosine kinase inhibitor. Br J
Haematol. 144:350–357. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Marfe G, Di Stefano C, Gambacurta A,
Ottone T, Martini V, Abruzzese E, Mologni L, Sinibaldi-Salimei P,
de Fabritis P, Gambacorti-Passerini C, et al: Sphingosine kinase 1
overexpression is regulated by signaling through PI3K, AKT2, and
mTOR in imatinib-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Exp
Hematol. 39:653–665. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Powell JA, Lewis AC, Zhu W, Toubia J,
Pitman MR, Wallington-Beddoe CT, Moretti PA, Iarossi D, Samaraweera
SE, Cummings N, et al: Targeting sphingosine kinase 1 induces
MCL1-dependent cell death in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
129:771–782. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sobue S, Nemoto S, Murakami M, Ito H,
Kimura A, Gao S, Furuhata A, Takagi A, Kojima T, Nakamura M, et al:
Implications of sphingosine kinase 1 expression level for the
cellular sphingolipid rheostat: Relevance as a marker for
daunorubicin sensitivity of leukemia cells. Int J Hematol.
87:266–275. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Vachharajani VT, Liu T, Wang X, Hoth JJ,
Yoza BK and McCall CE: Sirtuins link inflammation and metabolism. J
Immunol Res. 2016(8167273)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Roth M, Wang Z and Chen WY: Sirtuins in
hematological aging and malignancy. Crit Rev Oncog. 18:531–547.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li L, Osdal T, Ho Y, Chun S, McDonald T,
Agarwal P, Lin A, Chu S, Qi J, Li L, et al: SIRT1 activation by a
c-MYC oncogenic network promotes the maintenance and drug
resistance of human FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukemia stem cells.
Cell Stem Cell. 15:431–446. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhou L, Wang Q, Chen X, Fu L, Zhang X,
Wang L, Deng A, Li D, Liu J, Lv N, et al: AML1-ETO promotes SIRT1
expression to enhance leukemogenesis of t(8;21) acute myeloid
leukemia. Exp Hematol. 46:62–69. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li L, Wang L, Li L, Wang Z, Ho Y, McDonald
T, Holyoake TL, Chen W and Bhatia R: Activation of p53 by SIRT1
inhibition enhances elimination of CML leukemia stem cells in
combination with imatinib. Cancer Cell. 21:266–281. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li L and Bhatia R: Role of SIRT1 in the
growth and regulation of normal hematopoietic and leukemia stem
cells. Curr Opin Hematol. 22:324–329. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Giusto K, Patki M, Koya J, Ashby CR Jr,
Munnangi S, Patel K and Reznik SE: A vaginal nanoformulation of a
SphK inhibitor attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm birth
in mice. Nanomedicine (Lond). 14:2835–2851. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang T, Li X and Sun SL: EX527, a Sirt-1
inhibitor, induces apoptosis in glioma via activating the p53
signaling pathway. Anticancer Drugs. 31:19–26. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Peters GJ: From ‘targeted therapy’ to
targeted therapy. Anticancer Res. 39:3341–3345. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bhalla S, Tremblay D and Mascarenhas J:
Discontinuing tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in chronic
myelogenous leukemia: Current understanding and future directions.
Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 16:488–494. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Holyoake TL and Vetrie D: The chronic
myeloid leukemia stem cell: Stemming the tide of persistence.
Blood. 129:1595–1606. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gao Y, Gao F, Chen K, Tian ML and Zhao DL:
Sphingosine kinase 1 as an anticancer therapeutic target. Drug Des
Devel Ther. 9:3239–3245. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wallington-Beddoe CT, Bradstock KF and
Bendall LJ: Oncogenic properties of sphingosine kinases in
haematological malignancies. Br J Haematol. 161:623–638.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shida D, Takabe K, Kapitonov D, Milstien S
and Spiegel S: Targeting SphK1 as a new strategy against cancer.
Curr Drug Targets. 9:662–673. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Xie Z, Liu H and Geng M: Targeting
sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling for cancer therapy. Sci China
Life Sci. 60:585–600. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Qiu G, Li X, Che X, Wei C, He S, Lu J, Jia
Z, Pang K and Fan L: SIRT1 is a regulator of autophagy:
Implications in gastric cancer progression and treatment. FEBS
Lett. 589:2034–2042. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang W, Zhang J, Li Y, Yang X, He Y, Li T,
Ren F, Zhang J and Lin R: Divalproex sodium enhances the
anti-leukemic effects of imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia cells
partly through SIRT1. Cancer Lett. 356:791–799. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yang L, Weng W, Sun ZX, Fu XJ, Ma J and
Zhuang WF: SphK1 inhibitor II (SKI-II) inhibits acute myelogenous
leukemia cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 460:903–908. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Braun TP, Eide CA and Druker BJ: Response
and resistance to BCR-ABL1-targeted therapies. Cancer Cell.
37:530–542. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Holtz MS, Forman SJ and Bhatia R:
Nonproliferating CML CD34+ progenitors are resistant to apoptosis
induced by a wide range of proapoptotic stimuli. Leukemia.
19:1034–1041. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Roche-Lestienne C and Preudhomme C:
Mutations in the ABL kinase domain pre-exist the onset of imatinib
treatment. Semin Hematol. 40 (Suppl 2):S80–S82. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhang L, Wang X, Bullock AJ, Callea M,
Shah H, Song J, Moreno K, Visentin B, Deutschman D, Alsop DC, et
al: Anti-S1P antibody as a novel therapeutic strategy for VEGFR
TKI-resistant renal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:1925–1934.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Sun J, Li G, Liu Y, Ma M, Song K, Li H,
Zhu D, Tang X, Kong J and Yuan X: Targeting histone deacetylase
SIRT1 selectively eradicates EGFR TKI-resistant cancer stem cells
via regulation of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation in lung
adenocarcinoma. Neoplasia. 22:33–46. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kaymaz BT, Selvi N, Gündüz C, Aktan C,
Dalmızrak A, Saydam G and Kosova B: Repression of STAT3, STAT5A,
and STAT5B expressions in chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line
K-562 with unmodified or chemically modified siRNAs and induction
of apoptosis. Ann Hematol. 92:151–162. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Chorzalska A, Ahsan N, Rao RSP, Roder K,
Yu X, Morgan J, Tepper A, Hines S, Zhang P, Treaba DO, et al:
Overexpression of Tpl2 is linked to imatinib resistance and
activation of MEK-ERK and NF-κB pathways in a model of chronic
myeloid leukemia. Mol Oncol. 12:630–647. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Schafranek L, Nievergall E, Powell JA,
Hiwase DK, Leclercq T, Hughes TP and White DL: Sustained inhibition
of STAT5, but not JAK2, is essential for TKI-induced cell death in
chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 29:76–85. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Nambu T, Araki N, Nakagawa A, Kuniyasu A,
Kawaguchi T, Hamada A and Saito H: Contribution of
BCR-ABL-independent activation of ERK1/2 to acquired imatinib
resistance in K562 chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Sci.
101:137–142. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|