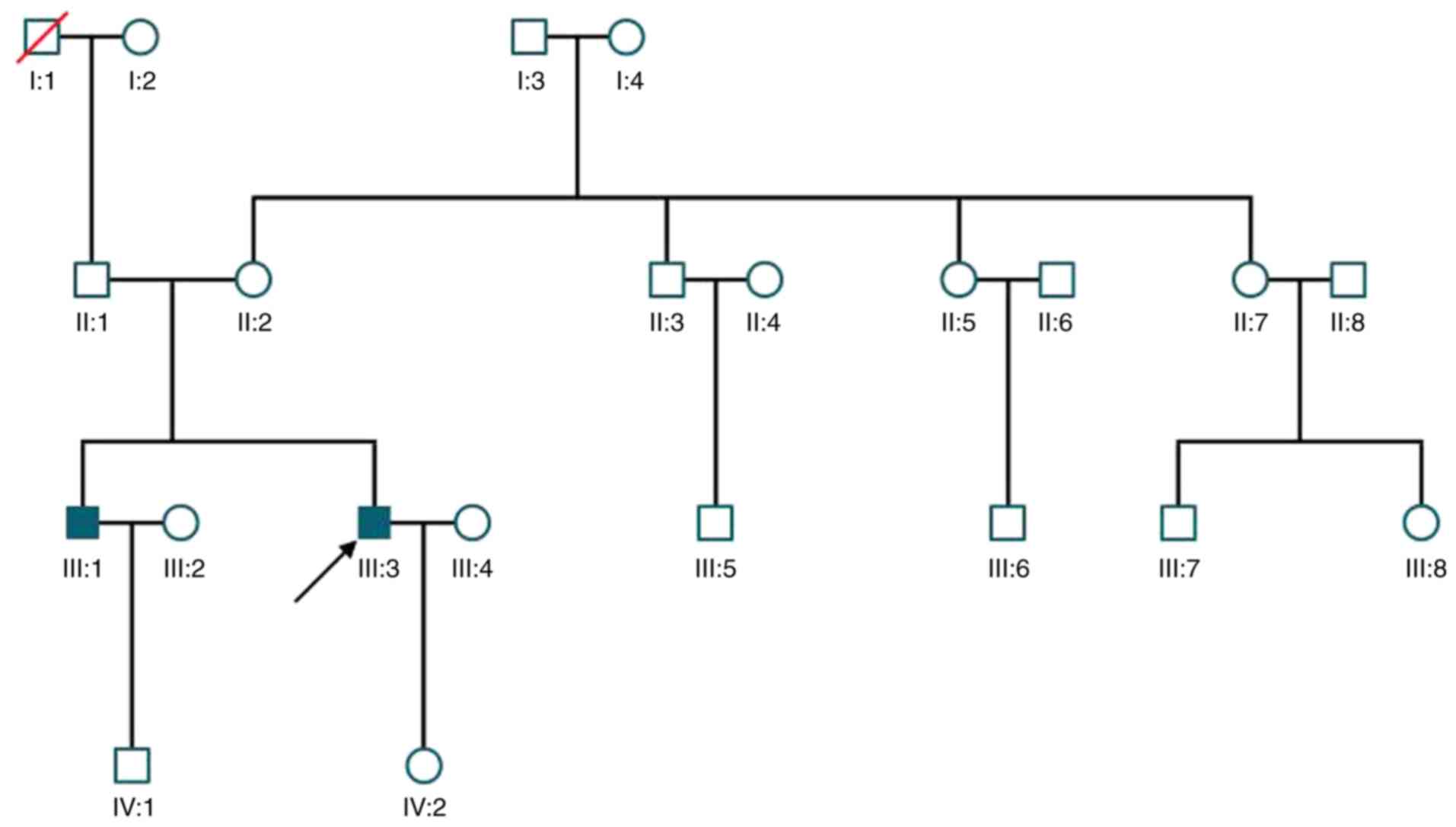
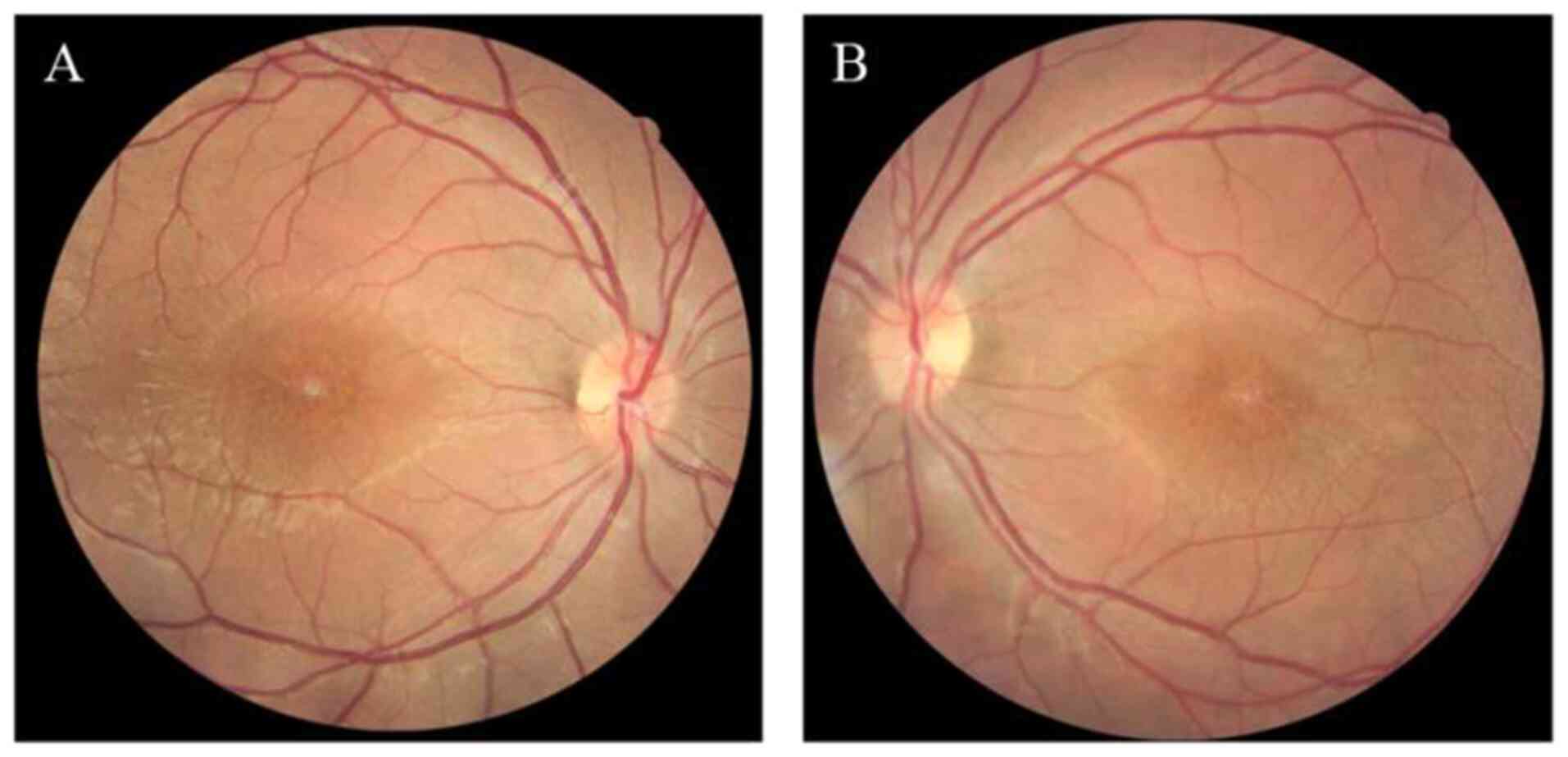
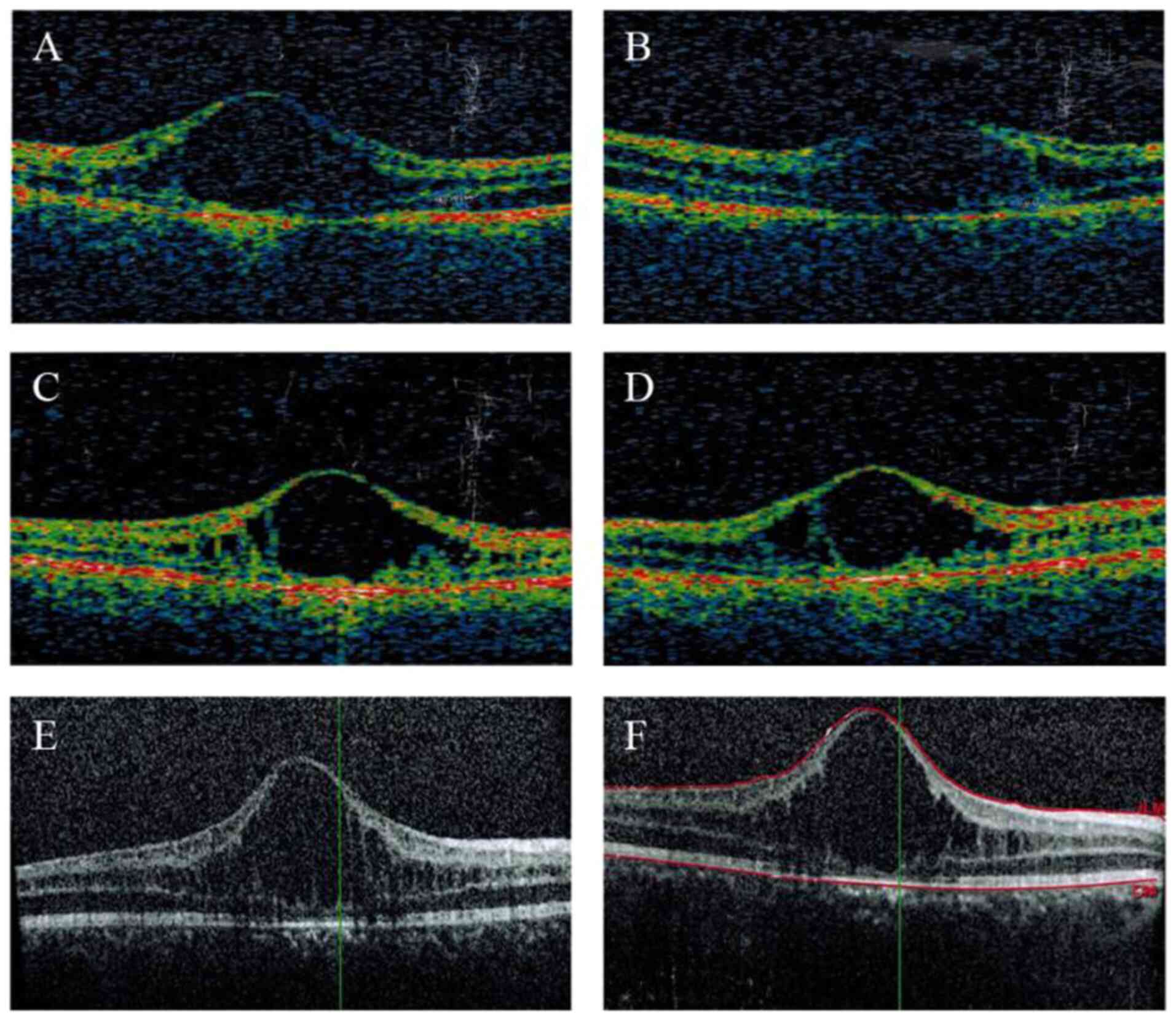
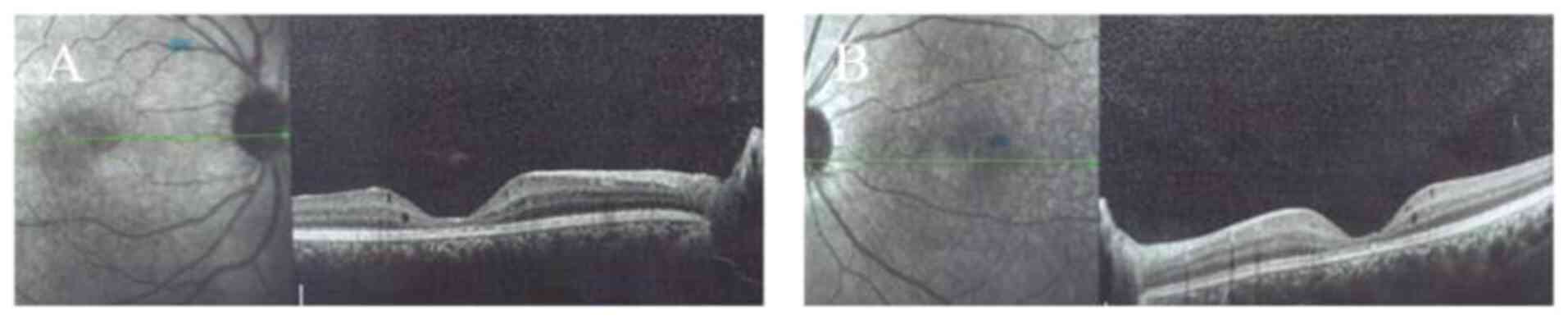
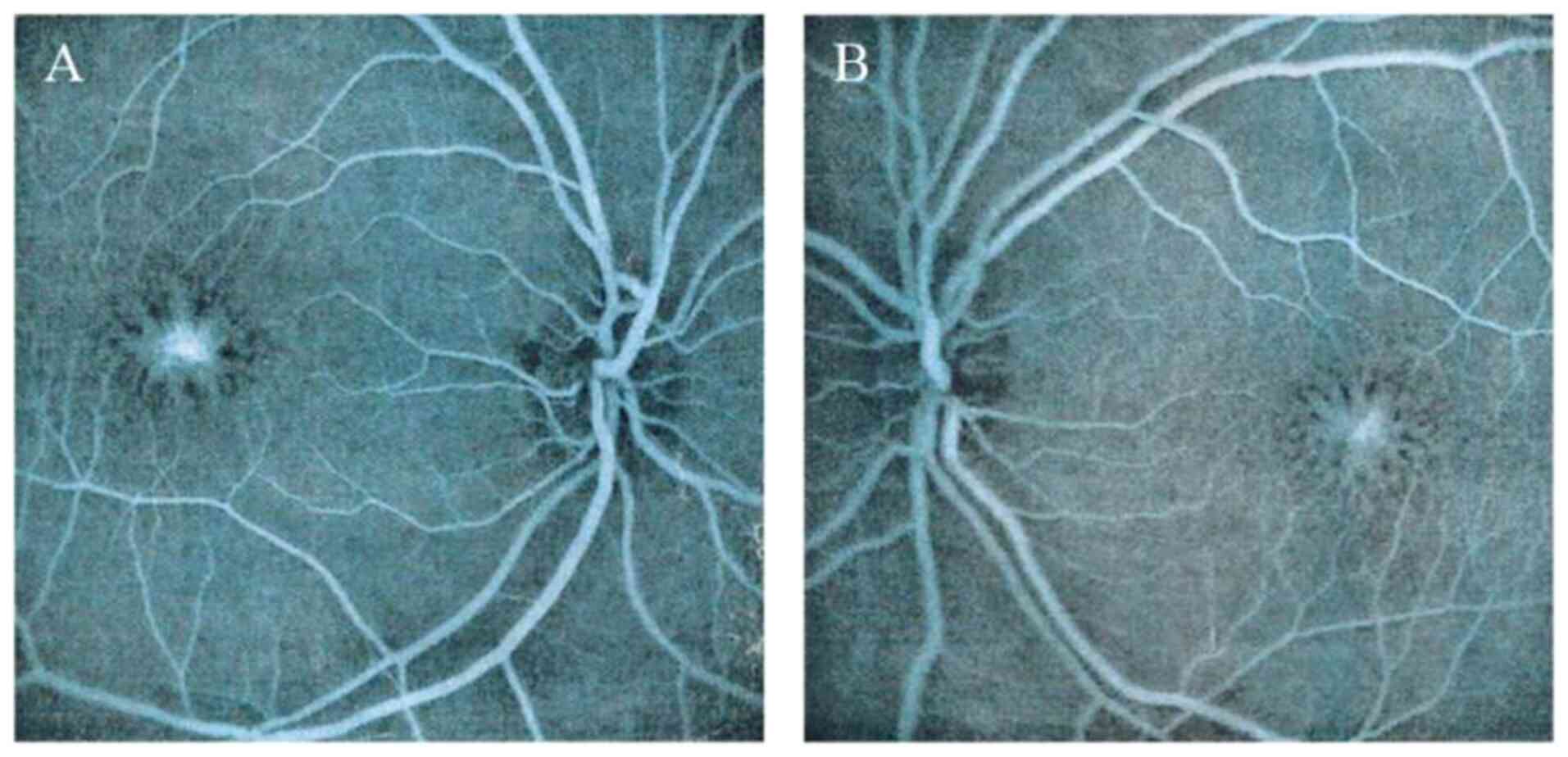
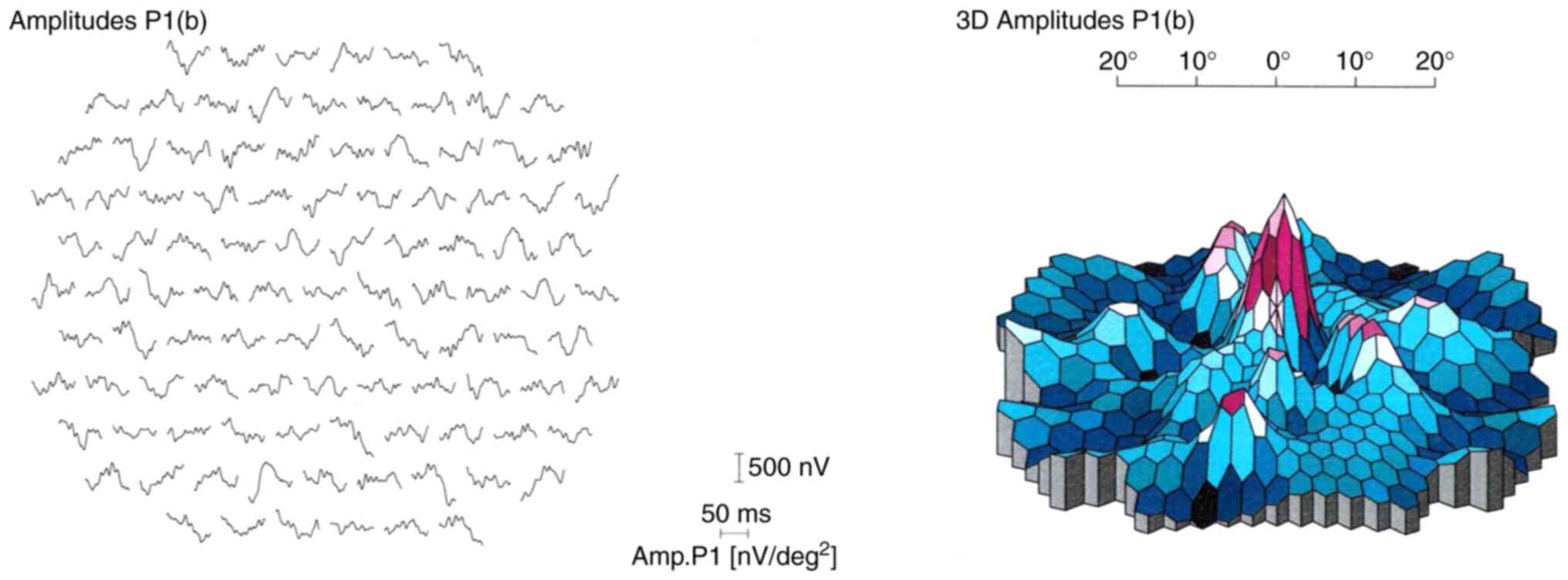
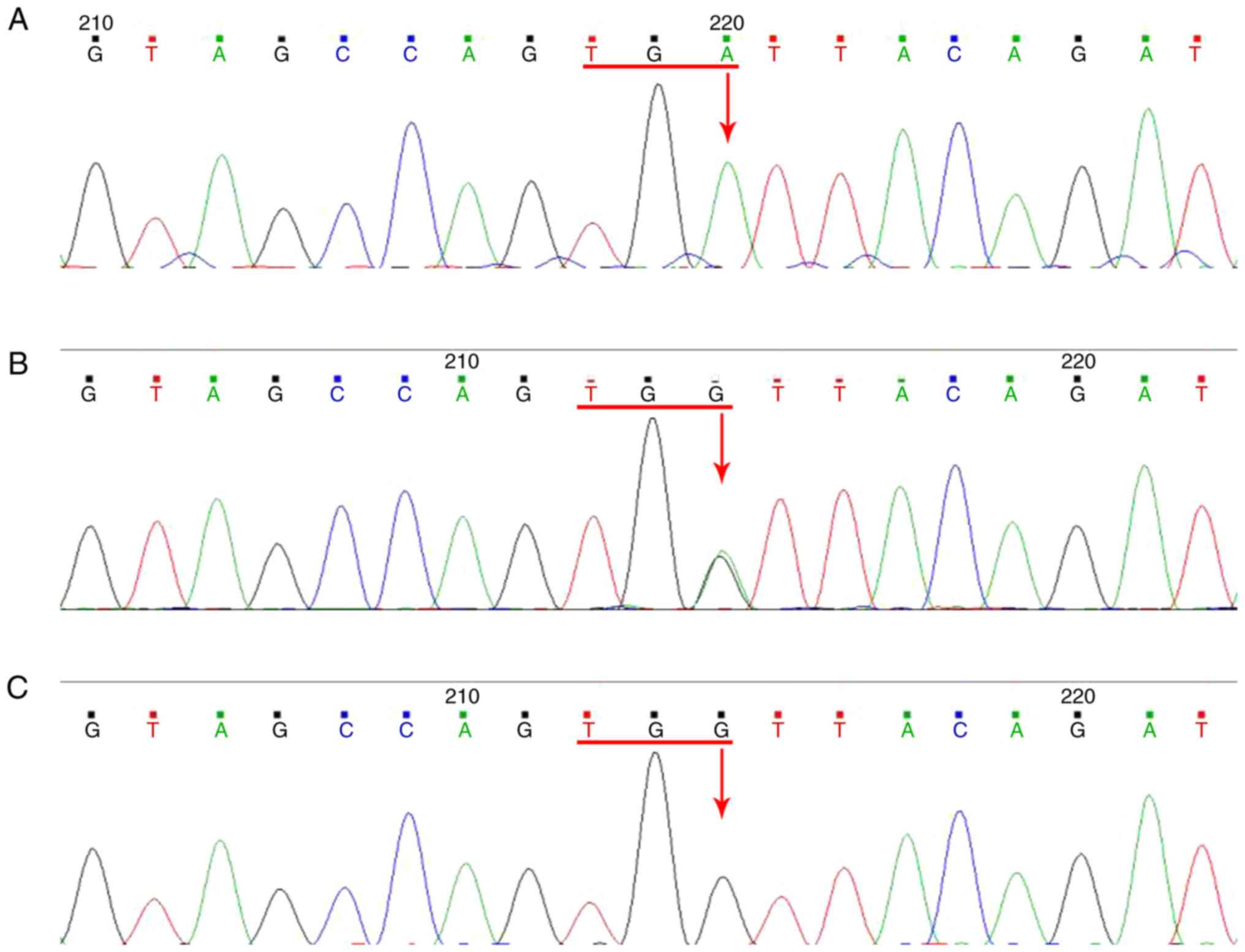
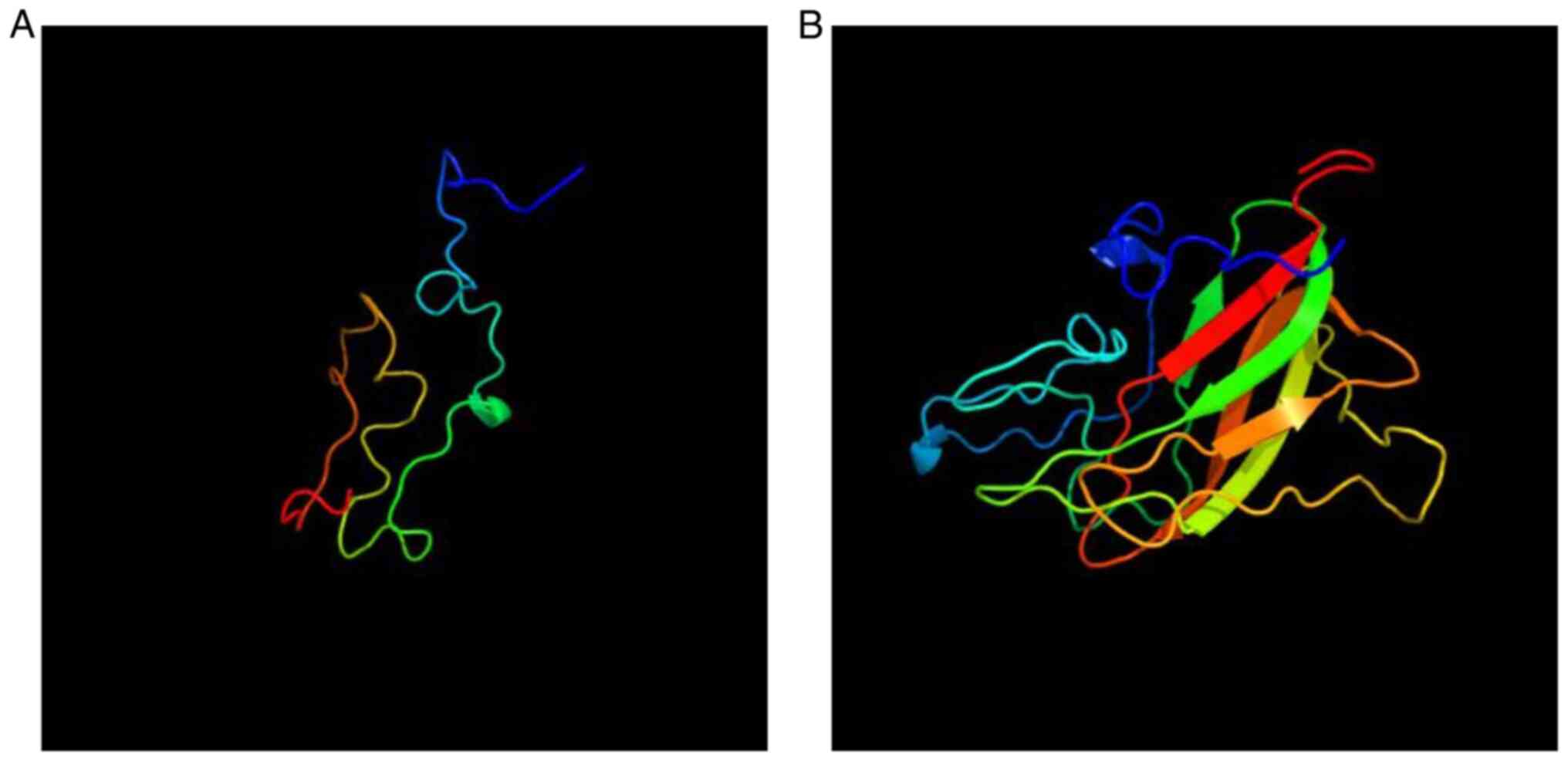
|
1
|
George ND, Yates JR and Moore AT: X linked
retinoschisis. Br J Ophthalmol. 79:697–702. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wieacker P, Wienker J, Dallapiccola B,
Bender K, Davies KE and Ropers HH: Linkage relationships between
retionschisis, Xg, and a cloned DNA seqence from the distal short
arm of the X chromosome. Hum Genet. 64:143–145. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Takada Y, Fariss RN, Tanikawa A, Zeng Y,
Carper D, Bush R and Sieving PA: A retinal neuronal developmental
wave of retinoschisin expression begins in ganglion cells during
layer formation. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 45:3302–3312.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wu WW, Wong JP, Kast J and Molday RS: RS1,
a discoidin domain-containing retinal cell adhesion protein
associated with X-linked retinoschisis, exists as a novel
disulfide-linked octamer. J Biol Chem. 280:10721–10730.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Renner AB, Kellner U, Fiebig B, Cropp E,
Foerster MH and Weber BHF: ERG variability in X-linked congenital
retinoschisis patients with mutation in the RS1 gene and the
diagnostic importance of fundus autofluorescence and OCT. Doc
Ophthalmol. 116:97–109. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang NK, Liu LL, Chen HM, Tsai S, Chang
TC, Tsai TH, Yang CM, Chao AN, Chen KJ, Kao LY, et al: Clinical
presentations of X-linked retinoschisis in Taiwanese patients
confirmed with genetic sequencing. Mol Vis. 21:487–501.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thobani A and Fishman GA: The use of
carbonic anhydease inhibitors in the retreatment of cystic macular
lesions in retinitis pigmentosa and X-linked retinoschisis. Retina.
31:312–315. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Haas J: Über das zusammenvorkommen von
veraenderungen der retina und choroides. Arch Augenheilkd.
37:343–348. 1898.
|
|
9
|
Kjellström S, Vijayasarathy C, Ponjavic V,
Sieving PA and Andréasson S: Long-term 12 year follow-up of
X-linked congenital retinoschisis. Ophthalmic Genet. 31:114–125.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kellner U, Brummer S, Foerster MH and
Wessing A: X-linked congenital retinoschisis. Graefes Arch Clin Exp
Ophthalmol. 228:432–437. 1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Apushkin MA, Fishman GA and Janowica MJ:
Correlated of optical coherencce tomography findings with visual
acuity and macular lesions in patients with X-linked retinoschisis.
Ophthalmology. 112:495–501. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kondo H, Oku K, Katagiri S, Hayashi T,
Nakano T, Iwata A, Kuniyoshi K, Kusaka S, Hiyoshi A, Uchio E, et
al: Novel mutations in the RS1 gene in Japanese patients with
X-linked congenital retinoschisis. Hum Genome Var.
6(3)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hu QR, Huang LZ, Chen XL, Xia HK, Li TQ
and Li XX: Genetic analysis and clinical features of X-linked
retinoschisis in Chinese patients. Sci Rep. 7(44060)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tian R, Jiang RX and Chen YX: Genetic and
phenotypic characteristics of six Chinese families with X-linked
juvenile retinoschisis. Chin Med J (Engl). 126:4392–4394.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang XF, Tu CS, Xing DJ, Gan DK, Xu GZ
and Jin ZB: R102W mutation in the RS1 gene responsible for
retinoschisis and recurrent glaucoma. Int J Ophthalmol. 7:169–172.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wu WW and Molday RS: Defective discoidin
domain structure subunit assembly, and endoplasmic reticulum
processing of retinoschisin are primary mechanisms responsible for
X-linked retinoschisis. J Biol Chem. 278:28139–28146.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sauer CG, Gehrig A, Warneke-Wittstock R,
Marquardt A, Ewing CC, Gibson A, Lorenz B, Jurklies B and Weber BH:
Positional cloning of the gene associated with X-linked juvenile
retinoschisis. Nat Genet. 17:164–170. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gehrig AE, Warneke-Witstock R, Sauer CG
and Weber BH: Isolation and characterization of the murine X-linked
juvenile retinoschisis (Rs 1 h) gene. Mamm Genome. 10:303–307.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Robert SM, Ulrich K and Bernhard HF:
X-linked juvenile retinoschisis: Clinical diagnosis, genetic
analysis, and molecular mechanisms. Prog Retin Eye Res. 31:195–212.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Baumgartner S, Hofmann K,
Chiquet-Ehrismann R and Bucher P: The discoidin domain family
revisited: New members from prokaryotes and a homology-based fold
prediction. Protein Sci. 7:1626–1631. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Raymond A, Ensslin MA and Shur BD:
SED1/MFG-E8: A bi-motif protein that orchestrated diverse cellular
interaction. J Cell Biochem. 106:957–966. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kim LS, Seiple W, Fishman GA and Szlyk JP:
Multifocal ERG findings in carriers of X-linked retinoschisis. Doc
Ophthalmol. 114:21–26. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Grayson C, Reid SN, Ellis JA, Rutherford
A, Sowden JC, Yates JR, Farber DB and Trump D: Retinoschisin, the
X-linked retinoschisis protein, is a secreted photoreceptor
protein, and is expressed and released by Weri-Rb1 cell. Hum Mol
Genet. 9:1873–1879. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fraternali F, Cavallo L and Musco G:
Effect of pathological mutations on the stability of a conserved
amino acid triad in retinoschisin. FEBS Lett. 544:21–26.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sergeev YV, Caruso RC, Meltzer MR, Smaoui
N, MacDonald IM and Sieving PA: Molecular modeling of retinoschisin
with functional analysis of pathogenic mutations from human
X-linked retinoschisis. Hum Mol Genet. 19:1302–1313.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhao C, Zhang Q, Jin HY and Zhao PQ:
Clinical observations of vitreoretinal surgery for four different
phenotypes of X-linked congenital retinoschisis. Int J Ophthalmol.
11:986–990. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Tantri A, Vrabec TR, Cu-Unjieng G, Frost
A, Annesley WH Jr and Donoso LA: X-linked retinoshisis: A clinical
and molecular genetic review. Surv Ophthalmol. 49:214–230.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zeng Y, Takada Y, Kjellstrom S, Hiriyanna
K, Tanikawa A, Wawrousedk E, Smaoui N, Caruso R, Bushu RA and
Sieving PA: RS-1 gene delivery to an adult Rs1h knockout mouse
model restores ERG b-wave with reversal of the electronegative
waveform of X-linked retinoschisis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
45:3279–3285. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Min SH, Molday LL, Seeliger MW, Dinculescu
A, Timmers AM, Janssen A, Tonagel F, Tanimoto N, Weber BH, Molday
RS and Hauswirth WW: Prolonged recovery of retinal
stucture/function after gene therapy in an Rs1h-deficient mouse
model of X-linked juvenile retinoschisis. Mol Ther. 12:644–651.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Bashar AE, Metcalfe AL, Viringipurampeer
IA, Yanai A, Gregory-Evans CY and Gregory-Evans K: An ex vivo gene
therapy approach in X-linked retinoschisis. Mol Vis. 22:718–733.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Apushkin MA and Fishman GA: Use of
dorzolamide for patients with X-linked retinoschisis. Retina.
26:741–745. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|