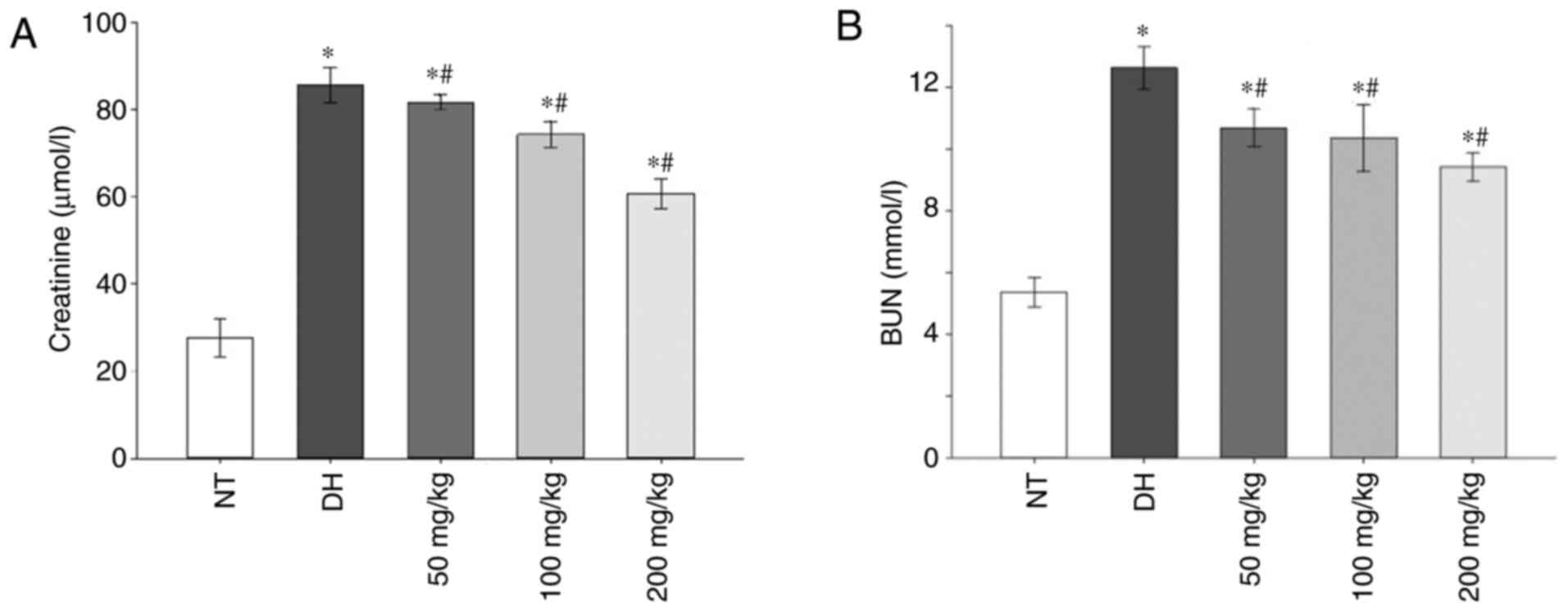
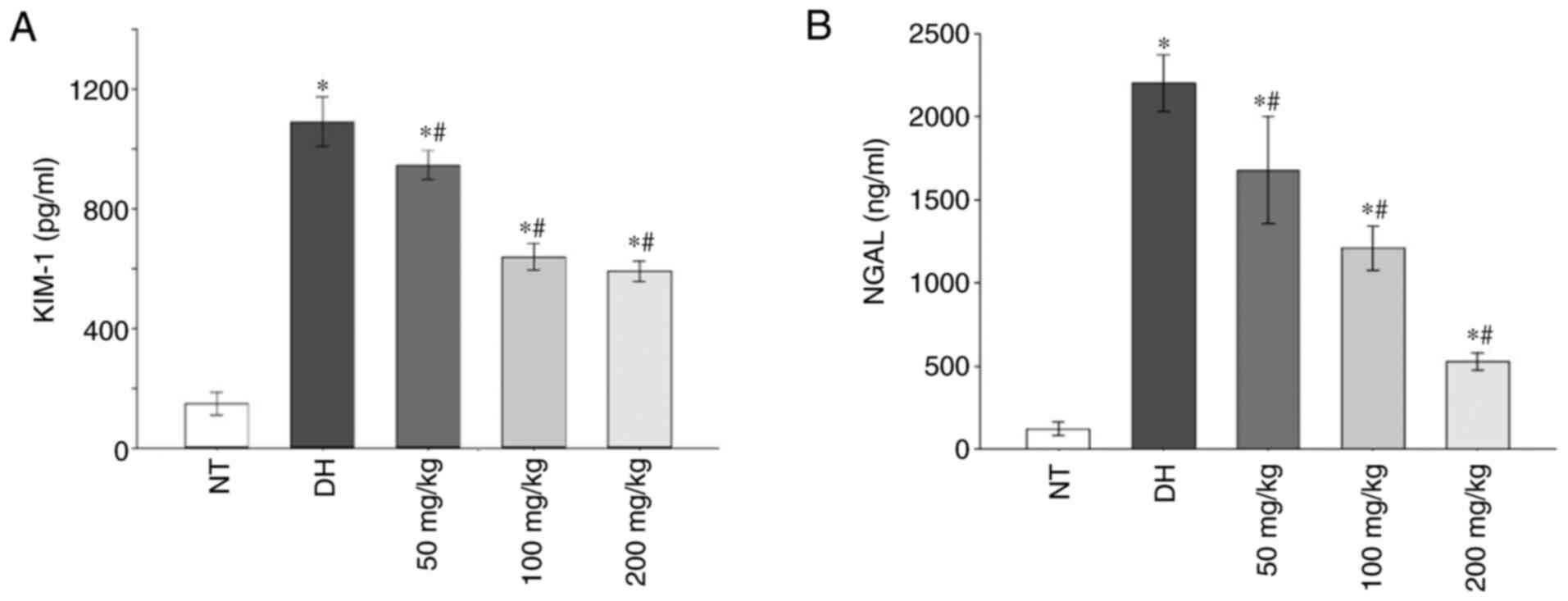
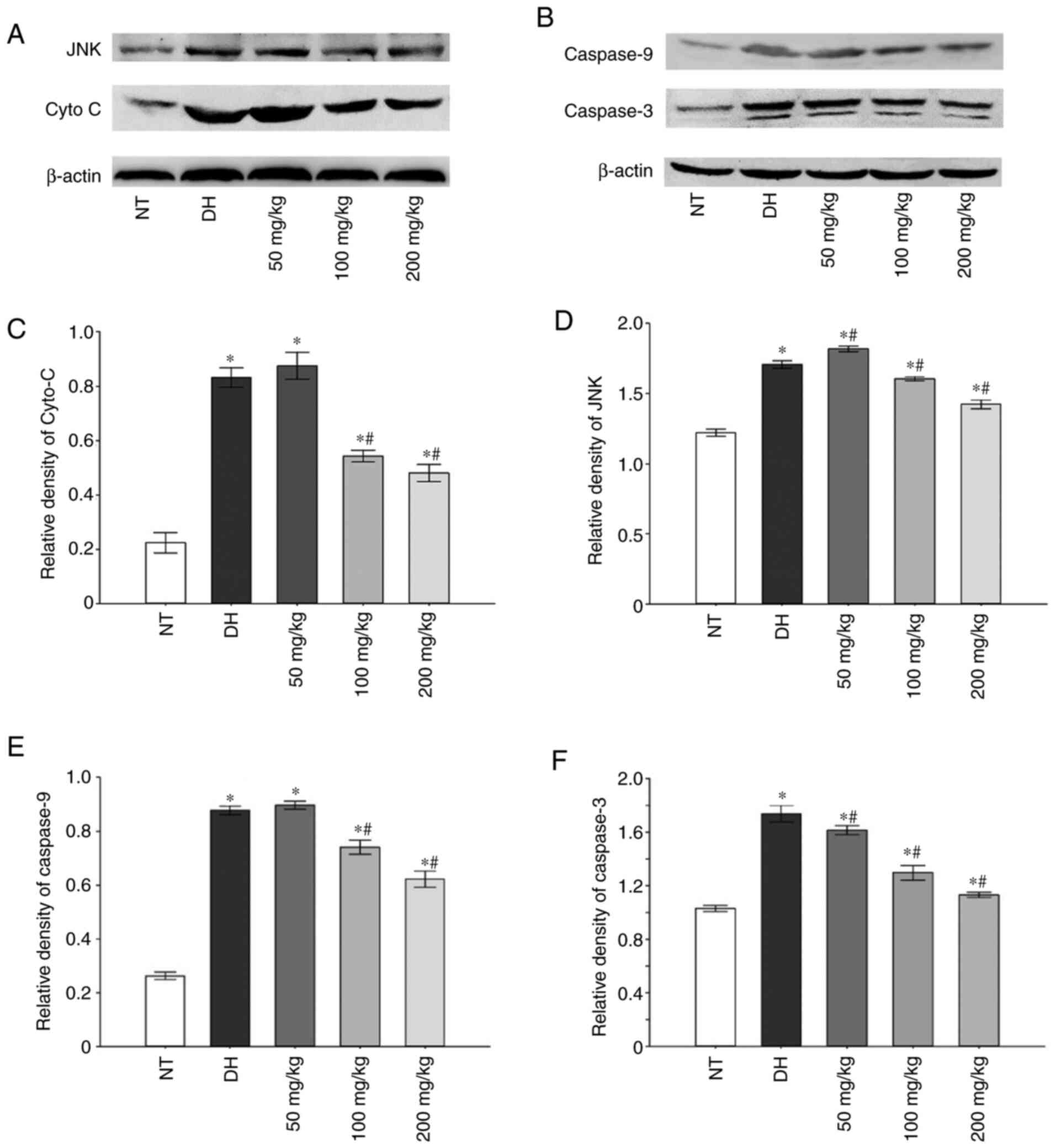
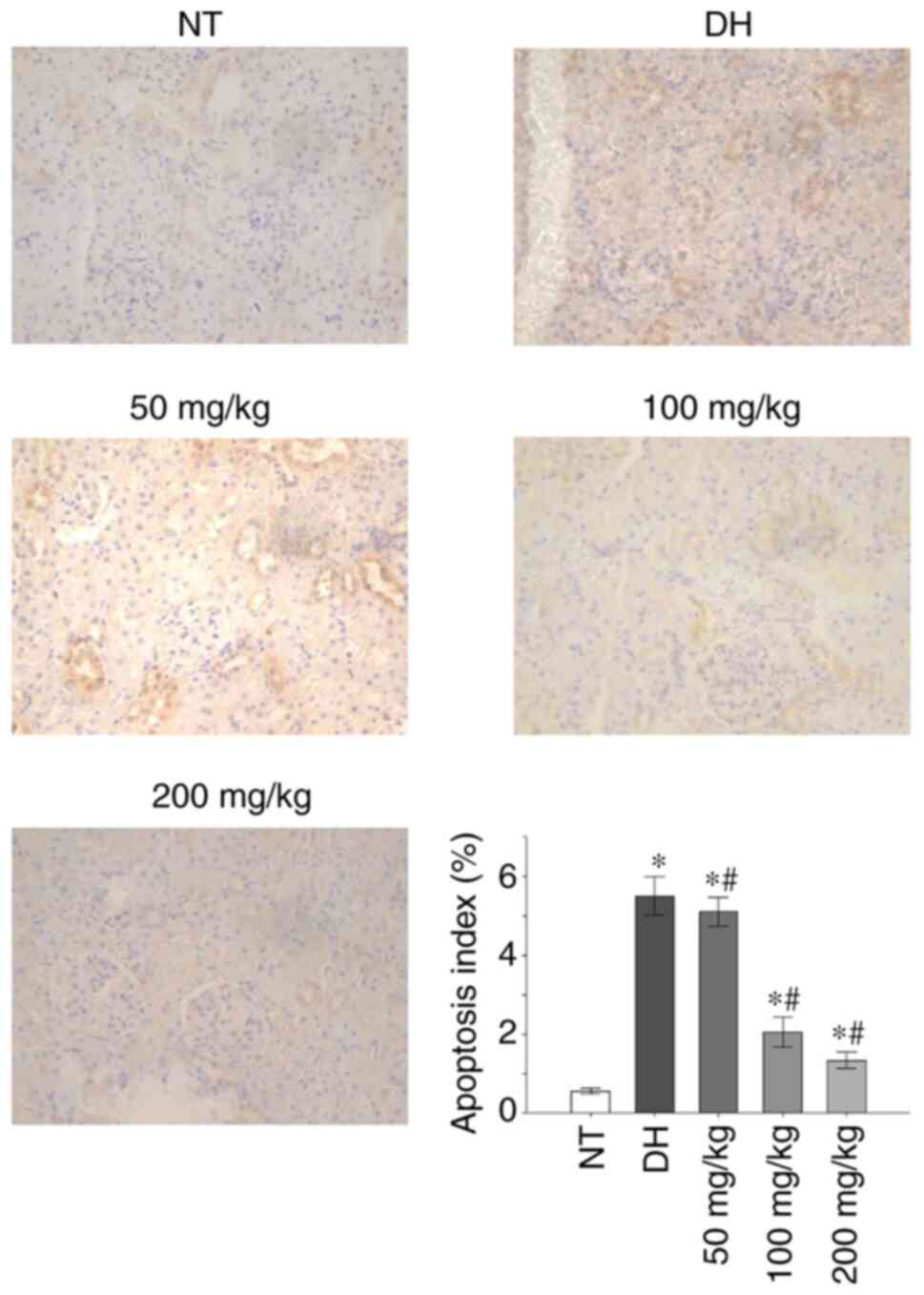
|
1
|
Bouchama A and Knochel JP: Heat stroke. N
Engl J Med. 346:1978–1988. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Al Mahri S and Bouchama A: Heatstroke.
Handb Clin Neurol. 157:531–545. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Heled Y, Fleischmann C and Epstein Y:
Cytokines and their role in hyperthermia and heatstroke. J Basic
Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 24:85–96. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bouchama A, Roberts G, Al Mohanna F,
El-Sayed R, Lach B, Chollet-Martin S, Ollivier V, Al Baradei R,
Loualich A, Nakeeb S, et al: Inflammatory, hemostatic, and clinical
changes in a baboon experimental model for heatstroke. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 98:697–705. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Roberts GT, Ghebeh H, Chishti MA,
Al-Mohanna F, El-Sayed R, Al-Mohanna F and Bouchama A:
Microvascular injury, thrombosis, inflammation, and apoptosis in
the pathogenesis of heatstroke: A study in baboon model.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:1130–1136. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Khogali M: Heat-related illnesses. Middle
East J Anaesthesiol. 12:531–572. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gong L, Zhang Q, Pan X, Chen S, Yang L,
Liu B, Yang W, Yu L, Xiao ZX, Feng XH, et al: p53 protects cells
from death at the heatstroke threshold temperature. Cell Rep.
29:3693–3707.e5. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lim CL and Mackinnon LT: The roles of
exercise-induced immune system disturbances in the pathology of
heat stroke: The dual pathway model of heat stroke. Sports Med.
36:39–64. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sakaguchi Y, Stephens CL, Makino M, Kaneko
T, Strebel FR, Danhauser LL, Jenkins GN and Bull JM: Apoptosis in
tumors and normal tissues induced by whole body hyperthermia in
rats. Cancer Res. 55:5459–5464. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Unlu A, Nayir E, Dogukan Kalenderoglu M,
Kirca O and Ozdogan M: Curcumin Turmeric) and cancer. J BUON.
21:1050–1060. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Newman RA and
Aggarwal BB: Bioavailability of curcumin: Problems and promises.
Mol Pharm. 4:807–818. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mirzaei H, Shakeri A, Rashidi B, Jalili A,
Banikazemi Z and Sahebkar A: Phytosomal curcumin: A review of
pharmacokinetic, experimental and clinical studies. Biomed
Pharmacother. 85:102–112. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
He L, Peng X, Zhu J, Liu G, Chen X, Tang
C, Liu H, Liu F and Peng Y: Protective effects of curcumin on acute
gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
93:275–282. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Abdel-Moneim AM, El-Toweissy MY, Ali AM,
Awad Allah AA, Darwish HS and Sadek IS: Curcumin ameliorates lead
(Pb(2+))-induced hemato-biochemical alterations and renal oxidative
damage in a rat model. Biol Trace Elem Res. 168:206–220.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hismiogullari AA, Hismiogullari SE, Karaca
O, Sunay FB, Paksoy S, Can M, Kus I, Seyrek K and Yavuz O: The
protective effect of curcumin administration on carbon
tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Pharmacol Rep.
67:410–416. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jiang J, Liu J, Li J, Tao L, Wang Z, Yang
L, Shi W and Ma N: Effect of curcumin on expressions of CD11b and
CD19 in peripheral blood of heat stroke rats in a simulation
dry-heat environment. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue.
31:221–224. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Cao W, Cao JJ, Liu JW, Li JJ, Shen CF,
Song LY, Ma N, Shi WH and Xu Q: Effects of curcumin pretreatment on
lung injury and HMGB-1 and ICAM-1 mRNA in heat stroke rats in
desert dry heat environment. Prog Mod Biomed. 18:652–656. 2018.
|
|
18
|
ou Zhou R, Liu JW, Zhang D and Zhang Q:
Heatstroke model for desert dry-heat environment and observed organ
damage. Am J Emerg Med. 32:573–579. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhu YH and Pei ZM: GSK2193874 treatment at
heatstroke onset reduced cell apoptosis in heatstroke mice. Cell
Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 64:36–42. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Geng Y, Ma Q, Liu YN, Peng N, Yuan FF, Li
XG, Li M, Wu YS, Li BL, Song WB, et al: Heatstroke induces liver
injury via IL-1β and HMGB1-induced pyroptosis. J Hepatol.
63:622–633. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ji J, Hong X, Su L and Liu Z: Proteomic
identification of hippocalcin and its protective role in
heatstroke-induced hypothalamic injury in mice. J Cell Physiol.
234:3775–3789. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hsu YL, Yu HS, Lin HC, Wu KY, Yang RC and
Kuo PL: Heat shock induces apoptosis through reactive oxygen
species involving mitochondrial and death receptor pathways in
corneal cells. Exp Eye Res. 93:405–412. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Milleron RS and Bratton SB: Heat shock
induces apoptosis independently of any known initiator
caspase-activating complex. J Biol Chem. 281:16991–17000.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
North S and Hainaut P: P53 and cell cycle
control: A finger in every pie. Pathol Biol (Paris). 48:255–270.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ye F, Deng PY, Li D, Luo D, Li NS, Deng S,
Deng HW and Li YJ: Involvement of endothelial cell-derived CGRP in
heat stress-induced protection of endothelial function. Vasc
Pharmacol. 46:238–246. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: A basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257.
1972.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jeong SY and Seol DW: The role of
mitochondria in apoptosis. BMB Rep. 41:11–22. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Santra S, Kaittanis C and Perez JM:
Cytochrome C encapsulating theranostic nanoparticles: A novel
bifunctional system for targeted delivery of therapeutic
membrane-impermeable proteins to tumors and imaging of cancer
therapy. Mol Pharm. 7:1209–1222. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yamada Y and Harashima H: Mitochondrial
drug delivery systems for macromolecule and their therapeutic
application to mitochondrial diseases. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
60:1439–1462. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wang Y, Xia C, Lun Z, Lv Y, Chen W and Li
T: Crosstalk between p38 MAPK and caspase-9 regulates
mitochondria-mediated apoptosis induced by
tetra-α-(4-carboxyphenoxy) phthalocyanine zinc photodynamic therapy
in LoVo cells. Oncol Rep. 39:61–70. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen YJ, Liu WH, Kao PH, Wang JJ and Chang
LS: Involvement of p38 MAPK- and JNK-modulated expression of Bcl-2
and Bax in Naja nigricollis CMS-9-induced apoptosis of human
leukemia K562 cells. Toxicon. 55:1306–1316. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Deng YT, Huang HC and Lin JK: Rotenone
induces apoptosis in MCF07 human breast cancer cell-mediated ROS
through JNK and p38 signaling. Mol Carcinog. 49:141–151.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kang YH and Lee SJ: The role of p38 MAPK
and JNK in Arsenic trioxide-induced mitochondrial cell death in
human cervical cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 217:23–33.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Su JC, Lin KL, Chien CM, Lu CM, Chen YL,
Chang LS and Lin SR: Novel indoloquinoline derivative, IQDMA,
induces G(2)/M phase arrest and apoptosis in A549 cells through
JNK/p38 MAPK signaling activation. Life Sci. 85:505–516.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|