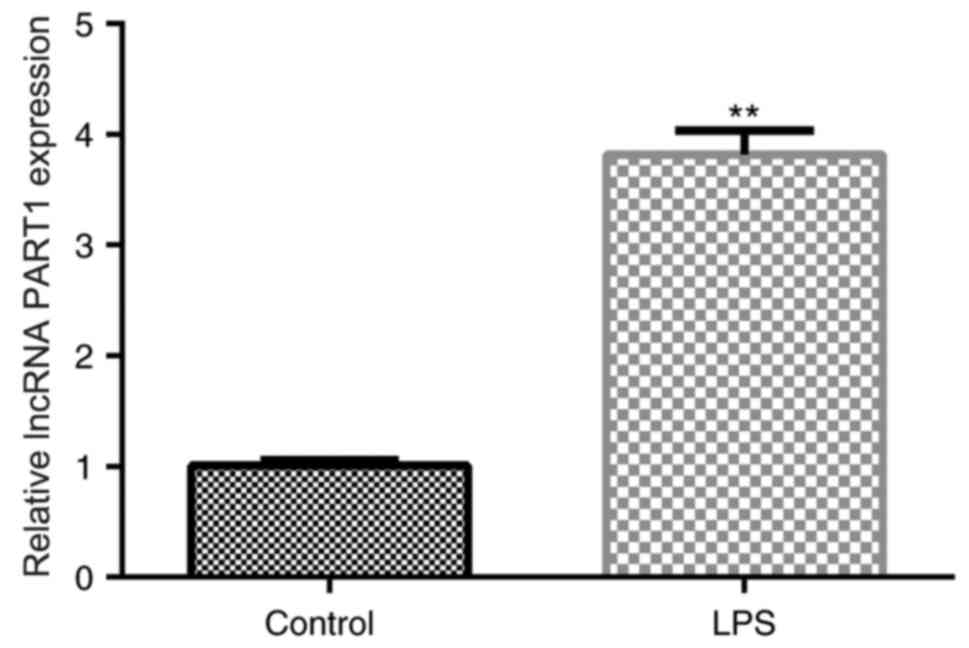
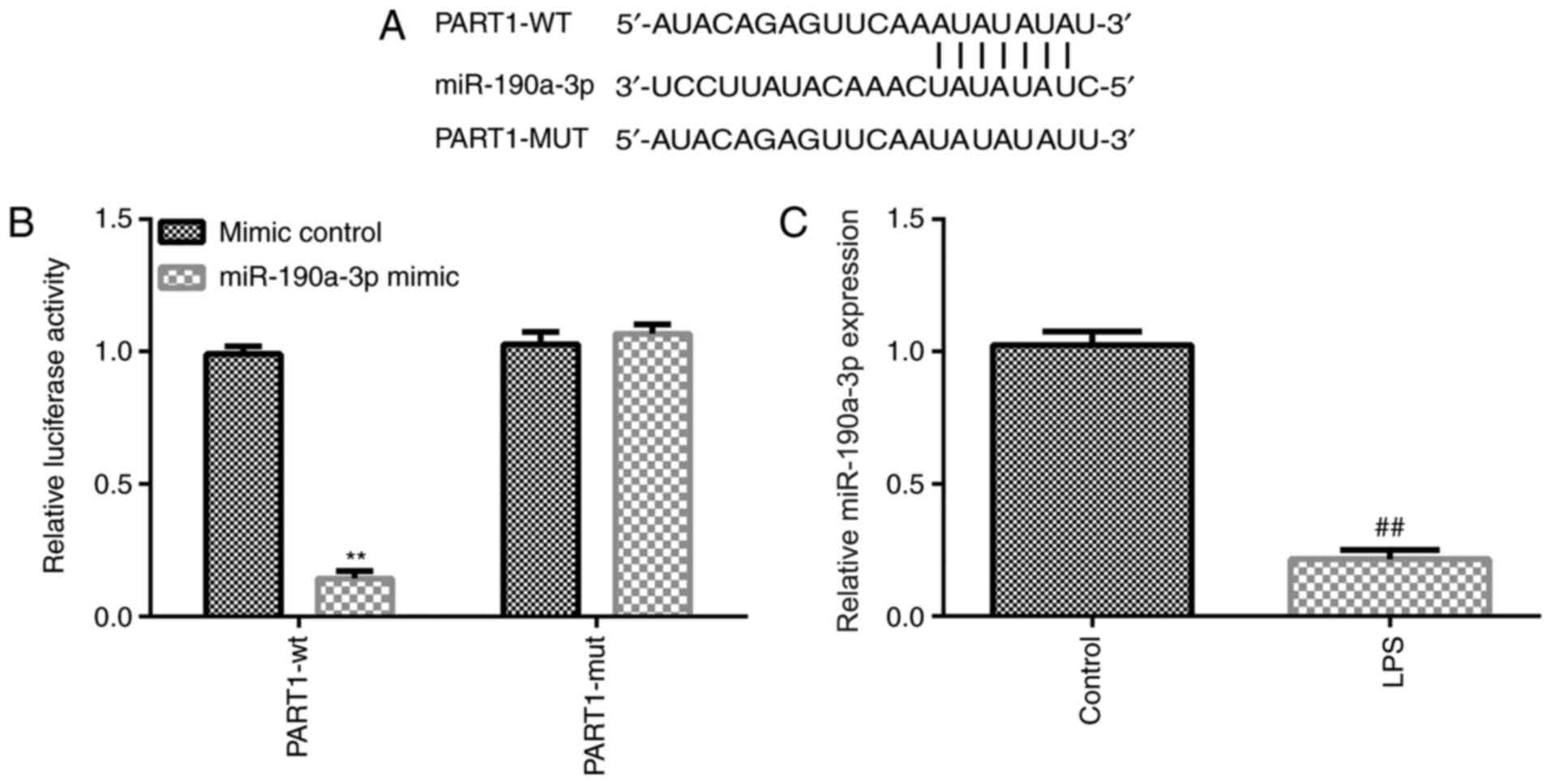
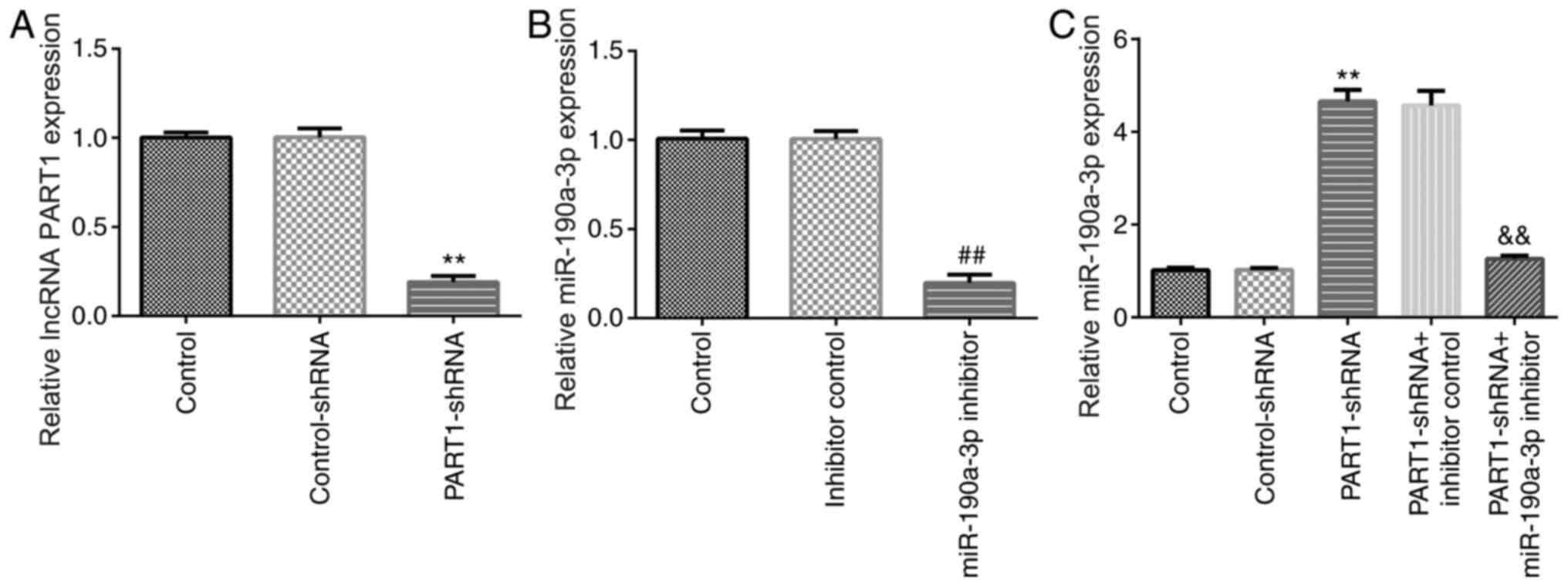
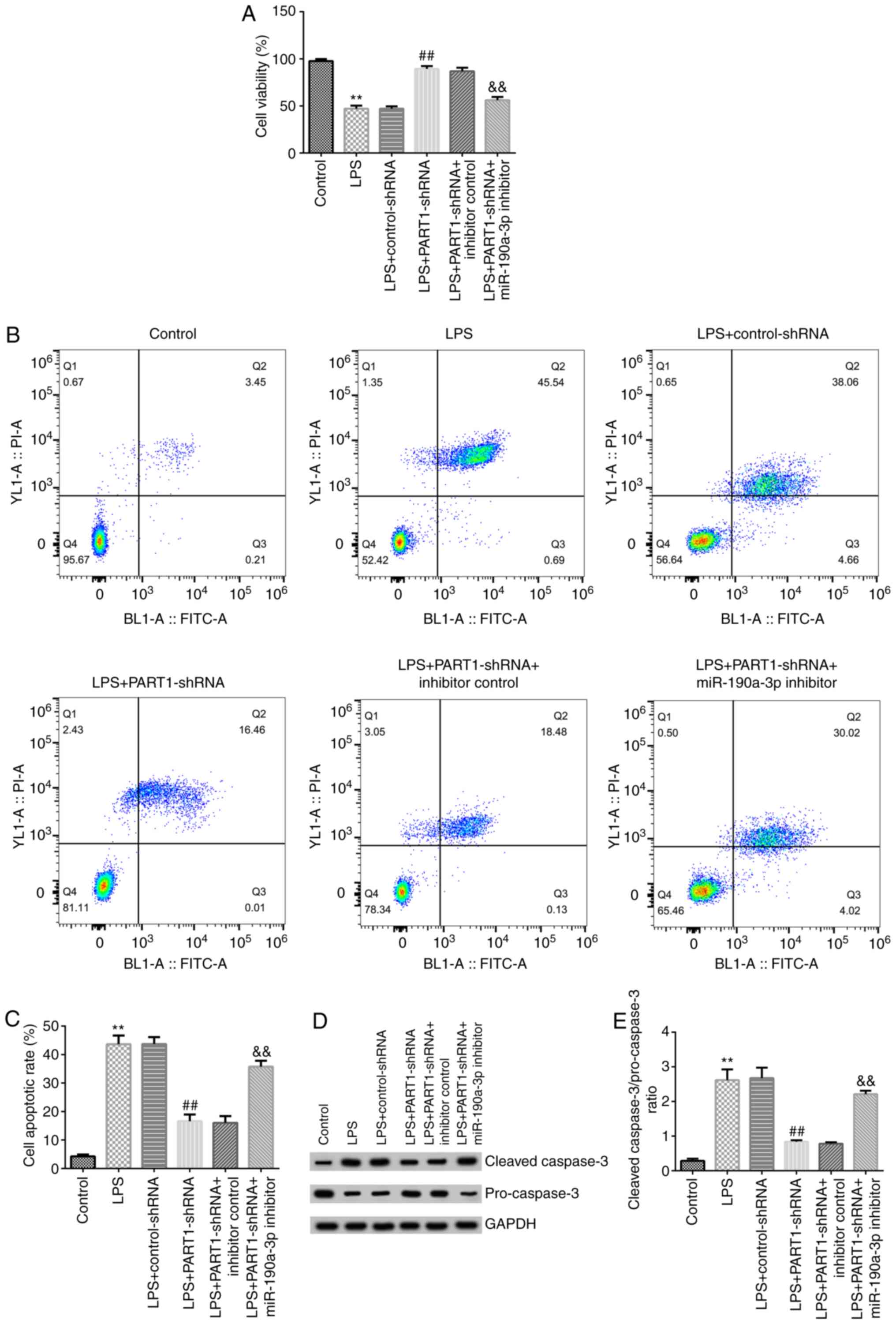
|
1
|
Hoy D, March L, Brooks P, Blyth F, Woolf
A, Bain C, Williams G, Smith E, Vos T, Barendregt J, et al: The
global burden of low back pain: Estimates from the global burden of
disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 73:968–974. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Walker BF: The prevalence of low back
pain: A systematic review of the literature from 1966 to 1998. J
Spinal Disord. 13:205–217. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Steenstra IA, Verbeek JH, Heymans MW and
Bongers PM: Prognostic factors for duration of sick leave in
patients sick listed with acute low back pain: A systematic review
of the literature. Occup Environ Med. 62:851–860. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Munir S, Rade M, Määttä JH, Freidin MB and
Williams FMK: Intervertebral disc biology: Genetic basis of disc
degeneration. Curr Mol Biol Rep. 4:143–150. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wu H, Shang Y, Yu J, Zeng X, Lin J, Tu M,
Cheang LH and Zhang J: Regenerative potential of human nucleus
pulposus resident stem/progenitor cells declines with ageing and
intervertebral disc degeneration. Int J Mol Med. 42:2193–2202.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Segar AH, Fairbank J and Urban J: Leptin
and the intervertebral disc: A biochemical link exists between
obesity, intervertebral disc degeneration and low back pain-an in
vitro study in a bovine model. Eur Spine J. 28:214–223.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kadow T, Sowa G, Vo N and Kang JD:
Molecular basis of intervertebral disc degeneration and
herniations: What are the important translational questions? Clin
Orthop Relat Res. 473:1903–1912. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cui S, Liu Z, Tang B, Wang Z and Li B:
lncRNA MAGI2-AS3 is down-regulated in intervertebral disc
degeneration and participates in the regulation of FasL expression
in nucleus pulposus cells. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.
21(149)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gao C, Ning B, Sang C and Zhang Y:
Rapamycin prevents the intervertebral disc degeneration via
inhibiting differentiation and senescence of annulus fibrosus
cells. Aging (Albany NY). 10:131–143. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jiang C, Guo Q, Jin Y, Xu JJ, Sun ZM, Zhu
DC, Lin JH, Tian NF, Sun LJ, Zhang XL and Wu YS: Inhibition of EZH2
ameliorates cartilage endplate degeneration and attenuates the
progression of intervertebral disc degeneration via demethylation
of Sox-9. EBioMedicine. 48:619–629. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tan Y, Yao X, Dai Z, Wang Y and Lv G: Bone
morphogenetic protein 2 alleviated intervertebral disc degeneration
through mediating the degradation of ECM and apoptosis of nucleus
pulposus cells via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med. 43:583–592.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu J, Liu ZX, Wu QN, Lu YX, Wong CW, Miao
L, Wang Y, Wang Z, Jin Y, He MM, et al: Long noncoding RNA AGPG
regulates PFKFB3-mediated tumor glycolytic reprogramming. Nat
Commun. 11(1507)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zou X, Guo ZH, Li Q and Wang PS: Long
noncoding RNA LINC00460 modulates MMP-9 to promote cell
proliferation, invasion and apoptosis by targeting miR-539 in
papillary thyroid cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 12:199–207.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Pei Q, Liu GS, Li HP, Zhang Y, Xu XC, Gao
H, Zhang W and Li T: Long noncoding RNA SNHG14 accelerates cell
proliferation, migration, invasion and suppresses apoptosis in
colorectal cancer cells by targeting miR-944/KRAS axis through
PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 23:9871–9881.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhu D, Yu Y, Wang W, Wu K, Liu D, Yang Y,
Zhang C, Qi Y and Zhao S: Long noncoding RNA PART1 promotes
progression of non-small cell lung cancer cells via JAK-STAT
signaling pathway. Cancer Med. 8:6064–6081. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhou T, Wu L, Ma N, Tang F, Zong Z and
Chen S: lncRNA PART1 regulates colorectal cancer via targeting
miR-150-5p/miR-520h/CTNNB1 and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 118(105637)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhao B, Lu M, Wang D, Li H and He X:
Genome-wide identification of long noncoding RNAs in human
intervertebral disc degeneration by RNA sequencing. Biomed Res Int.
2016(3684875)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gao D, Hao L and Zhao Z: Long non-coding
RNA PART1 promotes intervertebral disc degeneration through
regulating the miR-93/MMP2 pathway in nucleus pulposus cells. Int J
Mol Med. 46:289–299. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Attia H, Abdelrahman AH, Ibrahim MH, Eid
MM, Eid OM, Sallam MT, El Gammal MM and Kamel MM: Altered
expression of microRNAs in the bone marrow of multiple myeloma
patients and their relationship to cytogenetic aberrations. Curr
Pharm Biotechnol: Mar 20, 2020 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
20
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:1202–1207. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu B, Li J and Cairns MJ: Identifying
miRNAs, targets and functions. Brief Bioinform. 15:1–19.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Luo H, Han Y, Liu J and Zhang Y:
Identification of microRNAs in granulosa cells from patients with
different levels of ovarian reserve function and the potential
regulatory function of miR-23a in granulosa cell apoptosis. Gene.
686:250–260. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Veshkini A, Mohammadi-Sangcheshmeh A,
Alamouti AA, Kouhkan F and Salehi A: Maternal supplementation with
fish oil modulates inflammation-related MicroRNAs and genes in
suckling lambs. Trop Anim Health Prod. 52:1561–1572.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Shen S, Luo X, Gao K, Sun Y, Yao D and Zhu
L: Identification and integrative analysis of microRNAs and mRNAs
involved in proliferation and invasion of pressure-treated human
liver cancer cell lines. Mol Med Rep. 20:375–387. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gao H, Han Z, Huang S, Bai R, Ge X, Chen F
and Lei P: Intermittent hypoxia caused cognitive dysfunction relate
to miRNAs dysregulation in hippocampus. Behav Brain Res. 335:80–87.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jin Z, Piao L, Sun G, Lv C, Jing Y and Jin
R: Long non-coding RNA PART1 exerts tumor suppressive functions in
glioma via sponging miR-190a-3p and inactivation of PTEN/AKT
pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 13:1073–1086. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhu J, Tang H, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Qiu C,
Zhang L, Huang P and Li F: Kaempferol slows intervertebral disc
degeneration by modifying LPS-induced osteogenesis/adipogenesis
imbalance and inflammation response in BMSCs. Int Immunopharmacol.
43:236–242. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang H, Hao P, Zhang H, Xu C and Zhao J:
MicroRNA-223 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory
response by directly targeting Irak1 in the nucleus pulposus cells
of intervertebral disc. IUBMB Life. 70:479–490. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yuan M, Pai PJ, Liu X, Lam H and Chan BP:
Proteomic analysis of nucleus pulposus cell-derived extracellular
matrix niche and its effect on phenotypic alteration of dermal
fibroblasts. Sci Rep. 8(1512)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhang C, Gullbrand SE, Schaer TP, Lau YK,
Jiang Z, Dodge GR, Elliott DM, Mauck RL, Malhotra NR and Smith LJ:
Inflammatory cytokine and catabolic enzyme expression in a goat
model of intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res: Feb 24,
2020 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
32
|
Li L, Wan G, Han B and Zhang Z:
Echinacoside alleviated LPS-induced cell apoptosis and inflammation
in rat intestine epithelial cells by inhibiting the mTOR/STAT3
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 104:622–628. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Dong ZW and Yuan YF: Juglanin suppresses
fibrosis and inflammation response caused by LPS in acute lung
injury. Int J Mol Med. 41:3353–3365. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ren Q, Zhao S, Ren C and Ma Z: Astragalus
polysaccharide alleviates LPS-induced inflammation injury by
regulating miR-127 in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 32(2058738418759180)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Yang J, Zhou X, Wang N, Li Z,
Zhou Y, Feng J, Shen D and Zhao W: Knockdown of miR-222 inhibits
inflammation and the apoptosis of LPS-stimulated human
intervertebral disc nucleus pulposus cells. Int J Mol Med.
44:1357–1365. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shi X, Sun M, Liu H, Yao Y and Song Y:
Long non-coding RNAs: A new frontier in the study of human
diseases. Cancer Lett. 339:159–166. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sun M, Geng D, Li S, Chen Z and Zhao W:
lncRNA PART1 modulates toll-like receptor pathways to influence
cell proliferation and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Biol
Chem. 399:387–395. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lou T, Ke K, Zhang L, Miao C and Liu Y:
lncRNA PART1 facilitates the malignant progression of colorectal
cancer via miR-150-5p/LRG1 axis. J Cell Biochem. 121:4271–4281.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhuan B, Lu Y, Chen Q, Zhao X, Li P, Yuan
Q and Yang Z: Overexpression of the long noncoding RNA TRHDE-AS1
inhibits the progression of lung cancer via the miRNA-103/KLF4
axis. J Cell Biochem. 120:17616–17624. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Shu T, He L, Wang X, Pang M, Yang B, Feng
F, Wu Z, Liu C, Zhang S, Liu B, et al: Long noncoding RNA UCA1
promotes chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells via miRNA-145-5p/SMAD5 and
miRNA-124-3p/SMAD4 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 514:316–322.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Huang Y: The novel regulatory role of
lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med.
22:5768–5775. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wang W, Lou W, Ding B, Yang B, Lu H, Kong
Q and Fan W: A novel mRNA-miRNA-lncRNA competing endogenous RNA
triple sub-network associated with prognosis of pancreatic cancer.
Aging (Albany NY). 11:2610–2627. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Mi D, Cai C, Zhou B, Liu X, Ma P, Shen S,
Lu W and Huang W: Long non-coding RNA FAF1 promotes intervertebral
disc degeneration by targeting the Erk signaling pathway. Mol Med
Rep. 17:3158–3163. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Li Z, Li X, Chen C, Chan MTV, Wu WKK and
Shen J: Melatonin inhibits nucleus pulposus (NP) cell proliferation
and extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling via the melatonin
membrane receptors mediated PI3K-Akt pathway. J Pineal Res 63,
2017.
|
|
45
|
Fuchs Y and Steller H: Live to die another
way: Modes of programmed cell death and the signals emanating from
dying cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 16:329–344. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Soteriou D and Fuchs Y: A matter of life
and death: Stem cell survival in tissue regeneration and tumour
formation. Nat Rev Cancer. 18:187–201. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Guo Y, Tian L, Liu X, He Y, Chang S and
Shen Y: ERRFI1 inhibits proliferation and inflammation of nucleus
pulposus and is negatively regulated by miR-2355-5p in
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
44:E873–E881. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|