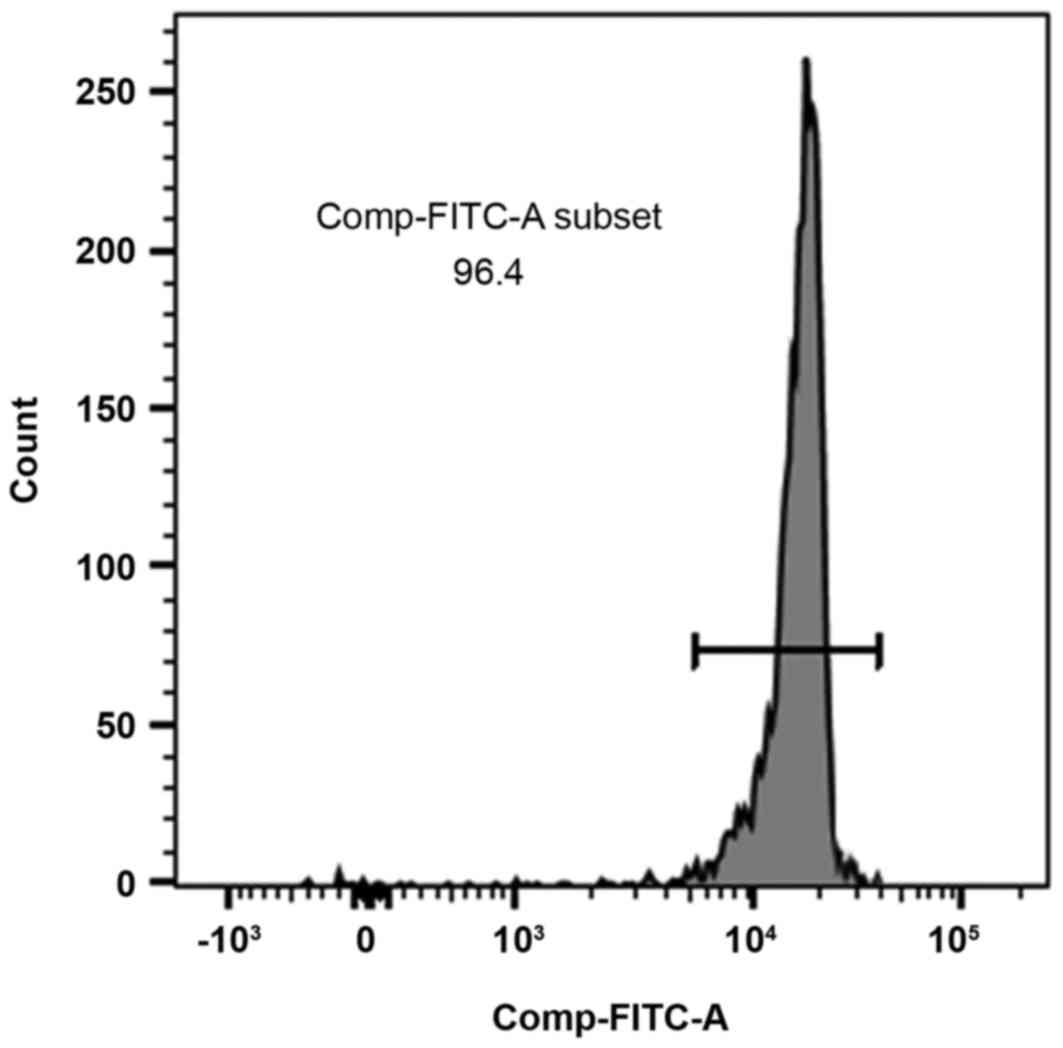
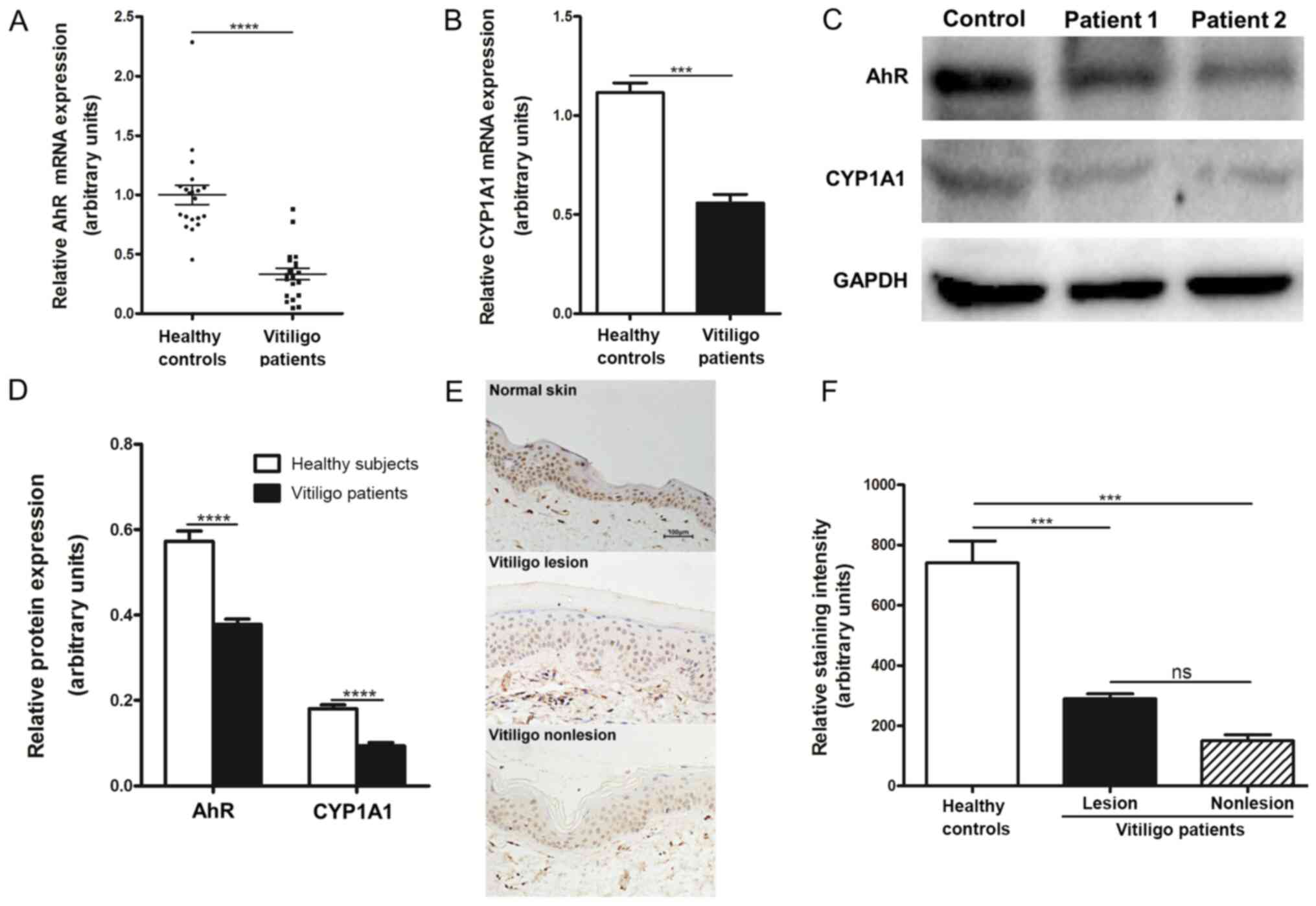
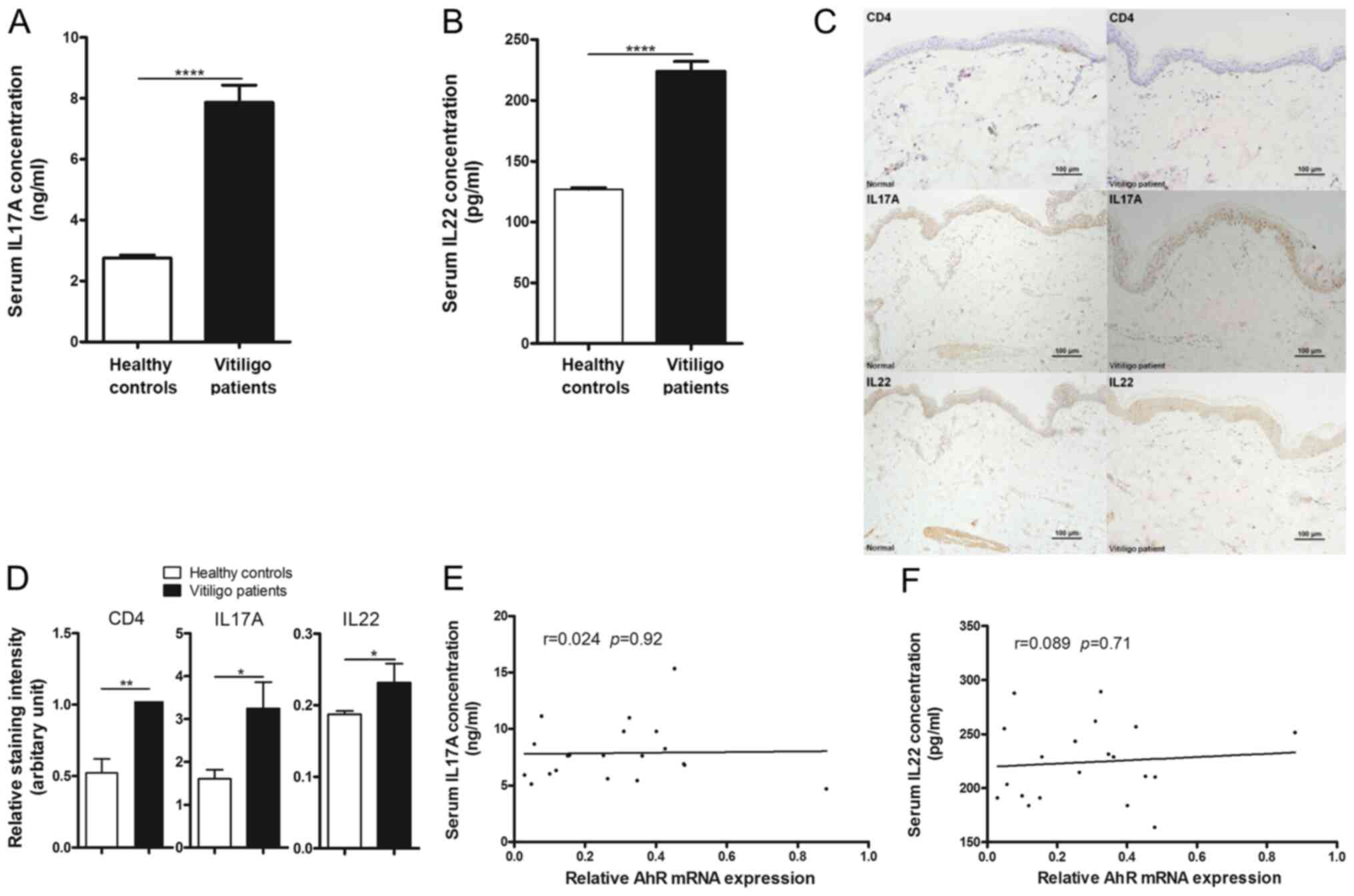
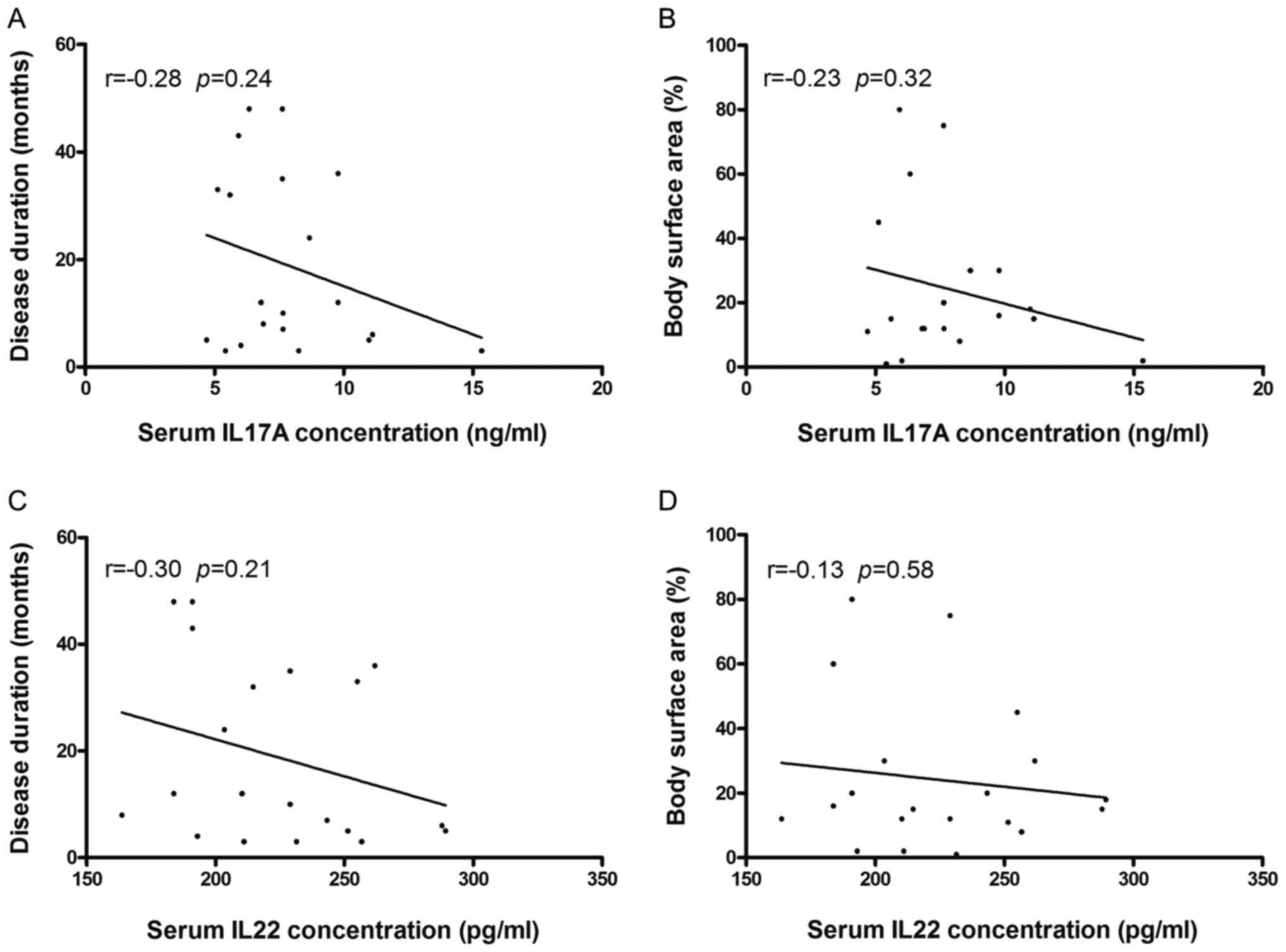
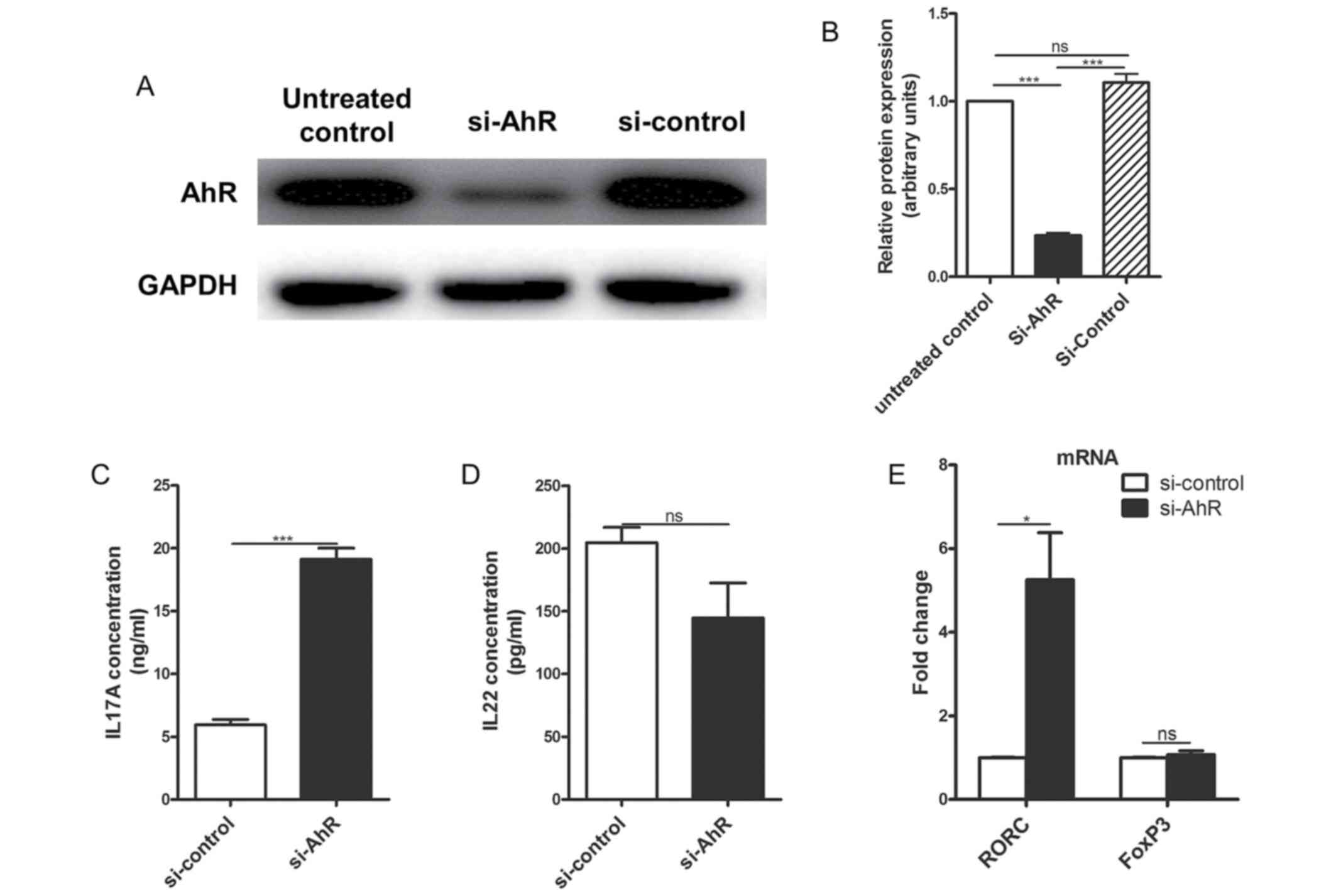
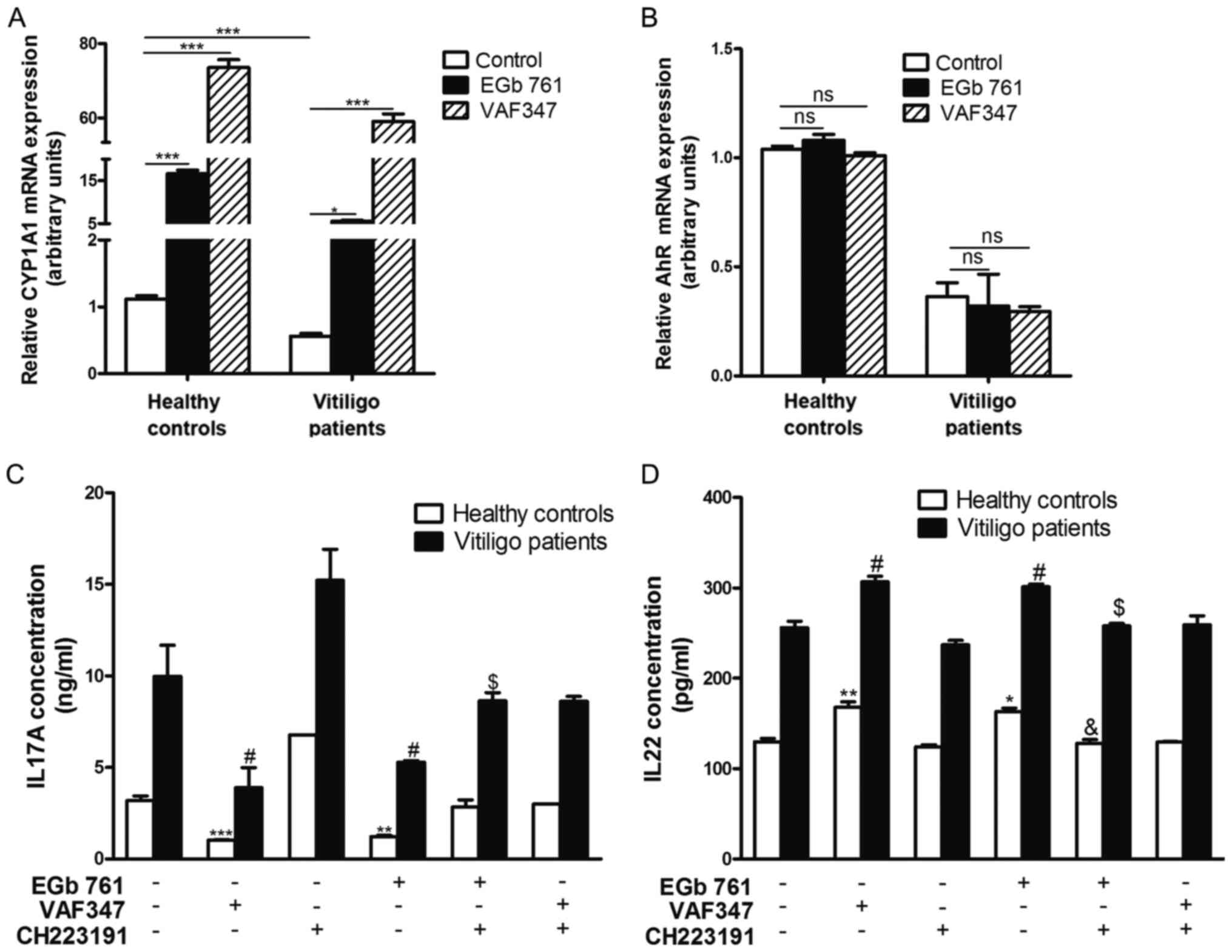
|
1
|
Ezzedine K, Lim HW, Suzuki T, Katayama I,
Hamzavi I, Lan CC, Goh BK, Anbar T, Silva de Castro C, Lee AY, et
al: Vitiligo Global Issue Consensus Conference Panelists. Revised
classification/nomenclature of vitiligo and related issues: The
Vitiligo Global Issues Consensus Conference. Pigment Cell Melanoma
Res. 25:E1–E13. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Alikhan A, Felsten LM, Daly M and
Petronic-Rosic V: Vitiligo: A comprehensive overview Part I.
Introduction, epidemiology, quality of life, diagnosis,
differential diagnosis, associations, histopathology, etiology, and
work-up. J Am Acad Dermatol. 65:473–491. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rodrigues M, Ezzedine K, Hamzavi I, Pandya
AG and Harris JE: Vitiligo Working Group. New discoveries in the
pathogenesis and classification of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol.
77:1–13. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yang XO, Pappu BP, Nurieva R, Akimzhanov
A, Kang HS, Chung Y, Ma L, Shah B, Panopoulos AD, Schluns KS, et
al: T helper 17 lineage differentiation is programmed by orphan
nuclear receptors ROR alpha and ROR gamma. Immunity. 28:29–39.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang L, Li YG, Li YH, Qi L, Liu XG, Yuan
CZ, Hu NW, Ma DX, Li ZF, Yang Q, et al: Increased frequencies of
Th22 cells as well as Th17 cells in the peripheral blood of
patients with ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS
One. 7(e31000)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Behfarjam F, Mansouri P and Jadali Z:
Imbalance of Peripheral Blood T Helper Type 17 Responses in
Patients with Vitiligo. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 17:171–178.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bhardwaj S, Rani S, Srivastava N, Kumar R
and Parsad D: Increased systemic and epidermal levels of IL-17A and
IL-1β promotes progression of non-segmental vitiligo. Cytokine.
91:153–161. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Czarnowicki T, He H, Leonard A, Kim HJ,
Kameyama N, Pavel AB, Li R, Estrada Y, Wen HC, Kimmel GW, et al:
Blood endotyping distinguishes the profile of vitiligo from that of
other inflammatory and autoimmune skin diseases. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 143:2095–2107. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sushama S, Dixit N, Gautam RK, Arora P,
Khurana A and Anubhuti A: Cytokine profile (IL-2, IL-6, IL-17,
IL-22, and TNF-α) in vitiligo-New insight into pathogenesis of
disease. J Cosmet Dermatol. 18:337–341. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Elela MA, Hegazy RA, Fawzy MM, Rashed LA
and Rasheed H: Interleukin 17, interleukin 22 and FoxP3 expression
in tissue and serum of non-segmental vitiligo: A case- controlled
study on eighty-four patients. Eur J Dermatol. 23:350–355.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Singh RK, Lee KM, Vujkovic-Cvijin I, Ucmak
D, Farahnik B, Abrouk M, Nakamura M, Zhu TH, Bhutani T, Wei M, et
al: The role of IL-17 in vitiligo: A review. Autoimmun Rev.
15:397–404. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mattapallil MJ, Kielczewski JL,
Zárate-Bladés CR, St Leger AJ, Raychaudhuri K, Silver PB,
Jittayasothorn Y, Chan CC and Caspi RR: Interleukin 22 ameliorates
neuropathology and protects from central nervous system
autoimmunity. J Autoimmun. 102:65–76. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Neil JA, Matsuzawa-Ishimoto Y,
Kernbauer-Hölzl E, Schuster SL, Sota S, Venzon M, Dallari S, Galvao
Neto A, Hine A, Hudesman D, et al: IFN-I and IL-22 mediate
protective effects of intestinal viral infection. Nat Microbiol.
4:1737–1749. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zenewicz LA: IL-22: There is a gap in our
knowledge. Immunohorizons. 2:198–207. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hahn ME: Aryl hydrocarbon receptors:
Diversity and evolution. Chem Biol Interact. 141:131–160.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Esser C, Rannug A and Stockinger B: The
aryl hydrocarbon receptor in immunity. Trends Immunol. 30:447–454.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wu Z, Mei X, Ying Z, Sun Y, Song J and Shi
W: Ultraviolet B inhibition of DNMT1 activity via AhR activation
dependent SIRT1 suppression in CD4+ T cells from systemic lupus
erythematosus patients. J Dermatol Sci. 86:230–237. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wu Z, Uchi H, Morino-Koga S,
Nakamura-Satomura A, Kita K, Shi W and Furue M: Z-Ligustilide
inhibits benzo(a)pyrene-induced CYP1A1 upregulation in cultured
human keratinocytes via ROS-dependent Nrf2 activation. Exp
Dermatol. 23:260–265. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rekik R, Ben Hmid A, Lajnef C, Zamali I,
Zaraa I and Ben Ahmed M: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR)
transcription is decreased in skin of vitiligo patients. Int J
Dermatol. 56:1509–1512. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Schallreuter KU, Salem MA, Gibbons NC,
Maitland DJ, Marsch E, Elwary SM and Healey AR: Blunted epidermal
L-tryptophan metabolism in vitiligo affects immune response and ROS
scavenging by Fenton chemistry, part 2: Epidermal
H2O2/ONOO(-)-mediated stress in vitiligo hampers indoleamine
2,3-dioxygenase and aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated immune
response signaling. FASEB J. 26:2471–2485. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tsuji G, Hashimoto-Hachiya A, Takemura M,
Kanemaru T, Ichihashi M and Furue M: Palladium and platinum
nanoparticles activate AHR and NRF2 in human
keratinocytes-implications in vitiligo therapy. J Invest Dermatol.
137:1582–1586. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
DeFeudis FV: A brief history of EGb 761
and its therapeutic uses. Pharmacopsychiatry. 36 (Suppl 1):S2–S7.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Parsad D, Pandhi R and Juneja A:
Effectiveness of oral Ginkgo biloba in treating limited,
slowly spreading vitiligo. Clin Exp Dermatol. 28:285–287.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Szczurko O and Boon HS: A systematic
review of natural health product treatment for vitiligo. BMC
Dermatol. 8(2)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Szczurko O, Shear N, Taddio A and Boon H:
Ginkgo biloba for the treatment of vitilgo vulgaris: An open
label pilot clinical trial. BMC Complement Altern Med.
11(21)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Whitton ME, Ashcroft DM and González U:
Therapeutic interventions for vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol.
59:713–717. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Koltermann A, Hartkorn A, Koch E, Fürst R,
Vollmar AM and Zahler S: Ginkgo biloba extract EGb 761
increases endothelial nitric oxide production in vitro and in vivo.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 64:1715–1722. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wu Z, Uchi H, Morino-Koga S, Shi W and
Furue M: Z-ligustilide ameliorated ultraviolet B-induced oxidative
stress and inflammatory cytokine production in human keratinocytes
through upregulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and suppression of NF-κB pathway.
Exp Dermatol. 24:703–708. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Behfarjam F and Jadali Z: Vitiligo
patients show significant up-regulation of aryl hydrocarbon
receptor transcription factor. An Bras Dermatol. 93:302–303.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang X, Li K, Liu L, Shi Q, Song P, Jian
Z, Guo S, Wang G, Li C and Gao T: AHR promoter variant modulates
its transcription and downstream effectors by allele-specific
AHR-SP1 interaction functioning as a genetic marker for vitiligo.
Sci Rep. 5(13542)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Rohlman D, Pham D, Yu Z, Steppan LB and
Kerkvliet NI: Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Mediated Perturbations in
Gene Expression during Early Stages of CD4(+) T-cell
Differentiation. Front Immunol. 3(223)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Alam MS, Maekawa Y, Kitamura A, Tanigaki
K, Yoshimoto T, Kishihara K and Yasutomo K: Notch signaling drives
IL-22 secretion in CD4+ T cells by stimulating the aryl hydrocarbon
receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:5943–5948. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Azizi G, Yazdani R and Mirshafiey A: Th22
cells in autoimmunity: A review of current knowledge. Eur Ann
Allergy Clin Immunol. 47:108–117. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Benghiat FS, Charbonnier LM, Vokaer B, De
Wilde V and Le Moine A: Interleukin 17-producing T helper cells in
alloimmunity. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 23:11–18. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Basak PY, Adiloglu AK, Ceyhan AM, Tas T
and Akkaya VB: The role of helper and regulatory T cells in the
pathogenesis of vitiligo. J Am Acad Dermatol. 60:256–260.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bassiouny DA and Shaker O: Role of
interleukin-17 in the pathogenesis of vitiligo. Clin Exp Dermatol.
36:292–297. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tembhre MK, Sharma VK, Sharma A,
Chattopadhyay P and Gupta S: T helper and regulatory T cell
cytokine profile in active, stable and narrow band ultraviolet B
treated generalized vitiligo. Clin Chim Acta. 424:27–32.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Plé C, Fan Y, Ait Yahia S, Vorng H,
Everaere L, Chenivesse C, Balsamelli J, Azzaoui I, de Nadai P,
Wallaert B, et al: Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons reciprocally
regulate IL-22 and IL-17 cytokines in peripheral blood mononuclear
cells from both healthy and asthmatic subjects. PLoS One.
10(e0122372)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Rajaraman G, Yang G, Chen J and Chang TK:
Modulation of CYP1B1 and CYP1A1 gene expression and activation of
aryl hydrocarbon receptor by Ginkgo biloba extract in
MCF-10A human mammary epithelial cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol.
87:674–683. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Jin UH, Park H, Li X, Davidson LA, Allred
C, Patil B, Jayaprakasha G, Orr AA, Mao L, Chapkin RS, et al:
Structure-dependent modulation of aryl hydrocarbon
receptor-mediated activities by flavonoids. Toxicol Sci.
164:205–17. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Pang C, Zhu C, Zhang Y, Ge Y, Li S, Huo S,
Xu T, Stauber RH and Zhao B: 2,3,7,8-Tetrachloodibenzo-p-dioxin
affects the differentiation of CD4 helper T cell. Toxicol Lett.
311:49–57. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|