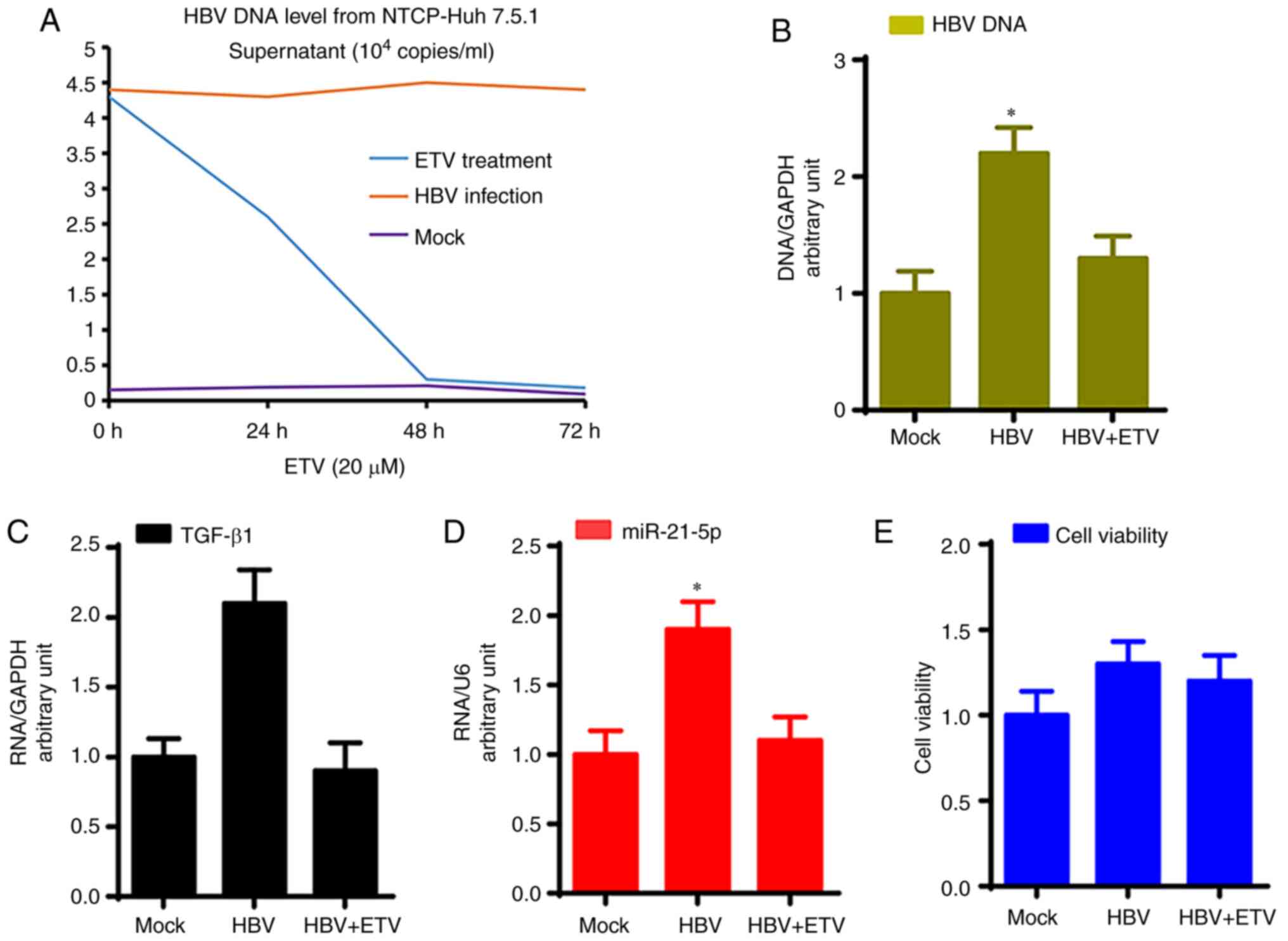
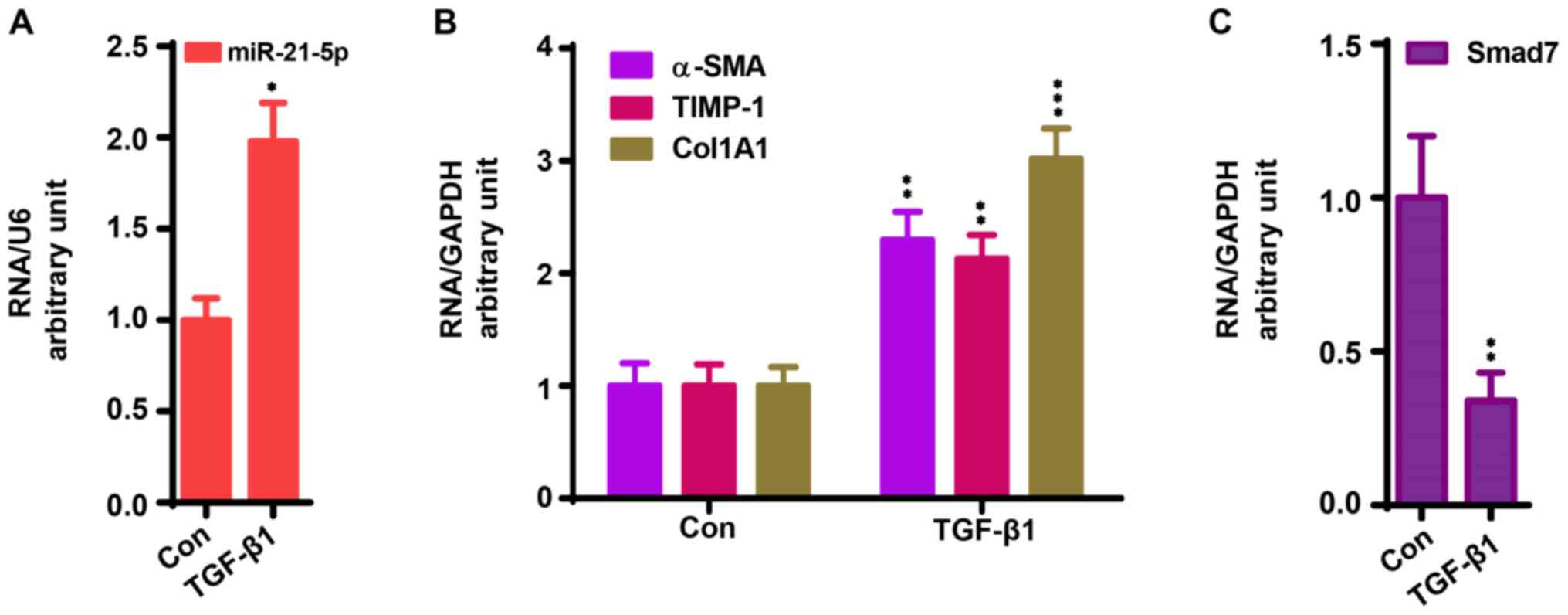
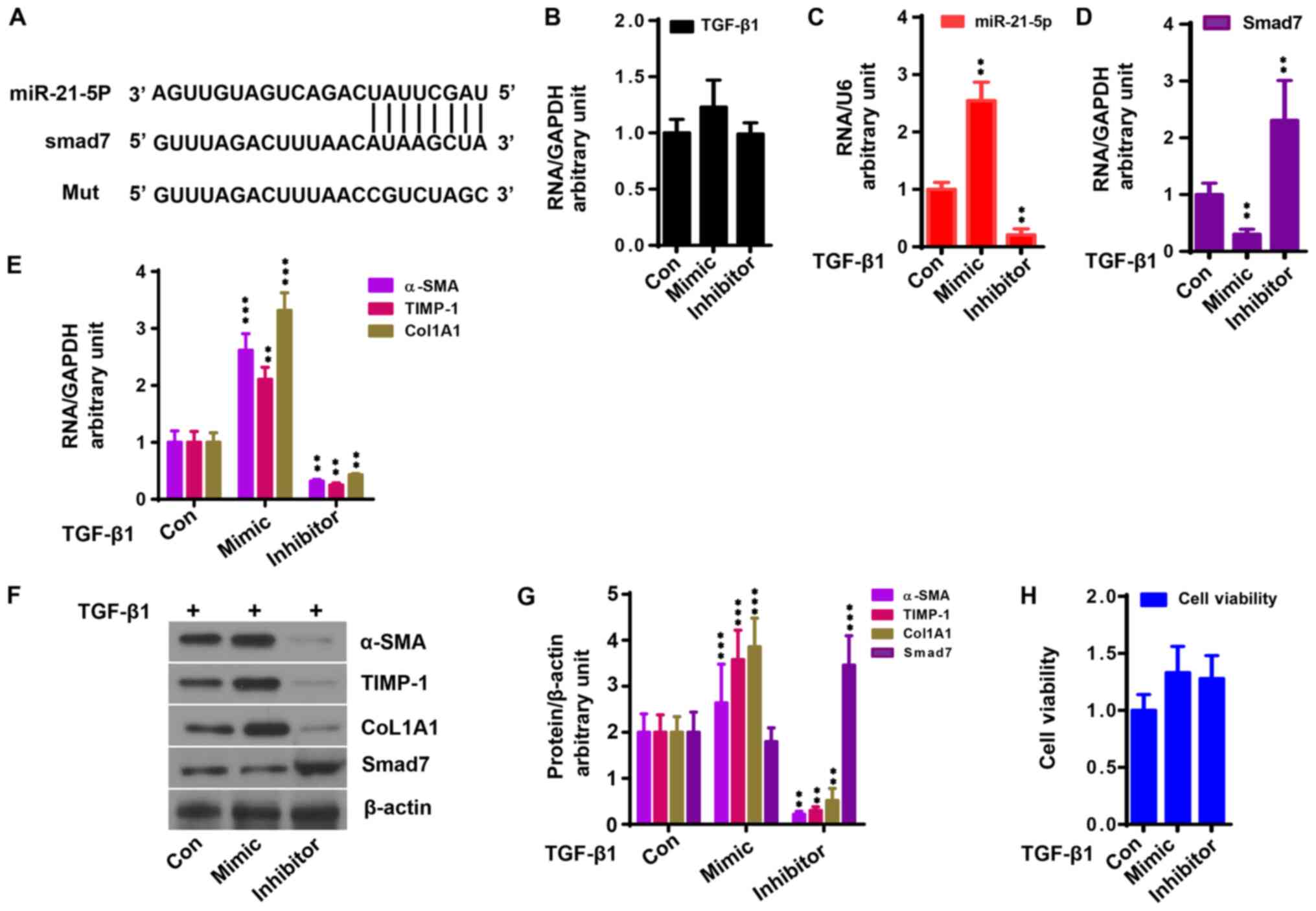
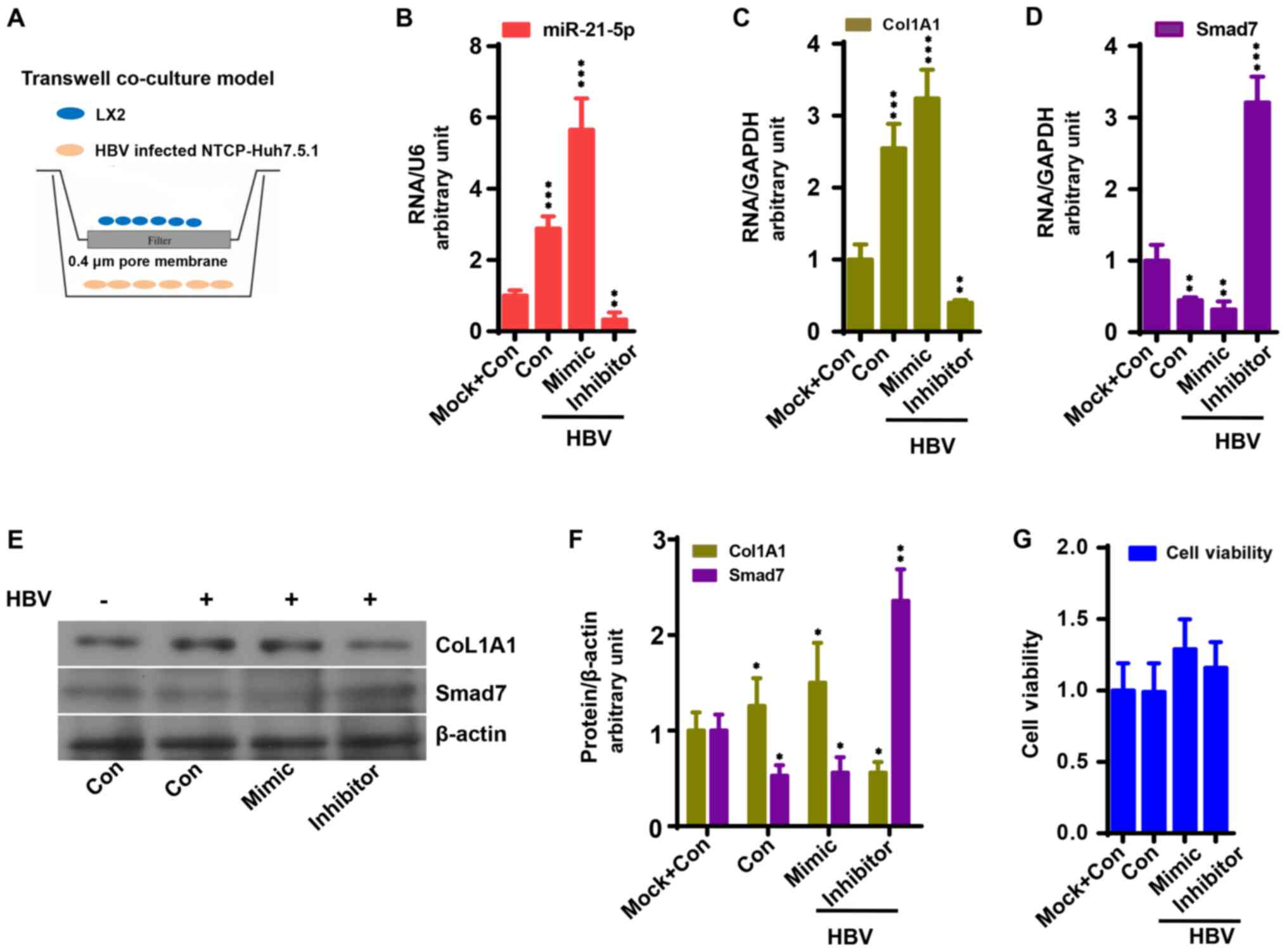
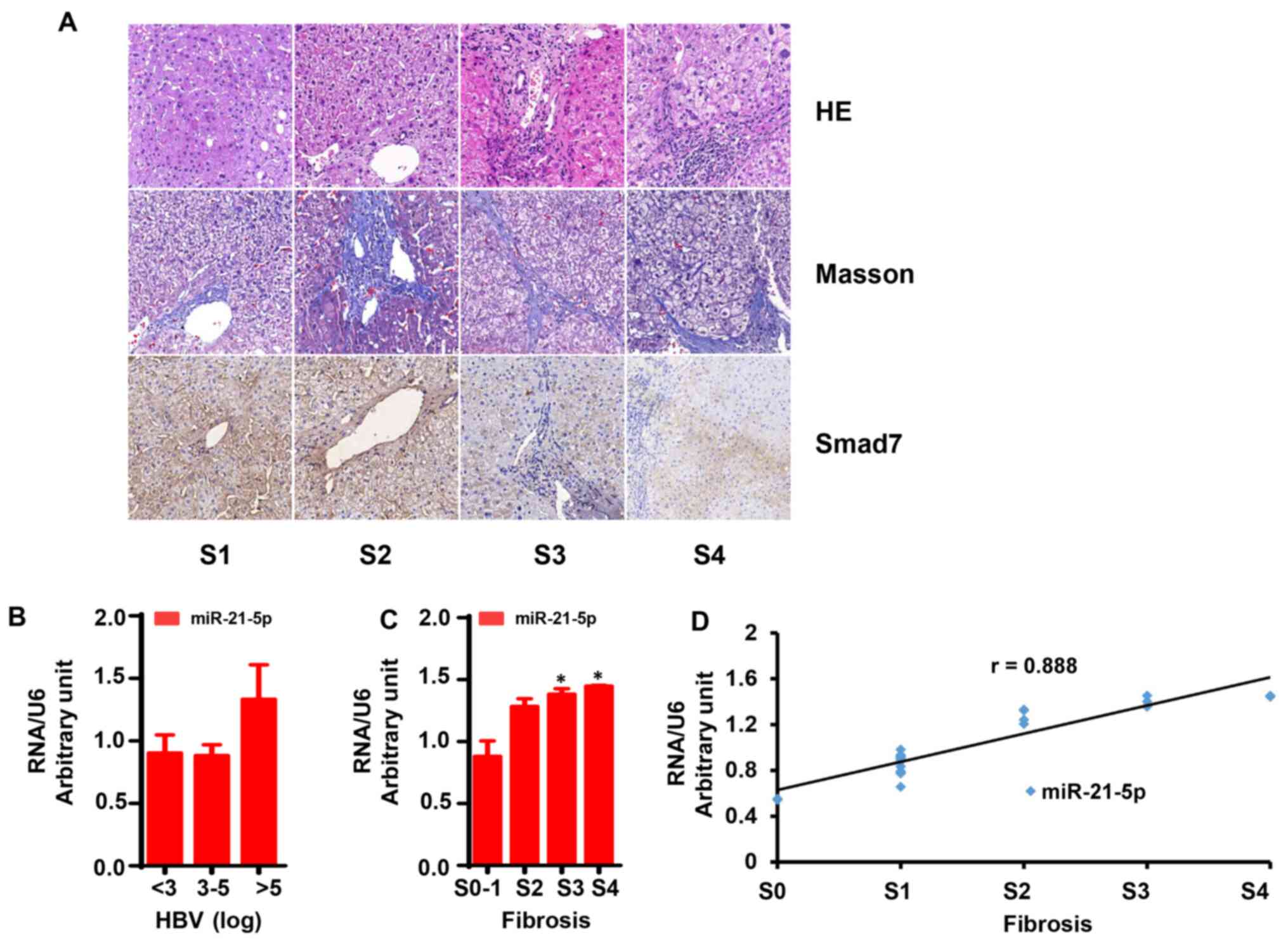
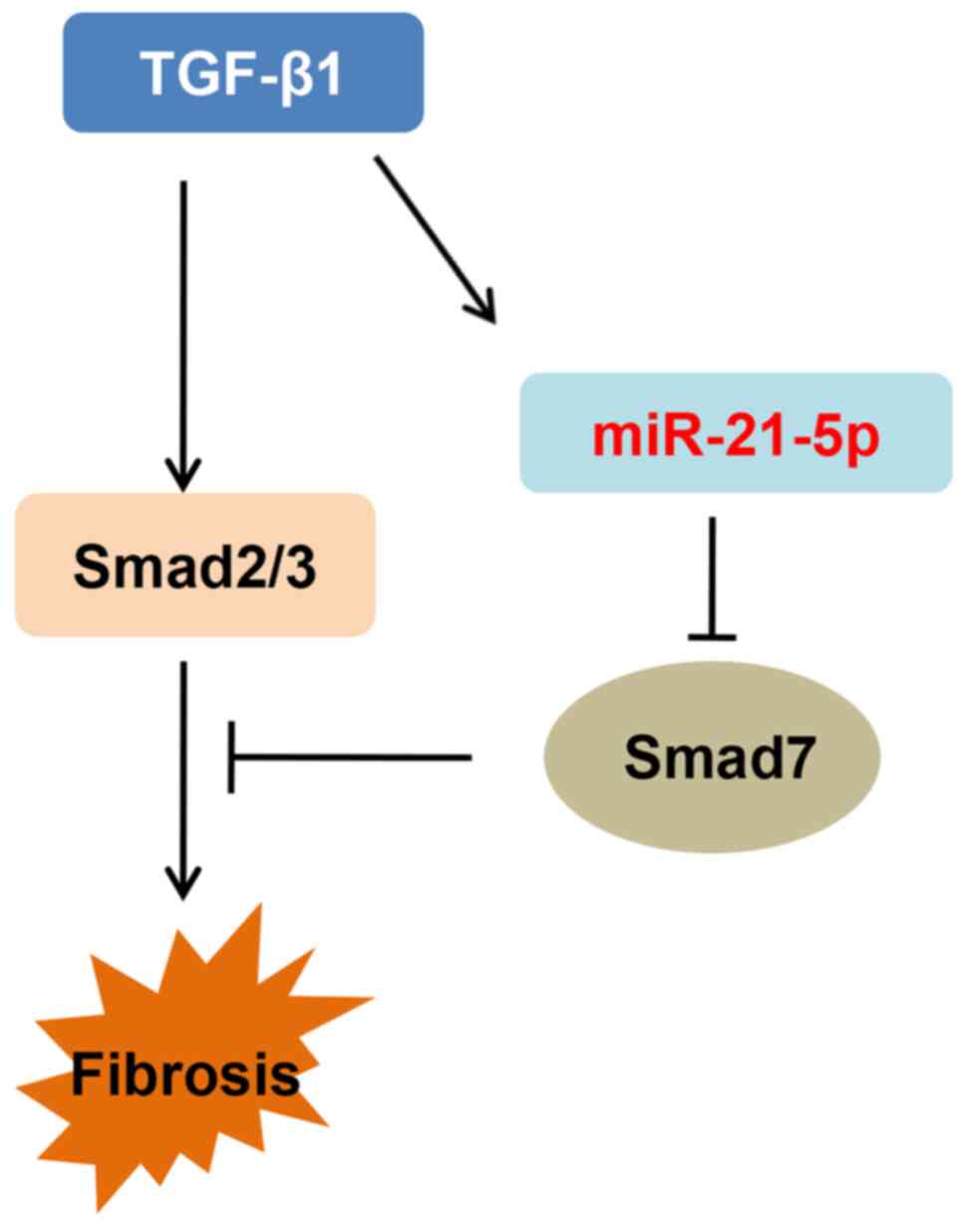
|
1
|
Zhang K, Shi Z, Zhang M, Dong X, Zheng L,
Li G, Han X, Yao Z, Han T and Hong W: Silencing lncRNA Lfar1
alleviates the classical activation and pyoptosis of macrophage in
hepatic fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. 11(132)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Su QD, Zhang S, Wang F, Liu H, Zhang GM,
Zheng H, Qiu F, Sun XJ, Liang XF, Bi SL, et al: Epidemiological
distribution of hepatitis B virus genotypes in 1-29-year-olds in
the mainland of China. Vaccine. 38:8238–8246. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mohd-Ismail NK, Lim Z, Gunaratne J and Tan
YJ: Mapping the interactions of HBV cccDNA with host factors. Int J
Mol Sci. 20(4276)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sun Y, Wu X, Zhou J, Meng T, Wang B, Chen
S, Liu H, Wang T, Zhao X, Wu S, et al: Persistent low level of
hepatitis B virus promotes fibrosis progression during therapy.
Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:2582–2591.e6. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Dai Y, Che F, Jiang X, Cui D, Zhou H, Xu
X, Sun C and Cheng J: Clinical characteristics and association
analysis of persistent low-level HBsAg expression in a physical
examination population with HBV infection. Exp Ther Med. 19:19–32.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kim J, Kang W, Kang SH, Park SH, Kim JY,
Yang S, Ha SY and Paik YH: Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 mediates
transforming growth factor-beta-induced hepatic stellate cell
activation and liver fibrosis. Sci Rep. 10(21018)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Clayton SW, Ban GI, Liu C and Serra R:
Canonical and noncanonical TGF-β signaling regulate fibrous tissue
differentiation in the axial skeleton. Sci Rep.
10(21364)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chang CJ, Lin CF, Lee CH, Chuang HC, Shih
FC, Wan SW, Tai C and Chen CL: Overcoming interferon (IFN)-γ
resistance ameliorates transforming growth factor (TGF)-β-mediated
lung fibroblast-to-myofibroblast transition and bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 183(114356)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Derynck R, Turley SJ and Akhurst RJ: TGFβ
biology in cancer progression and immunotherapy. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 18:9–34. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kori M and Arga KY: Pathways involved in
viral oncogenesis: New perspectives from virus-host protein
interactomics. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1866(165885)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ho CH, Chang TT and Chien RN: Telbivudine
on IgG-associated hypergammaglobulinemia and TGF-β1 hyperactivity
in hepatitis B virus-related liver cirrhosis. PLoS One.
14(e0225482)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xu Y, Sun X, Zhang R, Cao T, Cai SY, Boyer
JL, Zhang X, Li D and Huang Y: A positive feedback loop of TET3 and
TGF-β1 promotes liver fibrosis. Cell Rep. 30:1310–1318.e5.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim JY, Kim KM, Yang JH, Cho SS, Kim SJ,
Park SJ, Ahn SG, Lee GH, Yang JW, Lim SC, et al: Induction of E6AP
by microRNA-302c dysregulation inhibits TGF-β-dependent
fibrogenesis in hepatic stellate cells. Sci Rep.
10(444)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Li J, Wang S, Yang F, Zhou Y, Liu
Y, Zhu W and Shi X: HBx-associated long non-coding RNA activated by
TGF-β promotes cell invasion and migration by inducing autophagy in
primary liver cancer. Int J Oncol. 56:337–347. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li MH, Chen QQ, Zhang L, Lu HH, Sun FF,
Zeng Z, Lu Y, Yi W and Xie Y: Association of cytokines with
hepatitis B virus and its antigen. J Med Virol: Jul 14, 2020 (Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
16
|
Martin N, Ziegler DV, Parent R and Bernard
D: Hepatic stellate cell senescence in liver tumorigenesis.
Hepatology: Sep 15, 2020 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
17
|
Zhang J, Jiang N, Ping J and Xu L:
TGF-β1-induced autophagy activates hepatic stellate cells via the
ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med: Nov 3, 2020 (Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
18
|
Wang X, He Y, Mackowiak B and Gao B:
MicroRNAs as regulators, biomarkers and therapeutic targets in
liver diseases. Gut: Oct 30, 2020 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
19
|
Ezhilarasan D: MicroRNA interplay between
hepatic stellate cell quiescence and activation. Eur J Pharmacol.
885(173507)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Salimi S, Noorbakhsh F, Faghihzadeh S,
Ghaffarpour S and Ghazanfari T: Expression of miR-15b-5p,
miR-21-5p, and SMAD7 in lung tissue of sulfur mustard-exposed
individuals with long-term pulmonary complications. Iran J Allergy
Asthma Immunol. 18:332–339. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang W, Liu R, Su Y, Li H, Xie W and Ning
B: MicroRNA-21-5p mediates TGF-β-regulated fibrogenic activation of
spinal fibroblasts and the formation of fibrotic scars after spinal
cord injury. Int J Biol Sci. 14:178–188. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese
Medical Association; Chinese Society of Infectious Diseases. The
guideline of prevention and treatment for chronic hepatitis B: A
2019 update. Chin J Infect Dis. 37:711–736. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhu CL, Li WT, Li Y and Gao RT: Serum
levels of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 are correlated
with liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Dig
Dis. 13:558–563. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bedossa P and Poynard T: An algorithm for
the grading of activity in chronic hepatitis C The METAVIR
cooperative study group. Hepatology. 24:289–293. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Duan X, Li S, Holmes JA, Tu Z, Li Y, Cai
D, Liu X, Li W, Yang C, Jiao B, et al: MicroRNA 130a regulates both
hepatitis C virus and hepatitis B virus replication through a
central metabolic pathway. J Virol. 92:e02009–17. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li W, Yu X, Zhu C, Wang Z, Zhao Z, Li Y
and Zhang Y: Notum attenuates HBV-related liver fibrosis through
inhibiting Wnt 5a mediated non-canonical pathways. Biol Res.
52(10)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kisseleva T and Brenner D: Molecular and
cellular mechanisms of liver fibrosis and its regression. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol: Oct30, 2020 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
29
|
Liu L, Zhu J, Yang J, Li X, Yuan J, Wu J
and Liu Z: GP73 facilitates hepatitis B virus replication by
repressing the NF-κB signaling pathway. J Med Virol, February 20,
2020 (Online ahead of print).
|
|
30
|
Wang T, Dai Y, Lu W, Zhou H, Chen Y, Xu X,
Sun C and Cheng J: An epidemiological survey of HBV infection and
low-level HBsAg in military camps in eastern China. Medicine
(Baltimore). 97(e12201)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li Z, Hu Y, Wang H, Wang M, Gu X, Ping Y,
Zeng Q, Li H, Yan J and Yu Z: Predictors for the progression of
hepatic cirrhosis to hepatocellular carcinoma under long-term
antiviral therapy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 32:447–453.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yotsuyanagi H, Takano T, Tanaka M, Amano
K, Imamura M, Ogawa K, Yasunaka T, Yasui Y, Hayashi K, Tanaka Y, et
al: Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma in young
adults: Efficacy of nationwide selective vaccination. Hepatol Res.
50:182–189. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Duriez M, Mandouri Y, Lekbaby B, Wang H,
Schnuriger A, Redelsperger F, Guerrera CI, Lefevre M, Fauveau V,
Ahodantin J, et al: Alternative splicing of hepatitis B virus: A
novel virus/host interaction altering liver immunity. J Hepatol.
67:687–699. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yuan L, Jiang J, Liu X, Zhang Y, Zhang L,
Xin J, Wu K, Li X, Cao J, Guo X, et al: HBV infection-induced liver
cirrhosis development in dual-humanised mice with human bone
mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Gut. 68:2044–2056.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Bility MT, Cheng L, Zhang Z, Luan Y, Li F,
Chi L, Zhang L, Tu Z, Gao Y, Fu Y, et al: Hepatitis B virus
infection and immunopathogenesis in a humanized mouse model:
Induction of human-specific liver fibrosis and M2-like macrophages.
PLoS Pathog. 10(e1004032)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : Yan H, Zhong G, Xu
G, He W, Jing Z, Gao Z, Huang Y, Qi Y, Peng B, Wang H et al:
Sodium taurocholate cotransporting polypeptide is a functional
receptor for human hepatitis B and D virus. Elife 1: e00049,
2012.
|
|
36
|
Donkers JM, Appelman MD and van de Graaf
SFJ: Mechanistic insights into the inhibition of NTCP by myrcludex
B. JHEP Rep. 1:278–285. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Tian F, Liu Y, Gao J, Yang N, Shang X, Lv
J, Ba D, Zhou X, Zhang C and Ma X: Study on the association between
TGF-β1 and liver fibrosis in patients with hepatic cystic
echinococcosis. Exp Ther Med. 19:1275–1280. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Tao L, Xue D, Shen D, Ma W, Zhang J, Wang
X, Zhang W, Wu L, Pan K, Yang Y, et al: MicroRNA-942 mediates
hepatic stellate cell activation by regulating BAMBI expression in
human liver fibrosis. Arch Toxicol. 92:2935–2946. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Dewidar B, Meyer C, Dooley S and
Meindl-Beinker AN: TGF-β in hepatic stellate cell activation and
liver fibrogenesis-updated 2019. Cells. 8(1419)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Frangogiannis N: Transforming growth
factor-β in tissue fibrosis. J Exp Med.
217(e20190103)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Marvin DL, Heijboer R, Ten Dijke P and
Ritsma L: TGF-β signaling in liver metastasis. Clin Transl Med.
10(e160)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li W, Zhu C, Chen X, Li Y, Gao R and Wu Q:
Pokeweed antiviral protein down-regulates Wnt/β-catenin signalling
to attenuate liver fibrogenesis in vitro and in vivo. Dig Liver
Dis. 43:559–566. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sagnelli E, Potenza N, Onorato L, Sagnelli
C, Coppola N and Russo A: Micro-RNAs in hepatitis B virus-related
chronic liver diseases and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Hepatol. 10:558–570. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Zhi SC, Chen SZ, Li YY, Li JJ, Zheng YH
and Yu FX: Rosiglitazone inhibits activation of hepatic stellate
cells via up-regulating Micro-RNA-124-3p to alleviate hepatic
fibrosis. Dig Dis Sci. 64:1560–1570. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Sendi H, Mehrab-Mohseni M, Russo MW,
Steuerwald N, Jacobs C, Clemens MG and Bonkovsky HL: Baseline
hepatic levels of miR-29b and claudin are respectively associated
with the stage of fibrosis and HCV RNA in hepatitis C. Clin Exp
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1(105)2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li Q, Li B, Li Q, Wei S, He Z, Huang X,
Wang L, Xia Y, Xu Z, Li Z, et al: Exosomal miR-21-5p derived from
gastric cancer promotes peritoneal metastasis via
mesothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cell Death Dis.
9(854)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|