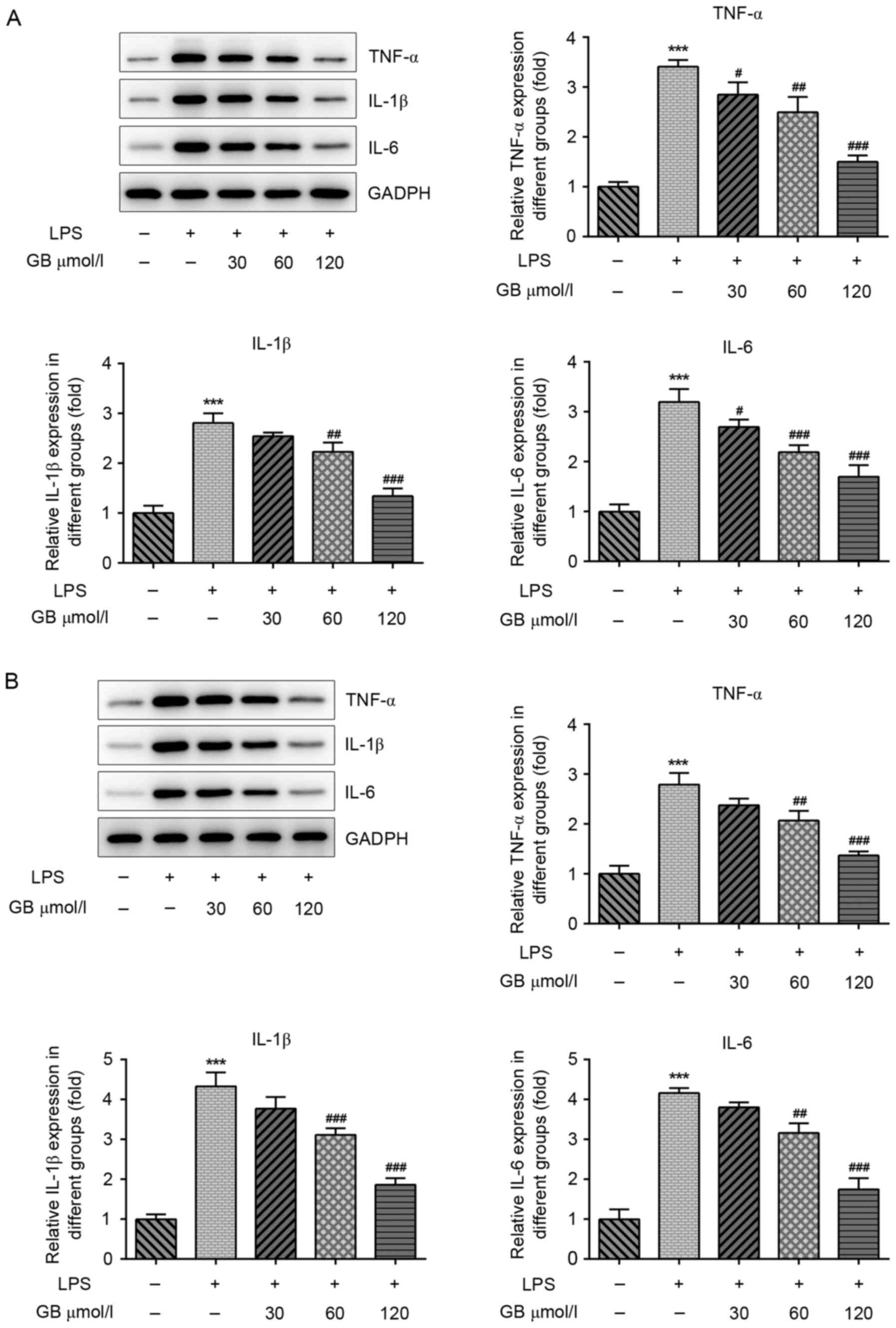
|
1
|
Klein RS, Garber C and Howard N:
Infectious immunity in the central nervous system and brain
function. Nat Immunol. 18:132–141. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Schain M and Kreisl WC: Neuroinflammation
in neurodegenerative disorders-a review. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep.
17(25)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Matsuda M, Huh Y and Ji RR: Roles of
inflammation, neurogenic inflammation, and neuroinflammation in
pain. J Anesth. 33:131–139. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Song I and Dityatev A: Crosstalk between
glia, extracellular matrix and neurons. Brain Res Bull.
136:101–108. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Allen NJ and Lyons DA: Glia as architects
of central nervous system formation and function. Science.
362:181–185. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kinney JW, Bemiller SM, Murtishaw AS,
Leisgang AM, Salazar AM and Lamb BT: Inflammation as a central
mechanism in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement (N Y).
4:575–590. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yang QQ and Zhou JW: Neuroinflammation in
the central nervous system: Symphony of glial cells. Glia.
67:1017–1035. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gonzalez H, Elgueta D, Montoya A and
Pacheco R: Neuroimmune regulation of microglial activity involved
in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. J
Neuroimmunol. 274:1–13. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Burguillos MA, Deierborg T, Kavanagh E,
Persson A, Hajji N, Garcia-Quintanilla A, Cano J, Brundin P,
Englund E, Venero JL and Joseph B: Caspase signalling controls
microglia activation and neurotoxicity. Nature. 472:319–324.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nabavi SM, Habtemariam S, Daglia M, Braidy
N, Loizzo MR, Tundis R and Nabavi SF: Neuroprotective effects of
ginkgolide B against ischemic stroke: A review of current
literature. Curr Top Med Chem. 15:2222–2232. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang G, Liu Z, Li M, Li Y, Alvi SS, Ansari
IA and Khan MS: Ginkgolide B mediated alleviation of inflammatory
cascades and altered lipid metabolism in HUVECs via targeting
PCSK-9 expression and functionality. Biomed Res Int.
2019(7284767)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Feng Z, Sun Q, Chen W, Bai Y, Hu D and Xie
X: The neuroprotective mechanisms of ginkgolides and bilobalide in
cerebral ischemic injury: A literature review. Mol Med.
25(57)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zheng PD, Mungur R, Zhou HJ, Hassan M,
Jiang SN and Zheng JS: Ginkgolide B promotes the proliferation and
differentiation of neural stem cells following cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury, both in vivo and in vitro. Neural
Regen Res. 13:1204–1211. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li MY, Chang CT, Han YT, Liao CP, Yu JY
and Wang TW: Ginkgolide B promotes neuronal differentiation through
the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in neural stem cells of the postnatal
mammalian subventricular zone. Sci Rep. 8(14947)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li W, Qinghai S, Kai L, Xue M, Lili N,
Jihua R, Zhengxiang L, Xiaoling L, Di G, Qi Y, et al: Oral
administration of Ginkgolide B alleviates hypoxia-induced neuronal
damage in rat hippocampus by inhibiting oxidative stress and
apoptosis. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 22:140–145. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Qu Z, Chen Y, Luo ZH, Shen XL and Hu YJ:
7-methoxyflavanone alleviates neuroinflammation in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglial cells by inhibiting
TLR4/MyD88/MAPK signalling and activating the Nrf2/NQO-1 pathway. J
Pharm Pharmacol. 72:385–395. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Norden DM, Trojanowski PJ, Villanueva E,
Navarro E and Godbout JP: Sequential activation of microglia and
astrocyte cytokine expression precedes increased Iba-1 or GFAP
immunoreactivity following systemic immune challenge. Glia.
64:300–316. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shabab T, Khanabdali R, Moghadamtousi SZ,
Kadir HA and Mohan G: Neuroinflammation pathways: A general review.
Int J Neurosci. 127:624–633. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ottum PA, Arellano G, Reyes LI,
Iruretagoyena M and Naves R: Opposing roles of interferon-gamma on
cells of the central nervous system in autoimmune
neuroinflammation. Front Immunol. 6(539)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, Marchetto MC
and Gage FH: Mechanisms underlying inflammation in
neurodegeneration. Cell. 140:918–934. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Ferreira ST, Clarke JR, Bomfim TR and De
Felice FG: Inflammation, defective insulin signaling, and neuronal
dysfunction in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 10 (1
Suppl):S76–S83. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Subhramanyam CS, Wang C, Hu Q and Dheen
ST: Microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative
diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 94:112–120. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tang Y and Le W: Differential roles of M1
and M2 microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Neurobiol.
53:1181–1194. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Baruch K, Kertser A, Porat Z and Schwartz
M: Cerebral nitric oxide represses choroid plexus NFκB-dependent
gateway activity for leukocyte trafficking. EMBO J. 34:1816–1828.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Han PF, Wei L, Duan ZQ, Zhang ZL, Chen TY,
Lu JG, Zhao RP, Cao XM, Li PC, Lv Z and Wei XC: Contribution of
IL-1β, 6 and TNF-α to the form of post-traumatic osteoarthritis
induced by ‘idealized’ anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction in
a porcine model. Int Immunopharmacol. 65:212–220. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Yu C, Zhang X, Chen H, Dong J, Lu
W, Song Z and Zhou W: Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide
induces cognitive dysfunction, mediated by neuronal inflammation
via activation of the TLR4 signaling pathway in C57BL/6 mice. J
Neuroinflammation. 15(37)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhu PC, Tong Q, Zhuang Z, Wang ZH, Deng
LH, Zheng GQ and Wang Y: Ginkgolide B for myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury: A preclinical systematic review and
meta-analysis. Front Physiol. 10(1292)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang R, Xu L, Zhang D, Hu B, Luo Q, Han
D, Li J and Shen C: Cardioprotection of ginkgolide B on myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammatory injury via regulation of
A20-NF-κB pathway. Front Immunol. 9(2844)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|