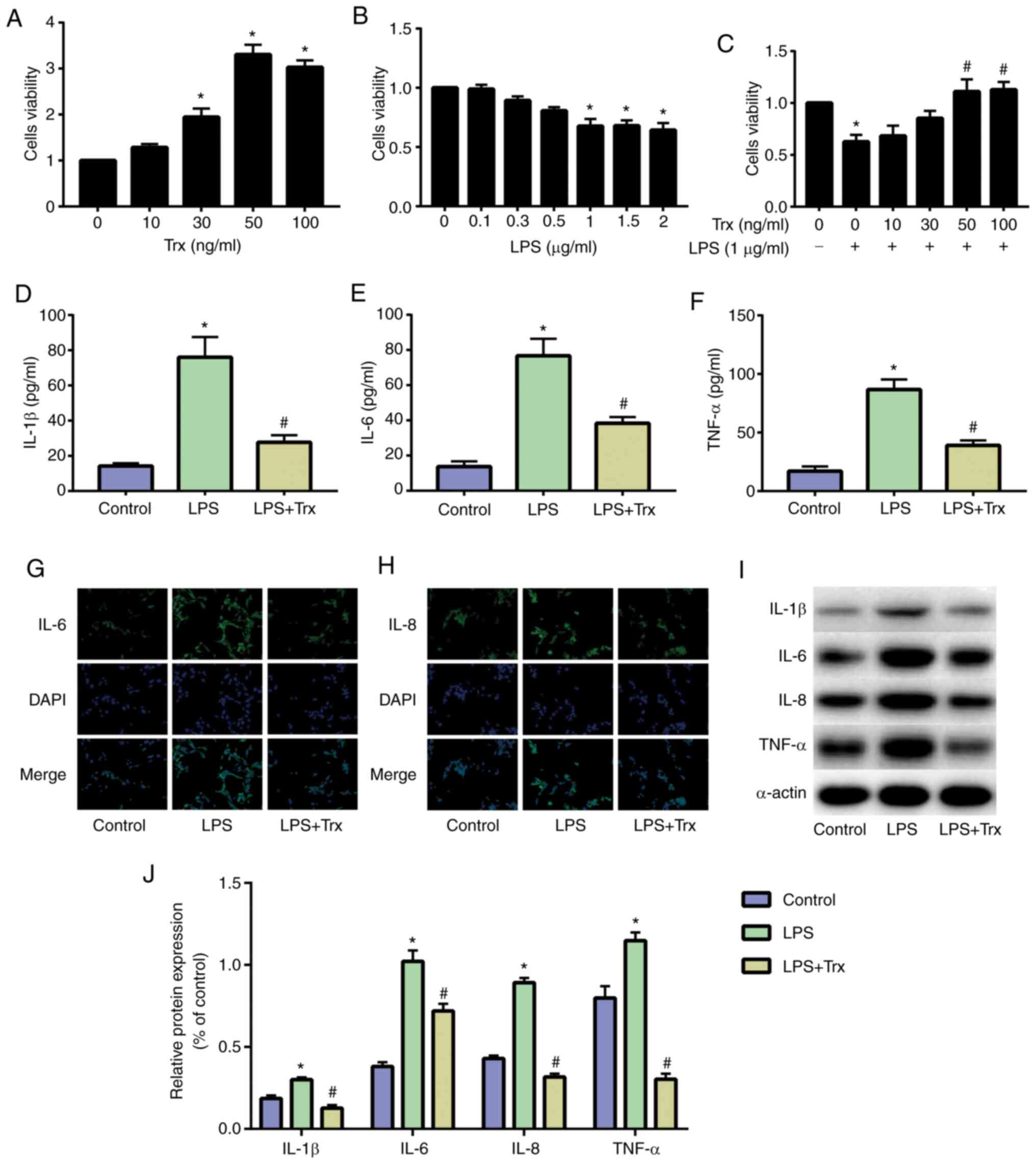
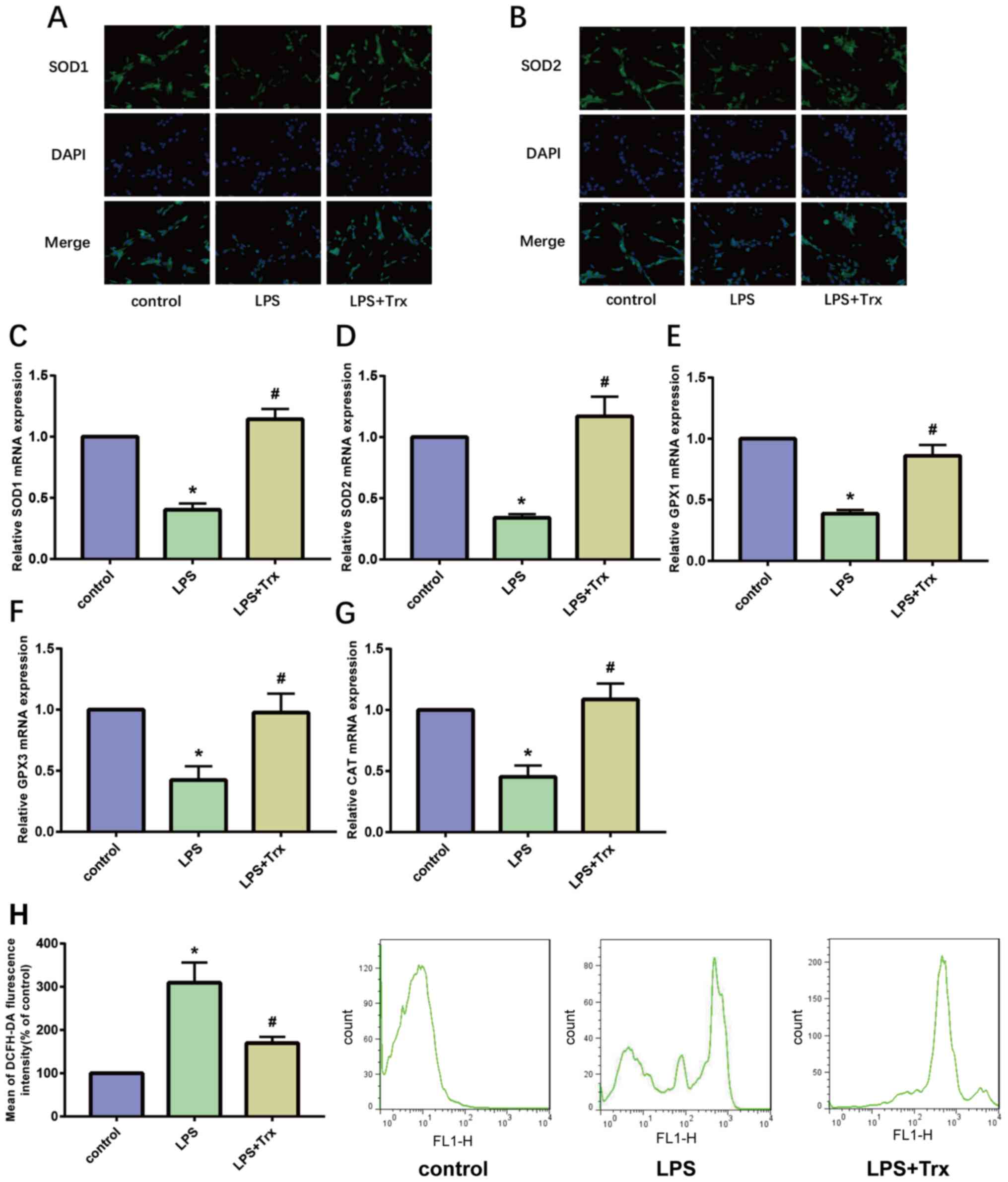
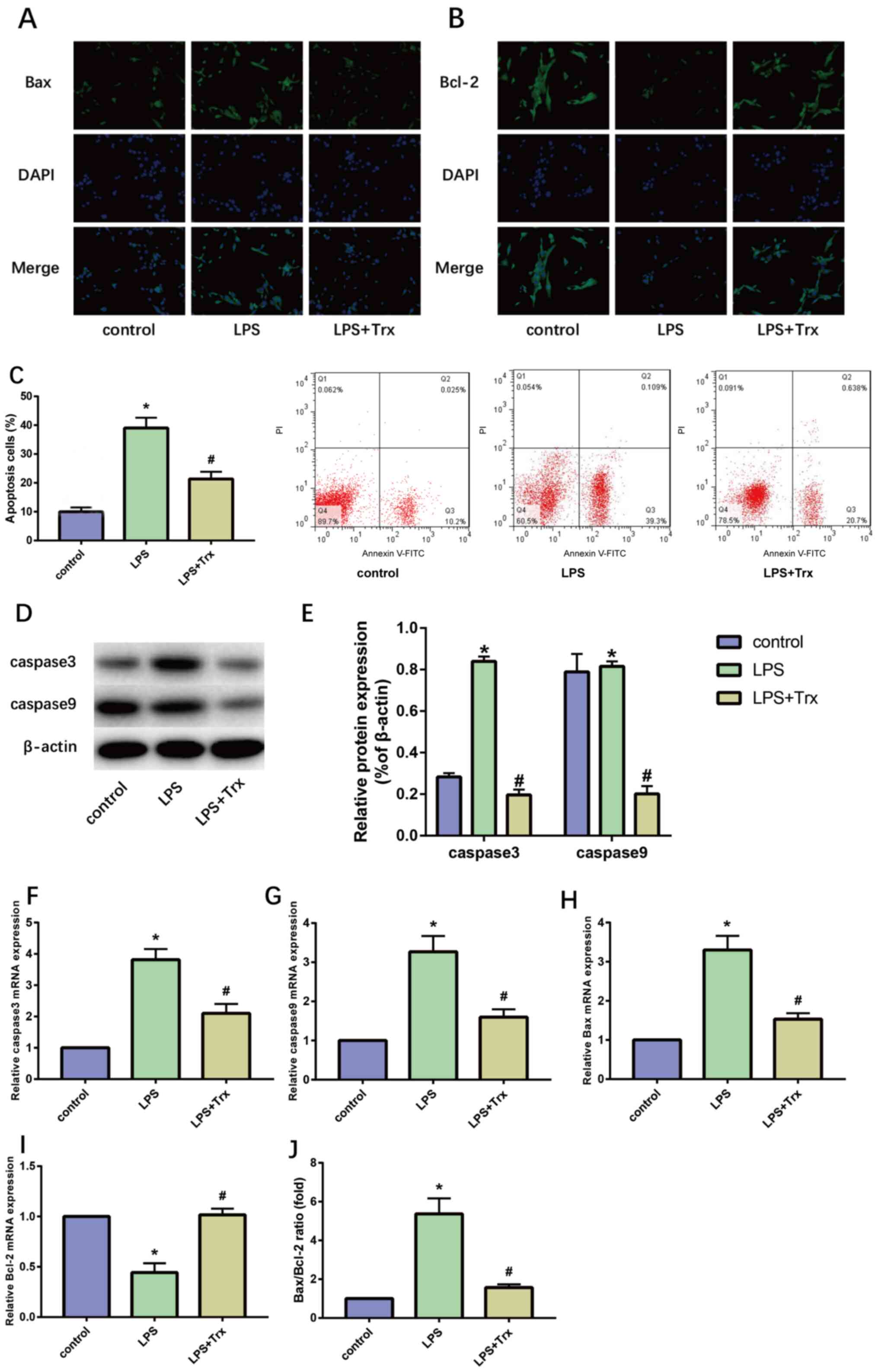
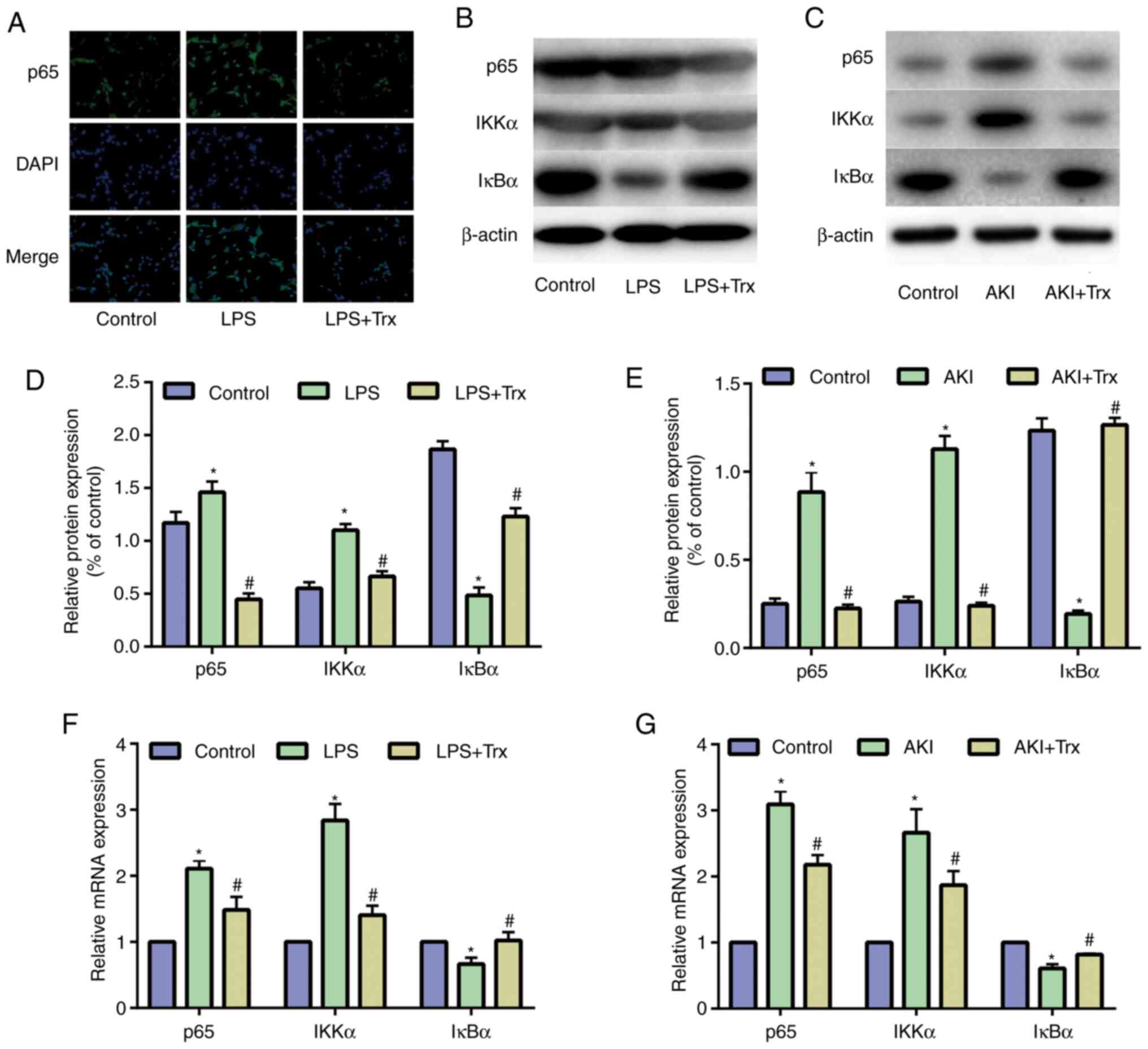
|
1
|
Wang YM, Han RL, Song SG, Yuan XP and Ren
XS: Inhibition of PARP overactivation protects acute kidney injury
of septic shock. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:6049–6056.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Pakula AM and Skinner RA: Acute kidney
injury in the critically Ill patient: A current review of the
literature. J Intensive Care Med. 31:319–324. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wald R, Kitchlu A, Harel Z and Silver SA:
Care of the acute kidney injury survivor. Nephron. 137:306–309.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Skube SJ, Katz SA, Chipman JG and
Tignanelli CJ: Acute kidney injury and sepsis. Surg Infect
(Larchmt). 19:216–224. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rahman M, Shad F and Smith MC: Acute
kidney injury: A guide to diagnosis and management. Am Fam
Physician. 86:631–639. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rydén L, Hertzberg D, Sartipy U and
Holzmann M: Acute kidney injury is a common and serious condition.
The clinical significance is great and probably underestimated.
Lakartidningen. 113(DXD3)2016.PubMed/NCBI(In Swedish).
|
|
7
|
Kampaktsis PN, Feldman DN and Charitakis
K: Strategies to avoid TAVI-related acute kidney injury. Curr Pharm
Des. 22:1950–1958. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang J, Li X, Han X, Liu R and Fang J:
Targeting the thioredoxin system for cancer therapy. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 38:794–808. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Léveillard T and Aït-Ali N: Cell signaling
with extracellular thioredoxin and thioredoxin-like proteins:
Insight into their mechanisms of action. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017(8475125)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mattoo RU, Farina Henriquez Cuendet A,
Subanna S, Finka A, Priya S, Sharma SK and Goloubinoff P: Synergism
between a foldase and an unfoldase: Reciprocal dependence between
the thioredoxin-like activity of DnaJ and the polypeptide-unfolding
activity of DnaK. Front Mol Biosci. 1(7)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jia J, Zeng X, Xu G and Wang Z: The
potential roles of redox enzymes in Alzheimer's disease: Focus on
thioredoxin. ASN Neuro. 13(1759091421994351)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yin Z, Ren H, Liu L, Chen W, Gan C, Jiao H
and Fan J: Thioredoxin protects skin flaps from
ischemia-reperfusion Injury: A novel prognostic and therapeutic
target. Plast Reconstr Surg. 137:511–521. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ueda S, Nakamura T, Yamada A, Teratani A,
Matsui N, Furukawa S, Hoshino Y, Narita M, Yodoi J and Nakamura H:
Recombinant human thioredoxin suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced
bronchoalveolar neutrophil infiltration in rat. Life Sci.
79:1170–1177. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shen J, Cui ZK, Yao F, Li K, Zhang Y, Chen
Z, Zhou Y, Xu S, Zhang Y, Jiang W, et al: TSC1 deletion in
fibroblasts alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney
injury. Clin Sci (Lond). 132:2087–2101. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Paller MS, Hoidal JR and Ferris TF: Oxygen
free radicals in ischemic acute renal failure in the rat. Clin
Invest. 74:1156–1164. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sanz AB, Sanchez-Niño MD, Ramos AM, Moreno
JA, Santamaria B, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J and Ortiz A: NF-kappaB in
renal inflammation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:1254–1262. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Peerapornratana S, Manrique-Caballero CL,
Gómez H and Kellum JA: Acute kidney injury from sepsis: Current
concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment.
Kidney Int. 96:1083–1099. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fragasso T, Ricci Z and Goldstein SL:
Pediatric acute kidney injury. Contrib Nephrol. 193:113–126.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Abdelraheem MB: Acute kidney injury in
low- and middle-income countries: Investigations, management and
prevention. Paediatr Int Child Health. 37:269–272. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen G, An N, Ye W, Huang S, Chen Y, Hu Z,
Shen E, Zhu J, Gong W, Tong G, et al: bFGF alleviates
diabetes-associated endothelial impairment by downregulating
inflammation via S-nitrosylation pathway. Redox Biol.
41(101904)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhou J and Chng WJ: Roles of thioredoxin
binding protein (TXNIP) in oxidative stress, apoptosis and cancer.
Mitochondrion. 13:163–169. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Benhar M: Application of a
thioredoxin-trapping mutant for analysis of the cellular
nitrosoproteome. Methods Enzymol. 585:285–294. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Ouyang Y, Peng Y, Li J, Holmgren A and Lu
J: Modulation of thiol-dependent redox system by metal ions via
thioredoxin and glutaredoxin systems. Metallomics. 10:218–228.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mata-Pérez C and Spoel SH:
Thioredoxin-mediated redox signalling in plant immunity. Plant Sci.
279:27–33. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lv Y, Bing Q, Lv Z, Xue J, Li S, Han B,
Yang Q, Wang X and Zhang Z: Imidacloprid-induced liver fibrosis in
quails via activation of the TGF-β1/Smad pathway. Sci Total
Environ. 705(135915)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu B, Yu H, Baiyun R, Lu J, Li S, Bing Q,
Zhang X and Zhang Z: Protective effects of dietary luteolin against
mercuric chloride-induced lung injury in mice: Involvement of
AKT/Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 113:296–302.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yang Q, Han B, Xue J, Lv Y, Li S, Liu Y,
Wu P, Wang X and Zhang Z: Hexavalent chromium induces mitochondrial
dynamics disorder in rat liver by inhibiting AMPK/PGC-1α signaling
pathway. Environ Pollut. 265(114855)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lv Y, Jiang H, Li S, Han B, Liu Y, Yang D,
Li J, Yang Q, Wu P and Zhang Z: Sulforaphane prevents
chromium-induced lung injury in rats via activation of the
Akt/GSK-3β/Fyn pathway. Environ Pollut. 259(113812)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Li S, Baiyun R, Lv Z, Li J, Han D, Zhao W,
Yu L, Deng N, Liu Z and Zhang Z: Exploring the kidney hazard of
exposure to mercuric chloride in mice: Disorder of mitochondrial
dynamics induces oxidative stress and results in apoptosis.
Chemosphere. 234:822–829. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen J and Chen LF: Methods to detect
NF-κB acetylation and methylation. Methods Mol Biol. 1280:395–409.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Neale PA, Leusch FDL and Escher BI: What
is driving the NF-κB response in environmental water extracts?
Chemosphere. 210:645–652. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lawrence T: The nuclear factor NF-kappaB
pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1(a001651)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Turkmen K: Inflammation, oxidative stress,
apoptosis, and autophagy in diabetes mellitus and diabetic kidney
disease: The four horsemen of the apocalypse. Int Urol Nephrol.
49:837–844. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lee JW, Kim SC, Ko YS, Lee HY, Cho E, Kim
MG, Jo SK, Cho WY and Kim HK: Renoprotective effect of paricalcitol
via a modulation of the TLR4-NF-κB pathway in
ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute kidney injury. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 444:121–127. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Nair AR, Masson GS, Ebenezer PJ, Del Piero
F and Francis J: Role of TLR4 in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
kidney injury: Protection by blueberry. Free Radic Biol Med.
71:16–25. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Korrapati MC, Shaner BE and Schnellmann
RG: Recovery from glycerol-induced acute kidney injury is
accelerated by suramin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 341:126–136.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|