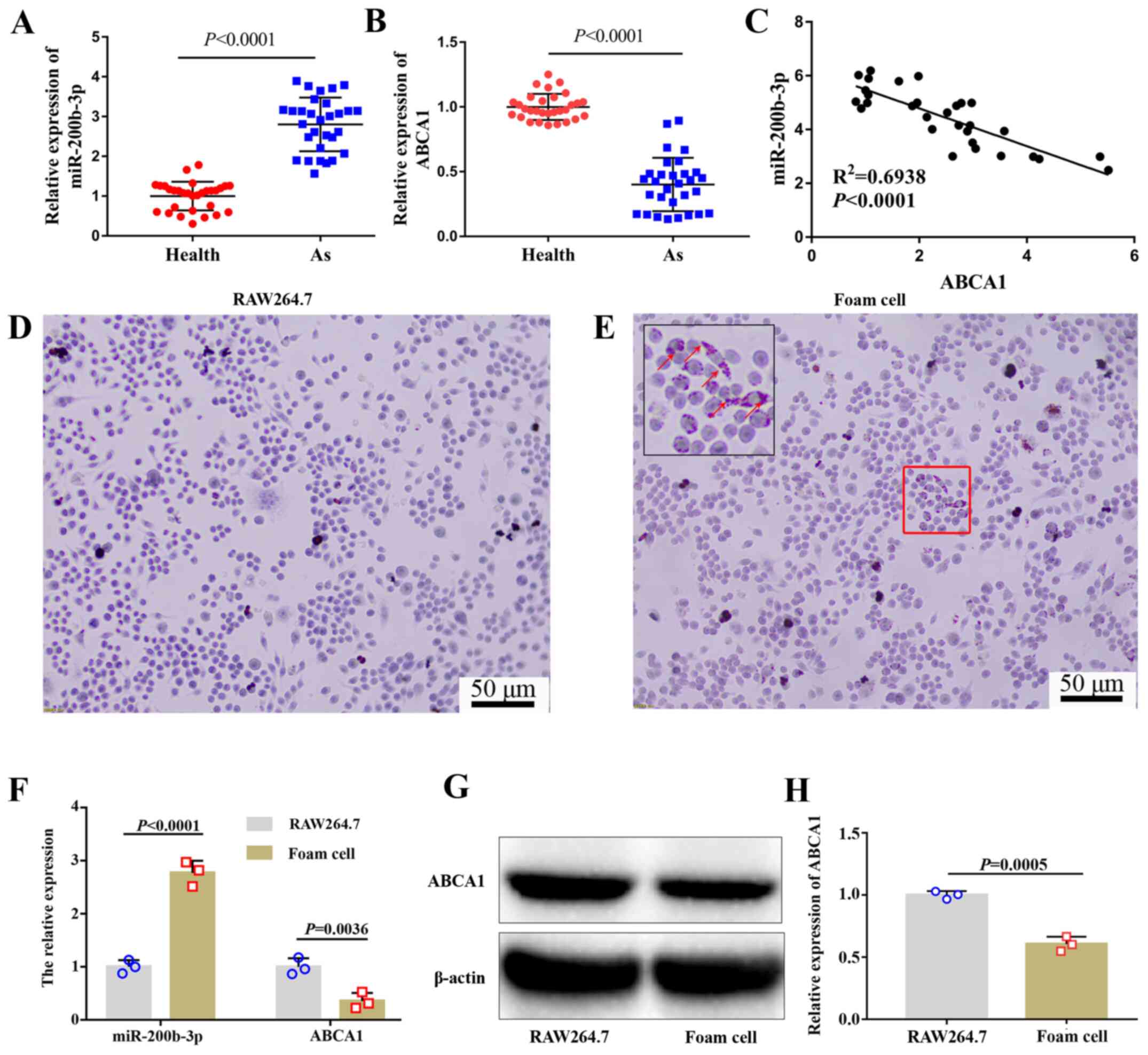
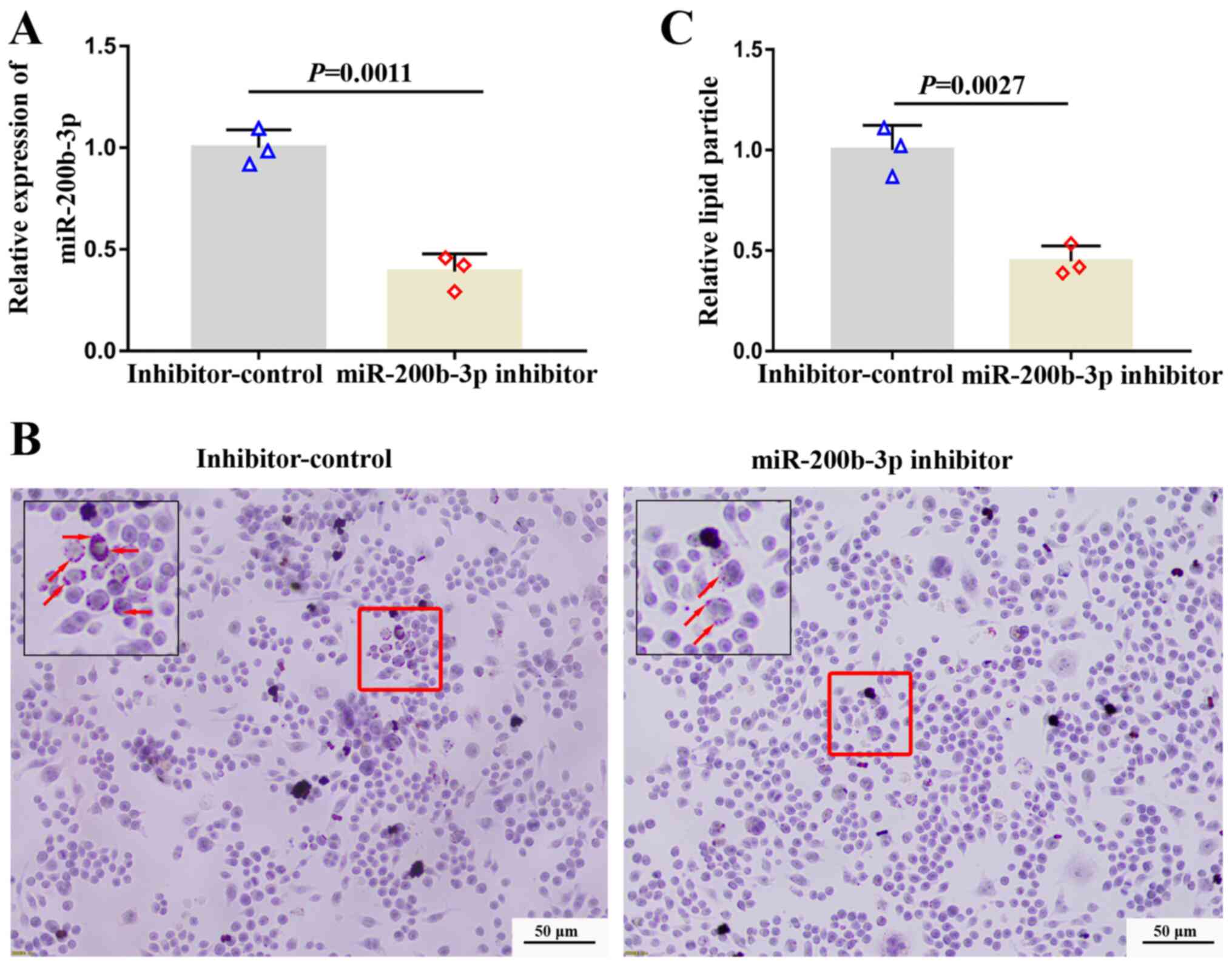
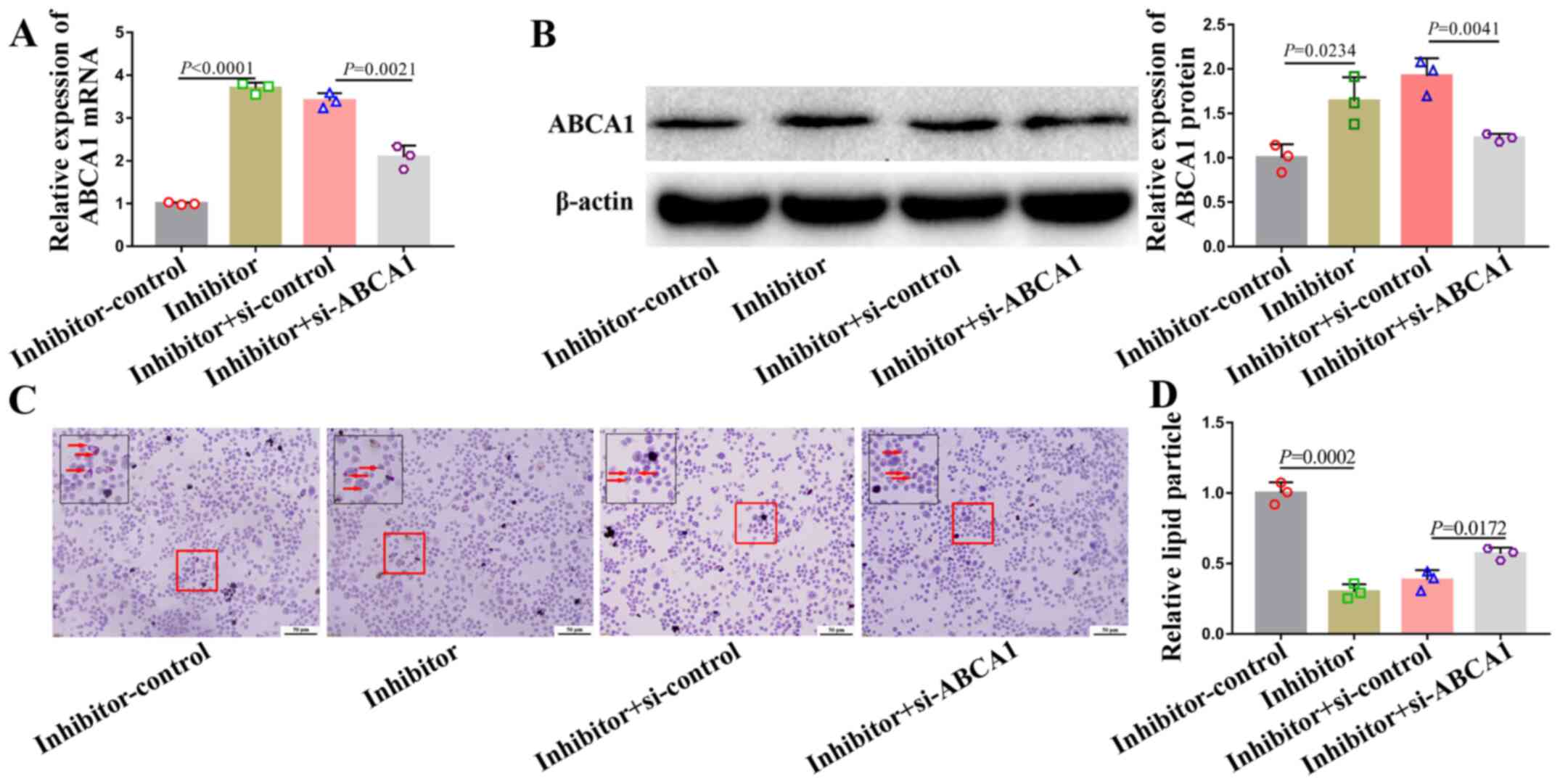
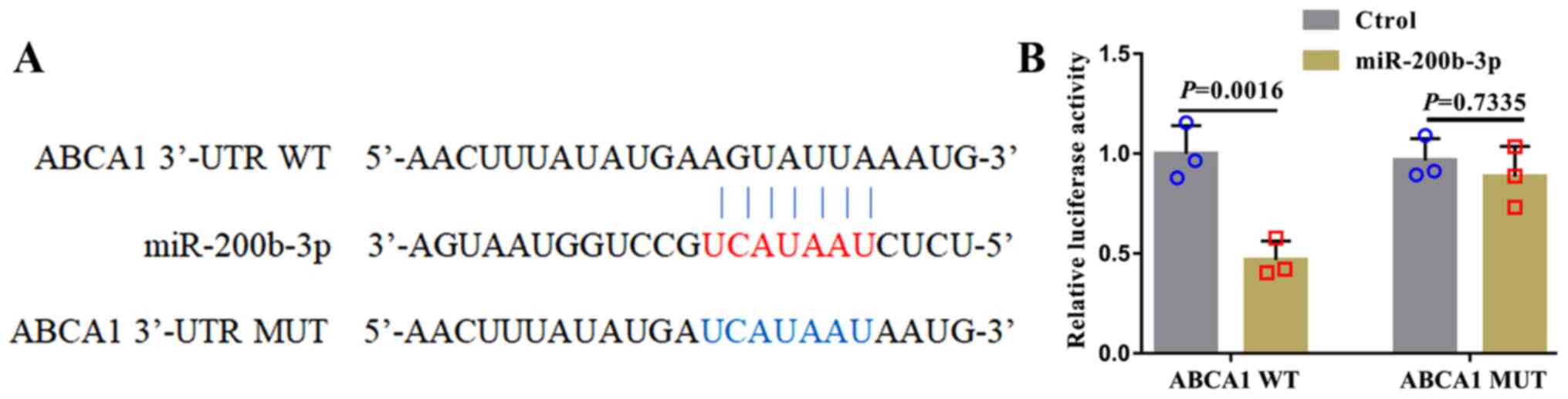|
1
|
Ference BA, Kastelein JJP and Catapano AL:
Lipids and lipoproteins in 2020. JAMA. 324:595–596. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Aguilar-Ballester M, Herrero-Cervera A,
Vinué Á, Martínez-Hervás S and González-Navarro H: Impact of
cholesterol metabolism in immune cell function and atherosclerosis.
Nutrients. 12(12)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li D, Liu Y, Zhang X, Lv H, Pang W, Sun X,
Gan LM, Hammock BD, Ai D and Zhu Y: Inhibition of soluble epoxide
hydrolase alleviated atherosclerosis by reducing monocyte
infiltration in Ldlr(-/-) mice. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 98:128–137.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Webb NR and Moore KJ: Macrophage-derived
foam cells in atherosclerosis: Lessons from murine models and
implications for therapy. Curr Drug Targets. 8:1249–1263.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jin P, Bian Y, Wang K, Cong G, Yan R, Sha
Y, Ma X, Zhou J, Yuan Z and Jia S: Homocysteine accelerates
atherosclerosis via inhibiting LXRα-mediated ABCA1/ABCG1-dependent
cholesterol efflux from macrophages. Life Sci. 214:41–50.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Demina EP, Miroshnikova VV and Schwarzman
AL: Role of the ABC transporters A1 and G1, key reverse cholesterol
transport proteins, in atherosclerosis. Mol Biol (Mosk).
50:223–230. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Russian).
|
|
7
|
Maranghi M, Truglio G, Gallo A, Grieco E,
Verrienti A, Montali A, Gallo P, Alesini F, Arca M and Lucarelli M:
A novel splicing mutation in the ABCA1 gene, causing Tangier
disease and familial HDL deficiency in a large family. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 508:487–493. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu L, Tan L, Yao J and Yang L: Long
non-coding RNA MALAT1 regulates cholesterol accumulation in
ox-LDL-induced macrophages via the microRNA-17-5p/ABCA1 axis. Mol
Med Rep. 21:1761–1770. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Han QA, Su D, Shi C, Liu P, Wang Y, Zhu B
and Xia X: Urolithin A attenuated ox-LDL-induced cholesterol
accumulation in macrophages partly through regulating miR-33a and
ERK/AMPK/SREBP1 signaling pathways. Food Funct. 11:3432–3440.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Koga M, Kanaoka Y, Inada K, Omine S,
Kataoka Y and Yamauchi A: Hesperidin blocks varenicline-aggravated
atherosclerotic plaque formation in apolipoprotein E knockout mice
by downregulating net uptake of oxidized low-density lipoprotein in
macrophages. J Pharmacol Sci. 143:106–111. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ren K, Li H, Zhou HF, Liang Y, Tong M,
Chen L, Zheng XL and Zhao GJ: Mangiferin promotes macrophage
cholesterol efflux and protects against atherosclerosis by
augmenting the expression of ABCA1 and ABCG1. Aging (Albany NY).
11:10992–11009. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang F, Zhang R, Zhang X, Wu Y, Li X,
Zhang S, Hou W, Ding Y, Tian J, Sun L, et al: Comprehensive
analysis of circRNA expression pattern and circRNA-miRNA-mRNA
network in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in rabbits. Aging
(Albany NY). 10:2266–2283. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Laffont B and Rayner KJ: MicroRNAs in the
pathobiology and therapy of atherosclerosis. Can J Cardiol.
33:313–324. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lee KH, Lim BJ, Ferreira VH, Min SY, Hong
YM, Jo JH and Han SH: Expression of human miR-200b-3p and -200c-3p
in cytomegalovirus-infected tissues. Biosci Rep.
38(BSR20180961)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xia L, Han Q, Chi C, Zhu Y, Pan J, Dong B,
Huang Y, Xia W, Xue W and Sha J: Transcriptional regulation of
PRKAR2B by miR-200b-3p/200c-3p and XBP1 in human prostate cancer.
Biomed Pharmacother. 124(109863)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wu YZ, Lin HY, Zhang Y and Chen WF:
miR-200b-3p mitigates oxaliplatin resistance via targeting TUBB3 in
colorectal cancer. J Gene Med. 22(e3178)2020.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liu K, Zhang W, Tan J, Ma J and Zhao J:
MiR-200b-3p functions as an oncogene by targeting ABCA1 in lung
adenocarcinoma. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
18(1533033819892590)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cao H, Jia Q, Yan L, Chen C, Xing S and
Shen D: Quercetin suppresses the progression of atherosclerosis by
regulating MST1-mediated autophagy in ox-LDL-induced RAW264.7
macrophage foam cells. Int J Mol Sci. 20(6093)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yin M, Lu J and Guo Z, Zhang Y, Liu J, Wu
T, Guo K, Luo T and Guo Z: Reduced SULT2B1b expression alleviates
ox-LDL-induced inflammation by upregulating miR-148-3P via
inhibiting the IKKβ/NF-κB pathway in macrophages. Aging (Albany
NY). 13:3428–3442. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Rahman MS and Woollard K: Atherosclerosis.
Adv Exp Med Biol. 1003:121–144. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kalaria RN: The pathology and
pathophysiology of vascular dementia. Neuropharmacology.
134:226–239. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Grimaldi V, Vietri MT, Schiano C, Picascia
A, De Pascale MR, Fiorito C, Casamassimi A and Napoli C: Epigenetic
reprogramming in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep.
17(476)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lechner K, von Schacky C, McKenzie AL,
Worm N, Nixdorff U, Lechner B, Kränkel N, Halle M, Krauss RM and
Scherr J: Lifestyle factors and high-risk atherosclerosis: Pathways
and mechanisms beyond traditional risk factors. Eur J Prev Cardiol.
27:394–406. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chistiakov DA, Bobryshev YV and Orekhov
AN: Macrophage-mediated cholesterol handling in atherosclerosis. J
Cell Mol Med. 20:17–28. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Boshuizen MC, Hoeksema MA, Neele AE, van
der Velden S, Hamers AA, Van den Bossche J, Lutgens E and de
Winther MP: Interferon-β promotes macrophage foam cell formation by
altering both cholesterol influx and efflux mechanisms. Cytokine.
77:220–226. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yuan Y, Li P and Ye J: Lipid homeostasis
and the formation of macrophage-derived foam cells in
atherosclerosis. Protein Cell. 3:173–181. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Babashamsi MM, Koukhaloo SZ, Halalkhor S,
Salimi A and Babashamsi M: ABCA1 and metabolic syndrome; a review
of the ABCA1 role in HDL-VLDL production, insulin-glucose
homeostasis, inflammation and obesity. Diabetes Metab Syndr.
13:1529–1534. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Jung D, Cao S, Liu M and Park S: A
Meta-analysis of the associations between the ATP-binding cassette
transporter ABCA1 R219K (rs2230806) polymorphism and the risk of
type 2 diabetes in Asians. Horm Metab Res. 50:308–316.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu M, Mei X, Herscovitz H and Atkinson D:
N-terminal mutation of apoA-I and interaction with ABCA1 reveal
mechanisms of nascent HDL biogenesis. J Lipid Res. 60:44–57.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Okamoto Y, Tomioka M, Ogasawara F, Nagaiwa
K, Kimura Y, Kioka N and Ueda K: C-terminal of ABCA1 separately
regulates cholesterol floppase activity and cholesterol efflux
activity. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 84:764–773. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Puntoni M, Sbrana F, Bigazzi F and
Sampietro T: Tangier disease: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and
management. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 12:303–311. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ouimet M, Barrett TJ and Fisher EA: HDL
and reverse cholesterol transport. Circ Res. 124:1505–1518.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Price NL, Rotllan N, Zhang X,
Canfrán-Duque A, Nottoli T, Suarez Y and Fernández-Hernando C:
Specific disruption of Abca1 targeting largely mimics the effects
of miR-33 knockout on macrophage cholesterol efflux and
atherosclerotic plaque development. Circ Res. 124:874–880.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wu YR, Shi XY, Ma CY, Zhang Y, Xu RX and
Li JJ: Liraglutide improves lipid metabolism by enhancing
cholesterol efflux associated with ABCA1 and ERK1/2 pathway.
Cardiovasc Diabetol. 18(146)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tan YL, Ou HX, Zhang M, Gong D, Zhao ZW,
Chen LY, Xia XD, Mo ZC and Tang CK: Tanshinone IIA promotes
macrophage cholesterol efflux and attenuates atherosclerosis of
apoE-/- mice by Omentin-1/ABCA1 pathway. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 20:422–432. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang Z, Zhang J, Zhang S, Yan S, Wang Z,
Wang C and Zhang X: MiR-30e and miR-92a are related to
atherosclerosis by targeting ABCA1. Mol Med Rep. 19:3298–3304.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yue Y, Zhang Z, Zhang L, Chen S, Guo Y and
Hong Y: miR-143 and miR-145 promote hypoxia-induced proliferation
and migration of pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells through
regulating ABCA1 expression. Cardiovasc Pathol. 37:15–25.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Goedeke L, Rotllan N, Canfrán-Duque A,
Aranda JF, Ramírez CM, Araldi E, Lin CS, Anderson NN, Wagschal A,
de Cabo R, et al: MicroRNA-148a regulates LDL receptor and ABCA1
expression to control circulating lipoprotein levels. Nat Med.
21:1280–1289. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|