|
1
|
Thompson LD: Laryngeal dysplasia, squamous
cell carcinoma, and variants. Surg Pathol Clin. 10:15–33.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Echanique KA, Desai SV, Marchiano E,
Spinazzi EF, Strojan P, Baredes S and Eloy JA: Laryngeal verrucous
carcinoma: A systematic review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
156:38–45. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kolator M, Kolator P and Zatoński T:
Assessment of quality of life in patients with laryngeal cancer: A
review of articles. Adv Clin Exp Med. 27:711–715. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Feng W, Yang Y, Xin ZH and Ni XG:
Misdiagnosis experience of laryngeal carcinoma with acute
laryngitis as the first symptom. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing
Wai Ke Za Zhi. 53(640)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
5
|
Obid R, Redlich M and Tomeh C: The
treatment of laryngeal cancer. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am.
31:1–11. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chang HY, Lee CH, Li YS, Huang JT, Lan SH,
Wang YF, Lai WW, Wang YC, Lin YJ, Liu HS and Cheng HC:
MicroRNA-146a suppresses tumor malignancy via targeting vimentin in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells with lower fibronectin
membrane assembly. J Biomed Sci. 27(102)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Escuin D, López-Vilaró L, Bell O, Mora J,
Moral A, Pérez JI, Arqueros C, Ramón Y, Cajal T, Lerma E and
Barnadas A: MicroRNA-1291 is associated with locoregional
metastases in patients with early-stage breast cancer. Front Genet.
11(562114)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Xu WG, Kuang YM, Wang D, Li Z and Xia RP:
Effect of miR-210 on proliferation and migration of pancreatic
cancer cells through regulating Runx3 level. J Biomater Tissue Eng.
10:1827–1831. 2020.
|
|
9
|
Chen L, Sun DZ, Fu YG, Yang PZ, Lv HQ, Gao
Y and Zhang XY: Upregulation of microRNA-141 suppresses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and lymph node metastasis in
laryngeal cancer through HOXC6-dependent TGF-β signaling pathway.
Cell Signal. 66(109444)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang B, Zang J, Yuan W, Jiang X and Zhang
F: The miR-136-5p/ROCK1 axis suppresses invasion and migration, and
enhances cisplatin sensitivity in head and neck cancer cells. Exp
Ther Med. 21(317)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu YB, Wang Y, Zhang MD, Yue W and Sun
CN: MicroRNA-29a functions as a tumor suppressor through targeting
STAT3 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol.
116(104521)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cossu AM, Mosca L, Zappavigna S, Misso G,
Bocchetti M, De Micco F, Quagliuolo L, Porcelli M, Caraglia M and
Boccellino M: Long non-coding RNAs as important biomarkers in
laryngeal cancer and other head and neck tumours. Int J Mol Sci.
20(3444)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Erkul E, Yilmaz I, Gungor A, Kurt O and
Babayigit MA: MicroRNA-21 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma:
Diagnostic and prognostic features. Laryngoscope. 127:E62–E66.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li W, Ma HP and Sun J: MicroRNA-34a/c
function as tumor suppressors in Hep-2 laryngeal carcinoma cells
and may reduce GALNT7 expression. Mol Med Rep. 9:1293–1298.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Guo Y, An R, Zhao R, Sun Y, Liu M and Tian
L: miR-375 exhibits a more effective tumor-suppressor function in
laryngeal squamous carcinoma cells by regulating KLF4 expression
compared with simple co-transfection of miR-375 and miR-206. Oncol
Rep. 36:952–960. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chai L, Kang XJ, Sun ZZ, Zeng MF, Yu SR,
Ding Y, Liang JQ, Li TT and Zhao J: MiR-497-5p, miR-195-5p and
miR-455-3p function as tumor suppressors by targeting hTERT in
melanoma A375 cells. Cancer Manag Res. 10:989–1003. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Feng C, Zhang L, Sun Y, Li X, Zhan L, Lou
Y, Wang Y, Liu L and Zhang Y: GDPD5, a target of miR-195-5p, is
associated with metastasis and chemoresistance in colorectal
cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 101:945–952. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu X, Zhou Y, Ning YE, Gu H, Tong Y and
Wang N: MiR-195-5p inhibits malignant progression of cervical
cancer by targeting YAP1. OncoTargets Ther. 13:931–944.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Poel D, Boyd LNC, Beekhof R, Schelfhorst
T, Pham TV, Piersma SR, Knol JC, Jimenez CR, Verheul HMW and
Buffart TE: Proteomic analysis of miR-195 and miR-497 replacement
reveals potential candidates that increase sensitivity to
oxaliplatin in MSI/P53wt colorectal cancer cells. Cells.
8(1111)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
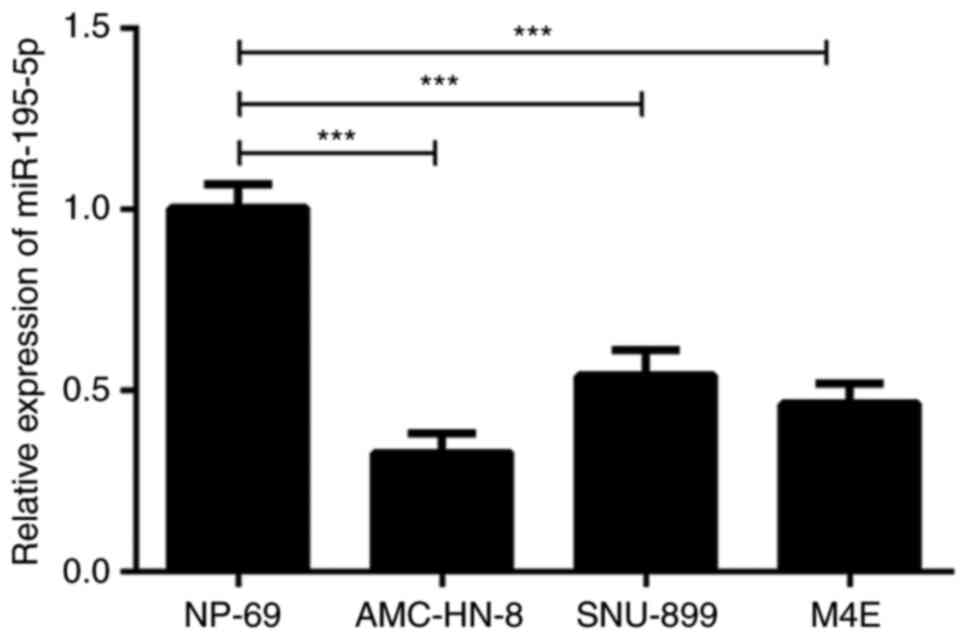
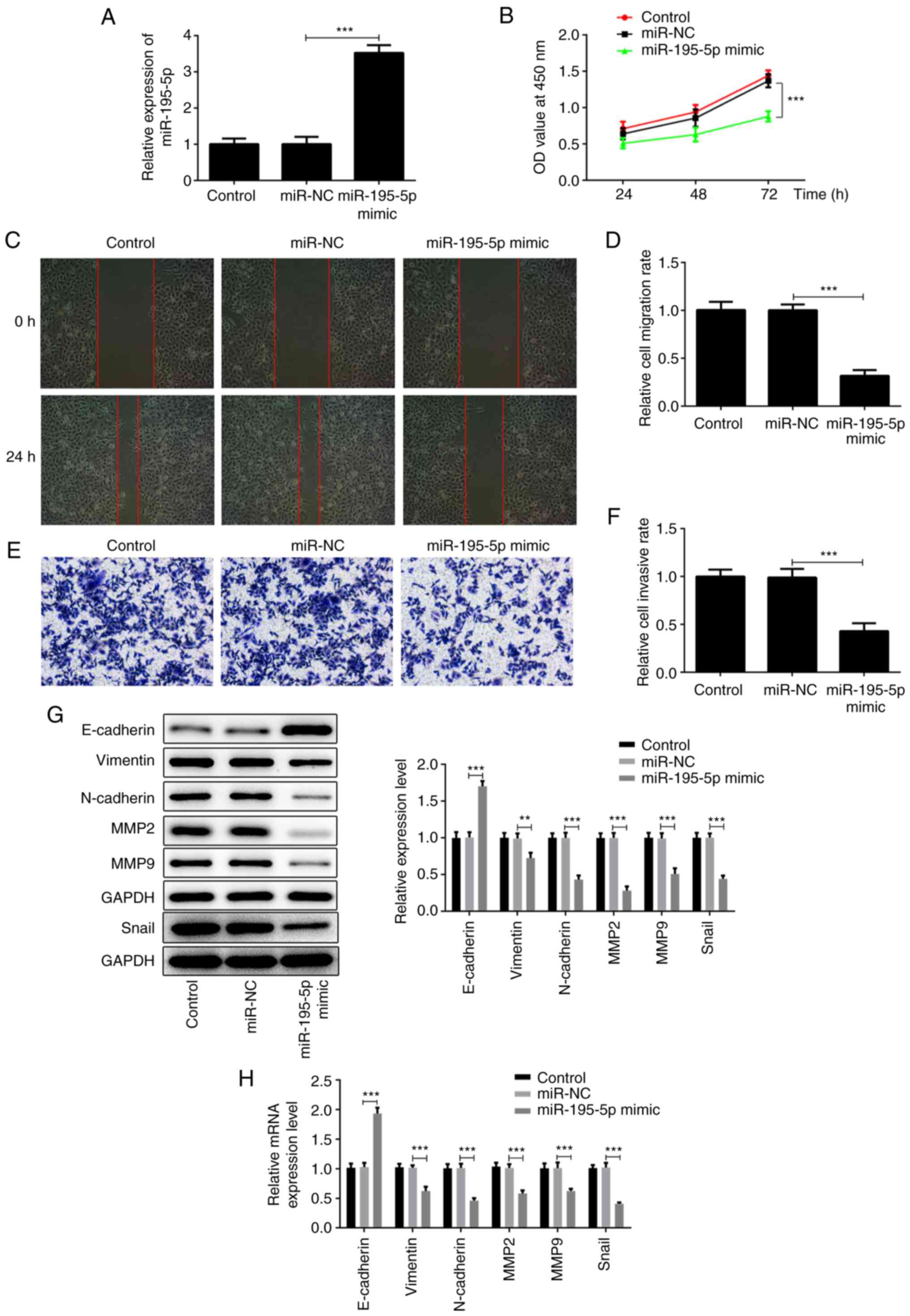
Pang H, Xu X, Dai L, Wang K and Yao X:
MicroRNA-195 is associated with regulating the pathophysiologic
process of human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep.
17:5283–5291. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cheng JZ, Chen JJ, Wang ZG, Yu D and Zu
YZ: The functional role of microRNAs in laryngeal carcinoma. Open
Life Sci. 12:460–464. 2017.
|
|
23
|
Wang PP, Ding SY, Sun YY, Li YH and Fu WN:
MYCT1 inhibits the adhesion and migration of laryngeal cancer cells
potentially through repressing collagen VI. Front Oncol.
10(564733)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Song Y, Yang M, Zhang H, Sun Y, Tao Y, Li
H, Zhang J, Li Y and Yang J: IL-17 affects the progression,
metastasis, and recurrence of laryngeal cancer via the inhibition
of apoptosis through activation of the PI3K/AKT/FAS/F pathways. J
Immunol Res. 2020(2953191)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li Y, Li D, Wang P, Zhu W and Yin W:
Tetrandrine partially reverses multidrug resistance of human
laryngeal cancer cells. J Int Med Res.
48(300060520944706)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shang Y, Wang LQ, Guo QY and Shi TL:
MicroRNA-196a overexpression promotes cell proliferation and
inhibits cell apoptosis through PTEN/Akt/FOXO1 pathway. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:2461–2472. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jin Y, Wang M, Hu H, Huang Q, Chen Y and
Wang G: Overcoming stemness and chemoresistance in colorectal
cancer through miR-195-5p-modulated inhibition of notch signaling.
Int J Biol Macromol. 117:445–453. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li Y, Di C, Li W, Cai W, Tan X, Xu L, Yang
L, Lou G and Yan Y: Oncomirs miRNA-221/222 and tumor suppressors
miRNA-199a/195 are crucial miRNAs in liver cancer: A systematic
analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 61:2315–2327. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yu X, Zhang Y, Ma X and Pertsemlidis A:
miR-195 potentiates the efficacy of microtubule-targeting agents in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 427:85–93. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zheng J, Xu T, Chen F and Zhang Y:
MiRNA-195-5p functions as a tumor suppressor and a predictive of
poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer by directly targeting
CIAPIN1. Pathol Oncol Res. 25:1181–1190. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kalluri R and Neilson EG:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for
fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 112:1776–1784. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang Q, Wang F, Zhong W, Ling H, Wang J,
Cui J, Xie T, Wen S and Chen J: RNA-binding protein RBM6 as a tumor
suppressor gene represses the growth and progression in
laryngocarcinoma. Gene. 697:26–34. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hwang KE, Kim HJ, Song IS, Park C, Jung
JW, Park DS, Oh SH, Kim YS and Kim HR: Salinomycin suppresses
TGF-β1-induced EMT by down-regulating MMP-2 and MMP-9 via the
AMPK/SIRT1 pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Med Sci.
18:715–726. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Karmakar D, Maity J, Mondal P, Shyam
Chowdhury P, Sikdar N, Karmakar P, Das C and Sengupta S: E2F5
promotes prostate cancer cell migration and invasion through
regulation of TFPI2, MMP-2 and MMP-9. Carcinogenesis. 41:1767–1780.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
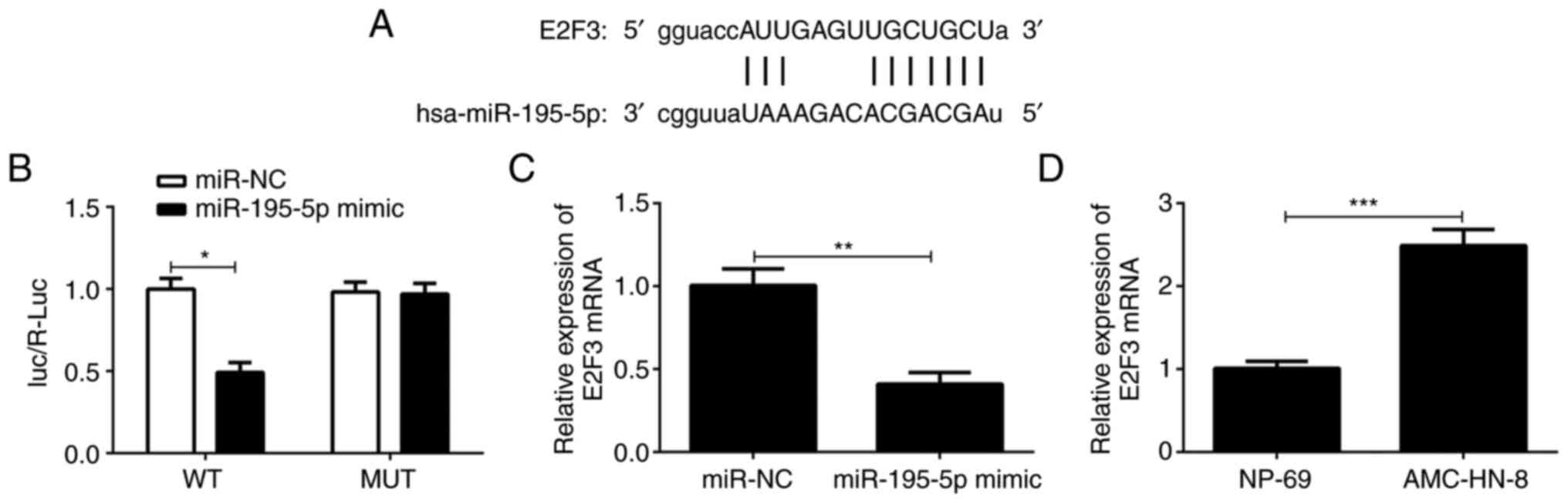
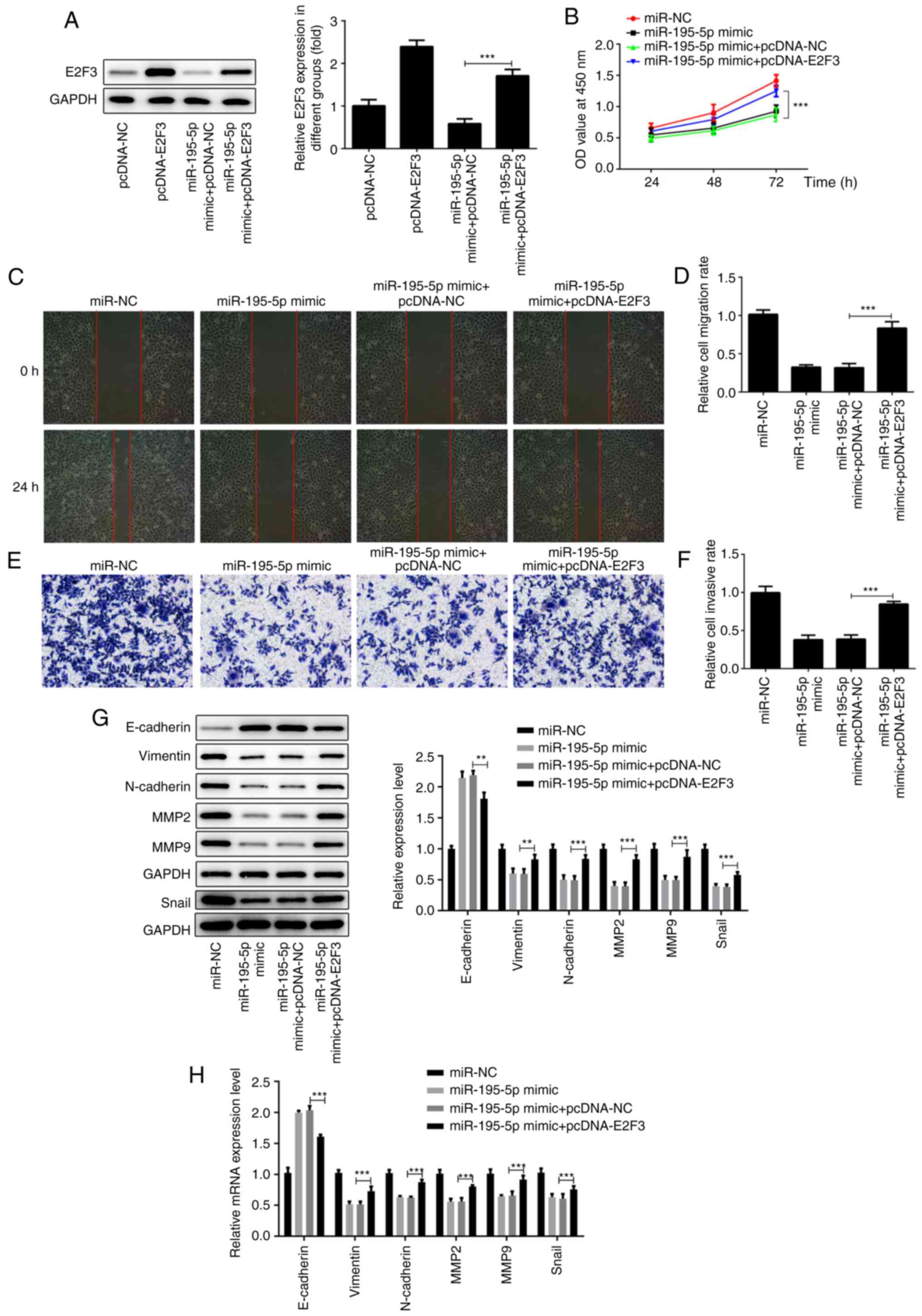
Miles WO, Tschöp K, Herr A, Ji JY and
Dyson NJ: Pumilio facilitates miRNA regulation of the E2F3
oncogene. Genes Dev. 26:356–368. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Tang W, Tang J, Qin J, Geng Q, Zhou Z, Li
B, Zhang J, Chen H, Xia Y and Wang X: Involvement of down-regulated
E2F3 in Hirschsprung's disease. J Pediatr Surg. 48:813–817.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Huang L, Luo J, Cai Q, Pan Q, Zeng H, Guo
Z, Dong W, Huang J and Lin T: MicroRNA-125b suppresses the
development of bladder cancer by targeting E2F3. Int J Cancer.
128:1758–1769. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ren XS, Yin MH, Zhang X, Wang Z, Feng SP,
Wang GX, Luo YJ, Liang PZ, Yang XQ, He JX and Zhang BL:
Tumor-suppressive microRNA-449a induces growth arrest and
senescence by targeting E2F3 in human lung cancer cells. Cancer
Lett. 344:195–203. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|