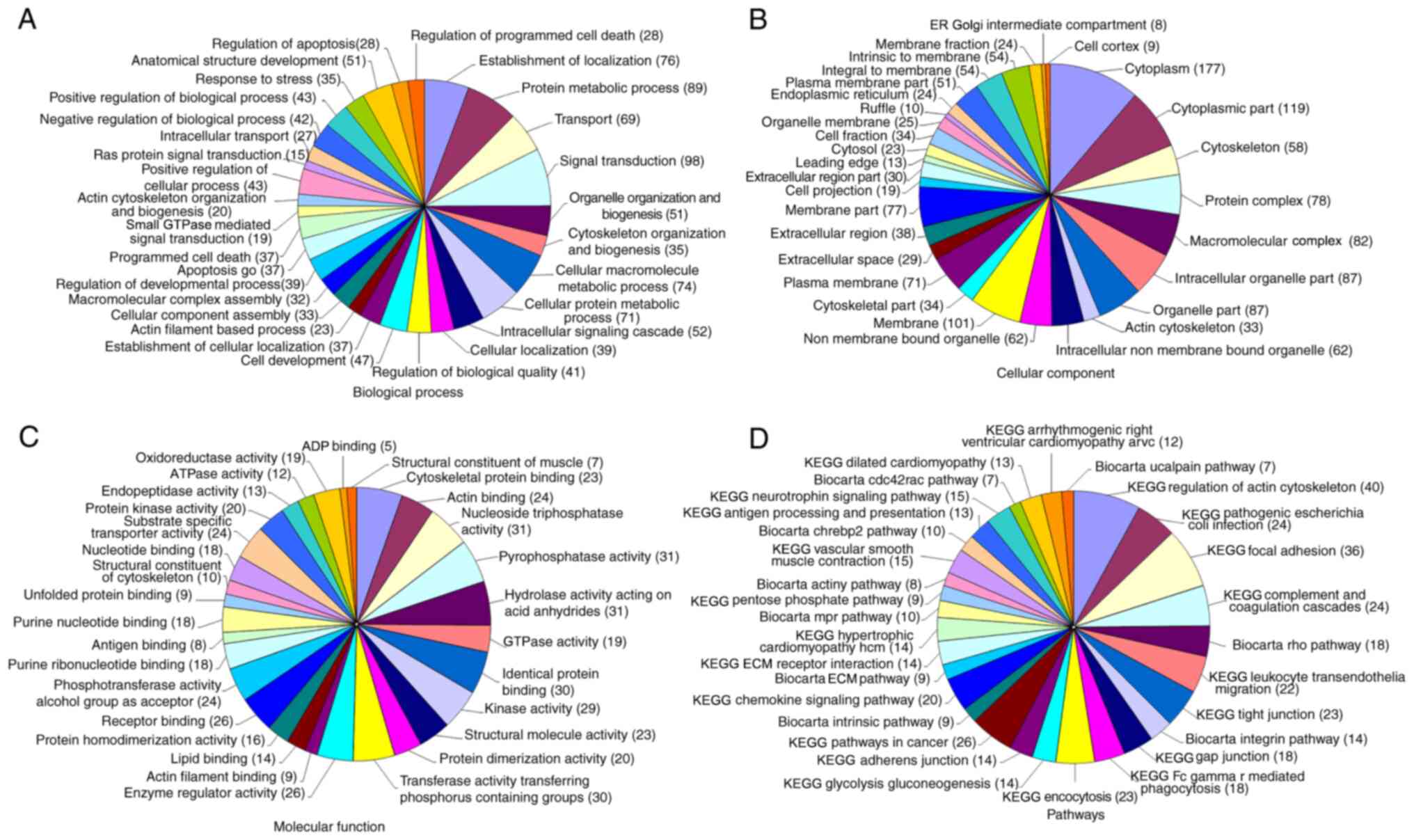
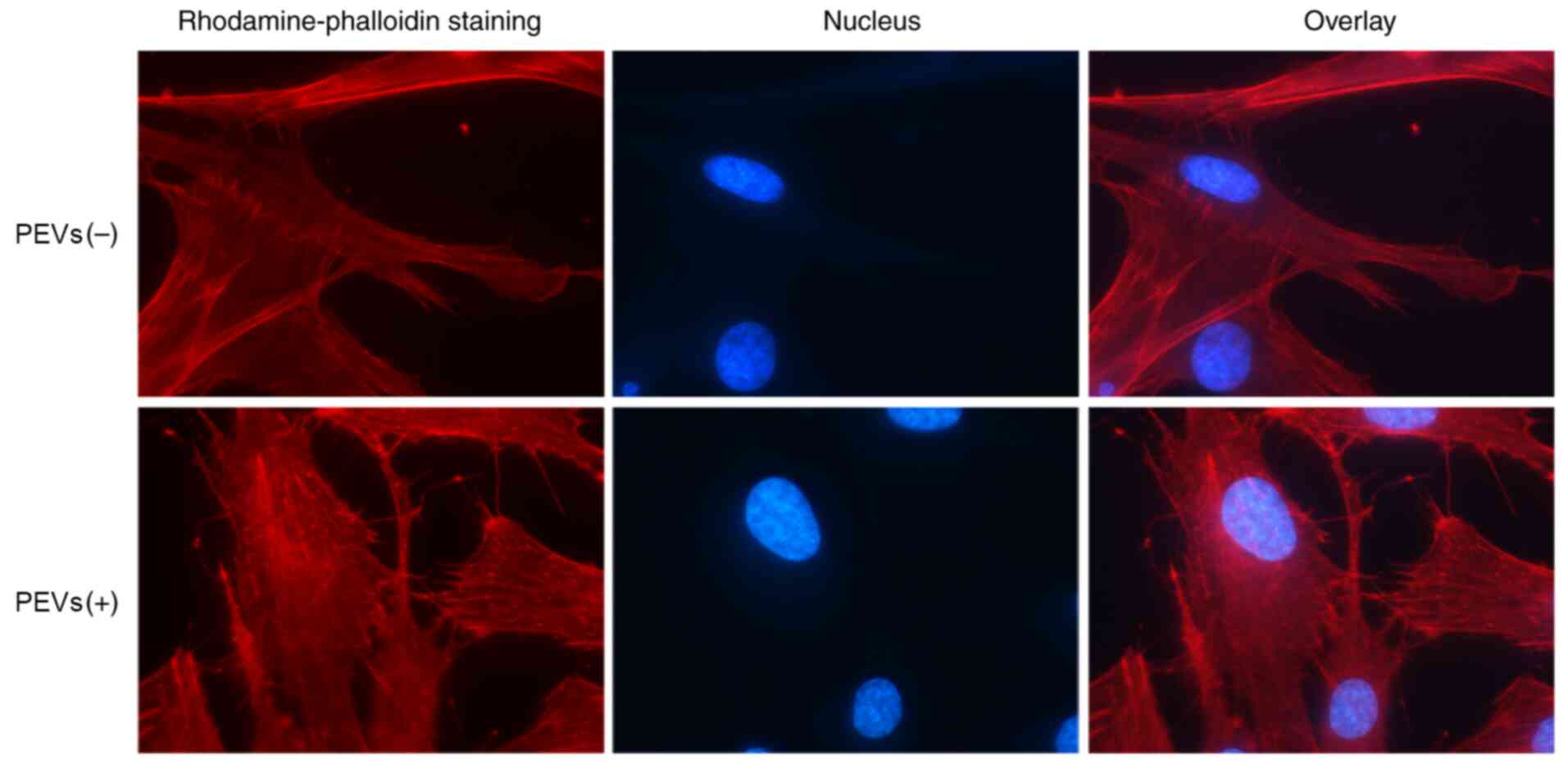
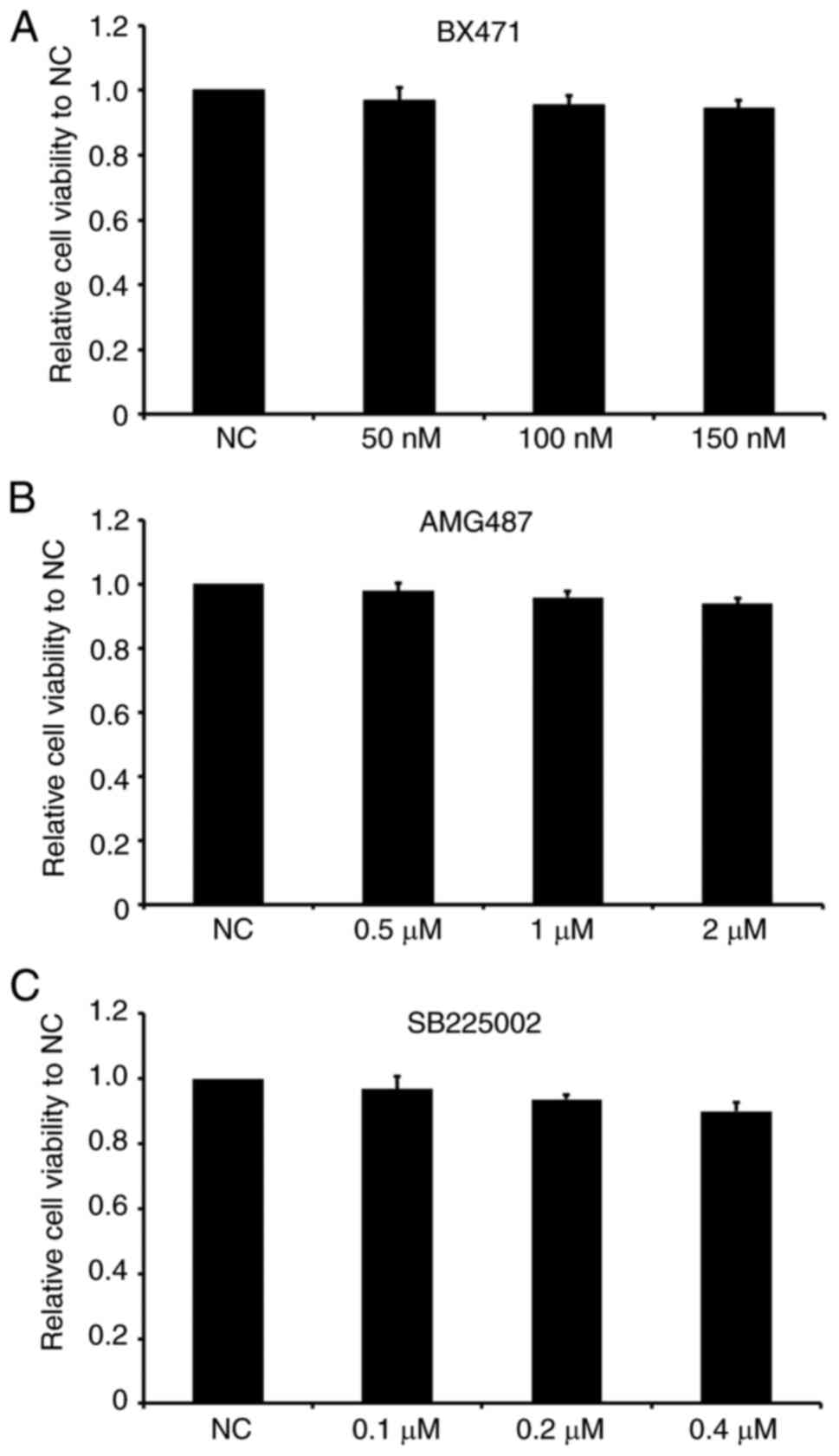
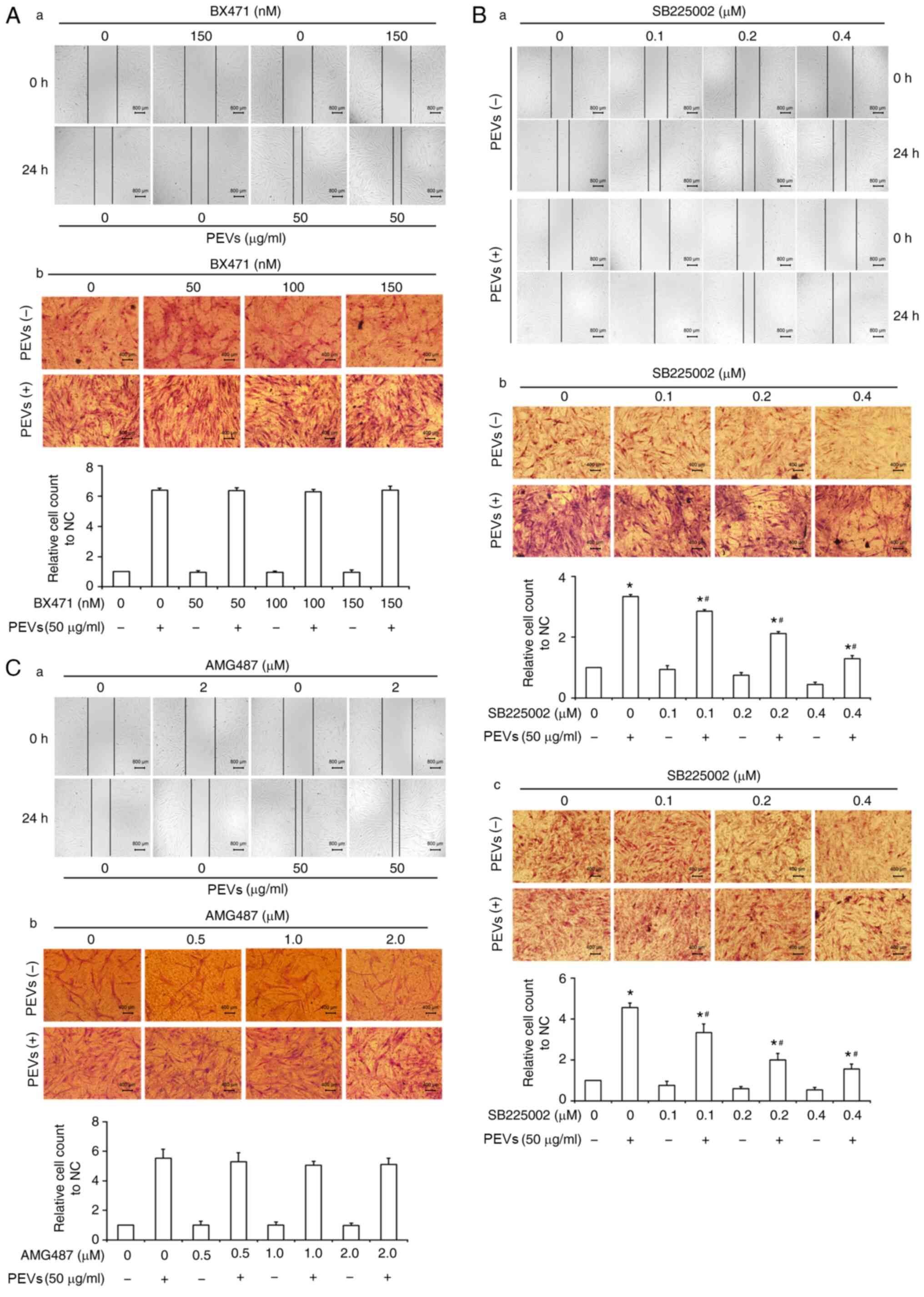
|
1
|
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, Burmester
GR, Emery P, Firestein GS, Kavanaugh A, McInnes IB, Solomon DH,
Strand V and Yamamoto K: Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
4(18001)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Román-Fernández IV, García-Chagollán M,
Cerpa-Cruz S, Jave-Suárez LF, Palafox-Sánchez CA, García-Arellano
S, Sánchez-Zuno GA and Muñoz-Valle JF: Assessment of CD40 and CD40L
expression in rheumatoid arthritis patients, association with
clinical features and DAS28. Clin Exp Med. 19:427–437.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bartok B and Firestein GS: Fibroblast-like
synoviocytes: Key effector cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Immunol
Rev. 233:233–255. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kawaguchi Y, Waguri-Nagaya Y, Tatematsu N,
Oguri Y, Kobayashi M, Nozaki M, Asai K, Aoyama M and Otsuka T: The
Janus kinase inhibitor tofacitinib inhibits TNF-α-induced
gliostatin expression in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes.
Clin Exp Rheumatol. 36:559–567. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schönfeld C, Pap T, Neumann E and
Müller-Ladner U: Fibroblasts as pathogenic cells in rheumatic
inflammation. Z Rheumatol. 74:33–38. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In German).
|
|
6
|
Müller-Ladner U, Pap T, Gay RE, Neidhart M
and Gay S: Mechanisms of disease: The molecular and cellular basis
of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Clin Pract
Rheumatol. 1:102–110. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ponomareva AA, Nevzorova TA, Mordakhanova
ER, Andrianova IA, Rauova L, Litvinov RI and Weisel JW:
Intracellular origin and ultrastructure of platelet-derived
microparticles. J Thromb Haemost. 15:1655–1667. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Rosińska J, Łukasik M and Kozubski W: The
impact of vascular disease treatment on Platelet-Derived
Microvesicles. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 31:627–644. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Vismara M, Zarà M, Negri S, Canino J,
Canobbio I, Barbieri SS, Moccia F, Torti M and Guidetti GF:
Platelet-derived extracellular vesicles regulate cell cycle
progression and cell migration in breast cancer cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1868(118886)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vajen T, Mause SF and Koenen RR:
Microvesicles from platelets: Novel drivers of vascular
inflammation. Thromb Haemost. 114:228–236. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sellam J, Proulle V, Jüngel A, Ittah M,
Miceli Richard C, Gottenberg JE, Toti F, Benessiano J, Gay S,
Freyssinet JM and Mariette X: Increased levels of circulating
microparticles in primary Sjögren's syndrome, systemic lupus
erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis and relation with disease
activity. Arthritis Res Ther. 11(R156)2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Olumuyiwa-Akeredolu OO, Page MJ, Soma P
and Pretorius E: Platelets: Emerging facilitators of cellular
crosstalk in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 15:237–248.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chaturvedi S, Cockrell E, Espinola R, His
L, Fulton S, Khan M, Li L, Fonseca F, Kundu S and McCrae KR:
Circulating microparticles in patients with antiphospholipid
antibodies: Characterization and associations. Thromb Res.
135:102–108. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Knijff-Dutmer EA, Koerts J, Nieuwland R,
Kalsbeek-Batenburg EM and van de Laar MA: Elevated levels of
platelet microparticles are associated with disease activity in
rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 46:1498–1503.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Boilard E, Nigrovic PA, Larabee K, Watts
GF, Coblyn JS, Weinblatt ME, Massarotti EM, Remold-O'Donnell E,
Farndale RW, Ware J and Lee DM: Platelets amplify inflammation in
arthritis via collagen-dependent microparticle production. Science.
327:580–583. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Puddu P, Puddu GM, Cravero E, Muscari S
and Muscari A: The involvement of circulating microparticles in
inflammation, coagulation and cardiovascular diseases. Can J
Cardiol. 26:140–145. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Italiano JE Jr, Mairuhu AT and Flaumenhaft
R: Clinical relevance of microparticles from platelets and
megakaryocytes. Curr Opin Hematol. 17:578–584. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Villar-Vesga J, Grajales C, Burbano C,
Vanegas-García A, Muñoz-Vahos CH, Vásquez G, Rojas M and Castaño D:
Platelet-derived microparticles generated in vitro resemble
circulating vesicles of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and
activate monocytes. Cell Immunol. 336:1–11. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Dashevsky O, Varon D and Brill A:
Platelet-derived microparticles promote invasiveness of prostate
cancer cells via upregulation of MMP-2 production. Int J Cancer.
124:1773–1777. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Janowska-Wieczorek A, Wysoczynski M,
Kijowski J, Marquez-Curtis L, Machalinski B, Ratajczak J and
Ratajczak MZ: Microvesicles derived from activated platelets induce
metastasis and angiogenesis in lung cancer. Int J Cancer.
113:752–760. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Barteneva NS, Fasler-Kan E, Bernimoulin M,
Stern JN, Ponomarev ED, Duckett L and Vorobjev IA: Circulating
microparticles: Square the circle. BMC Cell Biol.
14(23)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang W, Liu J, Yang B, Ma Z, Liu G, Shen W
and Zhang Y: Modulation of platelet-derived microparticles to
adhesion and motility of human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like
synoviocytes. PLoS One. 12(e0181003)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Grépin R, Guyot M, Giuliano S, Boncompagni
M, Ambrosetti D, Chamorey E, Scoazec JY, Negrier S, Simonnet H and
Pagès G: The CXCL7/CXCR1/2 axis is a key driver in the growth of
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 74:873–883.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Markov DA, Savkina M, Anikin M, Del Campo
M, Ecker K, Lambowitz AM, De Gnore JP and McAllister WT:
Identification of proteins associated with the yeast mitochondrial
RNA polymerase by tandem affinity purification. Yeast. 26:423–440.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Nadar M, Chan MY, Huang SW, Huang CC,
Tseng JT and Tsai CH: HuR binding to AU-rich elements present in
the 3' untranslated region of Classical swine fever virus. Virol J.
8(340)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Sun BO, Fang Y, Li Z, Chen Z and Xiang J:
Role of cellular cytoskeleton in epithelial-mesenchymal transition
process during cancer progression. Biomed Rep. 3:603–610.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
An G, Wu F, Huang S, Feng L, Bai J, Gu S
and Zhao X: Effects of CCL5 on the biological behavior of breast
cancer and the mechanisms of its interaction with tumor-associated
macrophages. Oncol Rep. 42:2499–2511. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Quemener C, Baud J, Boyé K, Dubrac A,
Billottet C, Soulet F, Darlot F, Dumartin L, Sire M, Grepin R, et
al: Dual roles for CXCL4 chemokines and CXCR3 in angiogenesis and
invasion of pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 76:6507–6519.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Guo Q, Jian Z, Jia B and Chang L: CXCL7
promotes proliferation and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells.
Oncol Rep. 37:1114–1122. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Szekanecz Z and Koch AE: Successes and
failures of chemokine-pathway targeting in rheumatoid arthritis.
Nat Rev Rheumatol. 12:5–13. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Miyabe Y, Lian J, Miyabe C and Luster AD:
Chemokines in rheumatic diseases: Pathogenic role and therapeutic
implications. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 15:731–746. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Karin N and Razon H: Chemokines beyond
chemo-attraction: CXCL10 and its significant role in cancer and
autoimmunity. Cytokine. 109:24–28. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Haringman JJ, Smeets TJ, Reinders-Blankert
P and Tak PP: Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression in paired
peripheral blood mononuclear cells and synovial tissue of patients
with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and reactive arthritis.
Ann Rheum Dis. 65:294–300. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Im CH, Park JA, Kim JY, Lee EY, Lee EB,
Kim Y and Song YW: CXCR3 polymorphism is associated with male
gender and pleuritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.
Hum Immunol. 75:466–469. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yeo L, Adlard N, Biehl M, Juarez M,
Smallie T, Snow M, Buckley CD, Raza K, Filer A and Scheel-Toellner
D: Expression of chemokines CXCL4 and CXCL7 by synovial macrophages
defines an early stage of rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis.
75:763–771. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Szekanecz Z, Koch AE and Tak PP: Chemokine
and chemokine receptor blockade in arthritis, a prototype of
immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Neth J Med. 69:356–366.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
DiDonato JA, Mercurio F and Karin M: NF-κB
and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol Rev.
246:379–400. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Dong YL, Kabir SM, Lee ES and Son DS:
CXCR2-driven ovarian cancer progression involves upregulation of
proinflammatory chemokines by potentiating NF-κB activation via
EGFR-transactivated Akt signaling. PLoS One.
8(e83789)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang Z, Tan X, Luo J, Cui B, Lei S, Si Z,
Shen L and Yao H: GNA13 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by
upregulating CXC chemokines via the NF-κB signaling pathway in
colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Med. 7:5611–5620. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|