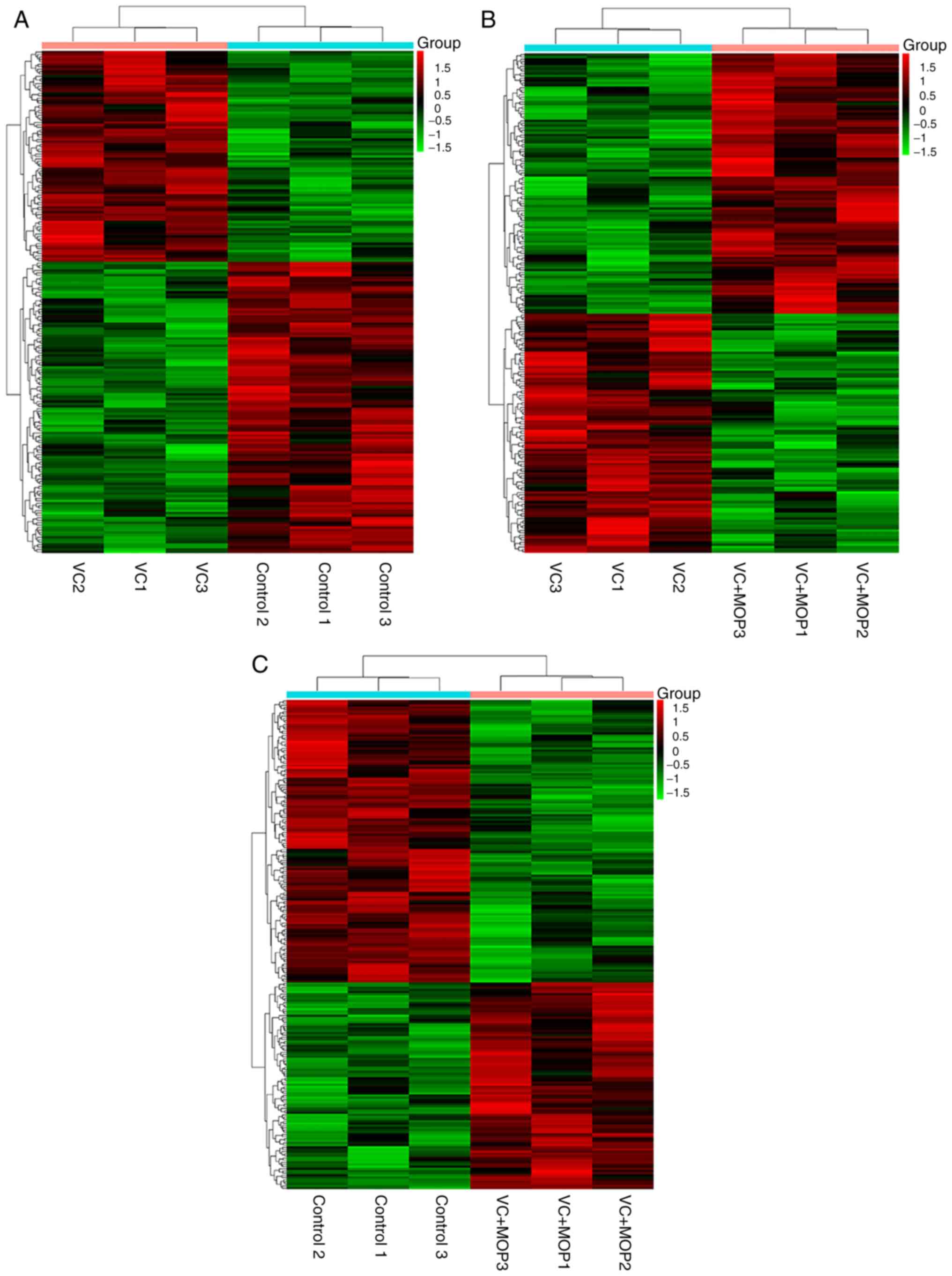
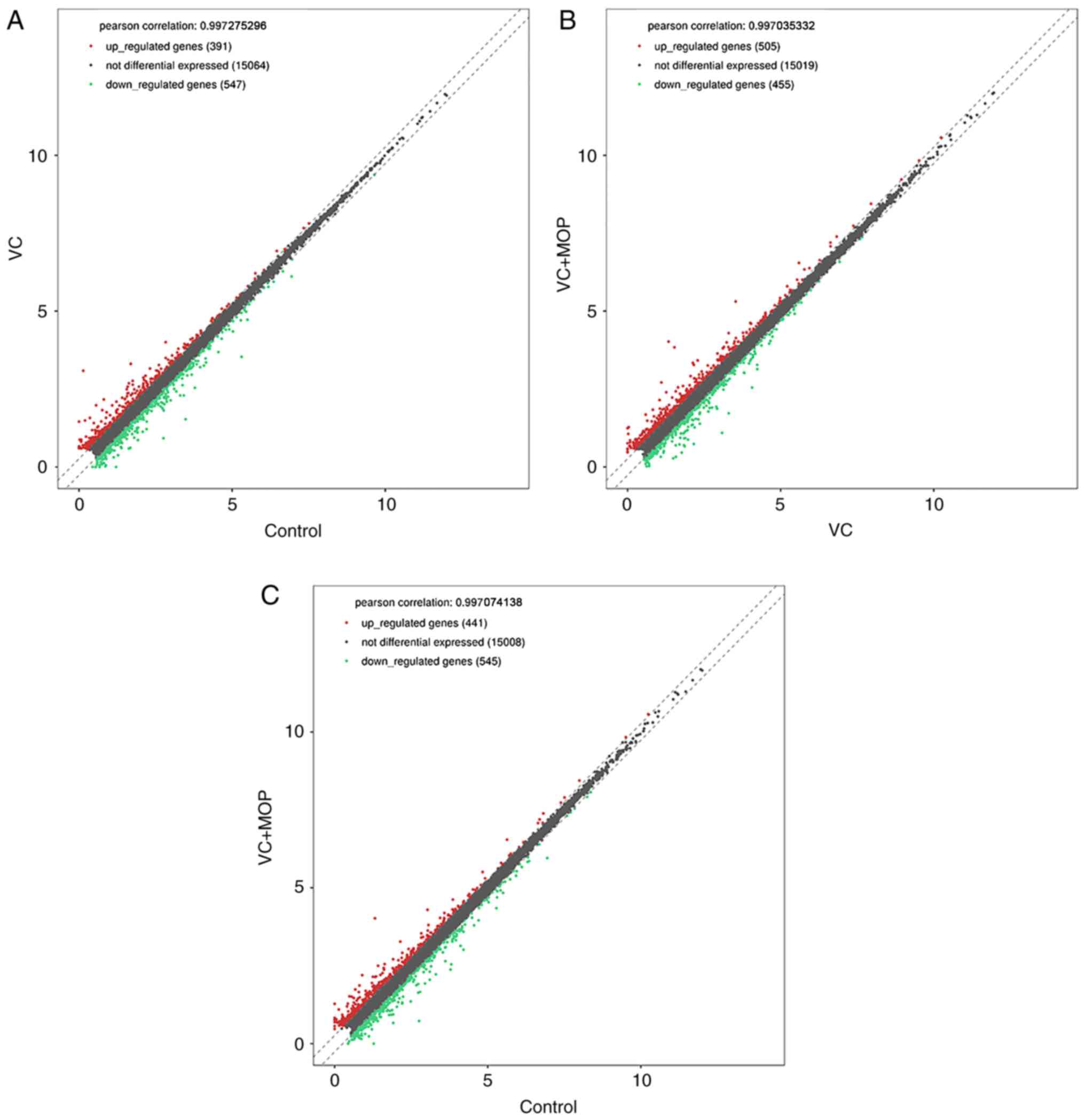
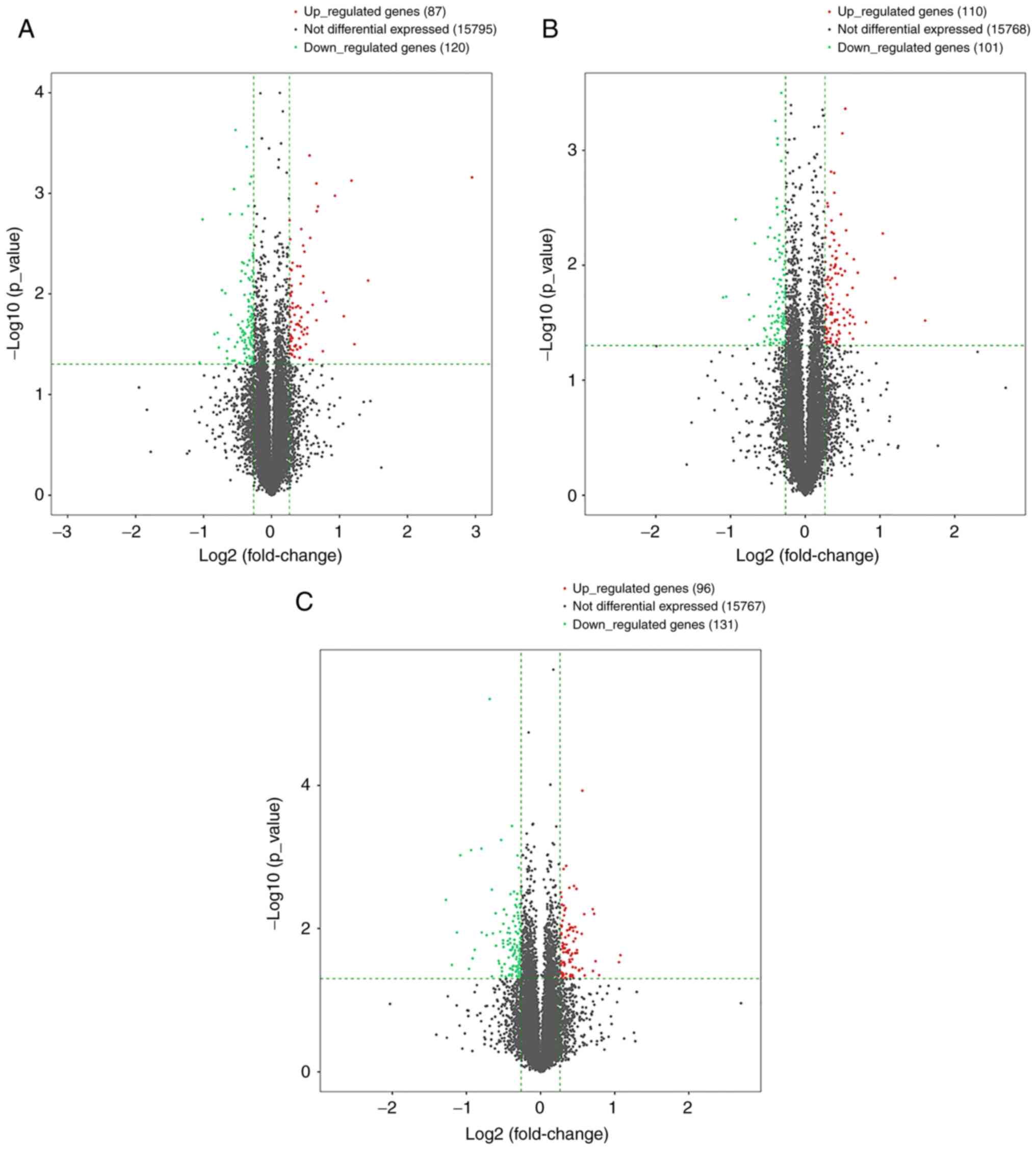
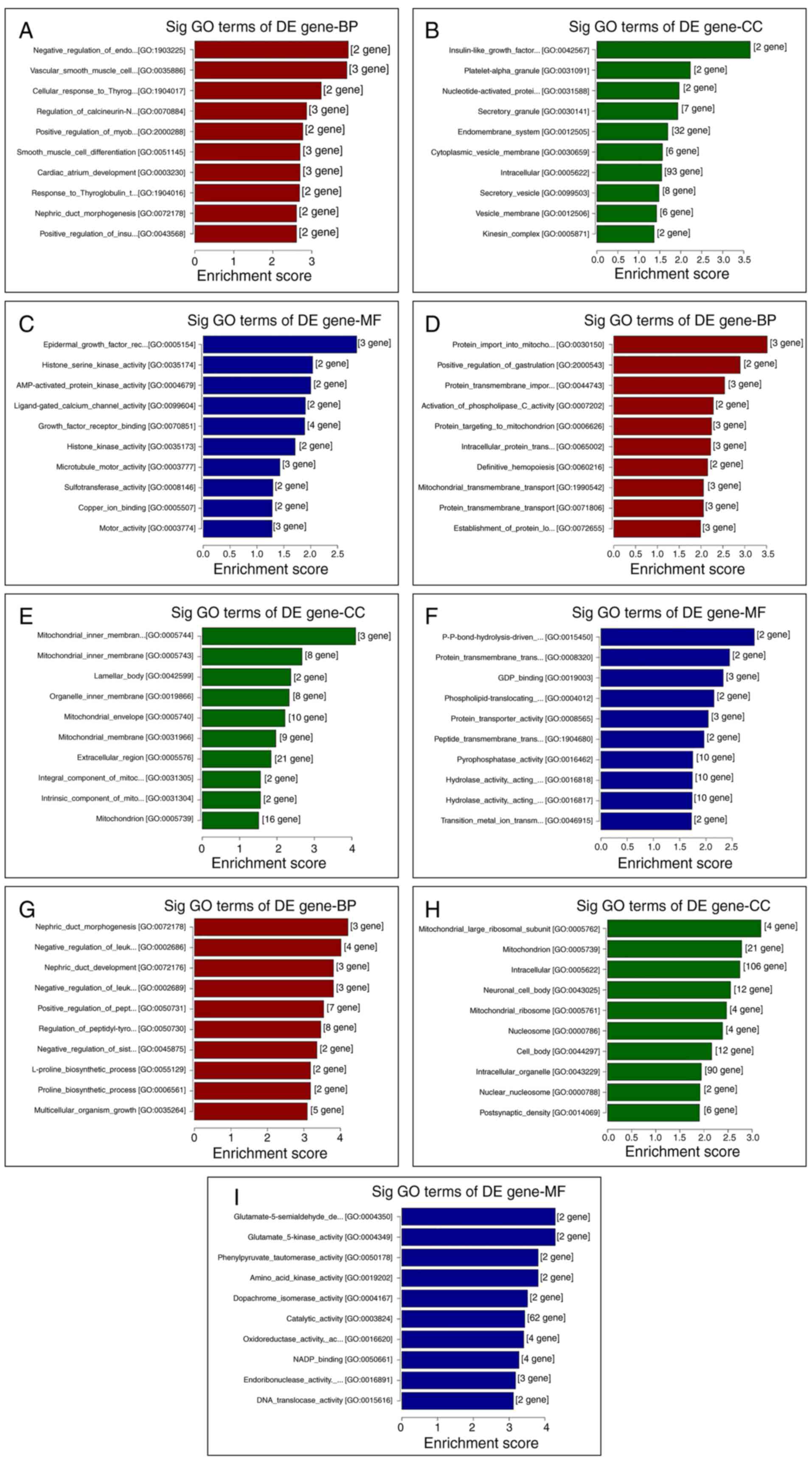
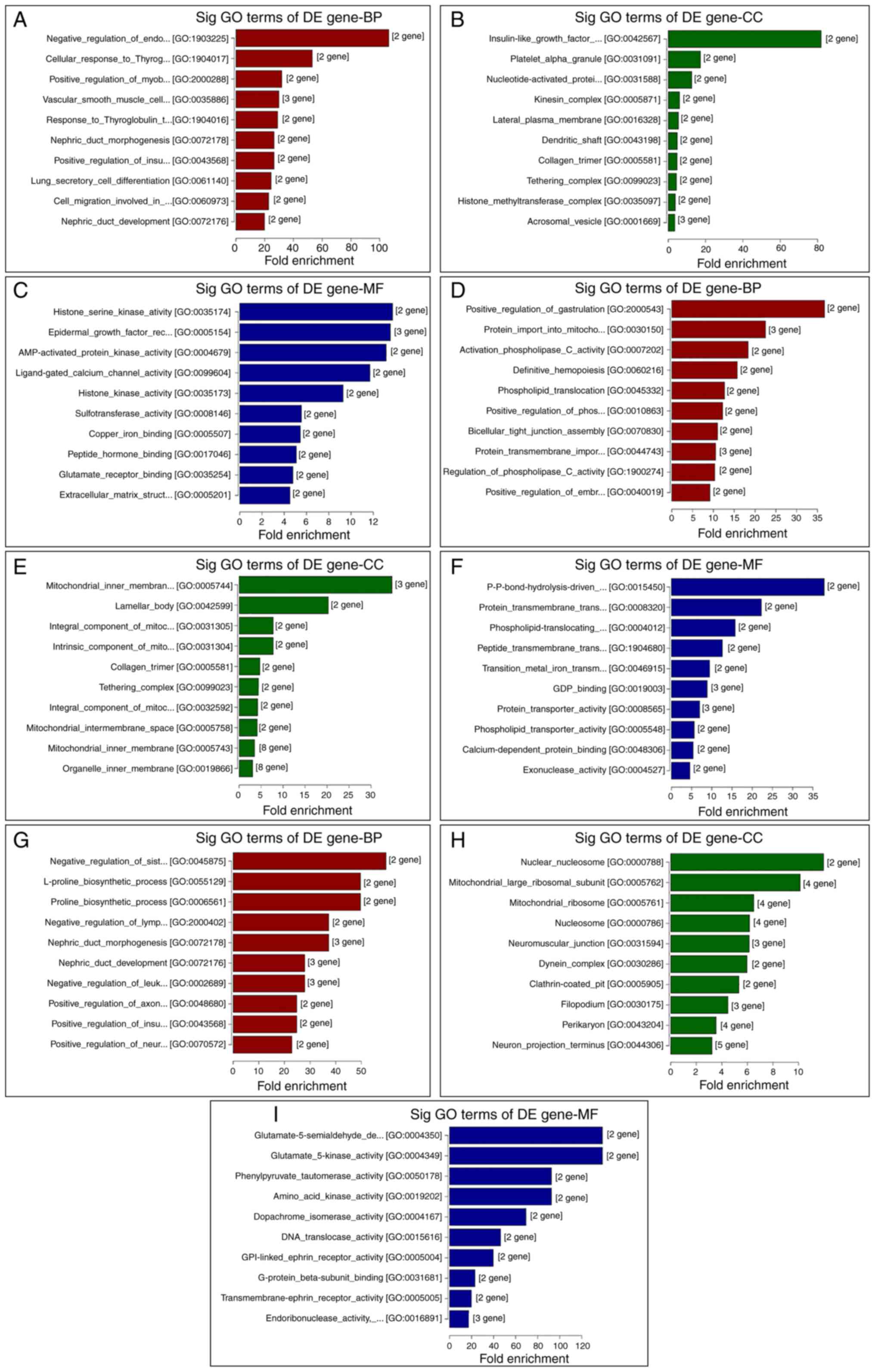
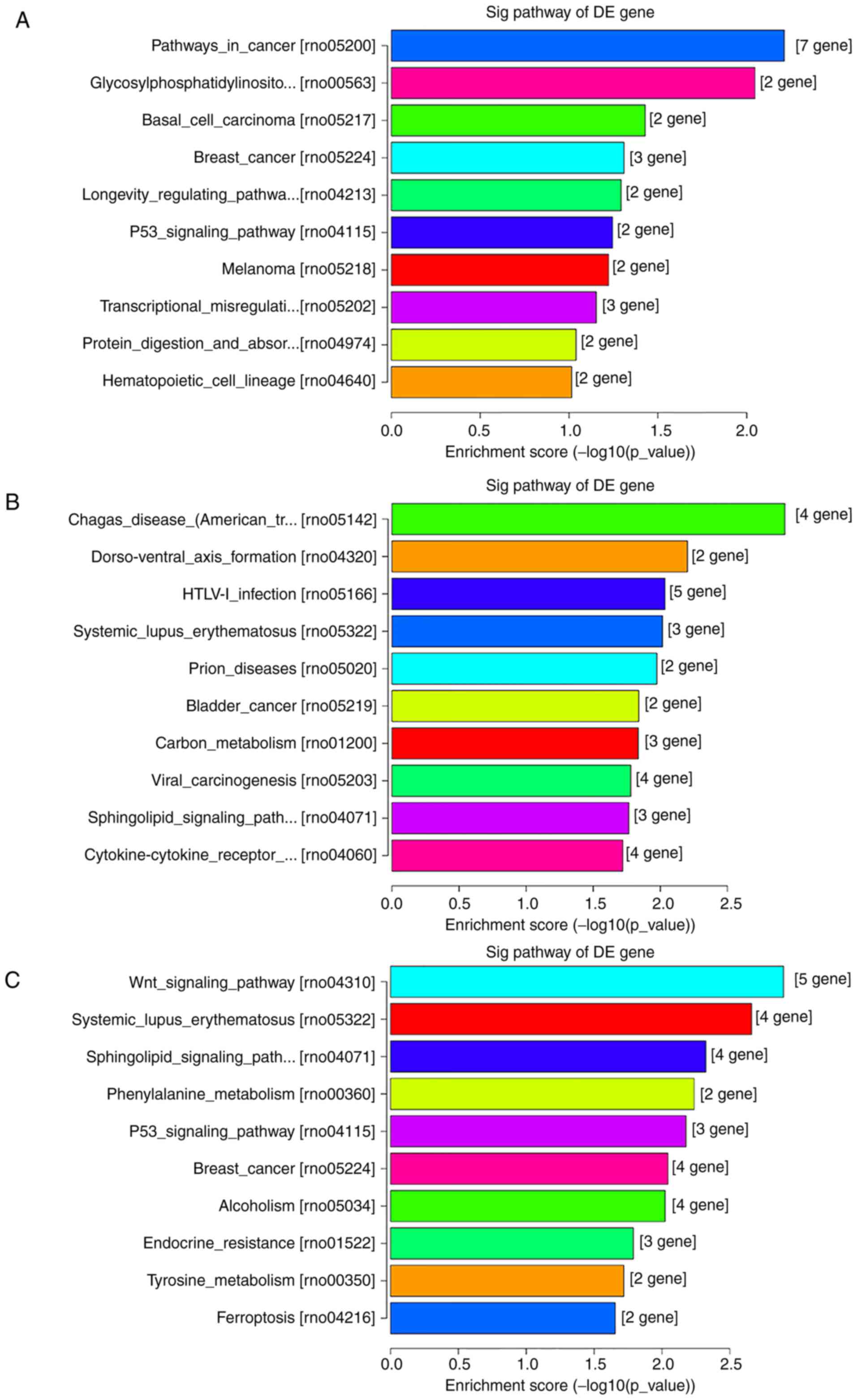
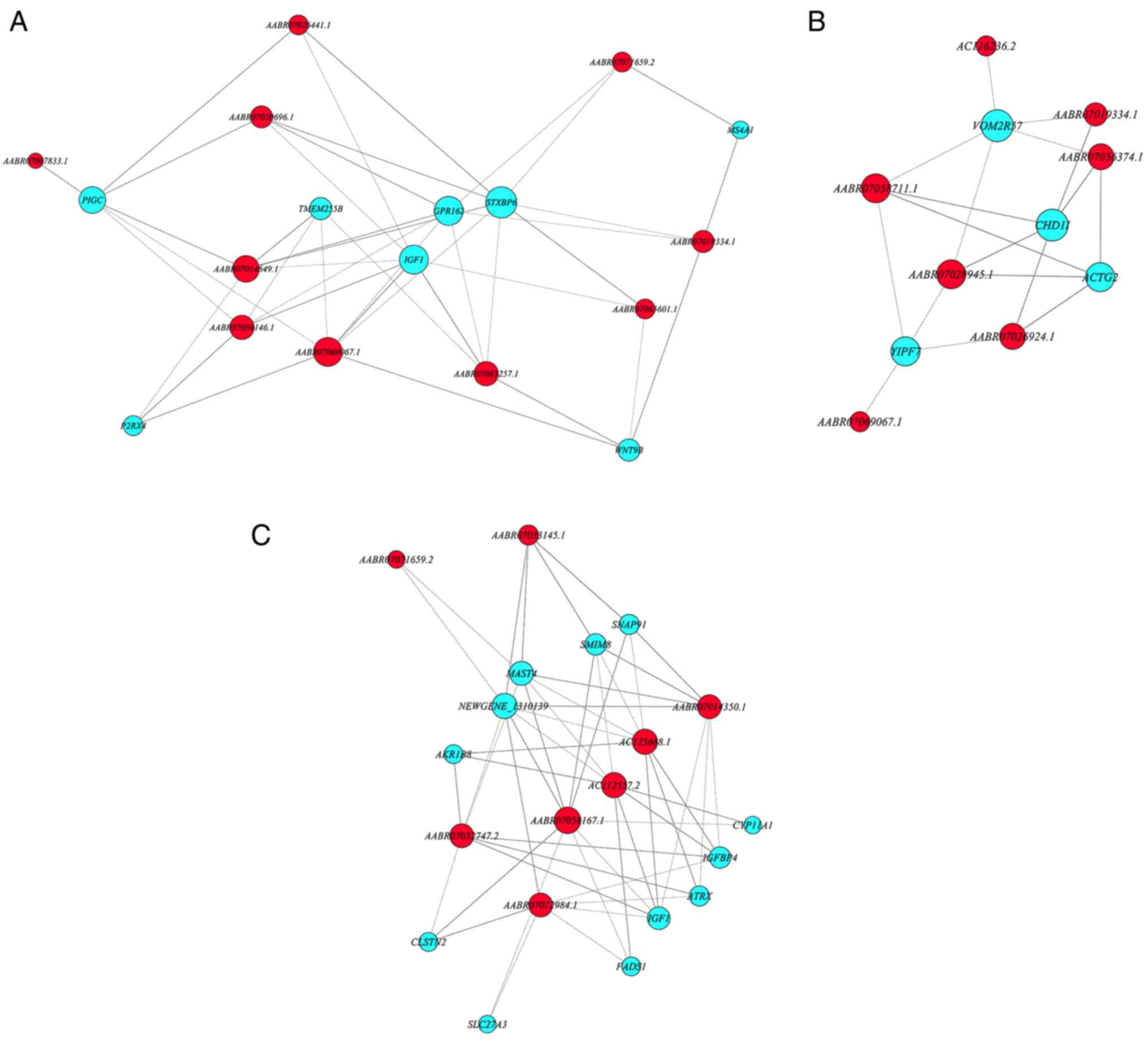
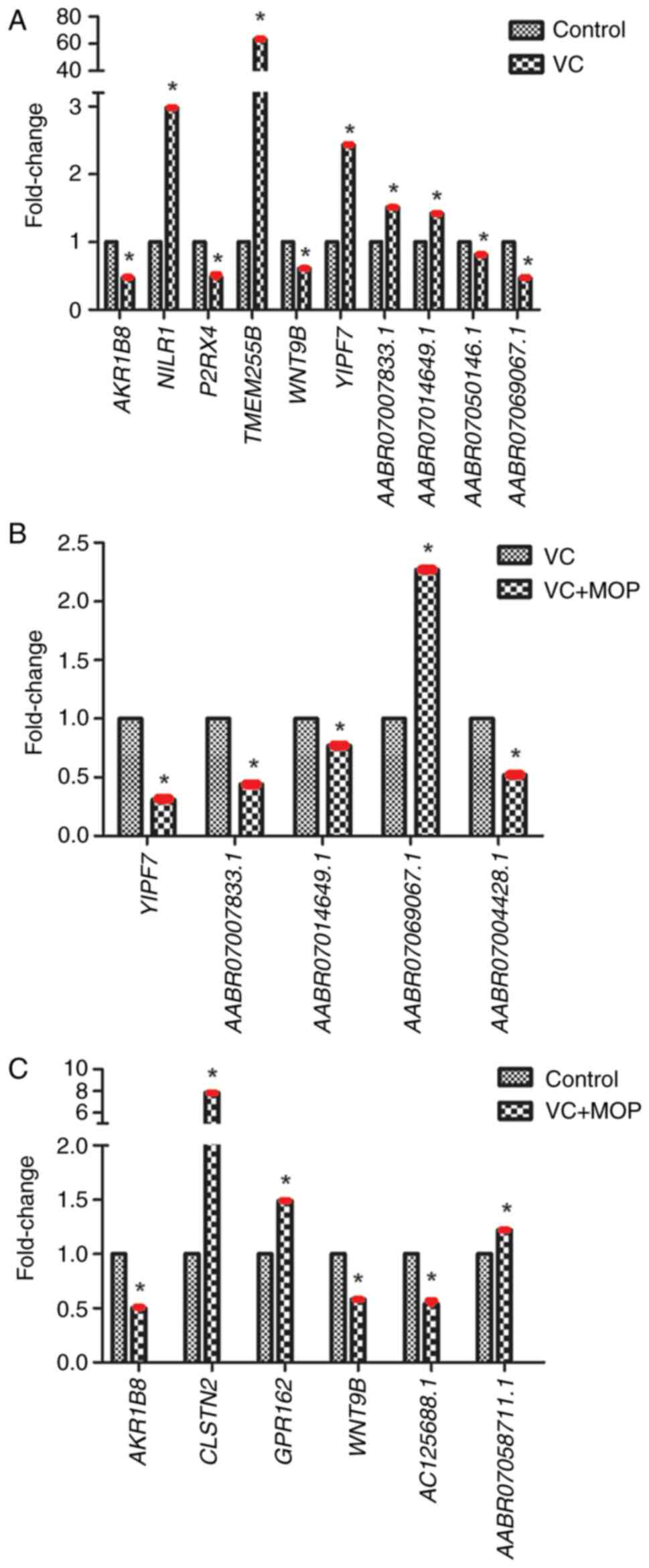
|
1
|
Leslie SW, Sajjad H and Siref LE:
Varicocele. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island,
FL, 2021.
|
|
2
|
Wang NN, Dallas K, Li S, Baker L and
Eisenberg ML: The association between varicocoeles and vascular
disease: An analysis of U.S. Claims data. Andrology. 6:99–103.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Reesink DJ, Huisman PM, Wiltink J, Kruger
AE and Lock TMT: Sneeze and pop: A ruptured varicocele; analysis of
literature, guided by a well-documented case-report. BMC Urol.
19(14)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sigalos JT and Pastuszak AW: Chronic
orchialgia: Epidemiology, diagnosis and evaluation. Transl Androl
Urol. 6 (Suppl 1):S37–S43. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Afshar A, Aliaghaei A, Nazarian H,
Abbaszadeh HA, Naserzadeh P, Fathabadi FF, Abdi S, Raee P,
Aghajanpour F, Norouzian M and Abdollahifar MA: Curcumin-loaded
iron particle improvement of spermatogenesis in azoospermic mouse
induced by long-term scrotal hyperthermia. Reprod Sci. 28:371–380.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jarow JP: Effects of varicocele on male
fertility. Hum Reprod Update. 7:59–64. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mehta A and Goldstein M: Microsurgical
varicocelectomy: A review. Asian J Androl. 15:56–60.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ahlberg NE, Bartley O and Chidekel N:
Right and left gonadal veins. An anatomical and statistical study.
Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 4:593–601. 1966.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bach PV, Najari BB and Goldstein M:
Varicocele-a case for early intervention. F1000Res.
5(1792)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chiba K, Ramasamy R, Lamb DJ and Lipshultz
LI: The varicocele: Diagnostic dilemmas, therapeutic challenges and
future perspectives. Asian J Androl. 18:276–281. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Fretz PC and Sandlow JI: Varicocele:
Current concepts in pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Urol
Clin North Am. 29:921–937. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Luo DY, Yang G, Liu JJ, Yang YR and Dong
Q: Effects of varicocele on testosterone, apoptosis and expression
of StAR mRNA in rat Leydig cells. Asian J Androl. 13:287–291.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Saypol DC, Howards SS, Turner TT and
Miller ED Jr: Influence of surgically induced varicocele on
testicular blood flow, temperature, and histology in adult rats and
dogs. J Clin Invest. 68:39–45. 1981.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Pastuszak AW and Wang R: Varicocele and
testicular function. Asian J Androl. 17:659–667. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ozbek E, Yurekli M, Soylu A, Davarci M and
Balbay MD: The role of adrenomedullin in varicocele and impotence.
BJU Int. 86:694–698. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim IT, Park HJ, Nam JH, Park YM, Won JH,
Choi J, Choe BK and Lee KT: In-vitro and in-vivo anti-inflammatory
and antinociceptive effects of the methanol extract of the roots of
Morinda officinalis. J Pharm Pharmacol. 57:607–615. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang L, Zhao X, Wang F, Lin Q and Wang W:
Effects of morinda officinalis polysaccharide on experimental
varicocele rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2016(5365291)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Marinov GK: On the design and prospects of
direct RNA sequencing. Brief Funct Genomics. 16:326–335.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li X, Wu Z, Fu X and Han W: lncRNAs:
Insights into their function and mechanics in underlying disorders.
Mutat Res Rev Mutat Res. 762:1–21. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kazimierczyk M, Kasprowicz MK, Kasprzyk ME
and Wrzesinski J: Human long noncoding RNA interactome: Detection,
characterization and function. Int J Mol Sci.
21(1027)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Li L, Zhuang Y, Zhao X and Li X: Long
non-coding RNA in neuronal development and neurological disorders.
Front Genet. 9(744)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hu Y, Lin J, Fang H, Fang J, Li C, Chen W,
Liu S, Ondrejka S, Gong Z, Reu F, et al: Targeting the
MALAT1/PARP1/LIG3 complex induces DNA damage and apoptosis in
multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 32:2250–2262. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Mirza AH, Kaur S and Pociot F: Long
non-coding RNAs as novel players in β cell function and type 1
diabetes. Hum Genomics. 11(17)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Hou YM, Gao F, Xiao JW, Li CC and
Tang Y: lncRNA GAS5 regulates myocardial infarction by targeting
the miR-525-5p/CALM2 axis. J Cell Biochem. 120:18678–18688.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Morlando M and Fatica A: Alteration of
epigenetic regulation by long noncoding RNAs in cancer. Int J Mol
Sci. 19(570)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang Y, Junjie P, Sanjun C and Ma Y: Long
non-coding RNAs in colorectal cancer: Progression and future
directions. J Cancer. 8:3212–3225. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Loewen G, Jayawickramarajah J, Zhuo Y and
Shan B: Functions of lncRNA HOTAIR in lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol.
7(90)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang X, Ruan Y, Wang X, Zhao W, Jiang Q,
Jiang C, Zhao Y, Xu Y, Sun F, Zhu Y, et al: Long intragenic
non-coding RNA lincRNA-p21 suppresses development of human prostate
cancer. Cell Prolif. 50(e12318)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dong H, Zhang Q, Li Y, Li L, Lan W, He J,
Li H, Xiong Y and Qin W: Extraction, characterization and
antioxidant activities of polysaccharides of Chuanminshen
violaceum. Int J Biol Macromol. 86:224–232. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xu SY, Liu JP, Huang X, Du LP, Shi FL,
Dong R, Huang XT, Zheng K, Liu Y and Cheong KL:
Ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction, characterization and
biological activity of pectin from jackfruit peel. Lwt. 90:577–582.
2018.
|
|
31
|
Turner TT: The study of varicocele through
the use of animal models. Hum Reprod Update. 7:78–84.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT and
Salzberg SL: Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with HISAT, StringTie and Ballgown. Nat Protoc.
11:1650–1667. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kim D, Langmead B and Salzberg SL: HISAT:
A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods.
12:357–360. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang T, Zheng T, Wang C, Zhang W, Jia D,
Wang R and Qiao B: Effects of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and
star D7 on testosterone synthesis. Acta Endocrinol (Buchar).
14:155–162. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Boyer A, Paquet M, Lague MN, Hermo L and
Boerboom D: Dysregulation of WNT/CTNNB1 and PI3K/AKT signaling in
testicular stromal cells causes granulosa cell tumor of the testis.
Carcinogenesis. 30:869–878. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Boyer A, Hermo L, Paquet M, Robaire B and
Boerboom D: Seminiferous tubule degeneration and infertility in
mice with sustained activation of WNT/CTNNB1 signaling in sertoli
cells. Biol Reprod. 79:475–485. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Takase HM and Nusse R: Paracrine
Wnt/β-catenin signaling mediates proliferation of undifferentiated
spermatogonia in the adult mouse testis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
113:E1489–E1497. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kerr GE, Young JC, Horvay K, Abud HE and
Loveland KL: Regulated Wnt/beta-catenin signaling sustains adult
spermatogenesis in mice. Biol Reprod. 90(3)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Tanimoto K, Suzuki K, Jokitalo E, Sakai N,
Sakaguchi T, Tamura D, Fujii G, Aoki K, Takada S, Ishida R, et al:
Characterization of YIPF3 and YIPF4, cis-golgi localizing yip
domain family proteins. Cell Struct Funct. 36:171–185.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kranjc T, Dempsey E, Cagney G, Nakamura N,
Shields DC and Simpson JC: Functional characterisation of the YIPF
protein family in mammalian cells. Histochem Cell Biol.
147:439–451. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kim SW, Jung YS, Ahn JB, Shin ES, Jang HW,
Lee HJ, Kim T, Kim DY, Bang D, Kim WH and Cheon JH: Identification
of genetic susceptibility loci for intestinal Behcet's disease. Sci
Rep. 7(39850)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kang HW, Yoon HY, Ha YS, Kim WT, Kim YJ,
Yun SJ, Lee SC and Kim WJ: FAM70B as a novel prognostic marker for
cancer progression and cancer-specific death in muscle-invasive
bladder cancer. Korean J Urol. 53:598–606. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Walenta L, Fleck D, Fröhlich T, von
Eysmondt H, Arnold GJ, Spehr J, Schwarzer JU, Köhn FM, Spehr M and
Mayerhofer A: ATP-mediated events in peritubular cells contribute
to sterile testicular inflammation. Sci Rep. 8(1431)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Jurga AM, Piotrowska A, Makuch W,
Przewlocka B and Mika J: Blockade of P2X4 receptors inhibits
neuropathic pain-related behavior by preventing MMP-9 activation
and, consequently, pronociceptive interleukin release in a rat
model. Front Pharmacol. 8(48)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tsuda M, Masuda T, Tozaki-Saitoh H and
Inoue K: P2X4 receptors and neuropathic pain. Front Cell Neurosci.
7(191)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Lalisse S, Hua J, Lenoir M, Linck N,
Rassendren F and Ulmann L: Sensory neuronal P2RX4 receptors
controls BDNF signaling in inflammatory pain. Sci Rep.
8(964)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Zech A, Wiesler B, Ayata CK, Schlaich T,
Dürk T, Hoßfeld M, Ehrat N, Cicko S and Idzko M: P2rx4 deficiency
in mice alleviates allergen-induced airway inflammation.
Oncotarget. 7:80288–80297. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Sadovnick AD, Gu BJ, Traboulsee AL,
Bernales CQ, Encarnacion M, Yee IM, Criscuoli MG, Huang X, Ou A,
Milligan CJ, et al: Purinergic receptors P2RX4 and P2RX7 in
familial multiple sclerosis. Hum Mutat. 38:736–744. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|