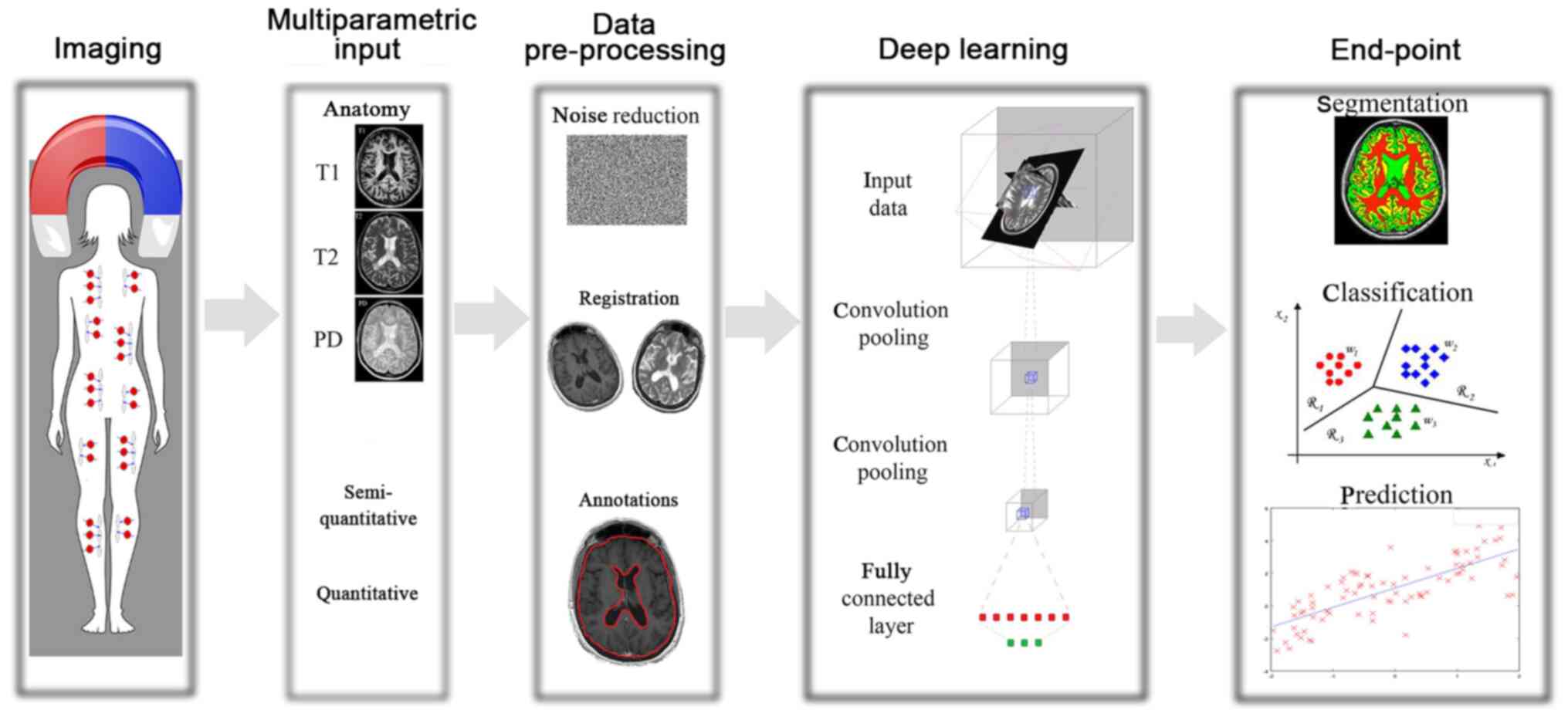
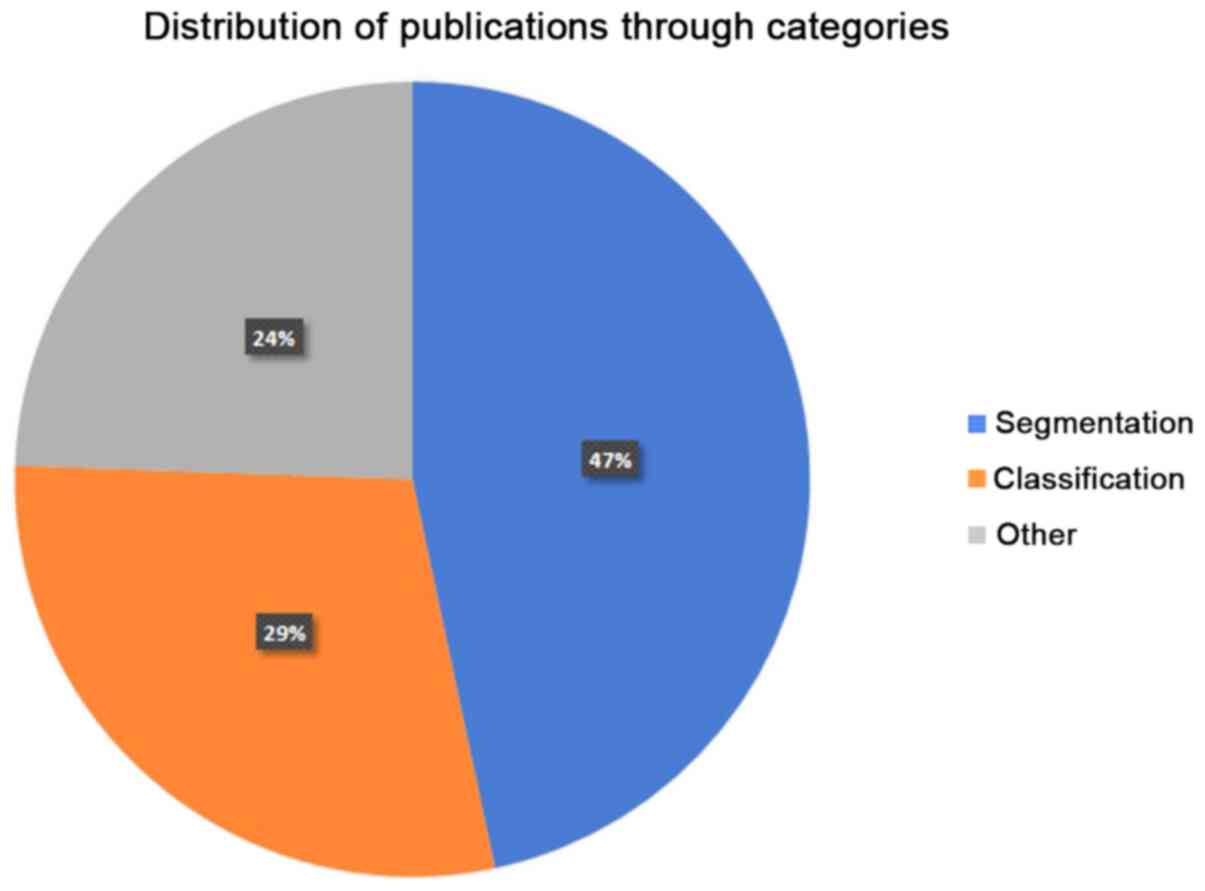
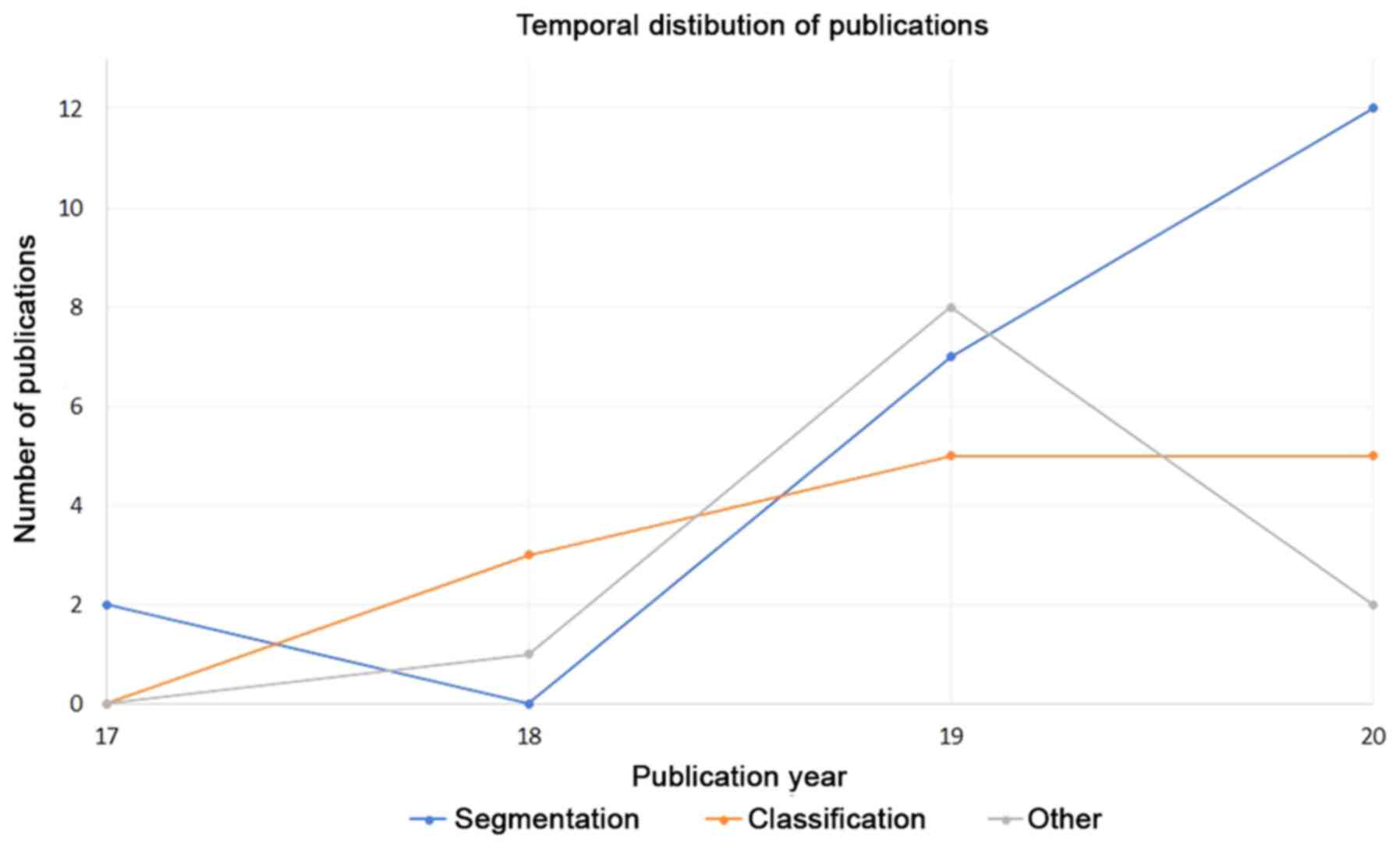
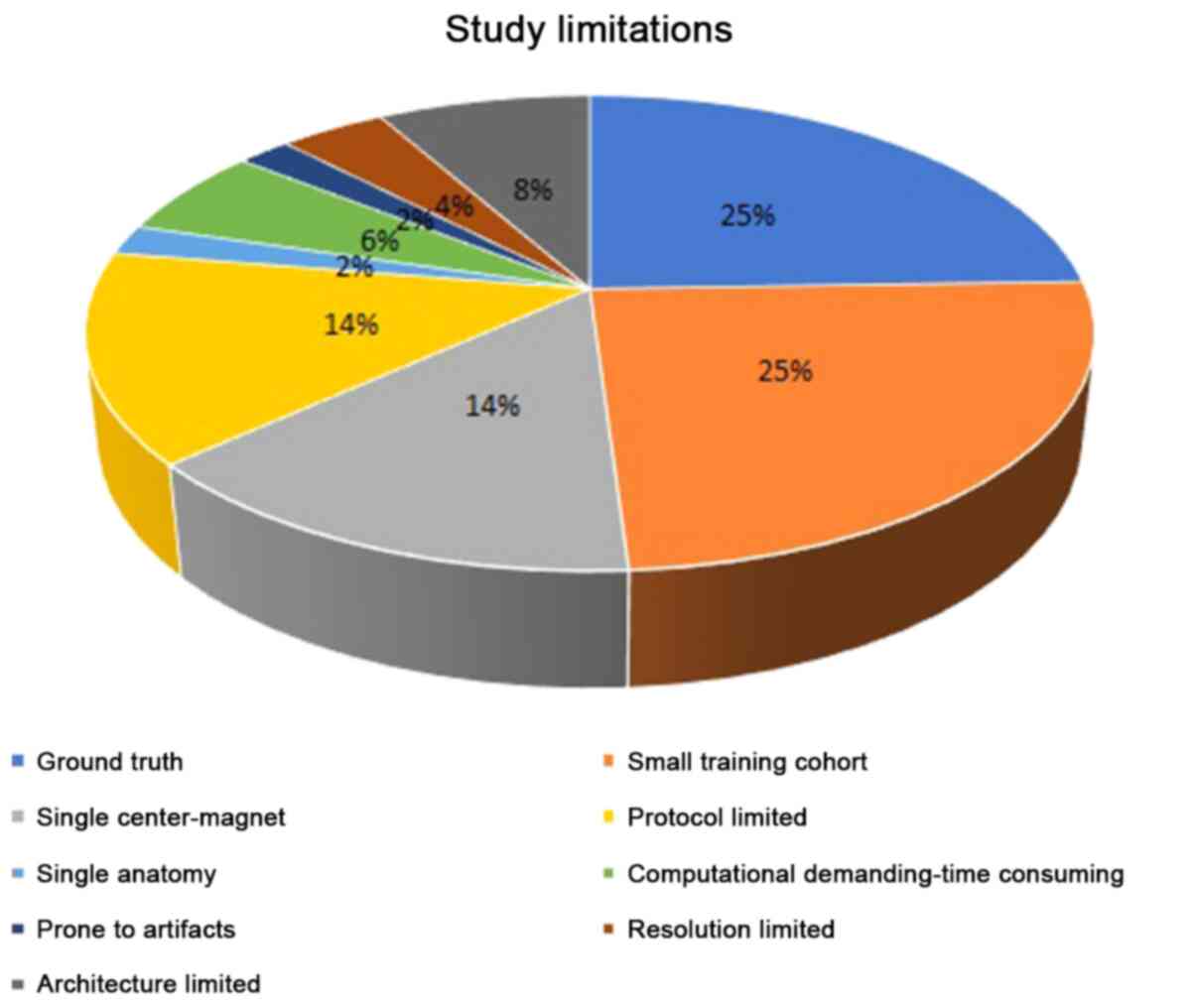
|
1
|
Ortiz GG, Pacheco-Moisés FP, Macías-Islas
MÁ, Flores-Alvarado LJ, Mireles-Ramírez MA, González-Renovato ED,
Hernández-Navarro VE, Sánchez-López AL and Alatorre-Jiménez MA:
Role of the blood-brain barrier in multiple sclerosis. Arch Med
Res. 45:687–697. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lopes Pinheiro MA, Kooij G, Mizee MR,
Kamermans A, Enzmann G, Lyck R, Schwaninger M, Engelhardt B and de
Vries HE: Immune cell trafficking across the barriers of the
central nervous system in multiple sclerosis and stroke. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1862:461–471. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Miller DH, Chard DT and Ciccarelli O:
Clinically isolated syndromes. Lancet Neurol. 11:157–169.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kappos L, Polman CH, Freedman MS, Edan G,
Hartung HP, Miller DH, Montalban X, Barkhof F, Bauer L, Jakobs P,
et al: Treatment with interferon beta-1b delays conversion to
clinically definite and McDonald MS in patients with clinically
isolated syndromes. Neurology. 67:1242–1249. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Fu Y, Talavage TM and Cheng JX: New
imaging techniques in the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Expert
Opin Med Diagn. 2:1055–1065. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Horsfield MA, Rovaris M, Rocca MA, Rossi
P, Benedict RH, Filippi M and Bakshi R: Whole-brain atrophy in
multiple sclerosis measured by two segmentation processes from
various MRI sequences. J Neurol Sci. 216:169–177. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
van Walderveen MA, Kamphorst W, Scheltens
P, van Waesberghe JH, Ravid R, Valk J, Polman CH and Barkhof F:
Histopathologic correlate of hypointense lesions on T1-weighted
spin-echo MRI in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 50:1282–1288.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bakshi R, Ariyaratana S, Benedict RH and
Jacobs L: Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance
imaging detects cortical and juxtacortical multiple sclerosis
lesions. Arch Neurol. 58:742–748. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Edan G, Filippi M,
Hartung HP, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Metz LM, McFarland HF, O'Connor
PW, et al: Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2005
revisions to the ‘McDonald Criteria’. Ann Neurol. 58:840–846.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Richards TL: Proton MR spectroscopy in
multiple sclerosis: Value in establishing diagnosis, monitoring
progression, and evaluating therapy. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
157:1073–1078. 1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pike GB, De Stefano N, Narayanan S,
Worsley KJ, Pelletier D, Francis GS, Antel JP and Arnold DL:
Multiple sclerosis: Magnetization transfer MR imaging of white
matter before lesion appearance on T2-weighted images. Radiology.
215:824–830. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Filippi M and Rocca MA: Magnetization
transfer magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of
neurological diseases. J Neuroimaging. 14:303–313. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rovaris M, Gass A, Bammer R, Hickman SJ,
Ciccarelli O, Miller DH and Filippi M: Diffusion MRI in multiple
sclerosis. Neurology. 65:1526–1532. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lapointe E, Li DKB, Traboulsee AL and
Rauscher A: What Have We Learned from Perfusion MRI in Multiple
Sclerosis? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 39:994–1000. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kotsiantis SB, Zaharakis I and Pintelas P:
Supervised machine learning: A review of classification techniques.
Emerging artificial intelligence applications in computer
engineering. 160:3–24. 2007.
|
|
16
|
Mortazavi D, Kouzani AZ and
Soltanian-Zadeh H: Segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions in MR
images: A review. Neuroradiology. 54:299–320. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Uddin M, Wang Y and Woodbury-Smith M:
Artificial intelligence for precision medicine in
neurodevelopmental disorders. NPJ Digit Med. 2(112)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bergsland N, Horakova D, Dwyer MG, Uher T,
Vaneckova M, Tyblova M, Seidl Z, Krasensky J, Havrdova E and
Zivadinov R: Gray matter atrophy patterns in multiple sclerosis: A
10-year source-based morphometry study. Neuroimage Clin.
17:444–451. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pontillo G, Petracca M, Cocozza S and
Brunetti A: The Development of Subcortical Gray Matter Atrophy in
Multiple Sclerosis: One Size Does Not Fit All. AJNR Am J
Neuroradiol. 41:E80–E81. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Almutairi AH, Hassan HA, Suppiah S,
Alomair OI, Alshoaibi A, Almutairi H and Mahmud R: Lesion load
assessment among multiple sclerosis patient using DIR, FLAIR, and
T2WI sequences. Egypt J Radiol Nucl Med. 51(209)2020.
|
|
21
|
Thompson AJ, Banwell BL, Barkhof F,
Carroll WM, Coetzee T, Comi G, Correale J, Fazekas F, Filippi M,
Freedman MS, et al: Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions
of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 17:162–173.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Valverde S, Cabezas M, Roura E,
González-Villà S, Pareto D, Vilanova JC, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira
À, Oliver A and Lladó X: Improving automated multiple sclerosis
lesion segmentation with a cascaded 3D convolutional neural network
approach. Neuroimage. 155:159–168. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Birenbaum A and Greenspan H: Multi-view
longitudinal CNN for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. Eng
Appl Artif Intell. 65:111–118. 2017.
|
|
24
|
Carass A, Roy S, Jog A, Cuzzocreo JL,
Magrath E, Gherman A, Button J, Nguyen J, Bazin PL, Calabresi PA,
et al: Longitudinal multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation data
resource. Data Brief. 12:346–350. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gros C, De Leener B, Badji A, Maranzano J,
Eden D, Dupont SM, Talbott J, Zhuoquiong R, Liu Y, Granberg T, et
al: Automatic segmentation of the spinal cord and intramedullary
multiple sclerosis lesions with convolutional neural networks.
Neuroimage. 184:901–915. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Milletari F, Navab N and Ahmadi SA: V-Net:
Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Volumetric Medical Image
Segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International
Conference on 3D Vision (3DV). IEEE, Stanford, CA, pp565-571,
2016.
|
|
27
|
De Leener B, Kadoury S and Cohen-Adad J:
Robust, accurate and fast automatic segmentation of the spinal
cord. Neuroimage. 98:528–536. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Aslani S, Dayan M, Storelli L, Filippi M,
Murino V, Rocca MA and Sona D: Multi-branch convolutional neural
network for multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. Neuroimage.
196:1–15. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sander L, Pezold S, Andermatt S, Amann M,
Meier D, Wendebourg MJ, Sinnecker T, Radue EW, Naegelin Y,
Granziera C, et al: Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative:
Accurate, rapid and reliable, fully automated MRI brainstem
segmentation for application in multiple sclerosis and
neurodegenerative diseases. Hum Brain Mapp. 40:4091–4104.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Iglesias JE, Van Leemput K, Bhatt P,
Casillas C, Dutt S, Schuff N, Truran-Sacrey D, Boxer A and Fischl
B: Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Bayesian
segmentation of brainstem structures in MRI. Neuroimage.
113:184–195. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hashemi SR, Salehi SSM, Erdogmus D, Prabhu
SP, Warfield SK and Gholipour A: Asymmetric Loss Functions and Deep
Densely Connected Networks for Highly Imbalanced Medical Image
Segmentation: Application to Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Detection.
IEEE Access. 7:721–1735. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Commowick O, Cervenansky F and Ameli R:
MSSEG challenge proceedings: multiple sclerosis lesions
segmentation challenge using a data management and processing
infrastructure. MICCAI, Athens, 2016.
|
|
33
|
Carass A, Roy S, Jog A, Cuzzocreo JL,
Magrath E, Gherman A, Button J, Nguyen J, Prados F, Sudre CH, et
al: Longitudinal multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation: Resource
and challenge. Neuroimage. 148:77–102. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gabr RE, Coronado I, Robinson M, Sujit SJ,
Datta S, Sun X, Allen WJ, Lublin FD, Wolinsky JS and Narayana PA:
Brain and lesion segmentation in multiple sclerosis using fully
convolutional neural networks: A large-scale study. Mult Scler.
26:1217–1226. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Weeda MM, Brouwer I, de Vos ML, de Vries
MS, Barkhof F, Pouwels PJW and Vrenken H: Comparing lesion
segmentation methods in multiple sclerosis: Input from one manually
delineated subject is sufficient for accurate lesion segmentation.
Neuroimage Clin. 24(102074)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Valverde S, Salem M, Cabezas M, Pareto D,
Vilanova JC, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira À, Salvi J, Oliver A and
Lladó X: One-shot domain adaptation in multiple sclerosis lesion
segmentation using convolutional neural networks. Neuroimage Clin.
21(101638)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Shiee N, Bazin PL, Ozturk A, Reich DS,
Calabresi PA and Pham DL: A topology-preserving approach to the
segmentation of brain images with multiple sclerosis lesions.
Neuroimage. 49:1524–1535. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Schmidt P: Bayesian Inference for
Structured Additive Regression Models for Large-Scale Problems with
Applications to Medical Imaging (unpublished PhD thesis).
Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München, 2016.
|
|
39
|
Griffanti L, Zamboni G, Khan A, Li L,
Bonifacio G, Sundaresan V, Schulz UG, Kuker W, Battaglini M,
Rothwell PM, et al: BIANCA (Brain Intensity AbNormality
Classification Algorithm): A new tool for automated segmentation of
white matter hyperintensities. Neuroimage. 141:191–205.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
McKinley R, Wepfer R, Aschwanden F,
Grunder L, Muri R, Rummel C, Verma R, Weisstanner C, Reyes M,
Salmen A, et al: Simultaneous lesion and neuroanatomy segmentation
in multiple sclerosis using deep neural networks.
arXiv:1901.07419.
|
|
41
|
Narayana PA, Coronado I, Sujit SJ,
Wolinsky JS, Lublin FD and Gabr RE: Deep-Learning-Based Neural
Tissue Segmentation of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis: Effect of
Training Set Size. J Magn Reson Imaging. 51:1487–1496.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Nair T, Precup D, Arnold DL and Arbel T:
Exploring uncertainty measures in deep networks for Multiple
sclerosis lesion detection and segmentation. Med Image Anal.
59(101557)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
McKinley R, Wepfer R, Aschwanden F,
Grunder L, Muri R, Rummel C, Verma R, Weisstanner C, Reyes M,
Salmen A, et al: Simultaneous lesion and brain segmentation in
multiple sclerosis using deep neural networks. Sci Rep.
11(1087)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Narayana PA, Coronado I, Sujit SJ, Sun X,
Wolinsky JS and Gabr RE: Are multi-contrast magnetic resonance
images necessary for segmenting multiple sclerosis brains? A large
cohort study based on deep learning. Magn Reson Imaging. 65:8–14.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Salem M, Valverde S, Cabezas M, Pareto D,
Oliver A, Salvi J, Rovira À and Lladó X: A fully convolutional
neural network for new T2-w lesion detection in multiple sclerosis.
Neuroimage Clin. 25(102149)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Brown RA, Fetco D, Fratila R, Fadda G,
Jiang S, Alkhawajah NM, Yeh EA, Banwell B, Bar-Or A and Arnold DL:
Canadian Pediatric Demyelinating Disease Network. Deep learning
segmentation of orbital fat to calibrate conventional MRI for
longitudinal studies. Neuroimage. 208(116442)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ackaouy A, Courty N, Vallée E, Commowick
O, Barillot C and Galassi F: Unsupervised Domain Adaptation With
Optimal Transport in Multi-Site Segmentation of Multiple Sclerosis
Lesions From MRI Data. Front Comput Neurosci. 14(19)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Commowick O, Istace A, Kain M, Laurent B,
Leray F, Simon M, Pop SC, Girard P, Améli R, Ferré JC, et al:
Objective Evaluation of Multiple Sclerosis Lesion Segmentation
using a Data Management and Processing Infrastructure. Sci Rep.
8(13650)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Coronado I, Gabr RE and Narayana PA: Deep
learning segmentation of gadolinium-enhancing lesions in multiple
sclerosis. Mult Scler. 27:219–527. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
La Rosa F, Abdulkadir A, Fartaria MJ,
Rahmanzadeh R, Lu PJ, Galbusera R, Barakovic M, Thiran JP,
Granziera C and Cuadra MB: Multiple sclerosis cortical and WM
lesion segmentation at 3T MRI: A deep learning method based on
FLAIR and MP2RAGE. Neuroimage Clin. 27(102335)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Gessert N, Krüger J, Opfer R, Ostwaldt AC,
Manogaran P, Kitzler HH, Schippling S and Schlaefer A: Multiple
sclerosis lesion activity segmentation with attention-guided
two-path CNNs. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 84(101772)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Essa E, Aldesouky D, Hussein SE and Rashad
MZ: Neuro-fuzzy patch-wise R-CNN for multiple sclerosis
segmentation. Med Biol Eng Comput. 58:2161–2175. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Barquero G, La Rosa F, Kebiri H, Lu PJ,
Rahmanzadeh R, Weigel M, Fartaria MJ, Kober T, Théaudin M, Du
Pasquier R, et al: RimNet: A deep 3D multimodal MRI architecture
for paramagnetic rim lesion assessment in multiple sclerosis.
Neuroimage Clin. 28(102412)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Gautam R and Sharma M: Prevalence and
Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders Using Different Deep Learning
Techniques: A Meta-Analysis. J Med Syst. 44(49)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Yoo Y, Tang LYW, Brosch T, Li DKB, Kolind
S, Vavasour I, Rauscher A, MacKay AL, Traboulsee A and Tam RC: Deep
learning of joint myelin and T1w MRI features in normal-appearing
brain tissue to distinguish between multiple sclerosis patients and
healthy controls. Neuroimage Clin. 17:169–178. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Wang SH, Tang C, Sun J, Yang J, Huang C,
Phillips P and Zhang YD: Multiple Sclerosis Identification by
14-Layer Convolutional Neural Network With Batch Normalization,
Dropout, and Stochastic Pooling. Front Neurosci.
12(818)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Zhang YD, Pan C, Sun J and Tang C:
Multiple sclerosis identification by convolutional neural network
with dropout and parametric ReLU. J Comput Sci. 28(818)2018.
|
|
58
|
Talo M, Baloglu UB, Yıldırım Ö and Acharya
UR: Application of deep transfer learning for automated brain
abnormality classification using MR images. Cogn Syst Res.
54:176–188. 2019.
|
|
59
|
Lu S, Lu Z and Zhang YD: Pathological
brain detection based on AlexNet and transfer learning. J Comput
Sci. 30:41–47. 2019.
|
|
60
|
McKinley R, Wepfer R, Grunder L,
Aschwanden F, Fischer T, Friedli C, Muri R, Rummel C, Verma R,
Weisstanner C, et al: Automatic detection of lesion load change in
Multiple Sclerosis using convolutional neural networks with
segmentation confidence. Neuroimage Clin. 25(102104)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Marzullo A, Kocevar G, Stamile C,
Durand-Dubief F, Terracina G, Calimeri F and Sappey-Marinier D:
Classification of Multiple Sclerosis Clinical Profiles via Graph
Convolutional Neural Networks. Front Neurosci.
13(594)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Eitel F, Soehler E, Bellmann-Strobl J,
Brandt AU, Ruprecht K, Giess RM, Kuchling J, Asseyer S, Weygandt M,
Haynes JD, et al: Uncovering convolutional neural network decisions
for diagnosing multiple sclerosis on conventional MRI using
layer-wise relevance propagation. Neuroimage Clin.
24(102003)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Narayana PA, Coronado I, Sujit SJ,
Wolinsky JS, Lublin FD and Gabr RE: Deep Learning for Predicting
Enhancing Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis from Noncontrast MRI.
Radiology. 294:398–404. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Maggi P, Fartaria MJ, Jorge J, La Rosa F,
Absinta M, Sati P, Meuli R, Du Pasquier R, Reich DS, Cuadra MB, et
al: CVSnet: A machine learning approach for automated central vein
sign assessment in multiple sclerosis. NMR Biomed.
33(e4283)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Wang Z, Yu Z, Wang Y, Zhang H, Luo Y, Shi
L, Wang Y and Guo C: 3D Compressed Convolutional Neural Network
Differentiates Neuromyelitis Optical Spectrum Disorders From
Multiple Sclerosis Using Automated White Matter Hyperintensities
Segmentations. Front Physiol. 11(612928)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Roca P, Attye A, Colas L, Tucholka A,
Rubini P, Cackowski S, Ding J, Budzik JF, Renard F, Doyle S, et al:
OFSEP Investigators; Steering Committee; Investigators; Imaging
group: Artificial intelligence to predict clinical disability in
patients with multiple sclerosis using FLAIR MRI. Diagn Interv
Imaging. 101:795–802. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Lopatina A, Ropele S, Sibgatulin R,
Reichenbach JR and Güllmar D: Investigation of Deep-Learning-Driven
Identification of Multiple Sclerosis Patients Based on
Susceptibility-Weighted Images Using Relevance Analysis. Front
Neurosci. 14(609468)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Sreekumari A, Shanbhag D, Yeo D, Foo T,
Pilitsis J, Polzin J, Patil U, Coblentz A, Kapadia A, Khinda J, et
al: A Deep Learning-Based Approach to Reduce Rescan and Recall
Rates in Clinical MRI Examinations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.
40:217–223. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Sujit SJ, Coronado I, Kamali A, Narayana
PA and Gabr RE: Automated image quality evaluation of structural
brain MRI using an ensemble of deep learning networks. J Magn Reson
Imaging. 50:1260–1267. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Lublin FD, Cofield SS, Cutter GR, Conwit
R, Narayana PA, Nelson F, Salter AR, Gustafson T and Wolinsky JS:
CombiRx Investigators. Randomized study combining interferon and
glatiramer acetate in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 73:327–340.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Zhao C, Shao M, Carass A, Li H, Dewey BE,
Ellingsen LM, Woo J, Guttman MA, Blitz AM, Stone M, et al:
Applications of a deep learning method for anti-aliasing and
super-resolution in MRI. Magn Reson Imaging. 64:132–141.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Jog A, Carass A and Prince JL: Self
Super-resolution for Magnetic Resonance Images. Med Image Comput
Comput Assist Interv. 9902:553–560. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Wei W, Poirion E, Bodini B, Durrleman S,
Colliot O, Stankoff B and Ayache N: Fluid-attenuated inversion
recovery MRI synthesis from multisequence MRI using
three-dimensional fully convolutional networks for multiple
sclerosis. J Med Imaging (Bellingham). 6(014005)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Ye DH, Zikic D, Glocker B, Criminisi A and
Konukoglu E: Modality propagation: coherent synthesis of
subject-specific scans with data-driven regularization. Med Image
Comput Comput Assist Interv. 13:606–613. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Jog A, Carass A, Pham DL and Prince JL:
RANDOM FOREST FLAIR RECONSTRUCTION FROM T1,
T2, AND PD-WEIGHTED MRI. Proc
IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging. 2014:1079–1082. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Ronneberger O, Fischer P and Brox T:
U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation.
Lect Notes Comput Sci. 9351:234–241. 2015.
|
|
77
|
Salem M, Valverde S, Cabezas M, Pareto D,
Oliver A, Salvi J, Rovira À and Lladó X: Multiple sclerosis lesion
synthesis in MRI using an encoder-decoder U-NET. IEEE Access.
7:25171–25184. 2019.
|
|
78
|
Wei W, Poirion E, Bodini B, Durrleman S,
Ayache N, Stankoff B and Colliot O: Predicting PET-derived
demyelination from multimodal MRI using sketcher-refiner
adversarial training for multiple sclerosis. Med Image Anal.
58(101546)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Finck T, Li H, Grundl L, Eichinger P,
Bussas M, Mühlau M, Menze B and Wiestler B: Deep-Learning Generated
Synthetic Double Inversion Recovery Images Improve Multiple
Sclerosis Lesion Detection. Invest Radiol. 55:318–323.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Yoon J, Gong E, Chatnuntawech I, Bilgic B,
Lee J, Jung W, Ko J, Jung H, Setsompop K, Zaharchuk G, et al:
Quantitative susceptibility mapping using deep neural network:
QSMnet. Neuroimage. 179:199–206. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Bollmann S, Rasmussen KGB, Kristensen M,
Blendal RG, Østergaard LR, Plocharski M, O'Brien K, Langkammer C,
Janke A and Barth M: DeepQSM-using deep learning to solve the
dipole inversion for quantitative susceptibility mapping.
Neuroimage. 195:373–383. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Dewey BE, Zhao C, Reinhold JC, Carass A,
Fitzgerald KC, Sotirchos ES, Saidha S, Oh J, Pham DL, Calabresi PA,
et al: DeepHarmony: A deep learning approach to contrast
harmonization across scanner changes. Magn Reson Imaging.
64:160–170. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Liu H, Xiang QS, Tam R, Dvorak AV, MacKay
AL, Kolind SH, Traboulsee A, Vavasour IM, Li DKB, Kramer JK, et al:
Myelin water imaging data analysis in less than one minute.
Neuroimage. 210(116551)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|