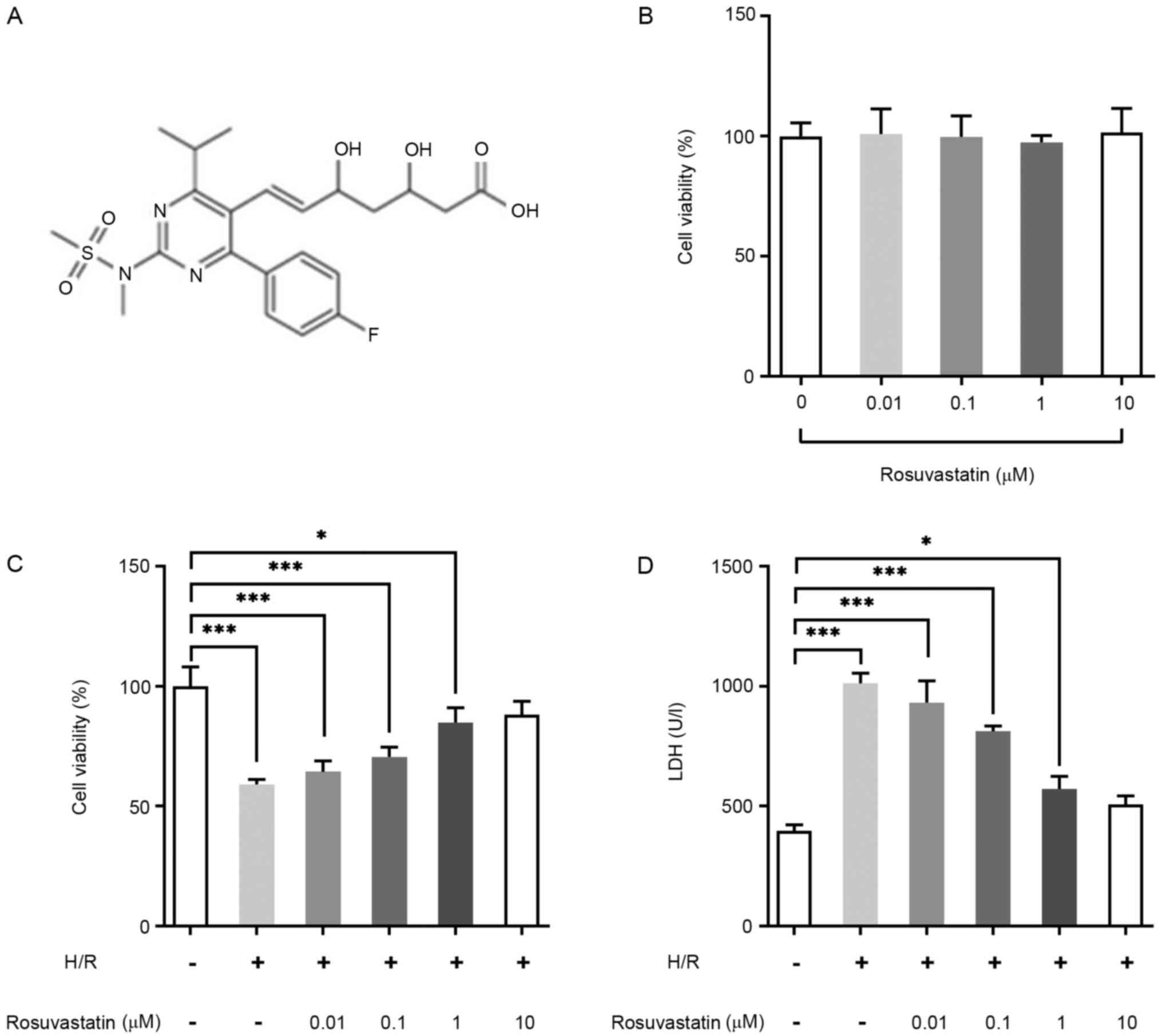
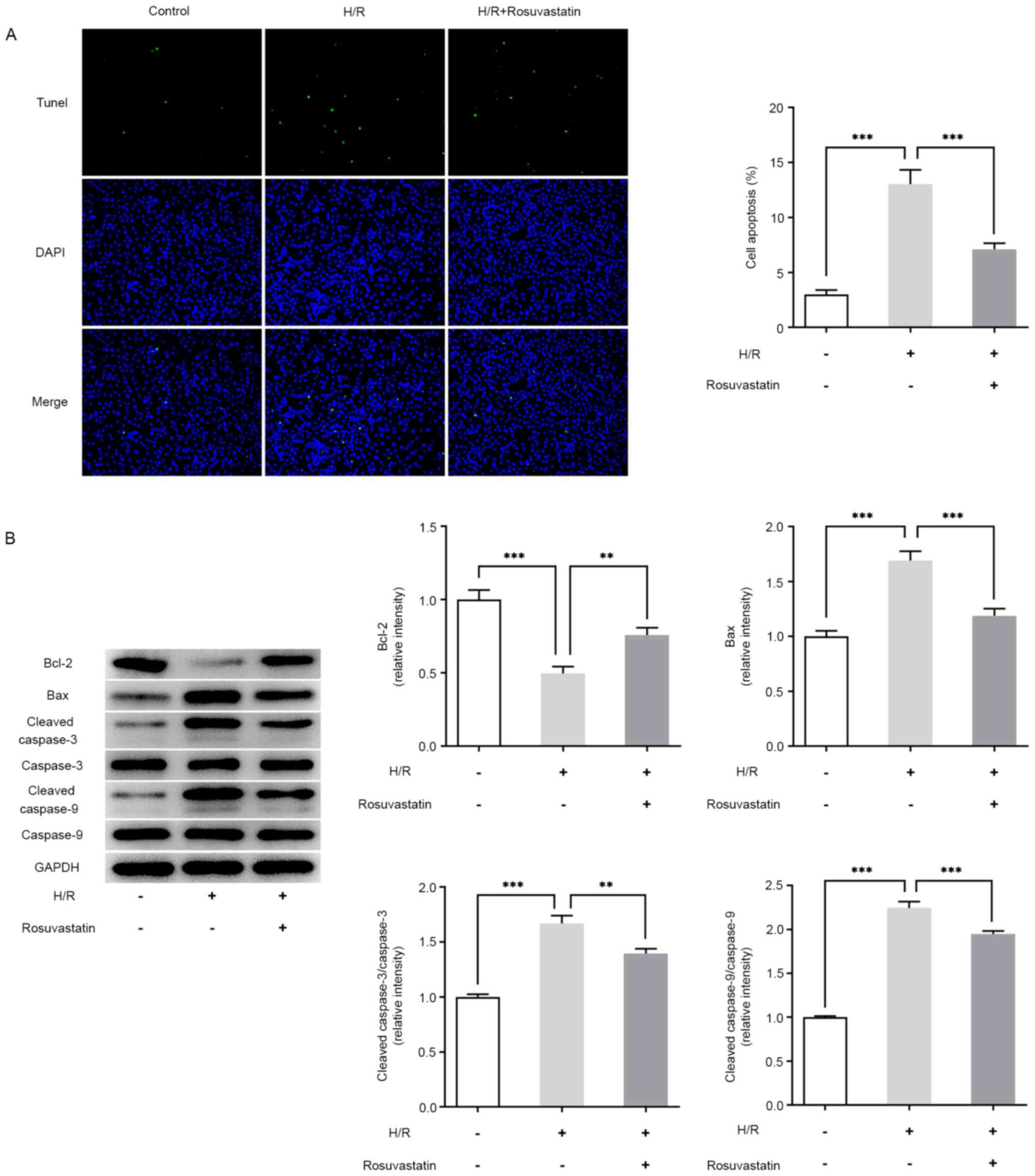
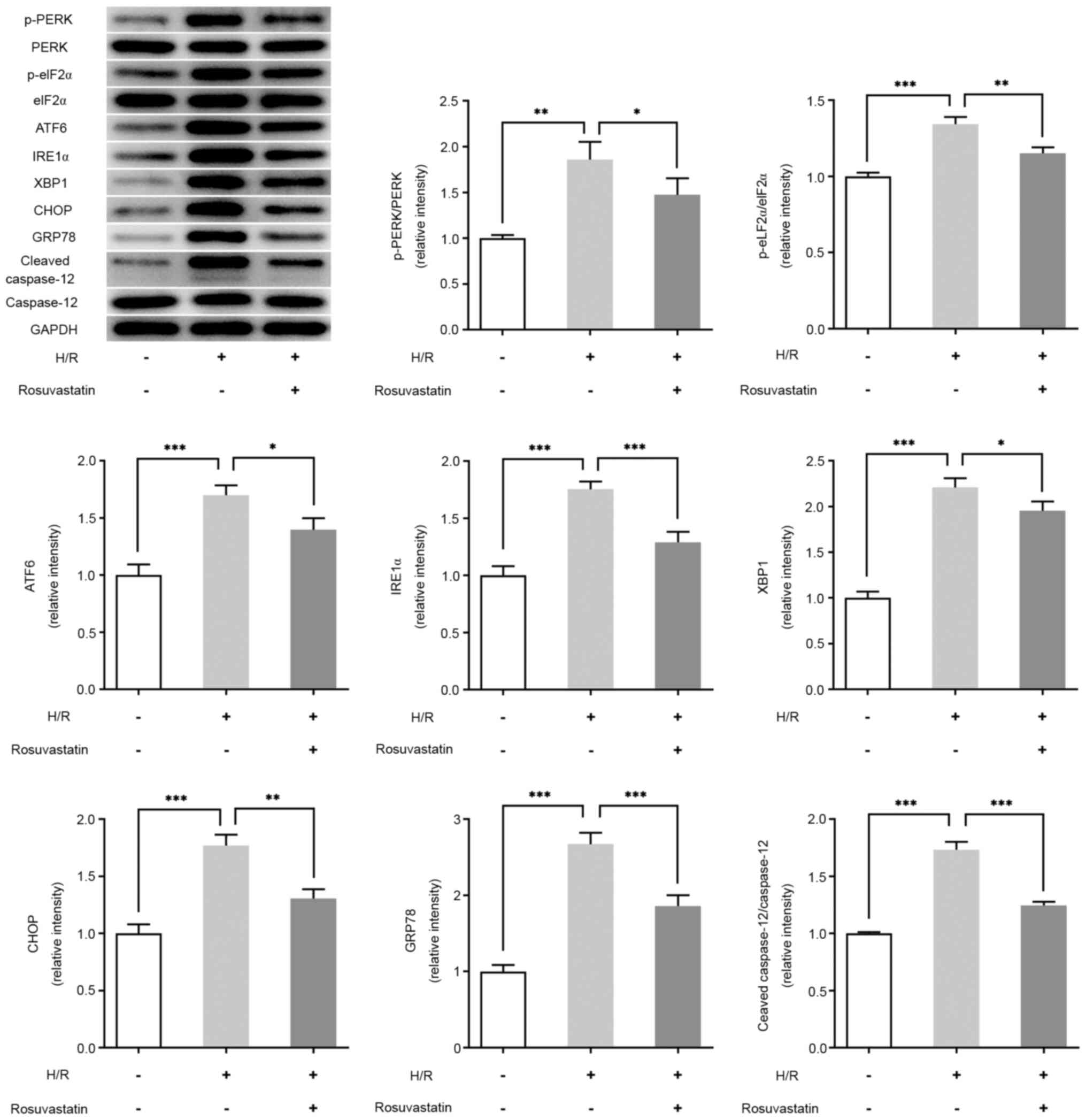
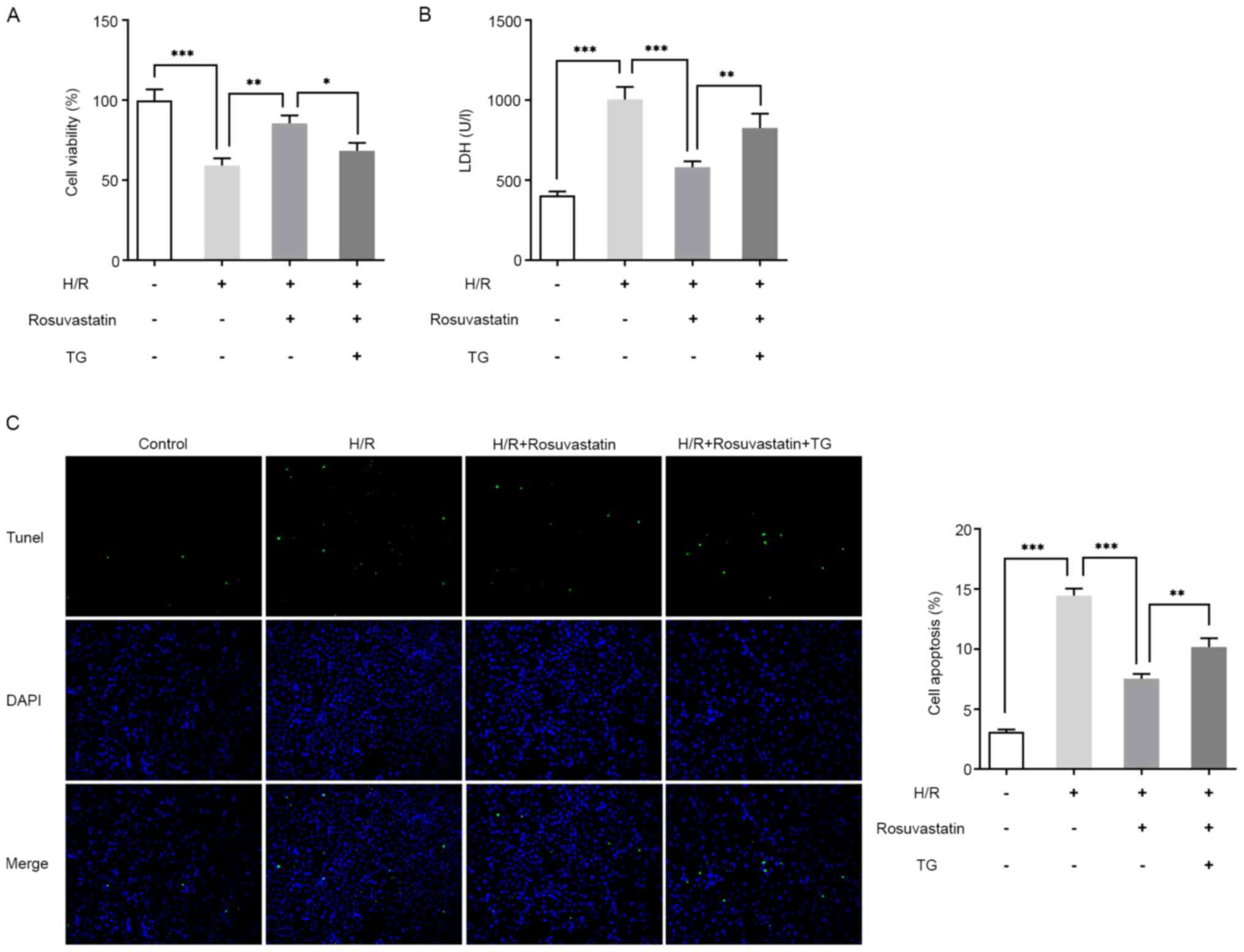
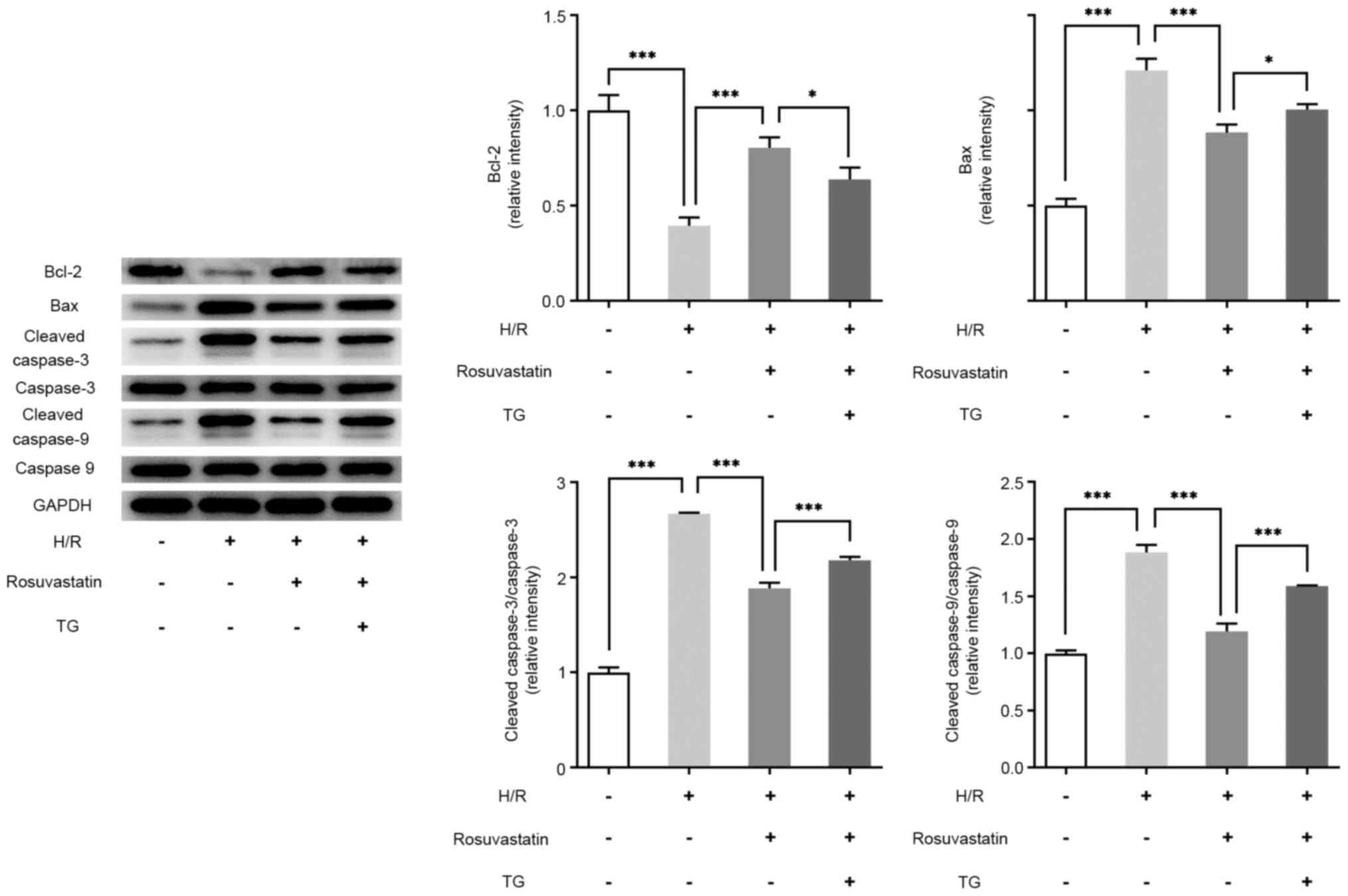
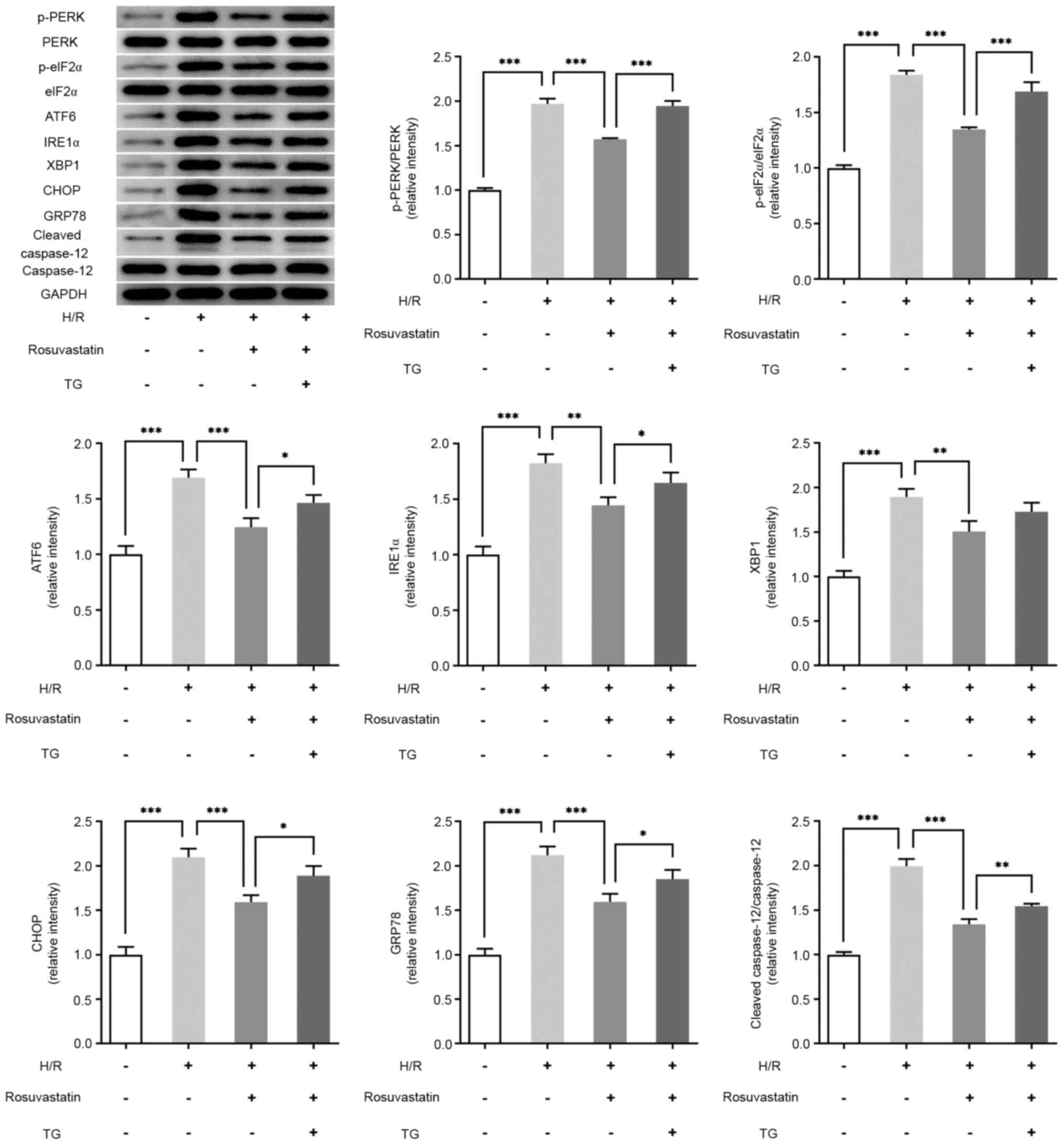
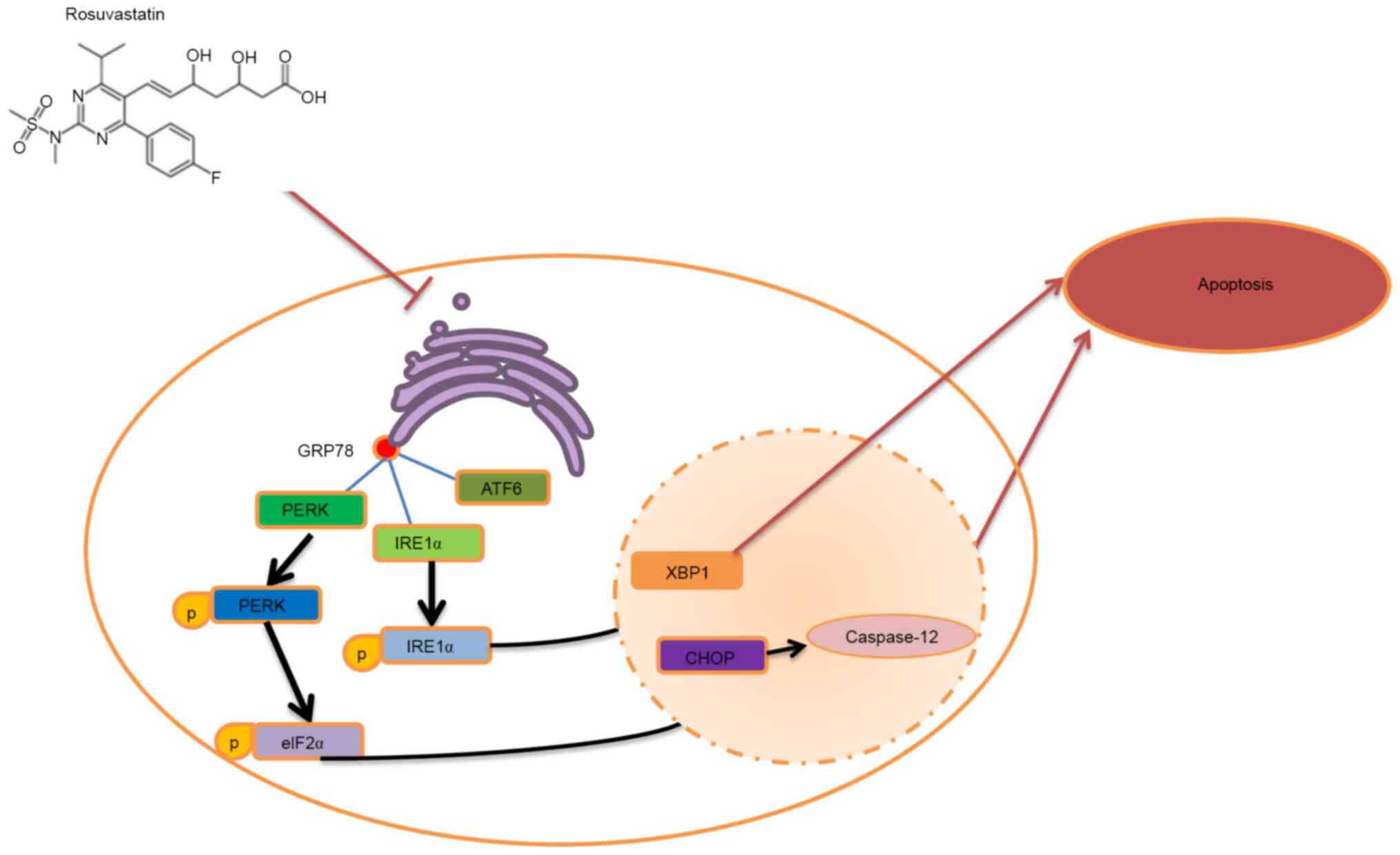
|
1
|
Wang M, Wang J, Liu Z, Guo X, Wang N, Jia
N, Zhang Y and Yuan J: Effects of intermedin on autophagy in
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neuropeptides. 68:15–21.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Deng Y, Zou W, Chen G, Shangguan S, Zhou
F, Jiang W and Li X: Comparative studies on the effects of
different doses of atorvastatin combined with aspirin on
inflammatory cytokines and carotid plaques in patients with
ischemic cerebrovascular disease. Int J Neurosci. 129:1133–1138.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wu MY, Yiang GT, Liao WT, Tsai AP, Cheng
YL, Cheng PW, Li CY and Li CJ: Current mechanistic concepts in
ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem.
46:1650–1667. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sun MS, Jin H, Sun X, Huang S, Zhang FL,
Guo ZN and Yang Y: Free radical damage in ischemia-reperfusion
injury: An obstacle in acute ischemic stroke after
revascularization therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018(3804979)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Xu F, Ma R, Zhang G, Wang S, Yin J, Wang
E, Xiong E, Zhang Q and Li Y: Estrogen and propofol combination
therapy inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress and remarkably
attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and OGD injury in
hippocampus. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:1596–1606. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lin YW, Chen TY, Hung CY, Tai SH, Huang
SY, Chang CC, Hung HY and Lee EJ: Melatonin protects brain against
ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Int J Mol Med. 42:182–192. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Feng D, Wang B, Wang L, Abraham N, Tao K,
Huang L, Shi W, Dong Y and Qu Y: Pre-ischemia melatonin treatment
alleviated acute neuronal injury after ischemic stroke by
inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent autophagy via
PERK and IRE1 signalings. J Pineal Res. 62:2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nakka VP, Gusain A and Raghubir R:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress plays critical role in brain damage
after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Neurotox Res.
17:189–202. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Xin Q, Ji B, Cheng B, Wang C, Liu H, Chen
X, Chen J and Bai B: Endoplasmic reticulum stress in cerebral
ischemia. Neurochem Int. 68:18–27. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ishige K, Osada N, Kosuge Y and Ito Y:
Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress in neurodegeneration
after transient global ischemia-reperfusion. Nihon Yakurigaku
Zasshi. 142:9–12. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Japanese).
|
|
11
|
Gong L, Tang Y, An R, Lin M, Chen L and Du
J: RTN1-C mediates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via ER
stress and mitochondria-associated apoptosis pathways. Cell Death
Dis. 8(e3080)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Feng SQ, Zong SY, Liu JX, Chen Y, Xu R,
Yin X, Zhao R, Li Y and Luo TT: VEGF antagonism attenuates cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury via inhibiting endoplasmic
reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis. Biol Pharm Bull. 42:692–702.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gutiérrez-Vargas JA, Cespedes-Rubio A and
Cardona-Gómez GP: Perspective of synaptic protection after
post-infarction treatment with statins. J Transl Med.
13(118)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Cortese F, Gesualdo M, Cortese A,
Carbonara S, Devito F, Zito A, Ricci G, Scicchitano P and Ciccone
MM: Rosuvastatin: Beyond the cholesterol-lowering effect. Pharmacol
Res. 107:1–18. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, Yang H, Jia G, Li L, Chen H, Bi J
and Wang C: The synergistic neuroprotective effects of combined
rosuvastatin and resveratrol pretreatment against cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis.
27:1697–1704. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ma M, Uekawa K, Hasegawa Y, Nakagawa T,
Katayama T, Sueta D, Toyama K, Kataoka K, Koibuchi N, Kuratsu J and
Kim-Mitsuyama S: Pretreatment with rosuvastatin protects against
focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats through
attenuation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Brain Res.
1519:87–94. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Engelhorn T, Doerfler A, Heusch G and
Schulz R: Reduction of cerebral infarct size by the AT1-receptor
blocker candesartan, the HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor rosuvastatin
and their combination. An experimental study in rats. Neurosci
Lett. 406:92–96. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xu JZ, Chai YL and Zhang YL: Effect of
rosuvastatin on high glucose-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress
in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Genet Mol Res.
15:2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Geng J, Xu H, Fu W, Yu X, Xu G, Cao H, Lin
G and Sui D: Rosuvastatin protects against endothelial cell
apoptosis in vitro and alleviates atherosclerosis in
ApoE-/- mice by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Exp Ther Med. 20:550–560. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen H and Li X: LncRNA ROR is involved in
cerebral hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury in PC12 cells via
regulating miR-135a-5p/ROCK1/2. Am J Transl Res. 11:6145–6158.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Oakes SA and Papa FR: The role of
endoplasmic reticulum stress in human pathology. Annu Rev Pathol.
10:173–194. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang K and Kaufman RJ: The unfolded
protein response: A stress signaling pathway critical for health
and disease. Neurology. 66 (2 Suppl 1):S102–S109. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Han ZW, Chang YC, Zhou Y, Zhang H, Chen L,
Zhang Y, Si JQ and Li L: GPER agonist G1 suppresses neuronal
apoptosis mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress after cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neural Regen Res. 14:1221–1229.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhong CJ, Chen MM, Lu M, Ding JH, Du RH
and Hu G: Astrocyte-specific deletion of Kir6.1/K-ATP channel
aggravates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through endoplasmic
reticulum stress in mice. Exp Neurol. 311:225–233. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang X, Chen J and Huang X: Rosuvastatin
attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via upregulating
miR-17-3p-mediated autophagy. Cell Reprogram. 21:323–330.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Vélez DE, Mestre-Cordero VE, Hermann R,
Perego J, Harriet S, Fernandez-Pazos MLM, Mourglia J and
Marina-Prendes MG: Rosuvastatin protects isolated hearts against
ischemia-reperfusion injury: Role of Akt-GSK-3β, metabolic
environment, and mitochondrial permeability transition pore. J
Physiol Biochem. 76:85–98. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Griffin JM, Kho D, Graham ES, Nicholson LF
and O'Carroll SJ: Statins inhibit fibrillary β-amyloid induced
inflammation in a model of the human blood brain barrier. PLoS One.
11(e0157483)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rodriguez-Perea AL, Gutierrez-Vargas J,
Cardona-Gómez GP, Guarin CJ, Rojas M and Hernández PA: Atorvastatin
modulates regulatory T cells and attenuates cerebral damage in a
model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. J
Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 12:152–162. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sohn HM, Hwang JY, Ryu JH, Kim J, Park S,
Park JW and Han SH: Simvastatin protects ischemic spinal cord
injury from cell death and cytotoxicity through decreasing
oxidative stress: In vitro primary cultured rat spinal cord model
under oxygen and glucose deprivation-reoxygenation conditions. J
Orthop Surg Res. 12(36)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Saleh DO, Mansour DF and Mostafa RE:
Rosuvastatin and simvastatin attenuate cisplatin-induced
cardiotoxicity via disruption of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-mediated apoptotic death in rats: Targeting ER-chaperone
GRP78 and calpain-1 pathways. Toxicol Rep. 7:1178–1186.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|