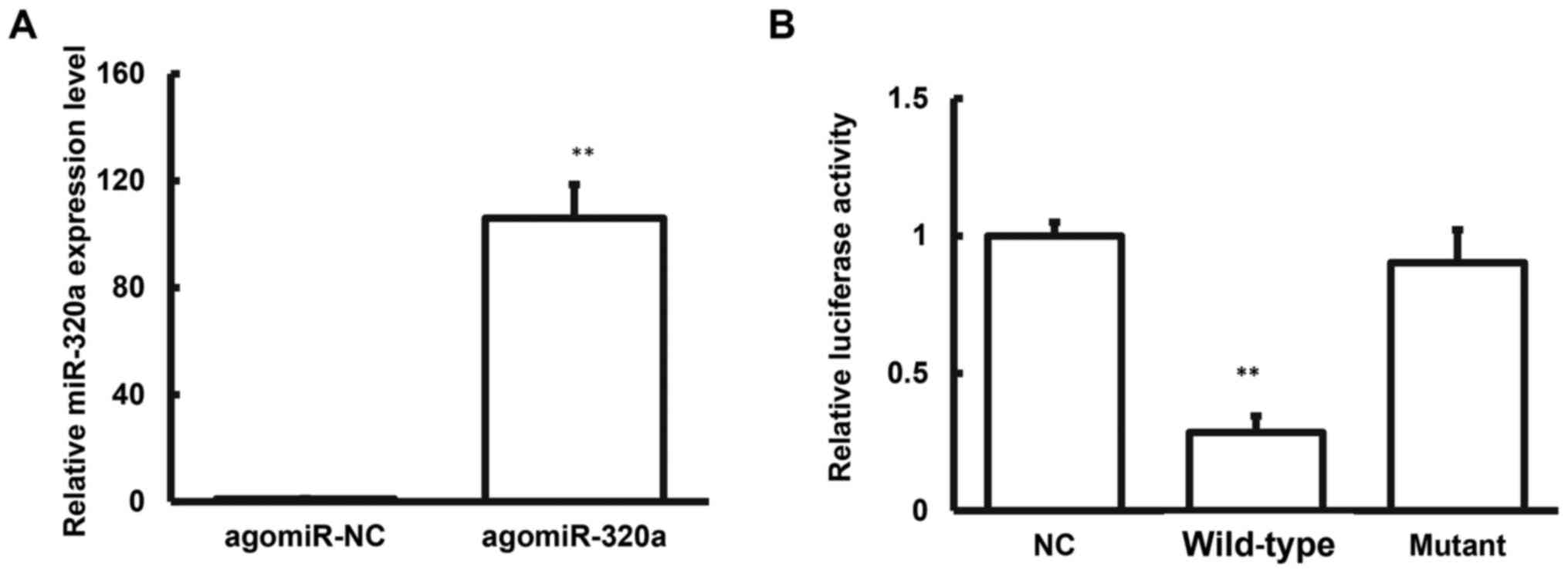
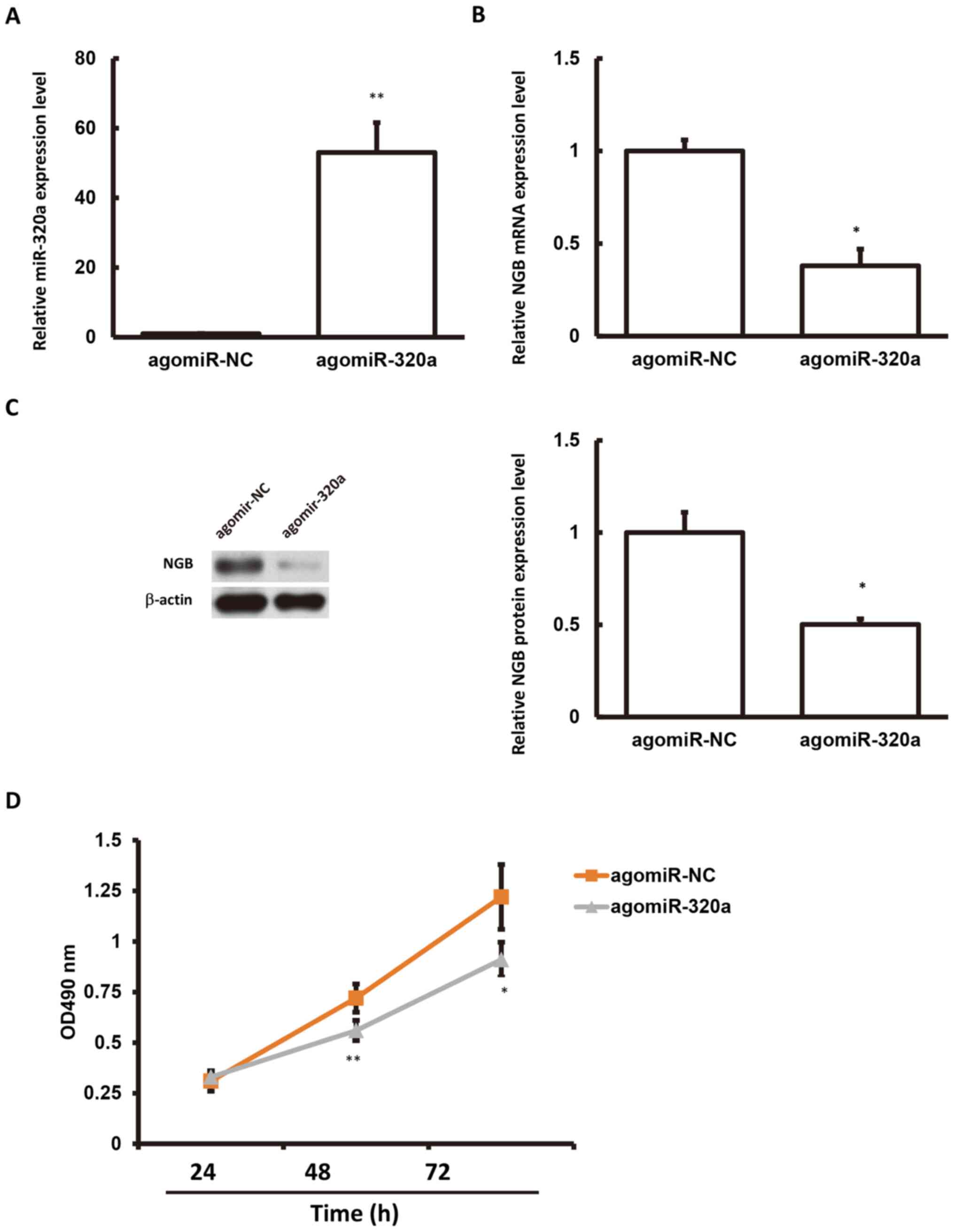
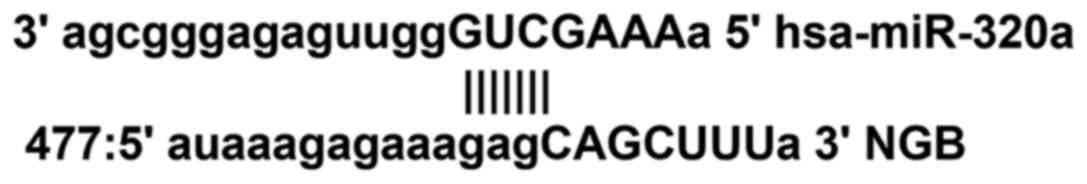|
1
|
Borozdina A, Qeva E, Cinicola M and
Bilotta F: Perioperative cognitive evaluation. Curr Opin
Anaesthesiol. 31:756–761. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Evered LA and Silbert BS: Postoperative
cognitive dysfunction and noncardiac surgery. Anesth Analg.
127:496–505. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Needham MJ, Webb CE and Bryden DC:
Postoperative cognitive dysfunction and dementia: What we need to
know and do. Br J Anaesth. 119 (Suppl 1):i115–i125. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Niu X, Zhang Q, Xiao D and Zhang Y: A
retrospective study of hemodynamic changes in patients after
off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery using impedance
cardiography. Med Sci Monit. 25:3454–3462. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Glumac S, Kardum G, Sodic L, Supe-Domic D
and Karanovic N: Effects of dexamethasone on early cognitive
decline after cardiac surgery: A randomised controlled trial. Eur J
Anaesthesiol. 34:776–784. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Glumac S, Kardum G and Karanovic N:
Postoperative cognitive decline after cardiac surgery: A narrative
review of current knowledge in 2019. Med Sci Monit. 25:3262–3270.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu YH, Wang DX, Li LH, Wu XM, Shan GJ, Su
Y, Li J, Yu QJ, Shi CX, Huang YN and Sun W: The effects of
cardiopulmonary bypass on the number of cerebral microemboli and
the incidence of cognitive dysfunction after coronary artery bypass
graft surgery. Anesth Analg. 109:1013–1022. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sanders RD, Xu J, Shu Y, Januszewski A,
Halder S, Fidalgo A, Sun P, Hossain M, Ma D and Maze M:
Dexmedetomidine attenuates isoflurane-induced neurocognitive
impairment in neonatal rats. Anesthesiology. 110:1077–1085.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Han C, Fu R and Lei W: Beneficial effects
of dexmedetomidine on early postoperative cognitive dysfunction in
pediatric patients with tonsillectomy. Exp Ther Med. 16:420–426.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ren X, Ma H and Zuo Z: Dexmedetomidine
postconditioning reduces brain injury after brain hypoxia-ischemia
in neonatal rats. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 11:238–247.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Barends CR, Absalom A, van Minnen B,
Vissink A and Visser A: Dexmedetomidine versus midazolam in
procedural sedation. A systematic review of efficacy and safety.
PLoS One. 12(e0169525)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chan AS, Saraswathy S, Rehak M, Ueki M and
Rao NA: Neuroglobin protection in retinal ischemia. Invest
Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 53:704–711. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ye SQ, Zhou XY, Lai XJ, Zheng L and Chen
XQ: Silencing neuroglobin enhances neuronal vulnerability to
oxidative injury by down-regulating 14-3-3gamma. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 30:913–918. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu X, Gao Y, Yao H, Zhou L, Sun D and
Wang J: Neuroglobin involvement in the course of arsenic toxicity
in rat cerebellar granule neurons. Biol Trace Elem Res.
155:439–446. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Khan AA, Mao XO, Banwait S,
DerMardirossian CM, Bokoch GM, Jin K and Greenberg DA: Regulation
of hypoxic neuronal death signaling by neuroglobin. FASEB.
22:1737–1747. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Uchida Y, Ohshima T, Sasaki Y, Suzuki H,
Yanai S, Yamashita N, Nakamura F, Takei K, Ihara Y, Mikoshiba K, et
al: Semaphorin3A signalling is mediated via sequential Cdk5 and
GSK3beta phosphorylation of CRMP2: Implication of common
phosphorylating mechanism underlying axon guidance and Alzheimer's
disease. Genes Cells. 10:165–179. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang C, Wang C, Deng M, Li L, Wang H, Fan
M, Xu W, Meng F, Qian L and He F: Full-length cDNA cloning of human
neuroglobin and tissue expression of rat neuroglobin. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 290:1411–1419. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bukauskas T, Kairyte M, Mickus R,
Puleikyte L and Macas A: Values of circulating molecular biomarkers
(microRNAs) for the evaluation of renal failure during urgent
abdominal sepsis anaesthesia. Acta Med Litu. 26:17–24.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Bell JD, Cho JE and Giffard RG: MicroRNA
changes in preconditioning-induced neuroprotection. Transl Stroke
Res. 8:585–596. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Barik M, Kumar A, Mishra PR and Kapoor PM:
Role of MicroRNA in cardiac anesthesia: An innovative consequences
and new possibility. Ann Card Anaesth. 20:274–275. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tadano T, Kakuta Y, Hamada S, Shimodaira
Y, Kuroha M, Kawakami Y, Kimura T, Shiga H, Endo K, Masamune A, et
al: MicroRNA-320 family is downregulated in colorectal adenoma and
affects tumor proliferation by targeting CDK6. World J Gastrointest
Oncol. 8:532–542. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
White RE and Giffard RG: MicroRNA-320
induces neurite outgrowth by targeting ARPP-19. Neuroreport.
23:590–595. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Berger M, Nadler JW, Browndyke J, Terrando
N, Ponnusamy V, Cohen HJ, Whitson HE and Mathew JP: Postoperative
cognitive dysfunction: Minding the gaps in our knowledge of a
common postoperative complication in the elderly. Anesthesiol Clin.
33:517–550. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Feinkohl I, Winterer G, Spies CD and
Pischon T: Cognitive reserve and the risk of postoperative
cognitive dysfunction. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 114:110–117.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Safavynia SA and Goldstein PA: The role of
neuroinflammation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction: Moving
from hypothesis to treatment. Front Psychiatry.
9(752)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sottas CE and Anderson BJ:
Dexmedetomidine: The new all-in-one drug in paediatric anaesthesia?
Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 30:441–451. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chi X, Liao M, Chen X, Zhao Y, Yang L, Luo
A and Yang H: Dexmedetomidine attenuates myocardial injury in
off-pump coronary artery bypass graft surgery. J Cardiothorac Vasc
Anesth. 30:44–50. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wystub S, Laufs T, Schmidt M, Burmester T,
Maas U, Saaler-Reinhardt S, Hankeln T and Reuss S: Localization of
neuroglobin protein in the mouse brain. Neurosci Lett. 346:114–116.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Reuss S, Saaler-Reinhardt S, Weich B,
Wystub S, Reuss MH, Burmester T and Hankeln T: Expression analysis
of NGB mRNA in rodent tissues. Neuroscience. 115:645–656.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Schmidt M, Giessl A, Laufs T, Hankeln T,
Wolfrum U and Burmester T: How does the eye breathe? Evidence for
neuroglobin-mediated oxygen supply in the mammalian retina. J Biol
Chem. 278:1932–1935. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sun Y, Jin K, Mao XO, Zhu Y and Greenberg
DA: NGB is up-regulated by and protects neurons from
hypoxic-ischemic injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:15306–15311.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Khan AA, Sun Y, Jin K, Mao XO, Chen S,
Ellerby LM and Greenberg DA: A NGB-overexpressing transgenic mouse.
Gene. 398:172–176. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Khan AA, Wang Y, Sun Y, Mao XO, Xie L,
Miles E, Graboski J, Chen S, Ellerby LM, Jin K and Greenberg DA:
Neuroglobin-overexpressing transgenic mice are resistant to
cerebral and myocardial ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:17944–17948. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang X, Liu J, Zhu H, Tejima E, Tsuji K,
Murata Y, Atochin DN, Huang PL, Zhang C and Lo EH: Effects of
neuroglobin overexpression on acute brain injury and long-term
outcomes after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 39:1869–1874.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
De Marinis E, Acaz-Fonseca E, Arevalo MA,
Ascenzi P, Fiocchetti M, Marino M and Garcia-Segura LM:
17β-Oestradiol anti-inflammatory effects in primary astrocytes
require oestrogen receptor β-mediated neuroglobin up-regulation. J
Neuroendocrinol. 25:260–270. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
De Marinis E, Marino M and Ascenzi P:
Neuroglobin, estrogens, and neuroprotection. IUBMB Life.
63:140–145. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sun JY, Huang Y, Li JP, Zhang X, Wang L,
Meng YL, Yan B, Bian YQ, Zhao J, Wang WZ, et al: MicroRNA-320a
suppresses human colon cancer cell proliferation by directly
targeting beta-catenin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 420:787–792.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang Y, He X, Liu Y, Ye Y, Zhang H, He P,
Zhang Q, Dong L, Liu Y and Dong J: microRNA-320a inhibits tumor
invasion by targeting neuropilin 1 and is associated with liver
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncol Rep. 27:685–694.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Gerber JM, Qin L, Kowalski J, Smith BD,
Griffin CA, Vala MS, Collector MI, Perkins B, Zahurak M, Matsui W,
et al: Characterization of chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. Am
J Hematol. 86:31–37. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Lu C, Liao Z, Cai M and Zhang G:
MicroRNA-320a downregulation mediates human liver cancer cell
proliferation through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol
Lett. 13:573–578. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|