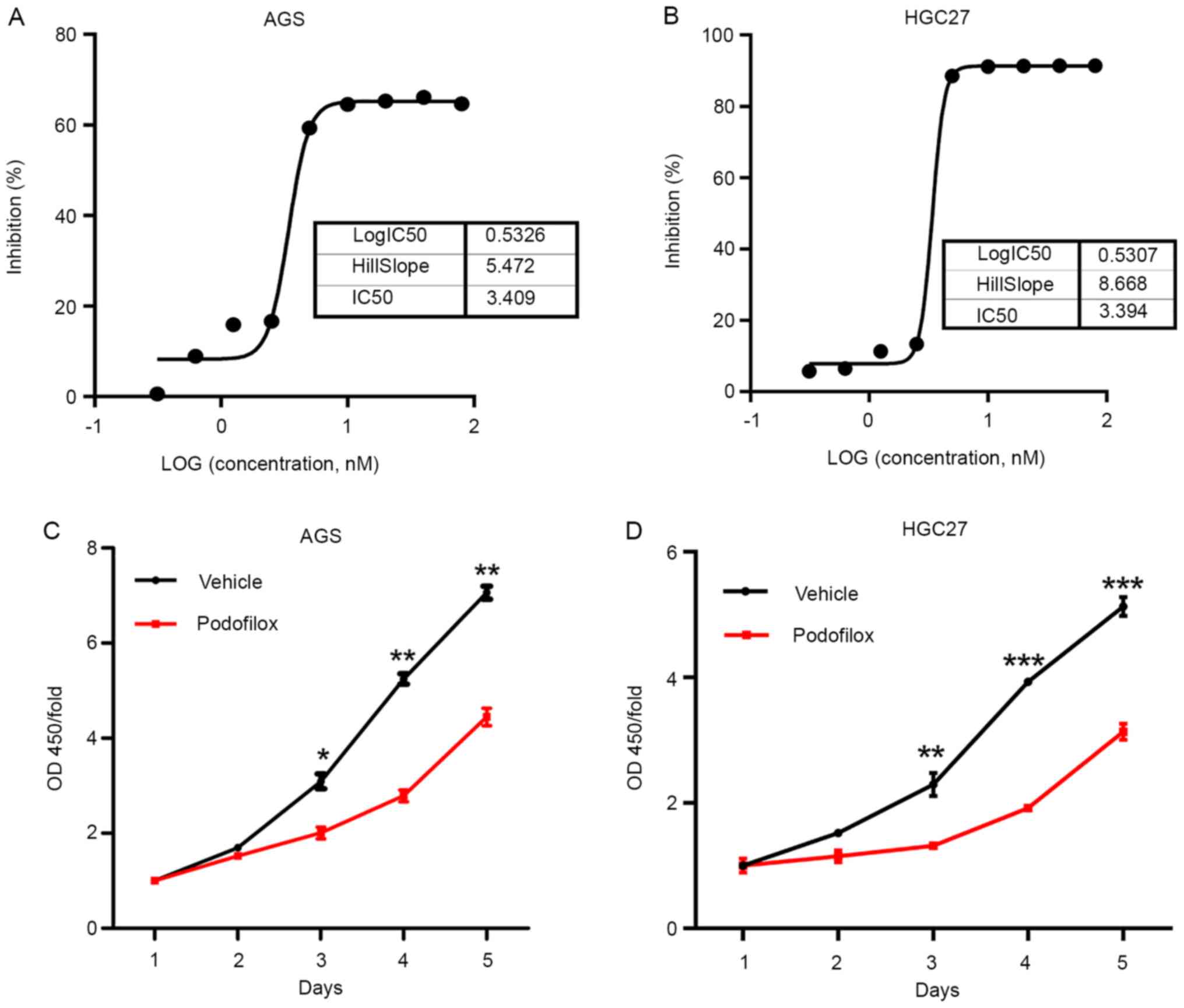
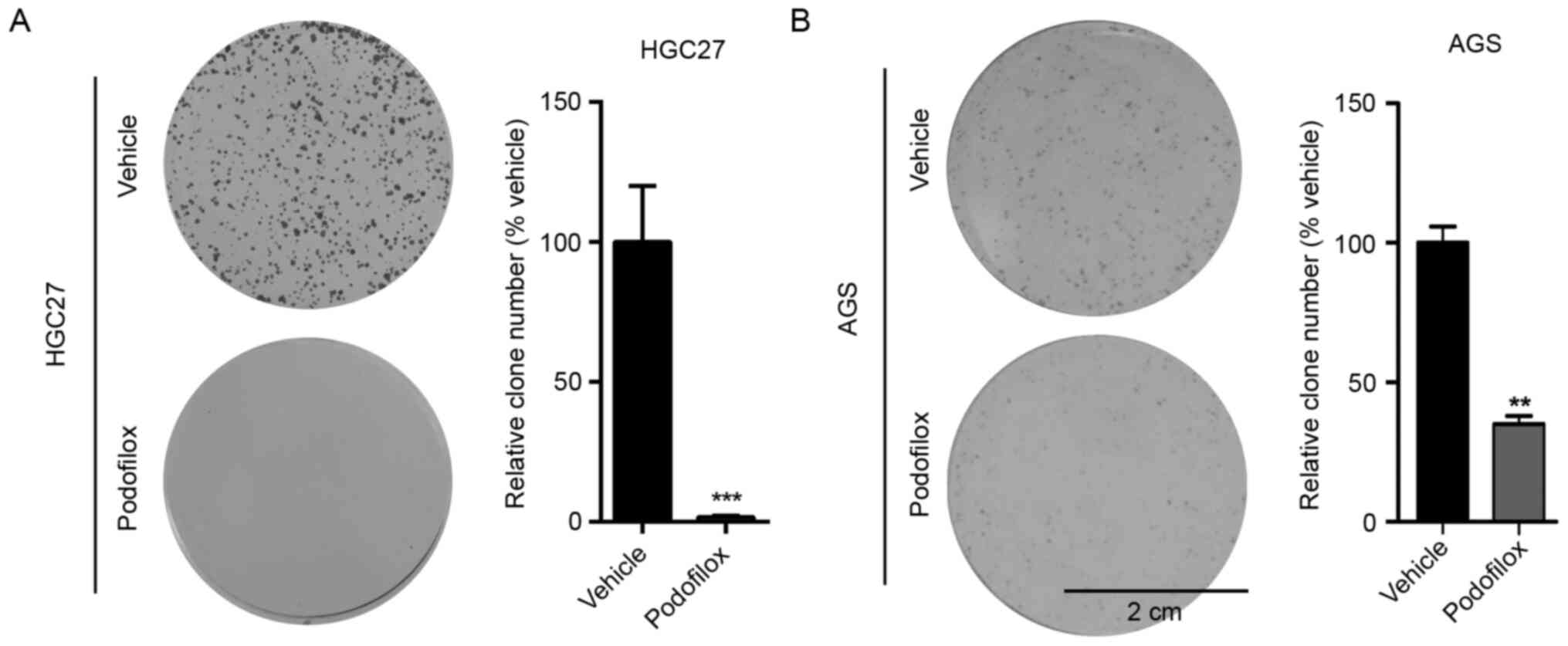
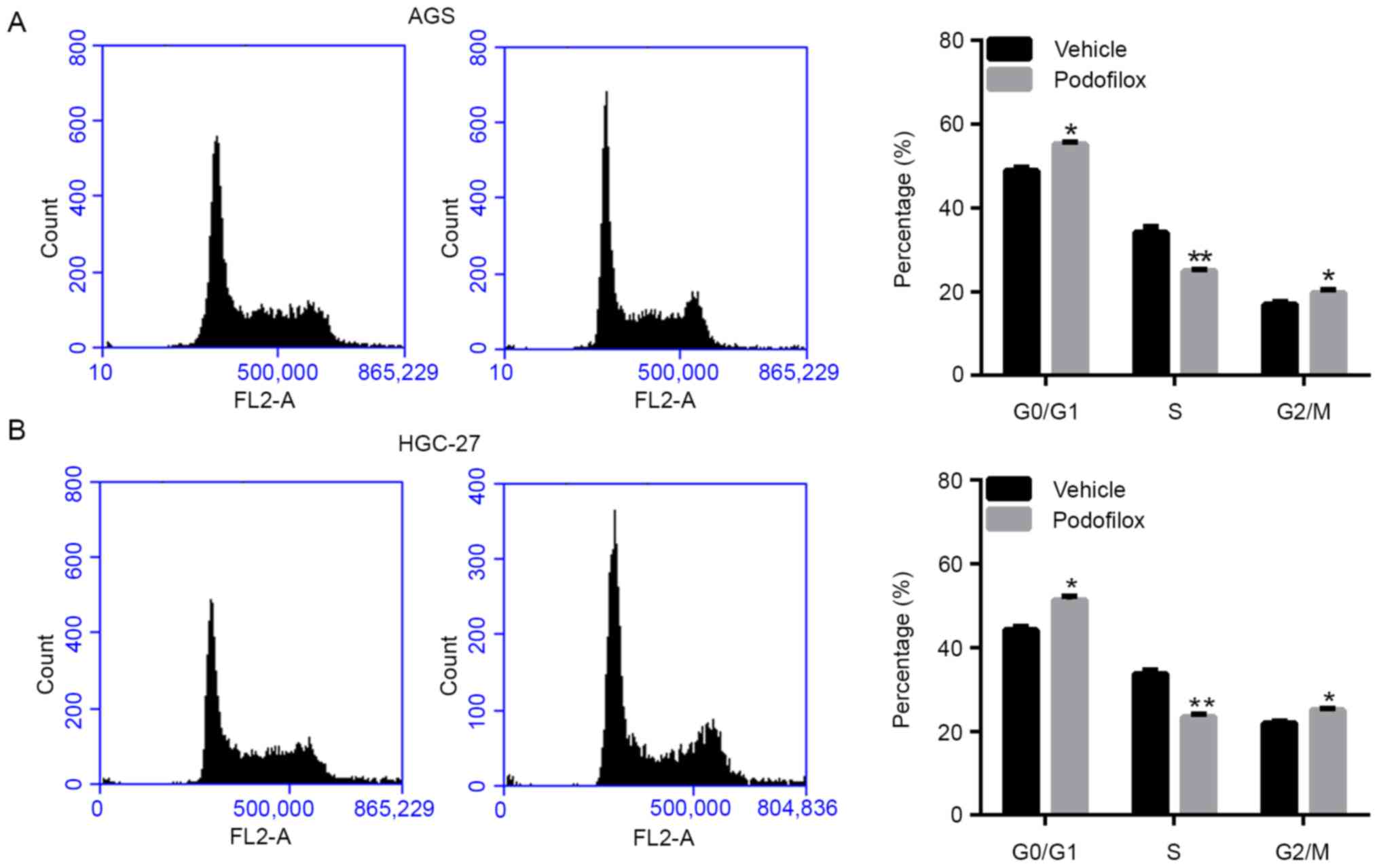
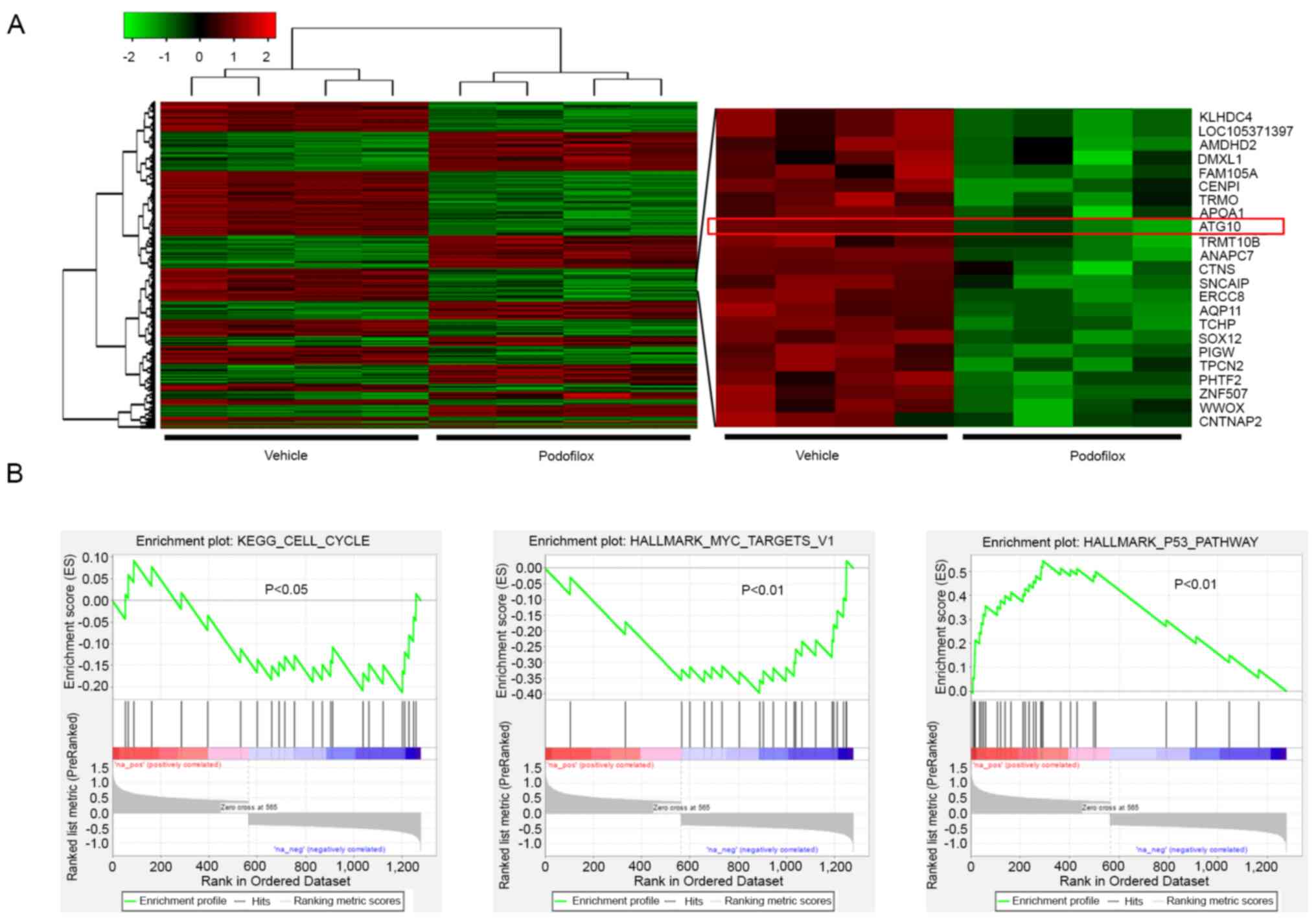
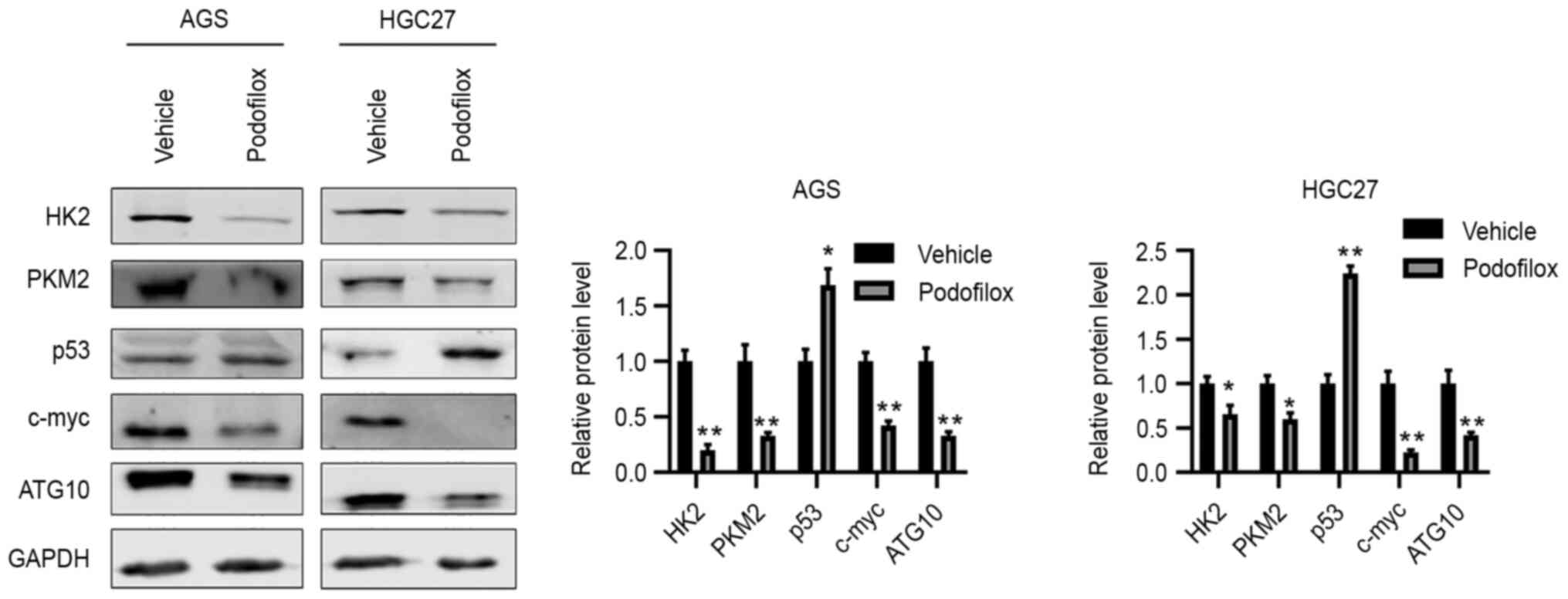
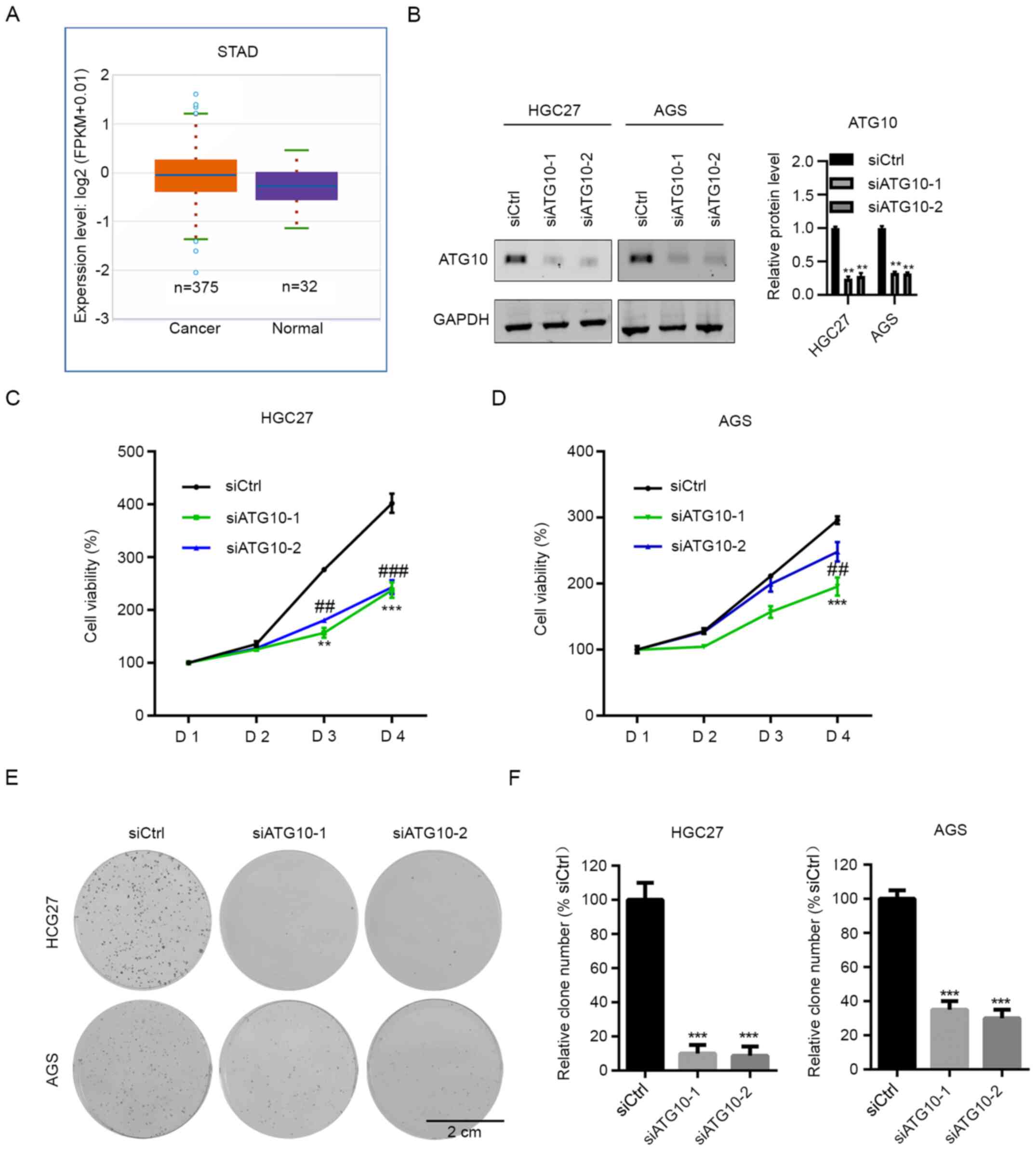
|
1
|
Joshi S and Badgwell B: Current treatment
and recent progress in gastric cancer. CA Cancer J Clin.
71:264–279. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ajani J, Lee J, Sano T, Janjigian Y, Fan D
and Song S: Gastric adenocarcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
3(17036)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wang LY, Zhao S, Lv GJ, Ma XJ and Zhang
JB: Mechanisms of resveratrol in the prevention and treatment of
gastrointestinal cancer. World J Clin Cases. 8:2425–2437.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Deng W, Jin L, Zhuo H, Vasiliou V and
Zhang Y: Alcohol consumption and risk of stomach cancer: A
meta-analysis. Chem Biol Interact. 336(109365)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lerner B and Llor X: Genetic gastric
cancer risk syndromes. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol.
18:604–615. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Huang K, Ramnarayanan K, Zhu F, Srivastava
S, Xu C, Tan ALK, Lee M, Tay S, Das K, Xing M, et al: Genomic and
epigenomic profiling of high-risk intestinal metaplasia reveals
molecular determinants of progression to gastric cancer. Cancer
Cell. 33:137–150.e5. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Machlowska J, Baj J, Sitarz M, Maciejewski
R and Sitarz R: Gastric Cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors,
classification, genomic characteristics and treatment strategies.
Int J Mol Sci. 21(4012)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shitara K, Bang Y, Iwasa S, Sugimoto N,
Ryu MH, Sakai D, Chung HC, Kawakami H, Yabusaki H, Lee J, et al:
Trastuzumab deruxtecan in previously treated HER2-positive gastric
cancer. N Engl J Med. 382:2419–2430. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu YQ, Tian J, Qian K, Zhao XB,
Morris-Natschke SL, Yang L, Nan X, Tian X and Lee KH: Recent
progress on C-4-modified podophyllotoxin analogs as potent
antitumor agents. Med Res Rev. 35:1–62. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Sun H, Xiao Z, Zhang G, Zhang D,
Bao X, Li F, Wu S, Gao Y and Wei N: DNA damage and apoptosis
induced by a potent orally podophyllotoxin derivative in breast
cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 16(52)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhao W, He L, Xiang TL and Tang YJ:
Discover 4β-NH-(6-aminoindole)-4-desoxy-podophyllotoxin with
nanomolar-potency antitumor activity by improving the tubulin
binding affinity on the basis of a potential binding site nearby
colchicine domain. Eur J Med Chem. 170:73–86. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Smyth E, Nilsson M, Grabsch H, van Grieken
N and Lordick F: Gastric cancer. Lancet. 396:635–648.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhao W, Cong Y, Li H, Li S, Shen Y, Qi Q,
Zhang Y, Li YZ and Tang YJ: Challenges and potential for improving
the druggability of podophyllotoxin-derived drugs in cancer
chemotherapy. Nat Prod Rep. 38:470–488. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cohen T, Schwarz T, Vigant F, Gardner T,
Hernandez R, Lee B and Tortorella D: The microtubule inhibitor
podofilox inhibits an early entry step of human cytomegalovirus.
Viruses. 8(295)2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tracz-Gaszewska Z and Dobrzyn P:
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 as a therapeutic target for the treatment
of cancer. Cancers (Basel). 11(948)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zi CT, Gao YS, Yang L, Feng SY, Huang Y,
Sun L, Jin Y, Xu FQ, Dong FW, Li Y, et al: Design, synthesis, and
biological evaluation of novel biotinylated podophyllotoxin
derivatives as potential antitumor agents. Front Chem.
7(434)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Paidakula S, Nerella S, Vadde R, Kamal A
and Kankala S: Design and synthesis of
4β-Acetamidobenzofuranone-podophyllotoxin hybrids and their
anti-cancer evaluation. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 29:2153–2156.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hao SY, Feng SL, Wang XR, Wang Z, Chen SW
and Hui L: Novel conjugates of podophyllotoxin and coumarin:
Synthesis, cytotoxicities, cell cycle arrest, binding CT DNA and
inhibition of Topo IIβ. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 29:2129–2135.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang W, Gao W, Zhang L, Zhang D, Zhao Z
and Bao Y: Deoxypodophyllotoxin inhibits cell viability and
invasion by blocking the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in human
glioblastoma cells. Oncol Rep. 41:2453–2463. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Huang T, Fu Y, Wang T, Zhao T, Guo
S, Sun Y, Yang Y and Li C: Antitumor activity of a novel dual
functional podophyllotoxin derivative involved PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathway. PLoS One. 14(e0215886)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li Y, Wang T, Sun Y, Huang T and Li C, Fu
Y, Li Y and Li C: p53-mediated PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway played a role
in ptox-induced EMT inhibition in liver cancer cell lines. Oxid Med
Cell Longev. 2019(2531493)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Guo W, Qiu Z, Wang Z, Wang Q, Tan N, Chen
T, Chen Z, Huang S, Gu J, Li J, et al: MiR-199a-5p is negatively
associated with malignancies and regulates glycolysis and lactate
production by targeting hexokinase 2 in liver cancer. Hepatology.
62:1132–1144. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sun W, Li J, Zhou L, Han J, Liu R, Zhang
H, Ning T, Gao Z, Liu B, Chen X and Ba Y: The
c-Myc/miR-27b-3p/ATG10 regulatory axis regulates chemoresistance in
colorectal cancer. Theranostics. 10:1981–1996. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Long L, Chen Y, Xu Y and Zhang L:
Design, synthesis and antineoplastic activity of novel hybrids of
podophyllotoxin and indirubin against human leukaemia cancer cells
as multifunctional anti-MDR agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
28:1817–1824. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ren J, Liu Y, Li L, Zhao Y, Li Z, Wu C,
Chen L and Hu K: OAMDP, a novel podophyllotoxin derivative, induces
apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and autophagy in hepatoma HepG2 cells.
Cell Biol Int. 42:194–204. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|