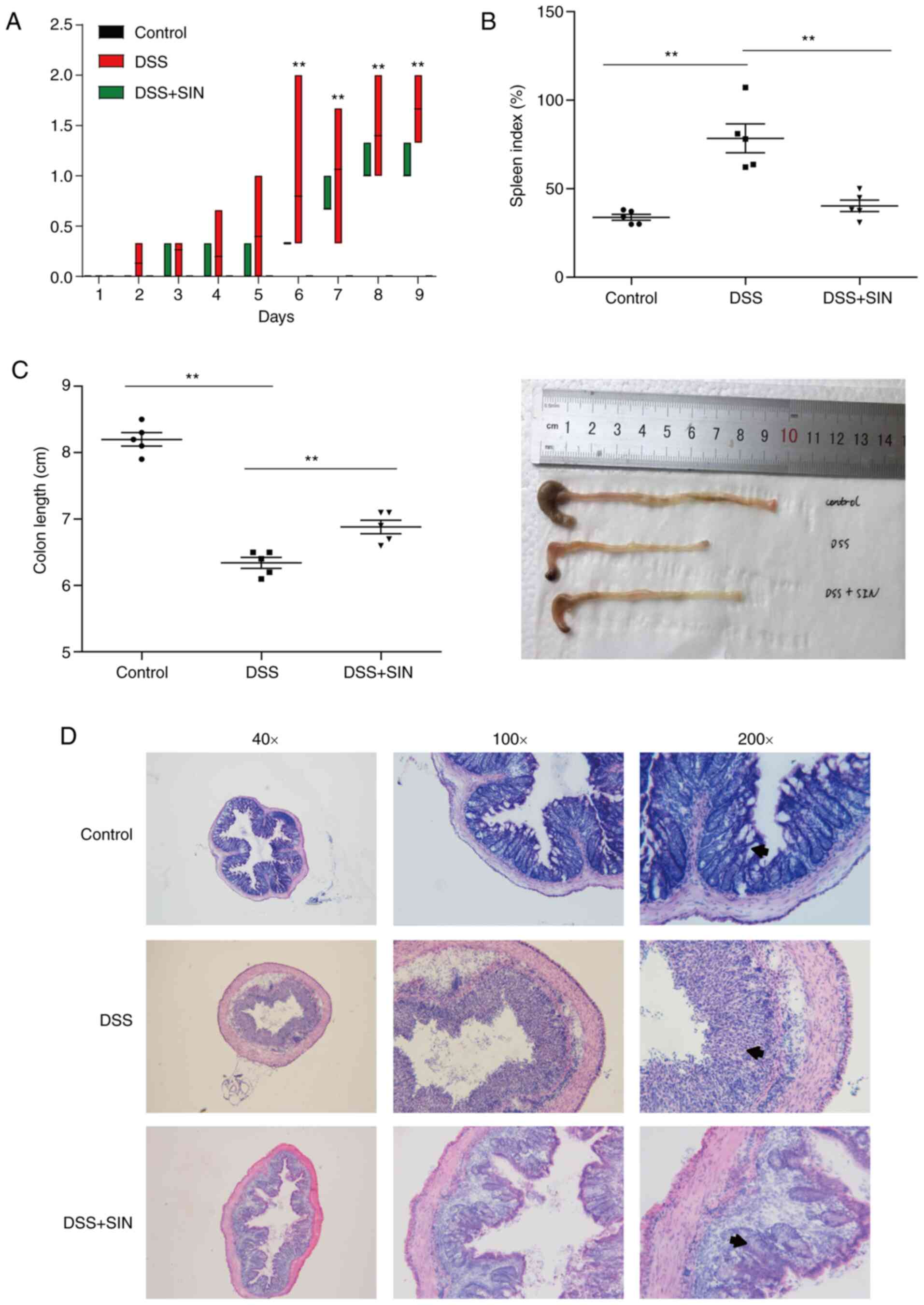
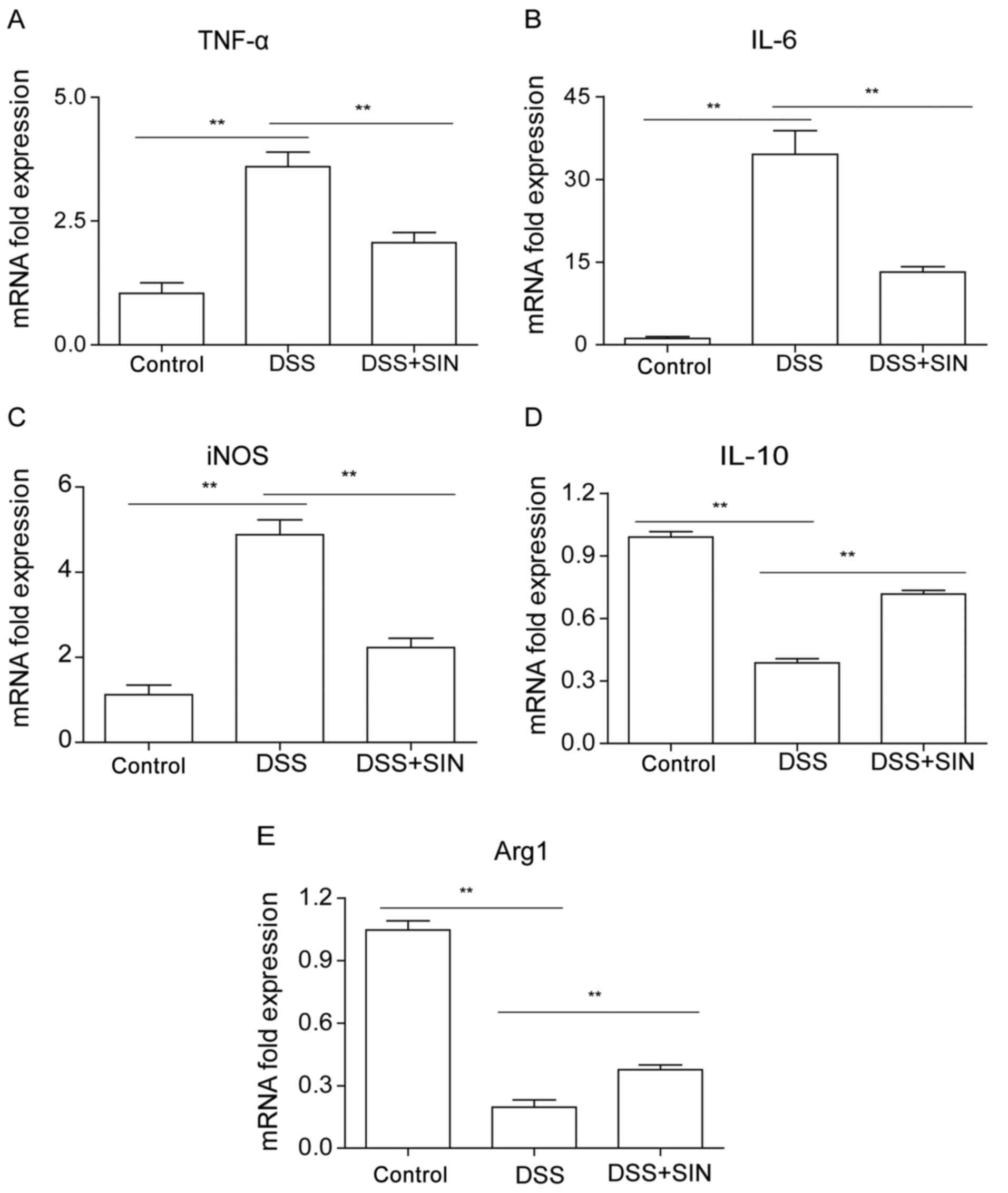
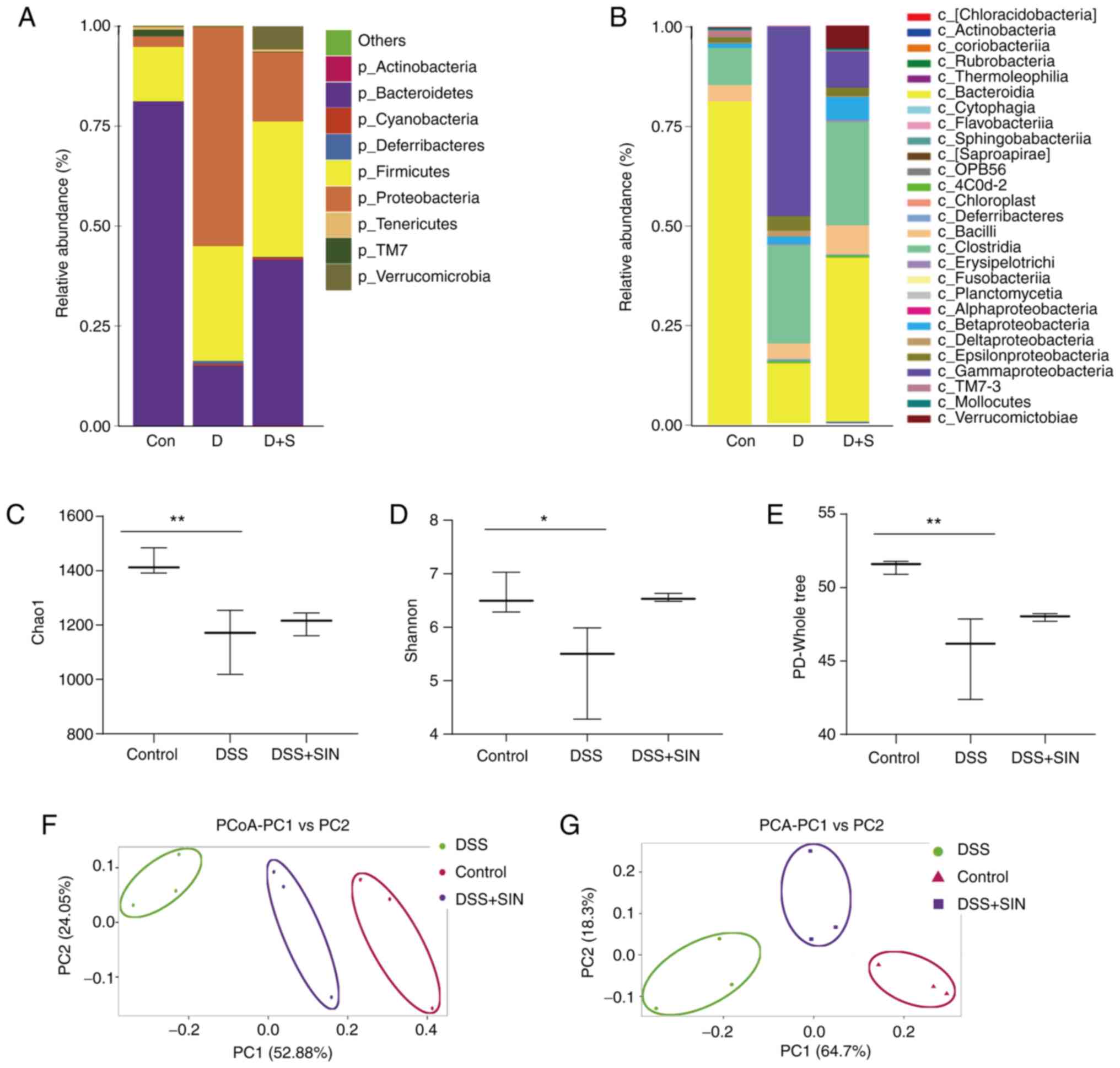
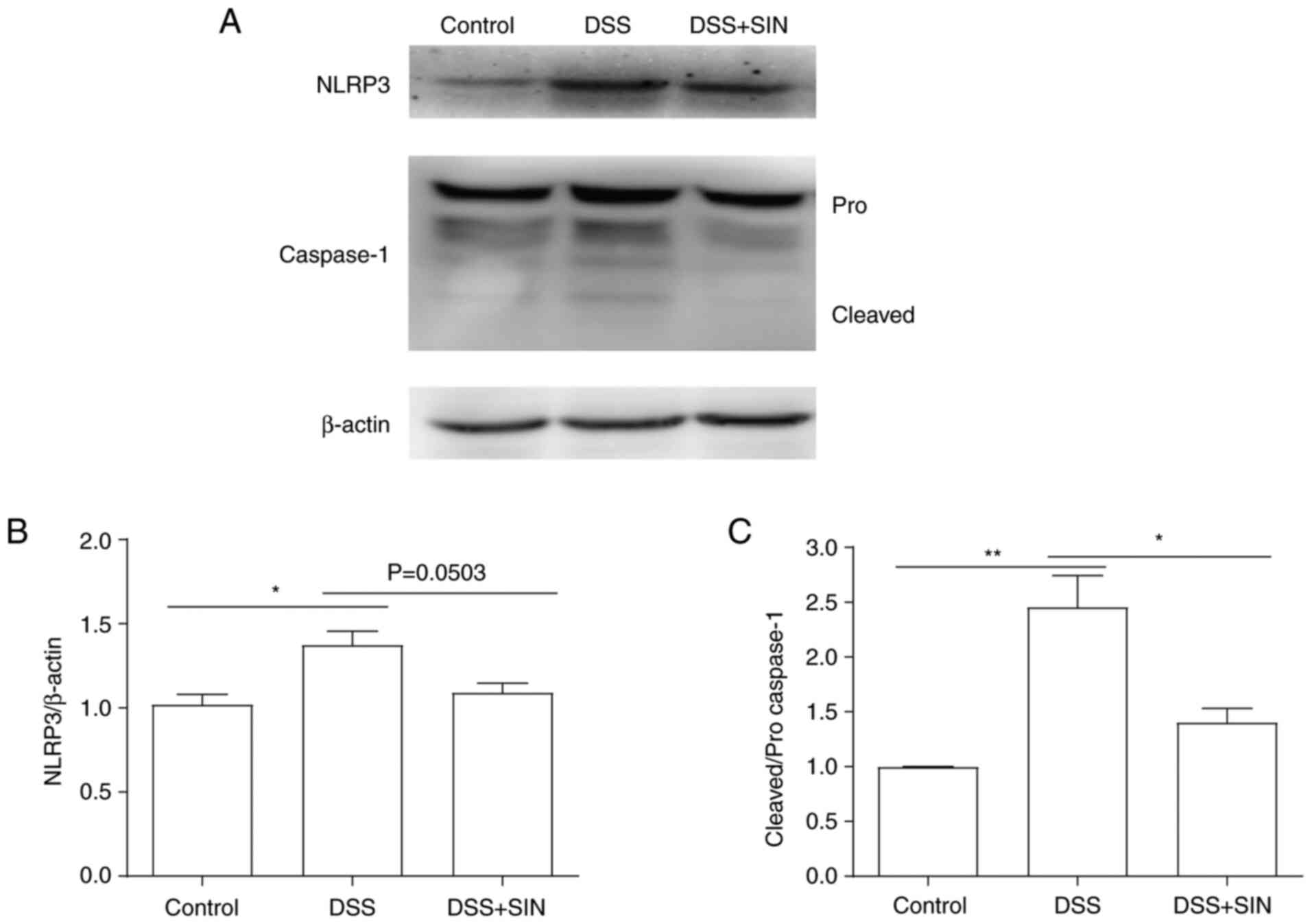
|
1
|
Null KD, Xu Y, Pasquale MK, Su C, Marren
A, Harnett J, Mardekian J, Manuchehri A and Healey P: Ulcerative
colitis treatment patterns and cost of care. Value Health.
20:752–761. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
van den Brink G, van Gaalen MAC, de Ridder
L, van der Woude CJ and Escher JC: Health care transition outcomes
in inflammatory bowel disease: A multinational delphi study. J
Crohns Colitis. 13:1163–1172. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Munyaka PM, Rabbi MF, Khafipour E and Ghia
JE: Acute dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis promotes gut
microbial dysbiosis in mice. J Basic Microbiol. 56:986–998.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Alavala S, Sangaraju R, Nalban N, Sahu BD,
Jerald MK, Kilari EK and Sistla R: Stevioside, a diterpenoid
glycoside, shows anti-inflammatory property against dextran
sulphate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice. Eur J
Pharmacol. 855:192–201. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Klimesova K, Kverka M, Zakostelska Z,
Hudcovic T, Hrncir T, Stepankova R, Rossmann P, Ridl J, Kostovcik
M, Mrazek J, et al: Altered gut microbiota promotes
colitis-associated cancer in IL-1 receptor-associated kinase
M-deficient mice. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 19:1266–1277. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang K, Jin X, You M, Tian W, Le Leu RK,
Topping DL, Conlon MA, Wu L and Hu F: Dietary propolis ameliorates
dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis and modulates the gut
microbiota in rats fed a western diet. Nutrients.
9(875)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yeom Y, Kim BS, Kim SJ and Kim Y: Sasa
quelpaertensis leaf extract regulates microbial dysbiosis by
modulating the composition and diversity of the microbiota in
dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis mice. BMC Complement Altern
Med. 16(481)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
He R, Li Y, Han C, Lin R, Qian W and Hou
X: L-Fucose ameliorates DSS-induced acute colitis via inhibiting
macrophage M1 polarization and inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome and
NF-kB activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 73:379–388. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Davis BK, Wen H and Ting JP: The
inflammasome NLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated
diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 29:707–735. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lian D, Lai J, Wu Y, Wang L and Chen Y,
Zhang Y, Boini KM, Huang Y and Chen Y: Cathepsin B-mediated NLRP3
inflammasome formation and activation in angiotensin II-induced
hypertensive mice: Role of macrophage digestion dysfunction. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 50:1585–1600. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
He X, Wei Z, Wang J, Kou J, Liu W, Fu Y
and Yang Z: Alpinetin attenuates inflammatory responses by
suppressing TLR4 and NLRP3 signaling pathways in DSS-induced acute
colitis. Sci Rep. 6(28370)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chan K, Liu ZQ, Jiang ZH, Zhou H, Wong YF,
Xu HX and Liu L: The effects of sinomenine on intestinal absorption
of paeoniflorin by the everted rat gut sac model. J Ethnopharmacol.
103:425–432. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen H, Wang Y, Jiao FZ, Yang F, Li X and
Wang LW: Sinomenine attenuates acetaminophen-induced acute liver
injury by decreasing oxidative stress and inflammatory response via
regulating TGF-β/smad pathway in vitro and in vivo. Drug Des Devel
Ther. 14:2393–2403. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li X, Wang K, Ren Y, Zhang L, Tang XJ,
Zhang HM, Zhao CQ, Liu PJ, Zhang JM and He JJ: MAPK signaling
mediates sinomenine hydrochloride-induced human breast cancer cell
death via both reactive oxygen species-dependent and -independent
pathways: An in vitro and in vivo study. Cell Death Dis.
5(e1356)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Tong B, Yu J, Wang T, Dou Y, Wu X, Kong L,
Dai Y and Xia Y: Sinomenine suppresses collagen-induced arthritis
by reciprocal modulation of regulatory T cells and Th17 cells in
gut-associated lymphoid tissues. Mol Immunol. 65:94–103.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Huang RY, Pan HD, Wu JQ, Zhou H, Li ZG,
Qiu P, Zhou YY, Chen XM, Xie ZX, Xiao Y, et al: Comparison of
combination therapy with methotrexate and sinomenine or leflunomide
for active rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized controlled clinical
trial. Phytomedicine. 57:403–410. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Yao YM, Tan ZR, Hu ZY, Guo X, Cheng ZN,
Wang LS and Zhou HH: Determination of sinomenine in human plasma by
HPLC/ESI/ion trap mass spectrum. Clin Chim Acta. 356:212–217.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Long LH, Wu PF, Chen XL, Zhang Z, Chen Y,
Li YY, Jin Y, Chen JG and Wang F: HPLC and LC-MS analysis of
sinomenine and its application in pharmacokinetic studies in rats.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 31:1508–1514. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu ZQ, Chan K, Zhou H, Jiang ZH, Wong YF,
Xu HX and Liu L: The pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of
sinomenine in rats and its protein binding ability in vitro. Life
Sci. 77:3197–3209. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhou Y, Liu H, Song J, Cao L, Tang L and
Qi C: Sinomenine alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-nduced colitis
via the Nrf2/NQO-1 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 18:3691–3698.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gkouskou KK, Deligianni C, Tsatsanis C and
Eliopoulos AG: The gut microbiota in mouse models of inflammatory
bowel disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 4(28)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG: Improving bioscience research reporting: The
ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. J Pharmacol
Pharmacother. 1:94–99. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bang B and Lichtenberger LM: Methods of
inducing inflammatory bowel disease in mice. Curr Protoc Pharmacol.
72:5.58.1–5.58.42. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Vong LB, Tomita T, Yoshitomi T, Matsui H
and Nagasaki Y: An orally administered redox nanoparticle that
accumulates in the colonic mucosa and reduces colitis in mice.
Gastroenterology. 143:1027–1036.e3. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Feldman AT and Wolfe D: Tissue processing
and hematoxylin and eosin staining. Methods Mol Biol. 1180:31–43.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Magoč T and Salzberg SL: FLASH: Fast
length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies.
Bioinformatics. 27:2957–2963. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang FG, Bai RX, Yan WM, Yan M, Dong LY
and Song MM: Differential composition of gut microbiota among
healthy volunteers, morbidly obese patients and post-bariatric
surgery patients. Exp Ther Med. 17:2268–2278. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Carter SJ, Hunter GR, Blackston JW, Liu N,
Lefkowitz EJ, Van Der Pol WJ, Morrow CD, Paulsen JA and Rogers LQ:
Gut microbiota diversity is associated with cardiorespiratory
fitness in post-primary treatment breast cancer survivors. Exp
Physiol. 104:529–539. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lozupone C and Knight R: UniFrac: A new
phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl
Environ Microbiol. 71:8228–8235. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lozupone C, Lladser ME, Knights D,
Stombaugh J and Knight R: UniFrac: An effective distance metric for
microbial community comparison. ISME J. 5:169–172. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Edgar RC: UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU
sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods. 10:996–998.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Dong T, Feng Q, Liu F, Chang LK, Zhou X,
Han M, Tian X, Zhong N and Liu S: Alteration of stomach microbiota
compositions in the progression of gastritis induces nitric oxide
in gastric cell. Exp Ther Med. 13:2793–2800. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kucharzik T, Koletzko S, Kannengiesser K
and Dignass A: Ulcerative colitis-diagnostic and therapeutic
algorithms. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 117:564–574. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Moreno Márquez C, Maldonado Pérez B and
Castro Laria L: Infliximab as rescue treatment in Sweet's syndrome
related to corticodependent ulcerative colitis. J Crohns Colitis.
12:755–756. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Park JH and Kim JK: Pristimerin, a
naturally occurring triterpenoid, attenuates tumorigenesis in
experimental colitis-associated colon cancer. Phytomedicine.
42:164–171. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zheng R, Ma J, Wang D, Dong W, Wang S, Liu
T, Xie R, Liu L, Wang B and Cao H: Chemopreventive effects of
silibinin on colitis-associated tumorigenesis by inhibiting
IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. Mediators Inflamm.
2018(1562010)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xiong H, Tian L, Zhao Z, Chen S, Zhao Q,
Hong J, Xie Y, Zhou N and Fu Y: The sinomenine enteric-coated
microspheres suppressed the TLR/NF-κB signaling in DSS-induced
experimental colitis. Int Immunopharmacol. 50:251–262.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wang K, Jin X, Li Q, Sawaya ACHF, Le Leu
RK, Conlon MA, Wu L and Hu F: Propolis from different geographic
origins decreases intestinal inflammation and bacteroides spp.
populations in a model of DSS-induced colitis. Mol Nutr Food Res.
62(e1800080)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wang W, Li X, Zheng D, Zhang D, Peng X,
Zhang X, Ai F, Wang X, Ma J, Xiong W, et al: Dynamic changes and
functions of macrophages and M1/M2 subpopulations during ulcerative
colitis-associated carcinogenesis in an AOM/DSS mouse model. Mol
Med Rep. 11:2397–2406. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Yao D, Dong M, Dai C and Wu S:
Inflammation and inflammatory cytokine contribute to the initiation
and development of ulcerative colitis and its associated cancer.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 25:1595–1602. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Guan Q and Zhang J: Recent advances: The
imbalance of cytokines in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel
disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2017(4810258)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhou X, Li W, Wang S, Zhang P, Wang Q,
Xiao J, Zhang C, Zheng X, Xu X, Xue S, et al: YAP aggravates
inflammatory bowel disease by regulating M1/M2 macrophage
polarization and gut microbial homeostasis. Cell Rep.
27:1176–1189.e5. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Aass HCD, Hellum M, Trøseid AS, Brandtzaeg
P, Berg JP, Øvstebø R and Henriksson CE: Whole-blood incubation
with the Neisseria meningitidis lpxL1 mutant induces less
pro-inflammatory cytokines than the wild type, and IL-10 reduces
the MyD88-dependent cytokines. Innate Immun. 24:101–111.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Liu L, Liang L, Liang H, Wang M, Lu B, Xue
M, Deng J and Chen Y: Fusobacterium nucleatum aggravates the
progression of colitis by regulating M1 macrophage polarization via
AKT2 pathway. Front Immunol. 10(1324)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Cui H, Cai Y, Wang L, Jia B, Li J, Zhao S,
Chu X, Lin J, Zhang X, Bian Y and Zhuang P: Berberine regulates
Treg/Th17 balance to treat ulcerative colitis through modulating
the gut microbiota in the colon. Front Pharmacol.
9(571)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ilott NE, Bollrath J, Danne C, Schiering
C, Shale M, Adelmann K, Krausgruber T, Heger A, Sims D and Powrie
F: Defining the microbial transcriptional response to colitis
through integrated host and microbiome profiling. ISME J.
10:2389–2404. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Forbes JD, Van Domselaar G and Bernstein
CN: The gut microbiota in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases.
Front Microbiol. 7(1081)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Gao X, Cao Q, Cheng Y, Zhao D, Wang Z,
Yang H, Wu Q, You L, Wang Y, Lin Y, et al: Chronic stress promotes
colitis by disturbing the gut microbiota and triggering immune
system response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:E2960–E2969.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhang M, Sun K, Wu Y, Yang Y, Tso P and Wu
Z: Interactions between intestinal microbiota and host immune
response in inflammatory bowel disease. Front Immunol.
8(942)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ishikawa D, Sasaki T, Osada T,
Kuwahara-Arai K, Haga K, Shibuya T, Hiramatsu K and Watanabe S:
Changes in intestinal microbiota following combination therapy with
fecal microbial transplantation and antibiotics for ulcerative
colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 23:116–125. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Ishikawa D, Sasaki T, Takahashi M,
Kuwahara-Arai K, Haga K, Ito S, Okahara K, Nakajima A, Shibuya T,
Osada T, et al: The microbial composition of bacteroidetes species
in ulcerative colitis is effectively improved by combination
therapy with fecal microbiota transplantation and antibiotics.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 24:2590–2598. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhu W, Winter MG, Byndloss MX, Spiga L,
Duerkop BA, Hughes ER, Büttner L, de Lima Romão E, Behrendt CL,
Lopez CA, et al: Precision editing of the gut microbiota
ameliorates colitis. Nature. 553:208–211. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Rathinam VAK and Chan FK: Inflammasome,
inflammation, and tissue homeostasis. Trends Mol Med. 24:304–318.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|