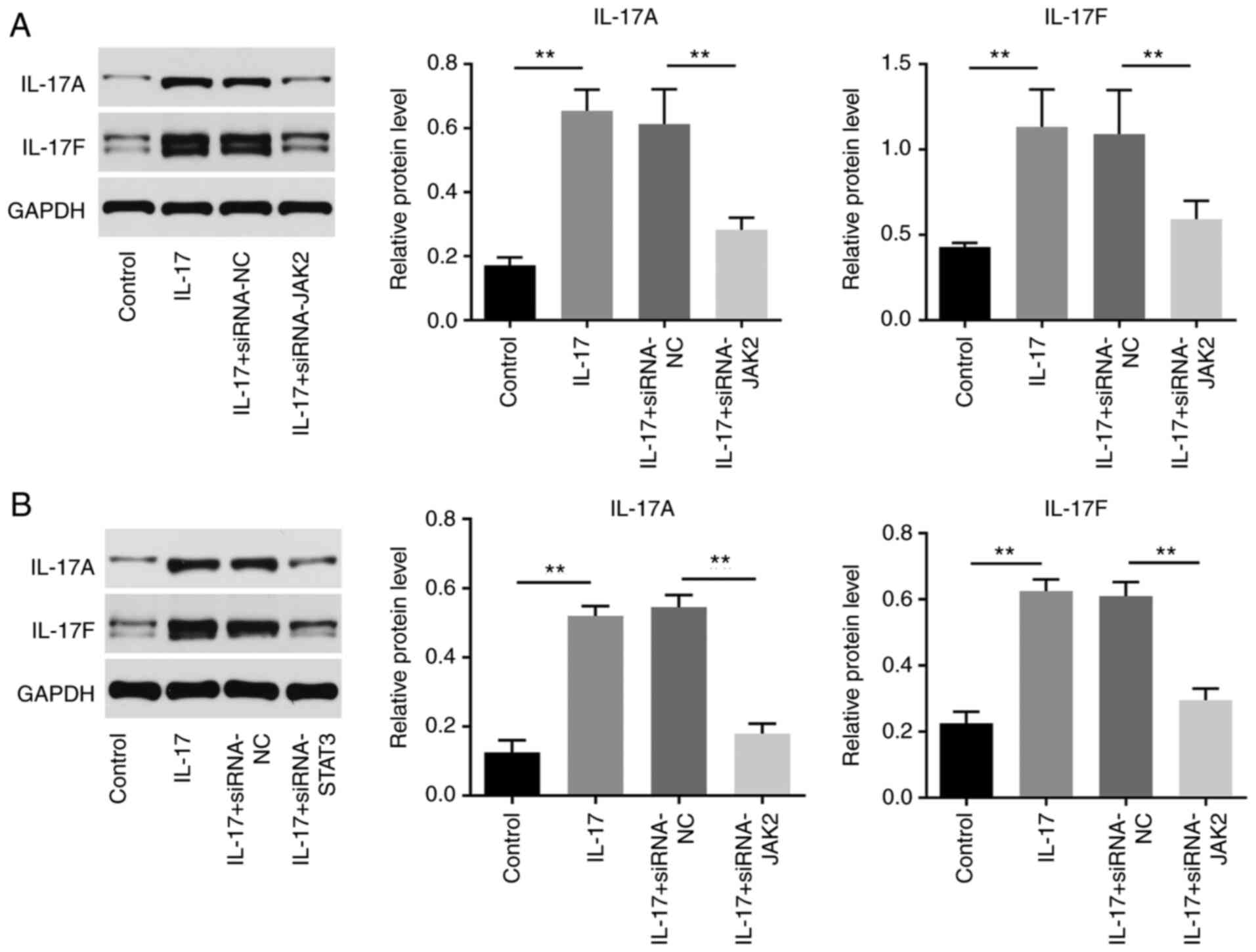
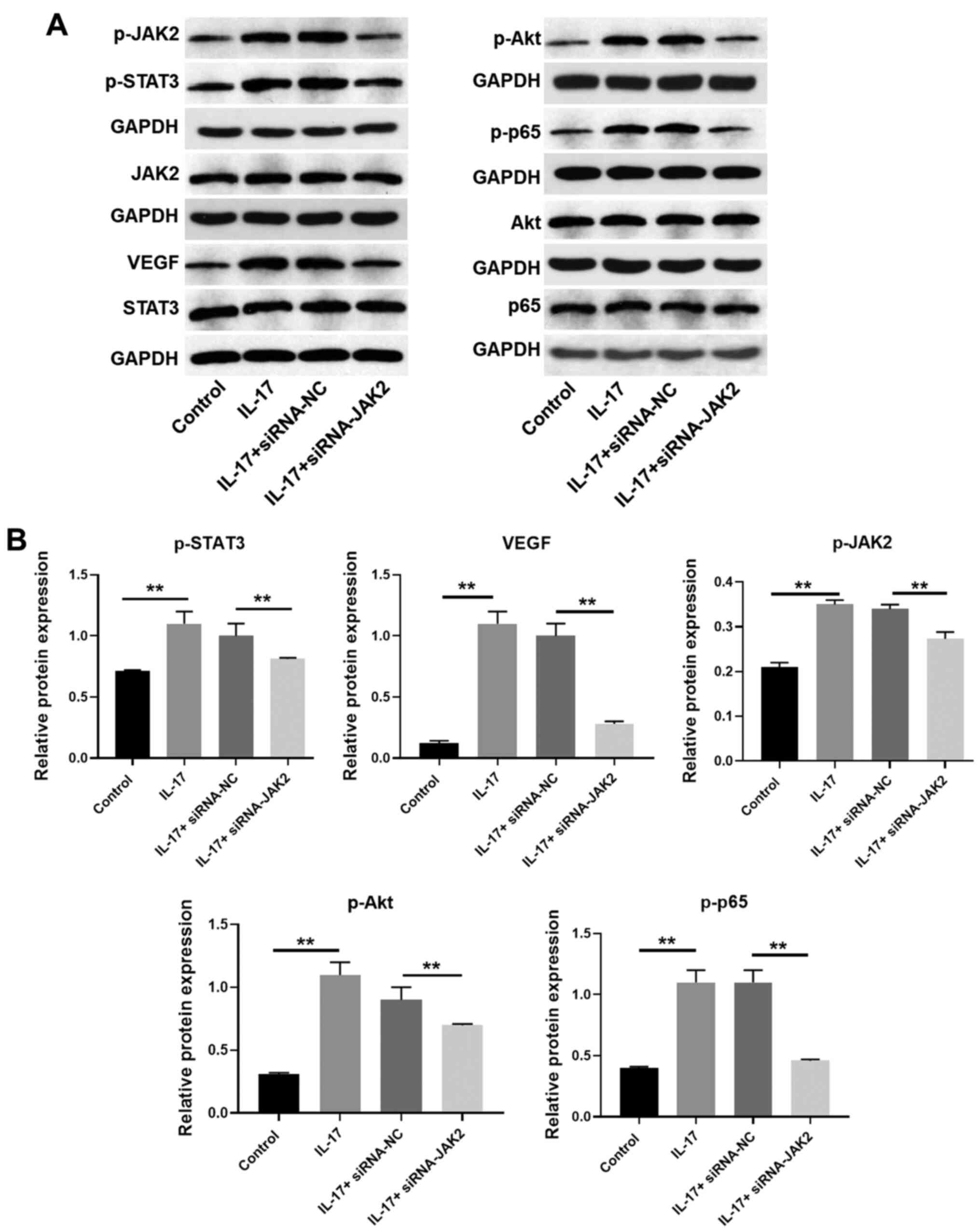
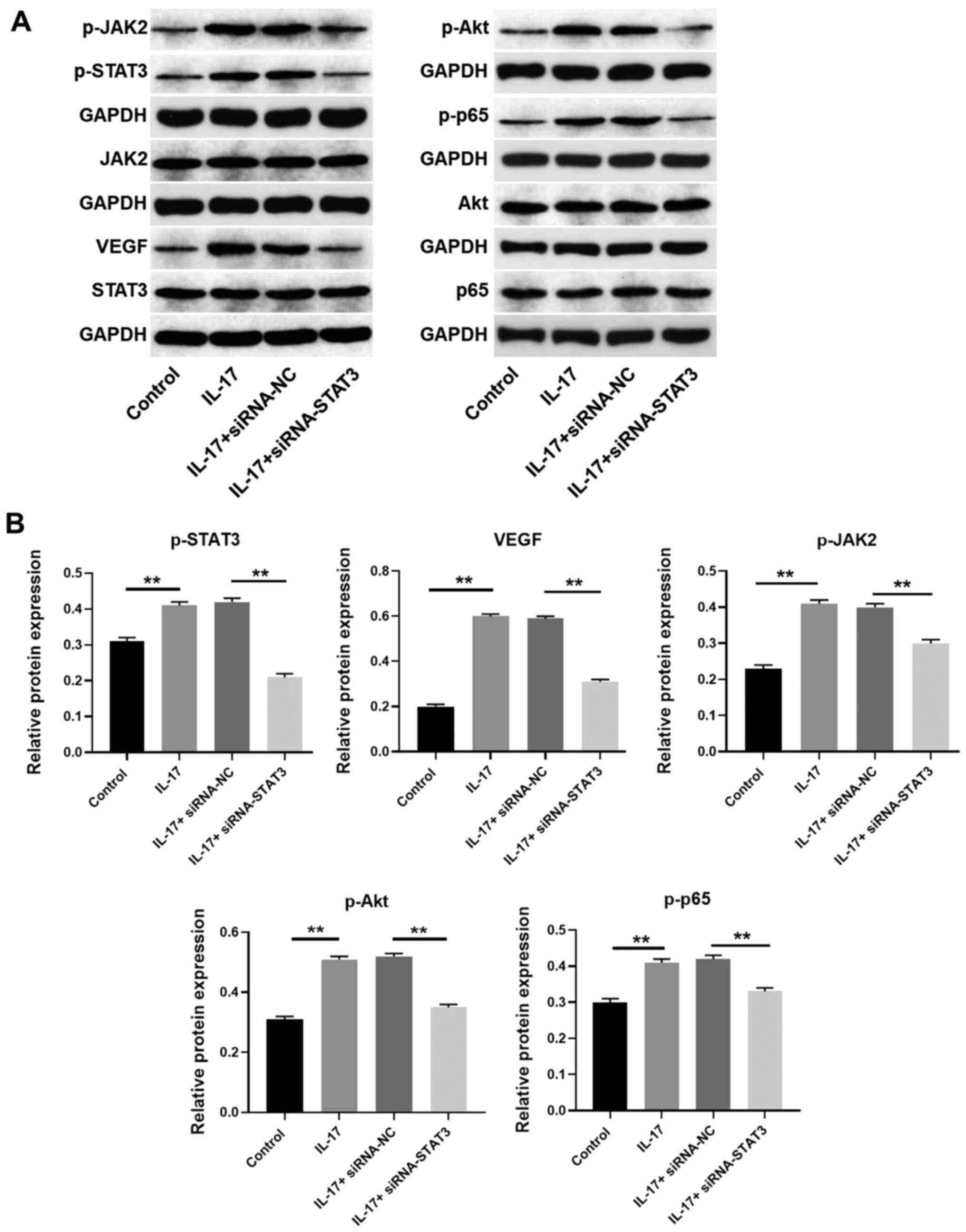
|
1
|
Tsikouras P, Zervoudis S, Manav B, Tomara
E, Iatrakis G, Romanidis C, Bothou A and Galazios G: Cervical
cancer: Screening, diagnosis and staging. J BUON. 21:320–325.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Benard VB, Thomas CC, King J, Massetti GM,
Doria-Rose VP and Saraiya M: Centers for Disease C and Prevention
(CDC). Vital signs: Cervical cancer incidence, mortality, and
screening-United States, 2007-2012. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep.
63:1004–1009. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeng SY, Liang MR, Li LY, Li L, Jiang W
and Zhong ML: Application of transvaginal external fascia
trachelectomy in the treatment of CIN and micro-invasive cervical
cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 35:543–546. 2013.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
4
|
Gilham C, Sargent A, Kitchener HC and Peto
J: HPV testing compared with routine cytology in cervical
screening: Long-term follow-up of ARTISTIC RCT. Health Technol
Assess. 23:1–44. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hong DK, Kim SA, Lim KT, Lee KH, Kim TJ
and So KA: Clinical outcome of high-grade cervical intraepithelial
neoplasia during pregnancy: A 10-year experience. Eur J Obstet
Gynecol Reprod Biol. 236:173–176. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cheng X, Feng Y, Wang X, Wan X, Xie X and
Lu W: The effectiveness of conization treatment for post-menopausal
women with high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Exp Ther
Med. 5:185–188. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ostojic DV, Vrdoljak-Mozetic D,
Stemberger-Papic S, Finderle A and Eminovic S: Cervical cytology
and HPV test in follow-up after conisation or LLETZ. Coll Antropol.
34:219–224. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Apgar BS, Kittendorf AL, Bettcher CM, Wong
J and Kaufman AJ: Update on ASCCP consensus guidelines for abnormal
cervical screening tests and cervical histology. Am Fam Physician.
80:147–155. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guo N, Shen G, Zhang Y, Moustafa AA, Ge D
and You Z: Interleukin-17 promotes migration and invasion of human
cancer cells through upregulation of MTA1 expression. Front Oncol.
9(546)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Alves JJ, De Medeiros Fernandes TAA, De
Araujo JM, Cobucci RN, Lanza DC, Bezerra FL, Andrade VS and
Fernandes JV: Th17 response in patients with cervical cancer. Oncol
Lett. 16:6215–6227. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Karabulut M, Usul Afsar C, Serimez M and
Karabulut S: Serum IL-17 levels can be diagnostic for gastric
cancer. J BUON. 24:1601–1609. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iwakura Y, Ishigame H, Saijo S and Nakae
S: Functional specialization of interleukin-17 family members.
Immunity. 34:149–162. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lotti F, Jarrar AM, Pai RK, Hitomi M,
Lathia J, Mace A, Gantt GA Jr, Sukhdeo K, DeVecchio J, Vasanji A,
et al: Chemotherapy activates cancer-associated fibroblasts to
maintain colorectal cancer-initiating cells by IL-17A. J Exp Med.
210:2851–2872. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Flies EJ, Mavoa S, Zosky GR, Mantzioris E,
Williams C, Eri R, Brook BW and Buettel JC: Urban-associated
diseases: Candidate diseases, environmental risk factors, and a
path forward. Environ Int. 133(105187)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Alshammari TK, Alghamdi H, Green TA, Niazy
A, Alkahdar L, Alrasheed N, Alhosaini K, Alswayyed M, Elango R,
Laezza F, et al: Assessing the role of toll-like receptor in
isolated, standard and enriched housing conditions. PLoS One.
14(e0222818)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nagarkoti S, Dubey M, Sadaf S, Awasthi D,
Chandra T, Jagavelu K, Kumar S and Dikshit M: Catalase
S-Glutathionylation by NOX2 and mitochondrial-derived ROS adversely
affects mice and human neutrophil survival. Inflammation.
42:2286–2296. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cong J, Liu R, Wang X, Sheng L, Jiang H,
Wang W, Zhang Y, Yang S and Li C: Association between
interluekin-17 gene polymorphisms and the risk of cervical cancer
in a Chinese population. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:9567–9573.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Miranda LN, Reginaldo FP, Souza DM, Soares
CP, Silva TG, Rocha KB, Jatoba CA, Donadi EA, Andrade JM, Goncalves
AK and Crispim JC: Greater expression of the human leukocyte
antigen-G (HLA-G) and interleukin-17 (IL-17) in cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia: Analytical cross-sectional study. Sao
Paulo Med J. 133:336–342. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Song Y, Yang M, Zhang H, Sun Y, Tao Y, Li
H, Zhang J, Li Y and Yang J: IL-17 affects the progression,
metastasis, and recurrence of laryngeal cancer via the inhibition
of apoptosis through activation of the PI3K/AKT/FAS/FASL pathways.
J Immunol Res. 2020(2953191)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lu W, He F, Lin Z, Liu S, Tang L, Huang Y
and Hu Z: Dysbiosis of the endometrial microbiota and its
association with inflammatory cytokines in endometrial cancer. Int
J Cancer. 148:1708–1716. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liao C, Zhang C, Jin L and Yang Y: IL-17
alters the mesenchymal stem cell niche towards osteogenesis in
cooperation with osteocytes. J Cell Physiol. 235:4466–4480.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Guo JQ, Liu J and Lu B: Expression of
gamma-delta T cells in immune microenvironment in children with
Henoch-Schonlein purpura. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi.
21:960–965. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
24
|
Siefker DT, Vu L, You D, McBride A, Taylor
R, Jones TL, DeVincenzo J and Cormier SA: Respiratory syncytial
virus disease severity is associated with distinct CD8+
T-cell profiles. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 201:325–334.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang J, Lu L, Luo Z, Li W, Lu Y, Tang Q
and Pu J: MiR-383 inhibits cell growth and promotes cell apoptosis
in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting IL-17 via STAT3 signaling
pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 120(109551)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang N, Wang Q, Tian Y, Xiong S, Li G and
Xu L: Expressions of IL-17 and TNF-α in patients with Hashimoto's
disease combined with thyroid cancer before and after surgery and
their relationship with prognosis. Clin Transl Oncol. 22:1280–1287.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kinoshita M, Kobayashi S, Gotoh K, Kubo M,
Hayashi K, Iwagami Y, Yamada D, Akita H, Noda T, Asaoka T, et al:
Heterogeneity of Treg/Th17 according to cancer progression and
modification in biliary tract cancers via self-producing cytokines.
Dig Dis Sci. 65:2937–2948. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Amara S, Majors C, Roy B, Hill S, Rose KL,
Myles EL and Tiriveedhi V: Critical role of SIK3 in mediating high
salt and IL-17 synergy leading to breast cancer cell proliferation.
PLoS One. 12(e0180097)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Varikuti S, Oghumu S, Elbaz M, Volpedo G,
Ahirwar DK, Alarcon PC, Sperling RH, Moretti E, Pioso MS, Kimble J,
et al: STAT1 gene deficient mice develop accelerated breast cancer
growth and metastasis which is reduced by IL-17 blockade.
Oncoimmunology. 6(e1361088)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zou Y, Dai SX, Chi HG, Li T, He ZW, Wang
J, Ye CG, Huang GL, Zhao B, Li WY, et al: Baicalin attenuates
TNBS-induced colitis in rats by modulating the Th17/Treg paradigm.
Arch Pharm Res. 38:1873–1887. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Song KH, Jung SY, Kang SM, Kim MH, Ahn J,
Hwang SG, Lee JH, Lim DS, Nam SY and Song JY: Induction of
immunogenic cell death by radiation-upregulated karyopherin alpha 2
in vitro. Eur J Cell Biol. 95:219–227. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Perez-Figueroa E, Sanchez-Cuaxospa M,
Martinez-Soto KA, Sanchez-Zauco N, Medina-Sanson A,
Jimenez-Hernandez E, Torres-Nava JR, Felix-Castro JM, Gomez A,
Ortega E, et al: Strong inflammatory response and Th1-polarization
profile in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia without
apparent infection. Oncol Rep. 35:2699–2706. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Souza CM, do Amaral CL, Souza SC, de Souza
ACP, de Cassia Alves Martins I, Contieri LS, Milanski M, Torsoni
AS, Ignacio-Souza LM and Torsoni MA: JAK2/STAT3 pathway is required
for alpha7nAChR-dependent expression of POMC and AGRP neuropeptides
in male mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 53:701–712. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fogg KC, Olson WR, Miller JN, Khan A,
Renner C, Hale I, Weisman PS and Kreeger PK: Alternatively
activated macrophage-derived secretome stimulates ovarian cancer
spheroid spreading through a JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Cancer Lett.
458:92–101. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wei L, Chen Y, Zhang C, Liu M and Xiong H:
Leptin induces IL-6 and IL-8 expression through leptin receptor
Ob-Rb in human dental pulp fibroblasts. Acta Odontol Scand.
77:205–212. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Song Q, Liu B, Li X, Zhang Q, Cao L, Xu M,
Meng Z, Wu X and Xu K: MiR-26a-5p potentiates metastasis of human
lung cancer cells by regulating ITGβ8-JAK2/STAT3 axis. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 501:494–500. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang L, Lu P, Guo X, Liu T, Luo X and Zhu
YT: Inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway protects mice from
the DDP-induced acute kidney injury in lung cancer. Inflamm Res.
68:751–760. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wu D, Dong W, Fang K and Wang M:
As4S4 exhibits good killing effect on
multiple myeloma cells via repressing SOCS1 methylation-mediated
JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
18(1533033819896806)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jing W, Guo X, Wang G, Bi Y, Han L, Zhu Q,
Qiu C, Tanaka M and Zhao Y: Breast cancer cells promote
CD169+ macrophage-associated immunosuppression through
JAK2-mediated PD-L1 upregulation on macrophages. Int
Immunopharmacol. 78(106012)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wang X, Yin H, Zhang L, Zheng D, Yang Y,
Zhang J, Jiang H, Ling X, Xin Y, Liang H, et al: The construction
and analysis of the aberrant lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network in non-small
cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 11:1772–1778. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Li X, Mak VCY, Zhou Y, Wang C, Wong ESY,
Sharma R, Lu Y, Cheung ANY, Mills GB and Cheung LWT: Deregulated
Gab2 phosphorylation mediates aberrant AKT and STAT3 signaling upon
PIK3R1 loss in ovarian cancer. Nat Commun. 10(716)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Deng F, Wang S, Zhang L, Xie X, Cai S, Li
H, Xie GL, Miao HL, Yang C, Liu X and Xia Z: Propofol through
upregulating caveolin-3 attenuates post-hypoxic mitochondrial
damage and cell death in H9C2 cardiomyocytes during hyperglycemia.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:279–292. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li YL, Gao L, Zucker IH and Schultz HD:
NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide anion mediates angiotensin
II-enhanced carotid body chemoreceptor sensitivity in heart failure
rabbits. Cardiovasc Res. 75:546–554. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wei Z, Jiang X, Qiao H, Zhai B, Zhang L,
Zhang Q, Wu Y, Jiang H and Sun X: STAT3 interacts with Skp2/p27/p21
pathway to regulate the motility and invasion of gastric cancer
cells. Cell Signal. 25:931–938. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Vona R, Gambardella L, Cittadini C,
Straface E and Pietraforte D: Biomarkers of oxidative stress in
metabolic syndrome and associated diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019(8267234)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Li K: Iron pathophysiology in friedreich's
ataxia. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1173:125–143. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Cho TM, Kim JY, Kim YJ, Sung D, Oh E, Jang
S, Farrand L, Hoang VH, Nguyen CT, Ann J, et al: C-terminal HSP90
inhibitor L80 elicits anti-metastatic effects in triple-negative
breast cancer via STAT3 inhibition. Cancer Lett. 447:141–153.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ucci M, Di Tomo P, Tritschler F, Cordone
VGP, Lanuti P, Bologna G, Di Silvestre S, Di Pietro N, Pipino C,
Mandatori D, et al: Anti-inflammatory role of carotenoids in
endothelial cells derived from umbilical cord of women affected by
gestational diabetes mellitus. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019(8184656)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Li Y, Cui N, Zheng PS and Yang WT: BMX/Etk
promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenicity of cervical cancer
cells through PI3K/AKT/mTOR and STAT3 pathways. Oncotarget.
8:49238–49252. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Steelman LS, Abrams SL, Whelan J, Bertrand
FE, Ludwig DE, Basecke J, Libra M, Stivala F, Milella M, Tafuri A,
et al: Contributions of the Raf/MEK/ERK, PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR and
Jak/STAT pathways to leukemia. Leukemia. 22:686–707.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Yang X, Yan H, Jiang N, Yu Z, Yuan J, Ni Z
and Fang W: IL-6 Trans-signaling drives a STAT3-dependent pathway
that leads to structural alterations of peritoneal membrane. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 318:F338–F353. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Buttura JR, Provisor Santos MN, Valieris
R, Drummond RD, Defelicibus A, Lima JP, Calsavara VF, Freitas HC,
Cordeiro de Lima VC, Fernanda Bartelli T, et al: Mutational
signatures driven by epigenetic determinants enable the
stratification of patients with gastric cancer for therapeutic
intervention. Cancers (Basel). 13(490)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhang Q, Wang HY, Woetmann A, Raghunath
PN, Odum N and Wasik MA: STAT3 induces transcription of the DNA
methyltransferase 1 gene (DNMT1) in malignant T lymphocytes. Blood.
108:1058–1064. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|