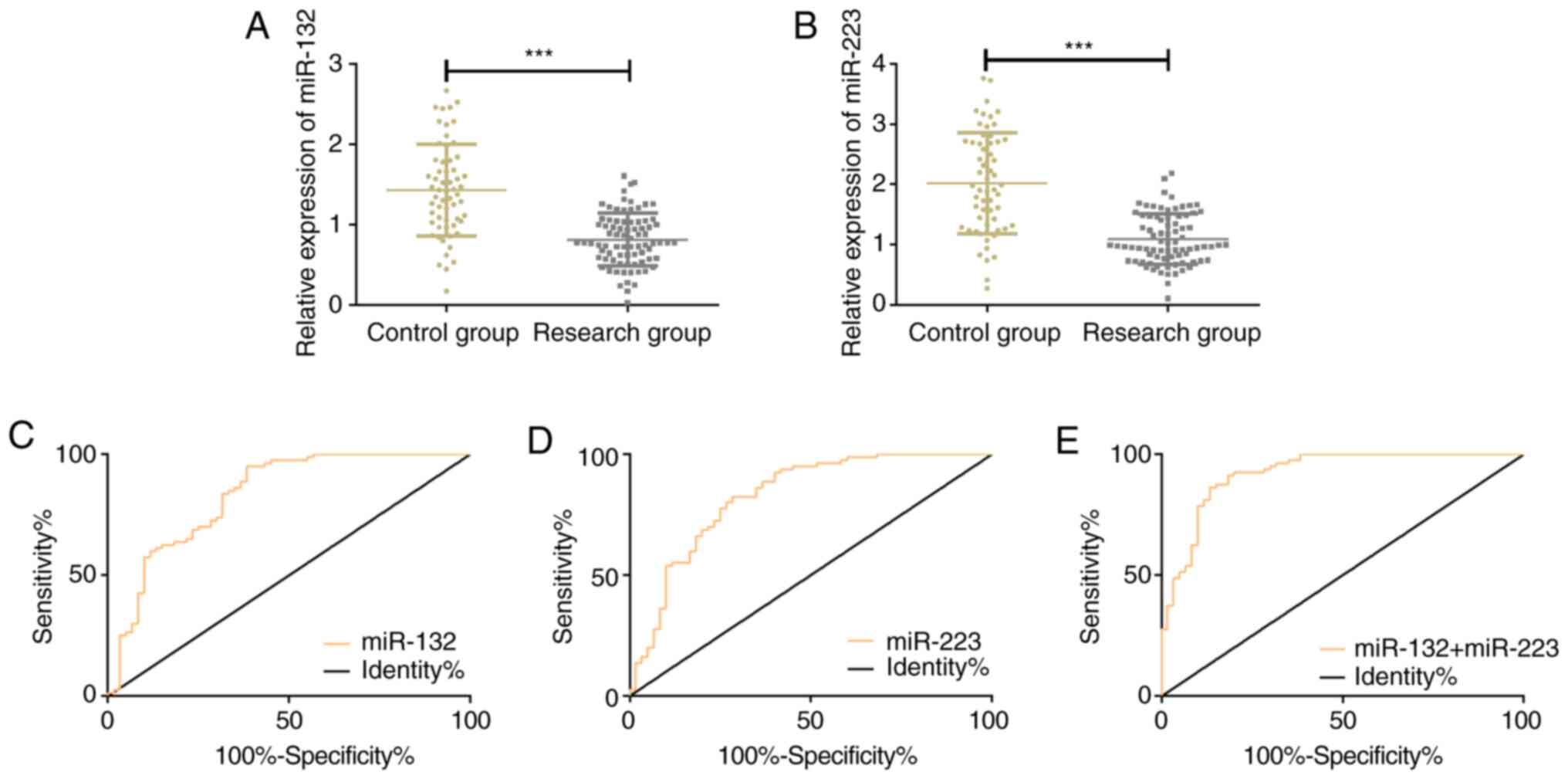
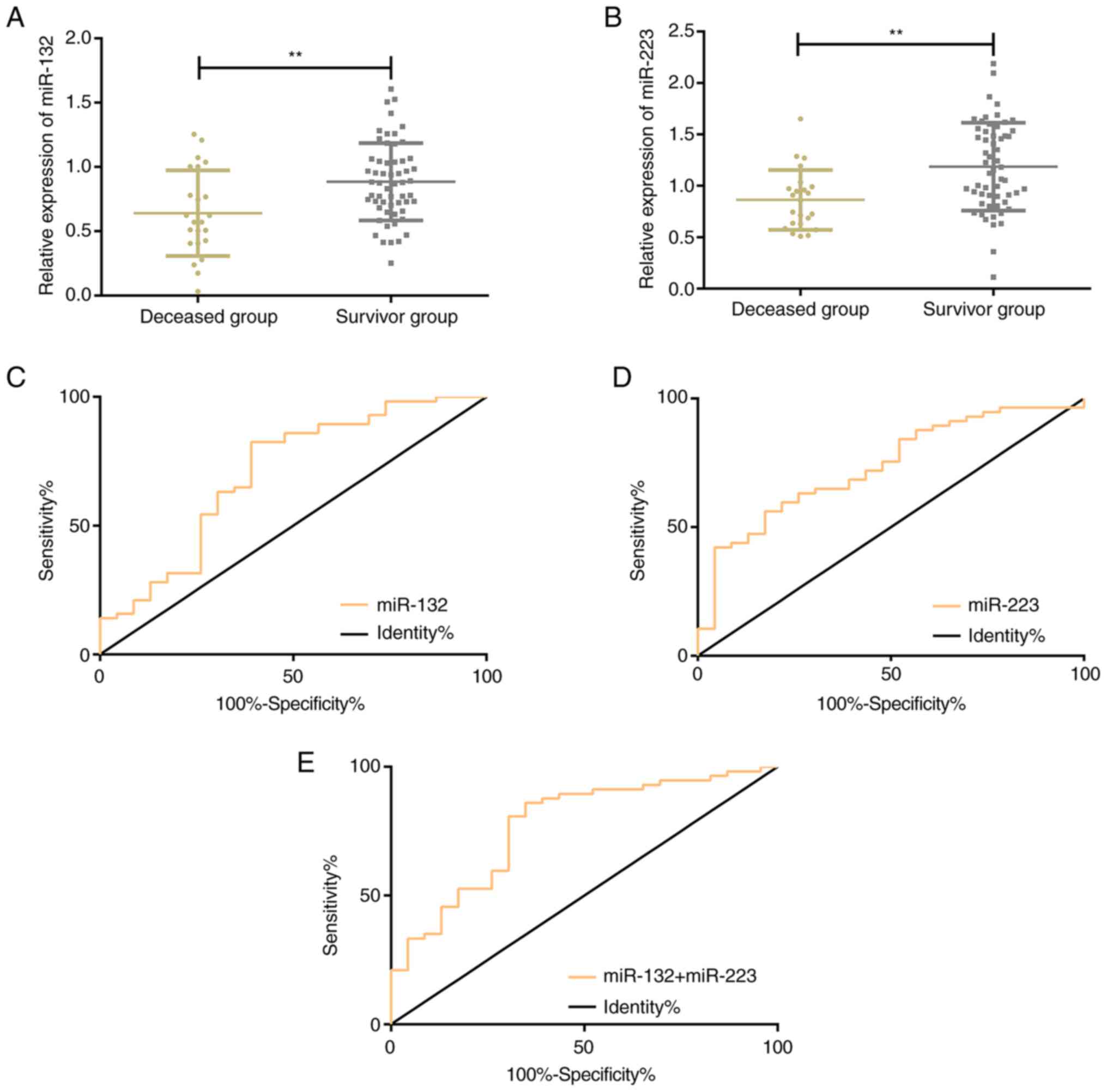
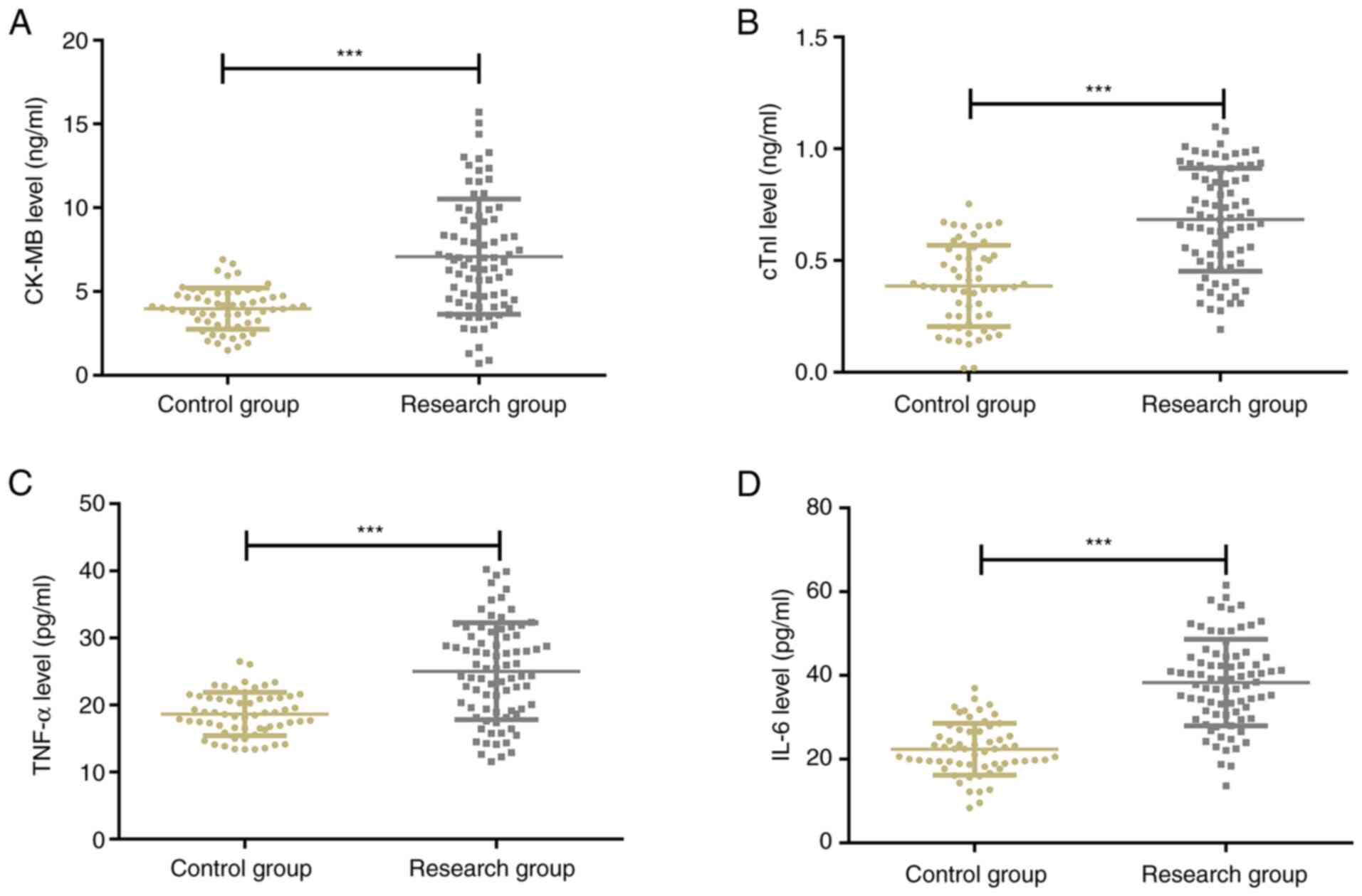
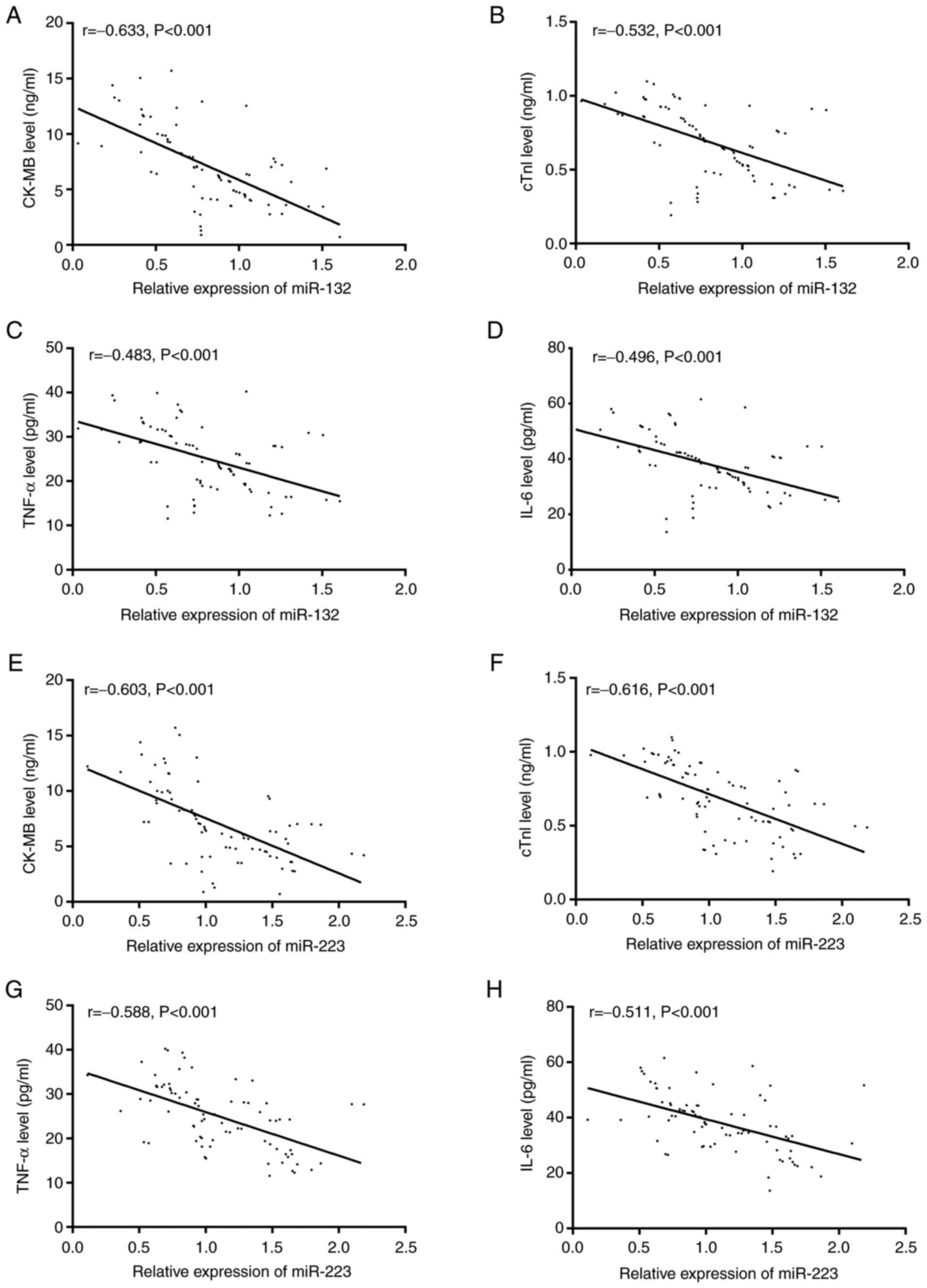
|
1
|
Sato R, Kuriyama A, Takada T, Nasu M and
Luthe SK: Prevalence and risk factors of sepsis-induced
cardiomyopathy: A retrospective cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore).
95(e5031)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yang F, Zhao LN, Sun Y and Chen Z:
Levosimendan as a new force in the treatment of sepsis-induced
cardiomyopathy: Mechanism and clinical application. J Int Med Res.
47:1817–1828. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dombrovskiy VY, Martin AA, Sunderram J and
Paz HL: Rapid increase in hospitalization and mortality rates for
severe sepsis in the United States: A trend analysis from 1993 to
2003. Crit Care Med. 35:1244–1250. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Russell JA and Walley KR: Update in sepsis
2012. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 187:1303–1307. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Semeraro N, Ammollo CT, Semeraro F and
Colucci M: Sepsis, thrombosis and organ dysfunction. Thromb Res.
129:290–295. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hochstadt A, Meroz Y and Landesberg G:
Myocardial dysfunction in severe sepsis and septic shock: More
questions than answers? J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 25:526–535.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Romero-Bermejo FJ, Ruiz-Bailen M,
Gil-Cebrian J and Huertos-Ranchal MJ: Sepsis-induced
cardiomyopathy. Curr Cardiol Rev. 7:163–183. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sato R and Nasu M: A review of
sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy. J Intensive Care.
3(48)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
An R, Feng J, Xi C, Xu J and Sun L:
miR-146a attenuates sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction by
suppressing IRAK1 and TRAF6 via targeting ErbB4 expression. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2018(7163057)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sluijter JP and Doevendans PA:
Sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction is controlled by small RNA
molecules. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 97:67–69. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zheng G, Pan M, Jin W, Jin G and Huang Y:
MicroRNA-135a is up-regulated and aggravates myocardial depression
in sepsis via regulating p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway. Int
Immunopharmacol. 45:6–12. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Qian Y, Song J, Ouyang Y, Han Q, Chen W,
Zhao X, Xie Y, Chen Y, Yuan W and Fan C: Advances in roles of
miR-132 in the nervous system. Front Pharmacol.
8(770)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mancuso R, Agostini S, Hernis A,
Zanzottera M, Bianchi A and Clerici M: Circulatory miR-223-3p
discriminates between Parkinson's and Alzheimer's patients. Sci
Rep. 9(9393)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li M, Shao H, Zhang X and Qin B:
Hesperidin alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation
in mice by promoting the miRNA-132 pathway. Inflammation.
39:1681–1689. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang JF, Yu ML, Yu G, Bian JJ, Deng XM,
Wan XJ and Zhu KM: Serum miR-146a and miR-223 as potential new
biomarkers for sepsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 394:184–188.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang H, Bei Y, Shen S, Huang P, Shi J,
Zhang J, Sun Q, Chen Y, Yang Y, Xu T, et al: miR-21-3p controls
sepsis-associated cardiac dysfunction via regulating SORBS2. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 94:43–53. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hashmat N, Shabbir I, Rahat T, Ijaz F and
Majeed S: Clinical profile and disease outcome of septic patients
at public sector hospital. Pak J Med Res. 54:44–47. 2015.
|
|
18
|
Zhuang YT, Xu DY, Wang GY, Sun JL, Huang Y
and Wang SZ: IL-6 induced lncRNA MALAT1 enhances TNF-α expression
in LPS-induced septic cardiomyocytes via activation of SAA3. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:302–309. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao A, Li G, Péoc'h M, Genin C and
Gigante M: Serum miR-210 as a novel biomarker for molecular
diagnosis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Exp Mol Pathol.
94:115–120. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kakihana Y, Ito T, Nakahara M, Yamaguchi K
and Yasuda T: Sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction:
Pathophysiology and management. J Intensive Care.
4(22)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang H, Bei Y, Huang P, Zhou Q, Shi J, Sun
Q, Zhong J, Li X, Kong X and Xiao J: Inhibition of miR-155 protects
against LPS-induced cardiac dysfunction and apoptosis in mice. Mol
Ther Nucleic Acids. 5(e374)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu F, Li Y, Jiang R, Nie C, Zeng Z, Zhao
N, Huang C, Shao Q, Ding C, Qing C, et al: miR-132 inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in alveolar macrophages by
the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. Exp Lung Res.
41:261–269. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Essandoh K and Fan GC: Role of
extracellular and intracellular microRNAs in sepsis. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1842:2155–2162. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Nahid MA, Yao B, Dominguez-Gutierrez PR,
Kesavalu L, Satoh M and Chan EK: Regulation of TLR2-mediated
tolerance and cross-tolerance through IRAK4 modulation by miR-132
and miR-212. J Immunol. 190:1250–1263. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Aziz F: The emerging role of miR-223 as
novel potential diagnostic and therapeutic target for inflammatory
disorders. Cell Immunol. 303:1–6. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Huang W, Yang Y, Wang Y, Peng T,
Chang J, Caldwell CC, Zingarelli B and Fan GC: Loss of
duplexmiR-223 (5p and 3p) aggravates myocardial depression and
mortality in polymicrobial sepsis. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1842:701–711. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chen H, Wang X, Yan X, Cheng X, He X and
Zheng W: LncRNA MALAT1 regulates sepsis-induced cardiac
inflammation and dysfunction via interaction with miR-125b and p38
MAPK/NFκB. Int Immunopharmacol. 55:69–76. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu J, Li J, Tian P, Guli B, Weng G, Li L
and Cheng Q: H2S attenuates sepsis-induced cardiac
dysfunction via a PI3K/Akt-dependent mechanism. Exp Ther Med.
17:4064–4072. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Qin YJ, Zhang XL, Yu YQ, Bian XH and Dong
SM: Cardioprotective effect of erythropoietin on sepsis-induced
myocardial injury in rats. World J Emerg Med. 4:215–222.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Han B, He Y, Li D, Ma X, Liu Q
and Hao J: MicroRNA-132 attenuates neurobehavioral and
neuropathological changes associated with intracerebral hemorrhage
in mice. Neurochem Int. 107:182–190. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang X, Gu H, Qin D, Yang L, Huang W,
Essandoh K, Wang Y, Caldwell CC, Peng T, Zingarelli B and Fan GC:
Exosomal miR-223 contributes to mesenchymal stem cell-elicited
cardioprotection in polymicrobial sepsis. Sci Rep.
5(13721)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|