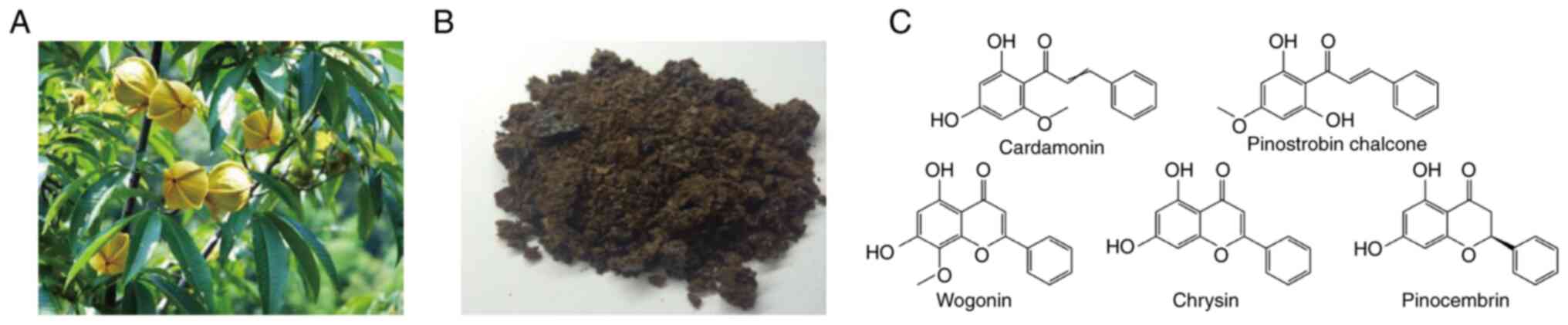
|
1
|
Eelen G, de Zeeuw P, Simons M and
Carmeliet P: Endothelial cell metabolism in normal and diseased
vasculature. Circ Res. 116:1231–1244. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Figarola JL, Singhal J, Rahbar S, Awasthi
S and Singhal SS: LR-90 prevents methylglyoxal-induced oxidative
stress and apoptosis in human endothelial cells. Apoptosis.
19:776–788. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li H, Horke S and Förstermann U: Oxidative
stress in vascular disease and its pharmacological prevention.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 34:313–319. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Toghueo K, Marie R and Boyom FF:
Endophytes from ethno-pharmacological plants: Sources of novel
antioxidants - A systematic review. Biocatal Agric Biotechnol: Nov
14, 2019 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
5
|
Mahdi A, Kövamees O and Pernow J:
Improvement in endothelial function in cardiovascular disease - Is
arginase the target? Int J Cardiol. 301:207–214. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Harvey AL, Edrada-Ebel R and Quinn RJ: The
re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics
era. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 14:111–129. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rao T, Tan Z, Peng J, Guo Y, Chen Y, Zhou
H and Ouyang D: The pharmacogenetics of natural products: A
pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic perspective. Pharmacol Res.
146(104283)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Beretta G and Facino RM: Recent advances
in the assessment of the antioxidant capacity of pharmaceutical
drugs: From in vitro to in vivo evidence. Anal Bioanal Chem.
398:67–75. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Olszowy M: What is responsible for
antioxidant properties of polyphenolic compounds from plants? Plant
Physiol Biochem. 144:135–143. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Brainina K, Tarasov A, Khamzina E, Stozhko
N and Vidrevich M: Contact hybrid potentiometric method for on-site
and in situ estimation of the antioxidant activity of fruits and
vegetables. Food Chem. 309(125703)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wen L, Jiang Y, Yang J, Zhao Y, Tian M and
Yang B: Structure, bioactivity, and synthesis of methylated
flavonoids. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1398:120–129. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chen GL, Fan MX, Wu JL, Li N and Guo MQ:
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of flavonoids from
lotus plumule. Food Chem. 277:706–712. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wei L, Yang M, Huang L and Lin Li J:
Antibacterial and antioxidant flavonoid derivatives from the fruits
of Metaplexis japonica. Food Chem. 289:308–312.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Feng S, Wang L, Belwal T, Li L and Luo Z:
Phytosterols extraction from hickory (Carya cathayensis
Sarg.) husk with a green direct citric acid hydrolysis extraction
method. Food Chem. 315(126217)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xiang L, Wang Y, Yi X, Wang X and He X:
Chemical constituent and antioxidant activity of the husk of
Chinese Hickory. J Funct Foods. 23:378–388. 2016.
|
|
16
|
Zhu X, Li W, Yu Y, Jiang F and Ding Z:
Total flavonoids preparation of the Carya cathayensis Sarg.
leaves. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan. 31:147–149. 2013.
|
|
17
|
Shen Y, Liu NN, Min XU, Zhang K, Jiang FS,
Chen JZ, Tian SS and Ding ZS: HPLC determination of the content of
the five flavonoid aglycones from the leaves of Carya
cathayensis Sarg. Yaowu Fenxi Zazhi. 33:804–807. 2013.
|
|
18
|
Cao XD, Ding ZS, Jiang FS, Ding XH, Chen
JZ, Chen SH and Lv GY: Antitumor constituents from the leaves of
Carya cathayensis. Nat Prod Res. 26:2089–2094.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tian SS, Jiang FS, Zhang K, Zhu XX, Jin B,
Lu JJ and Ding ZS: Flavonoids from the leaves of Carya
cathayensis Sarg. inhibit vascular endothelial growth
factor-induced angiogenesis. Fitoterapia. 92:34–40. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Abu Bakar MF, Mohamed M, Rahmat A, Burr SA
and Fry JR: Cellular assessment of the extract of bambangan
(Mangifera pajang) as a potential cytoprotective agent for
the human hepatocellular HepG2 cell line. Food Chem. 136:18–25.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TDL: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen S, Tang Y, Qian Y, Chen R, Zhang L,
Wo L and Chai H: Allicin prevents
H2O2-induced apoptosis of Huvecs by
inhibiting an oxidative stress pathway. BMC Complement Altern Med.
14(321)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jansen F, Li Q, Pfeifer A and Werner N:
Endothelial- and immune cell-derived extracellular vesicles in the
regulation of cardiovascular health and disease. JACC Basic Transl
Sci. 2:790–807. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sugamura K and Keaney JF Jr: Reactive
oxygen species in cardiovascular disease. Free Radic Biol Med.
51:978–992. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Srivastava KK and Kumar R: Stress,
oxidative injury and disease. Indian J Clin Biochem. 30:3–10.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ma X, Zhang K, Li H, Han S, Ma Z and Tu P:
Extracts from Astragalus membranaceus limit myocardial cell
death and improve cardiac function in a rat model of myocardial
ischemia. J Ethnopharmacol. 149:720–728. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ghaffari H, Ghassam BJ and Prakash HS:
Hepatoprotective and cytoprotective properties of Hyptis suaveolens
against oxidative stress-induced damage by CCl(4) and H(2)O(2).
Asian Pac J Trop Med. 5:868–874. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kwok HH, Ng WY, Yang MS, Mak NK, Wong RN
and Yue PY: The ginsenoside protopanaxatriol protects endothelial
cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced cell injury and cell death by
modulating intracellular redox status. Free Radic Biol Med.
48:437–445. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Cohen G and Hochstein P: Glutathione
peroxidase: The primary agent for the elimination of hydrogen
peroxide in erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 2:1420–1428.
1963.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Wu P, Ma G, Li N, Deng Q, Yin Y and Huang
R: Investigation of in vitro and in vivo antioxidant activities of
flavonoids rich extract from the berries of Rhodomyrtus
tomentosa(Ait.) Hassk. Food Chem. 173:194–202. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wu Y, Wang Y and Nabi X: Protective effect
of Ziziphora clinopodioides flavonoids against
H2O2-induced oxidative stress in HUVEC cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 117(109156)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xu F, Ren L, Song M, Shao B, Han Y, Cao Z
and Li Y: Fas- and mitochondria-mediated signaling pathway involved
in osteoblast apoptosis induced by AlCl3. Biol Trace Elem Res.
184:173–185. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Miura M, Chen XD, Allen MR, Bi Y, Gronthos
S, Seo BM, Lakhani S, Flavell RA, Feng XH, Robey PG, et al: A
crucial role of caspase-3 in osteogenic differentiation of bone
marrow stromal stem cells. J Clin Invest. 114:1704–1713.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Lindqvist LM, Heinlein M, Huang DC and
Vaux DL: Prosurvival Bcl-2 family members affect autophagy only
indirectly, by inhibiting Bax and Bak. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
111:8512–8517. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chen J, Gu Y, Shao Z, Luo J and Tan Z:
Propofol protects against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative
stress and cell dysfunction in human umbilical vein endothelial
cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 339:43–54. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Alamdary SZ, Khodagholi F, Shaerzadeh F,
Ansari N, Sonboli A and Tusi SK: S. choloroleuca, S.
mirzayanii and S. santolinifolia protect PC12 cells from
H(2)O(2)-induced apoptosis by blocking the intrinsic pathway.
Cytotechnology. 64:403–419. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang B, Luo T, Chen D and Ansley DM:
Propofol reduces apoptosis and up-regulates endothelial nitric
oxide synthase protein expression in hydrogen peroxide-stimulated
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Anesth Analg.
105:1027–1033. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Al-Azayzih A, Gao F, Goc A and Somanath
PR: TGFβ1 induces apoptosis in invasive prostate cancer and bladder
cancer cells via Akt-independent, p38 MAPK and JNK/SAPK-mediated
activation of caspases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 427:165–170.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shi L, Yu X, Yang H and Wu X: Advanced
glycation end products induce human corneal epithelial cells
apoptosis through generation of reactive oxygen species and
activation of JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. PLoS One.
8(e66781)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Abbas A, Abdelsamea MM and Gaber MM:
Classification of Covid-19 in chest X-Ray images using detrac deep
convolutional neural network. Appl Intell. 51:854–864. 2020.
|