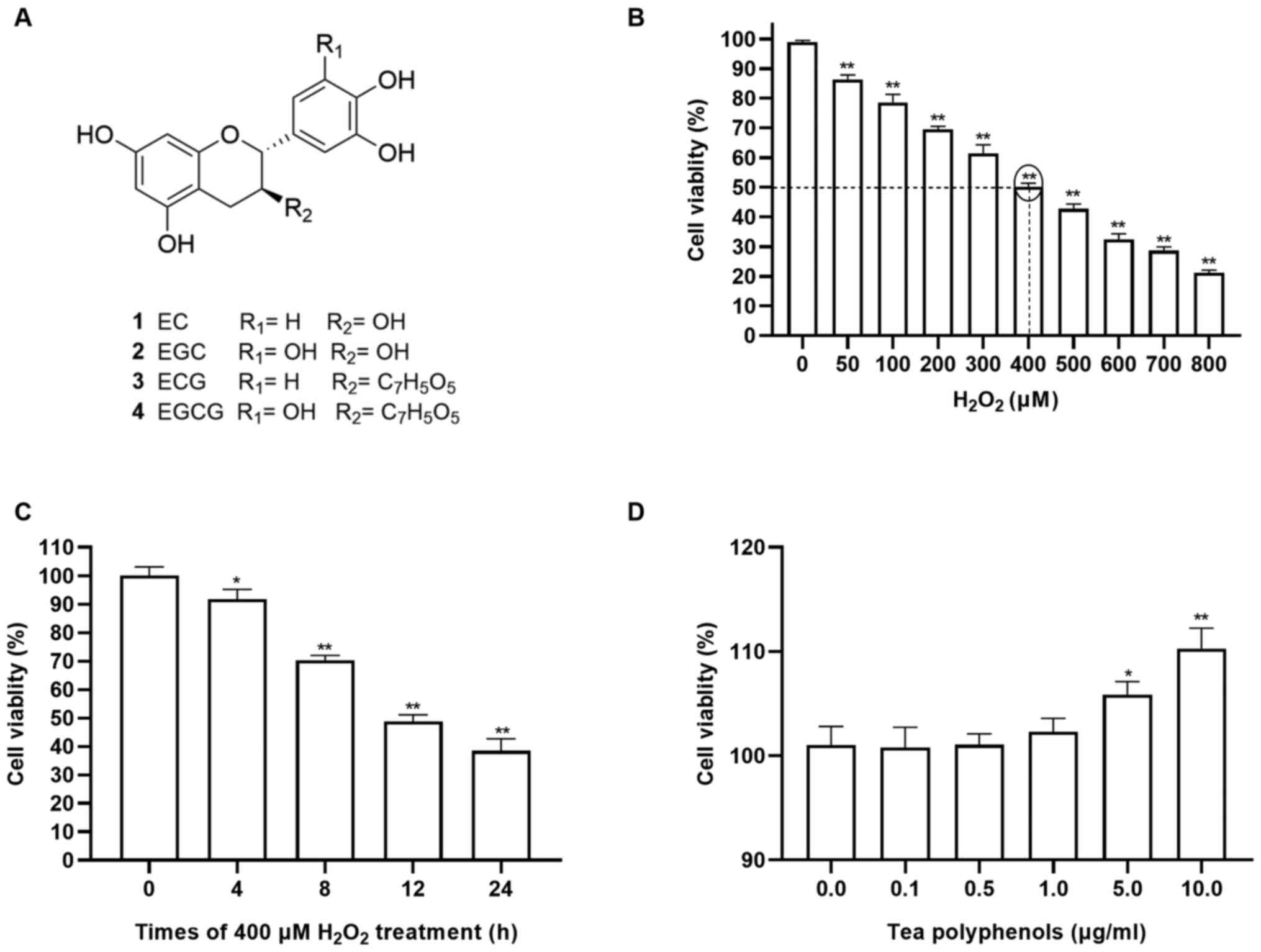
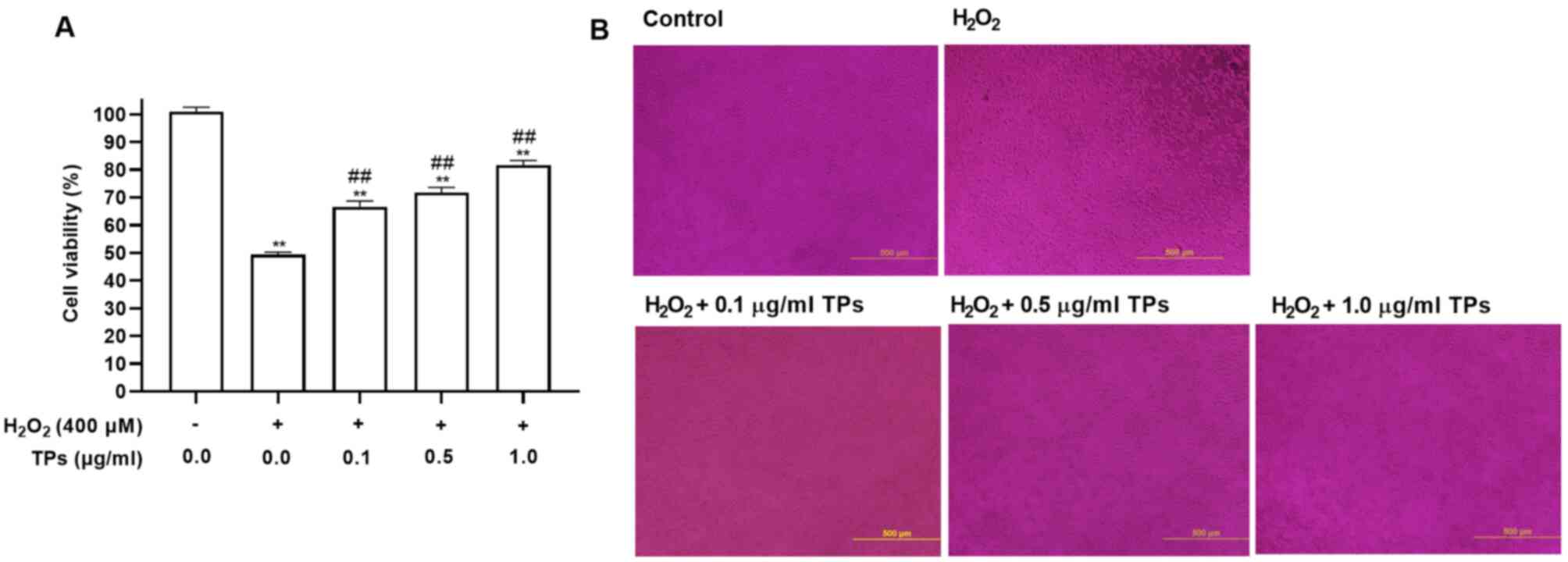
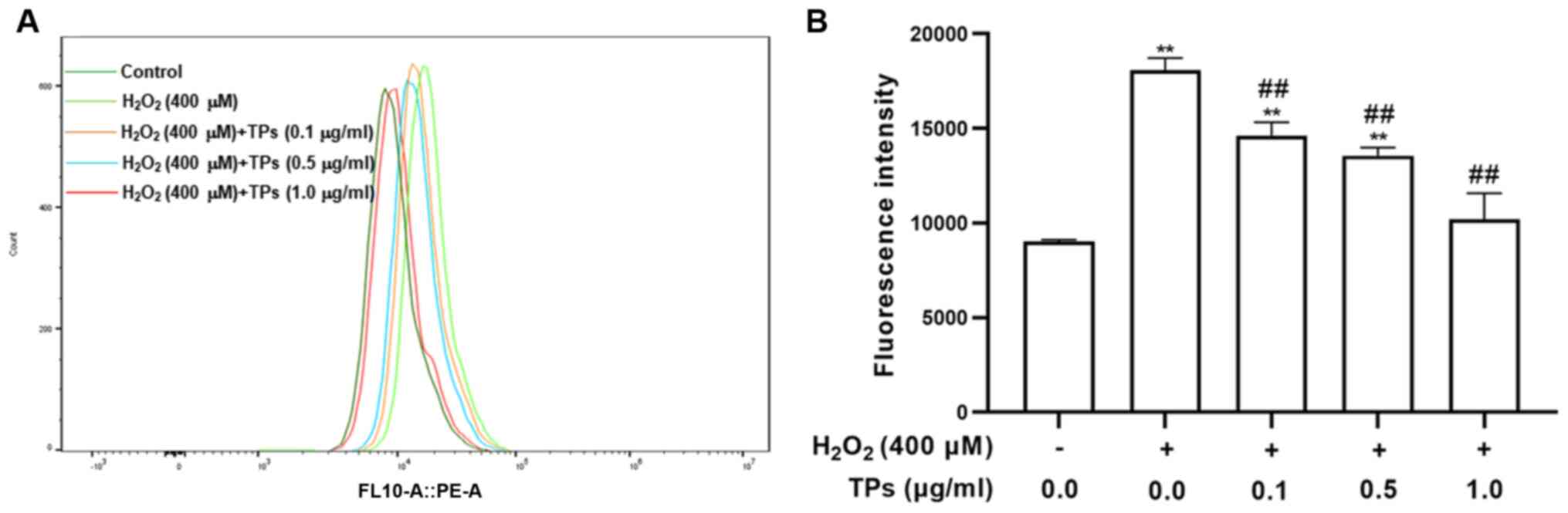
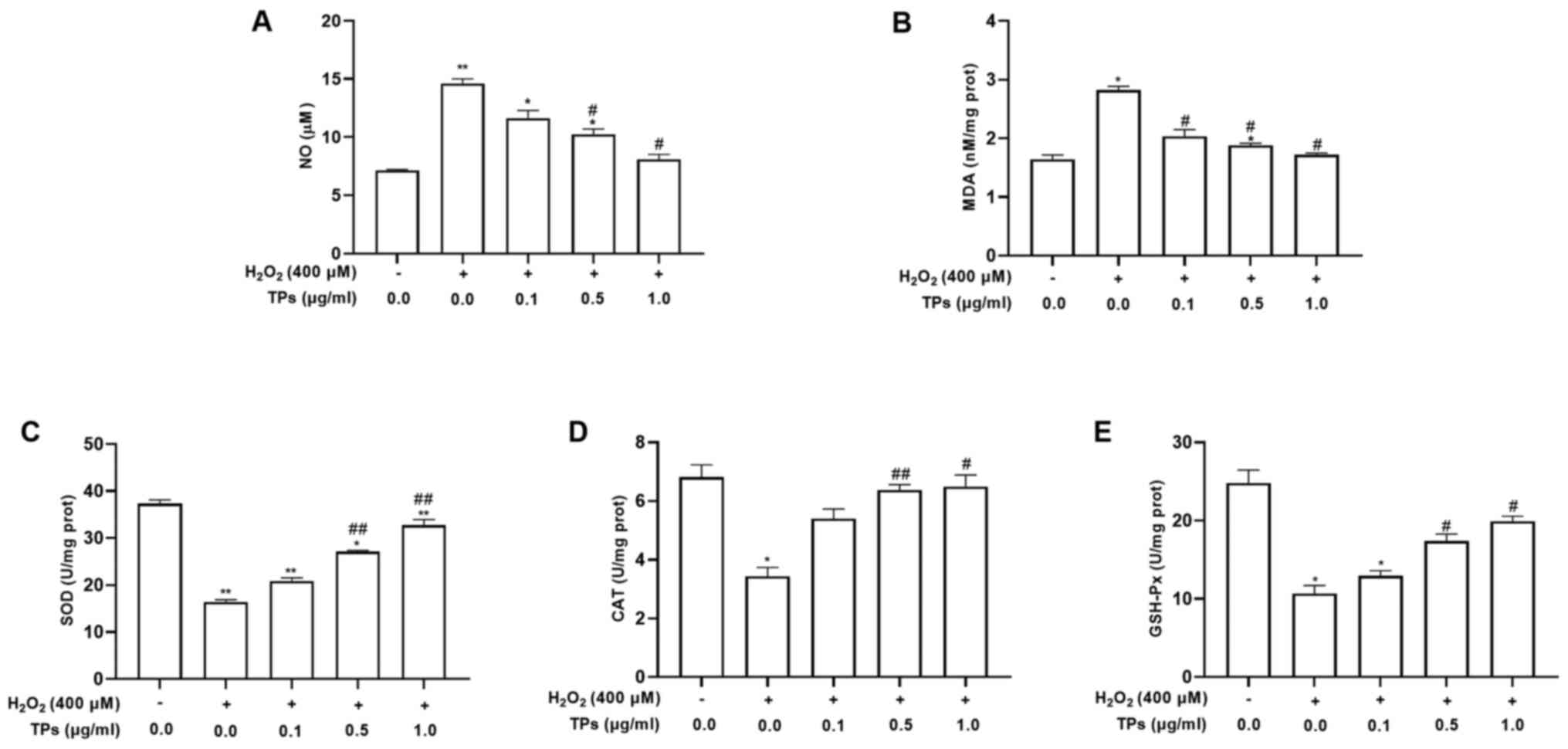
|
1
|
Yang CS, Kim S, Yang GY, Lee MJ, Liao J,
Chung JY and Ho CT: Inhibition of carcinogenesis by tea:
Bioavailability of tea polyphenols and mechanisms of actions. Proc
Soc Exp Biol Med. 220:213–217. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Khan N and Mukhtar H: Tea polyphenols in
promotion of human health. Nutrients. 11(39)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zuo AR, Dong HH, Yu YY, Shu QL, Zheng LX,
Yu XY and Cao SW: The antityrosinase and antioxidant activities of
flavonoids dominated by the number and location of phenolic
hydroxyl groups. Chin Med. 13(51)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ganesan K and Xu B: A critical review on
polyphenols and health benefits of black soybeans. Nutrients.
9(455)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Namal Senanayake SPJ: Green tea extract:
Chemistry, antioxidant properties and food applications - A review.
J Funct Foods. 5:1529–1541. 2013.
|
|
6
|
Gundimeda U, McNeill TH, Fan TK, Deng R,
Rayudu D, Chen Z, Cadenas E and Gopalakrishna R: Green tea
catechins potentiate the neuritogenic action of brain-derived
neurotrophic factor: Role of 67-kDa laminin receptor and hydrogen
peroxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 445:218–224. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ueda-Wakagi M, Nagayasu H, Yamashita Y and
Ashida AH: Green tea ameliorates hyperglycemia by promoting the
translocation of glucose transporter 4 in the skeletal muscle of
diabetic rodents. Int J Mol Sci. 20(2436)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
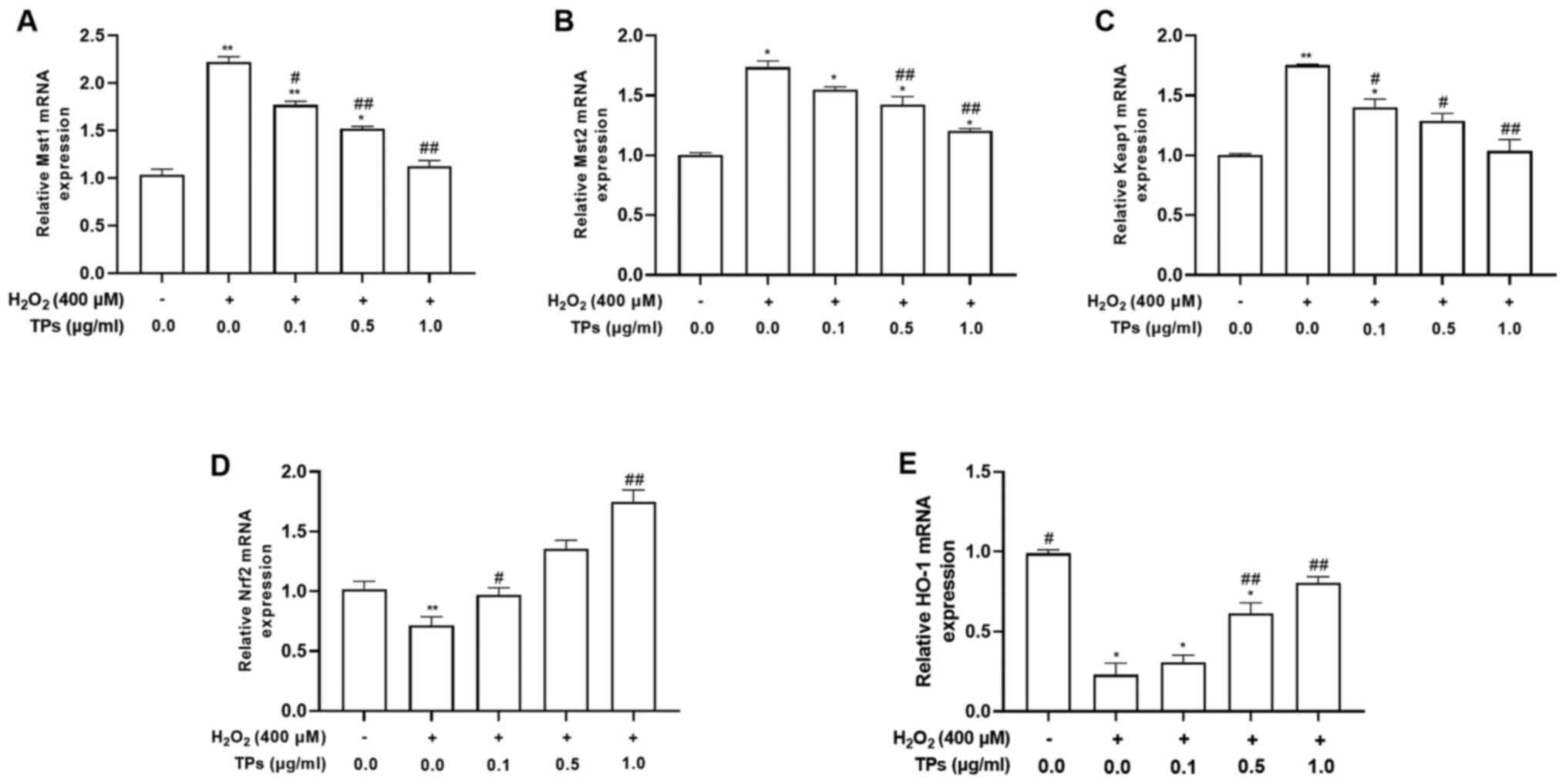
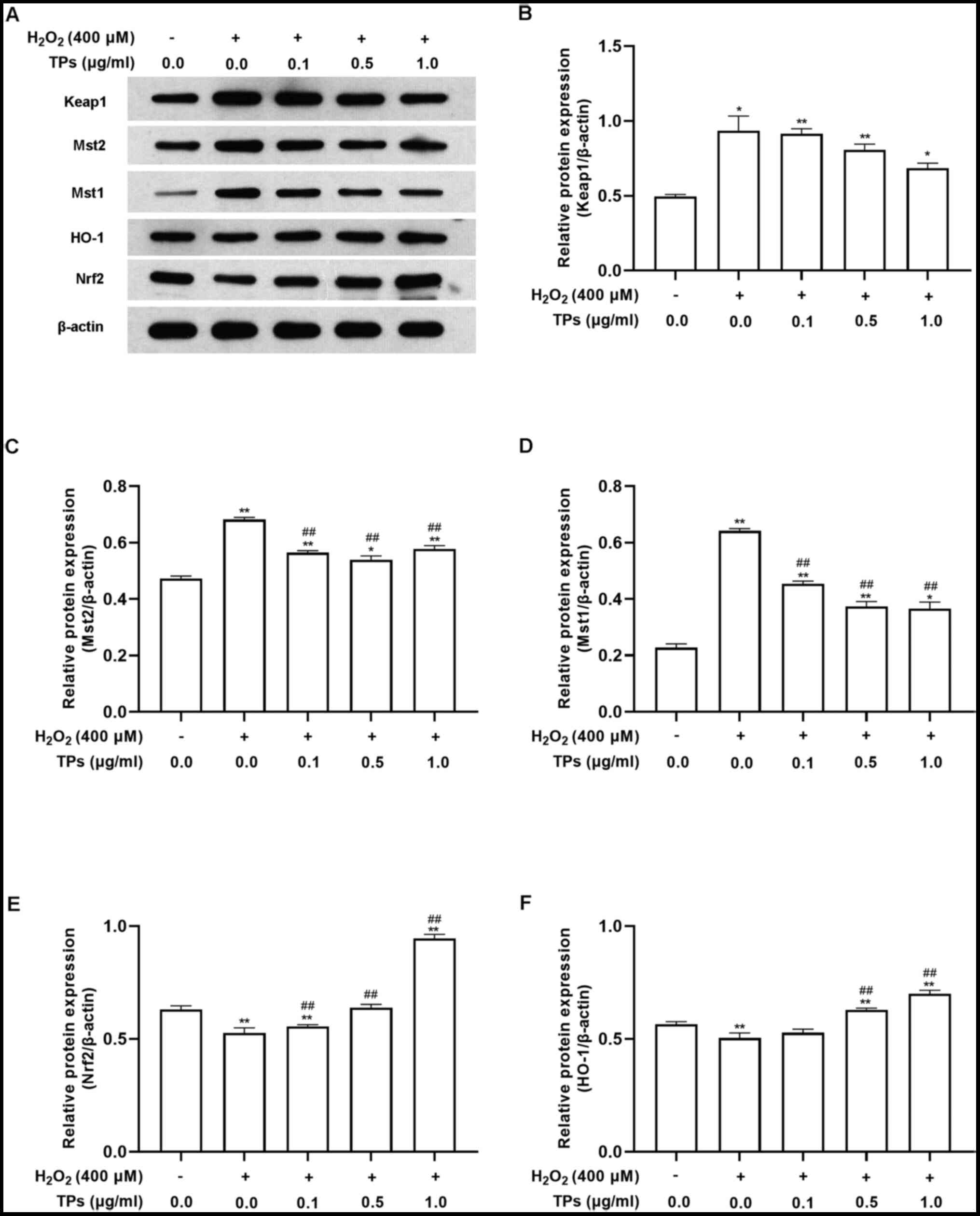
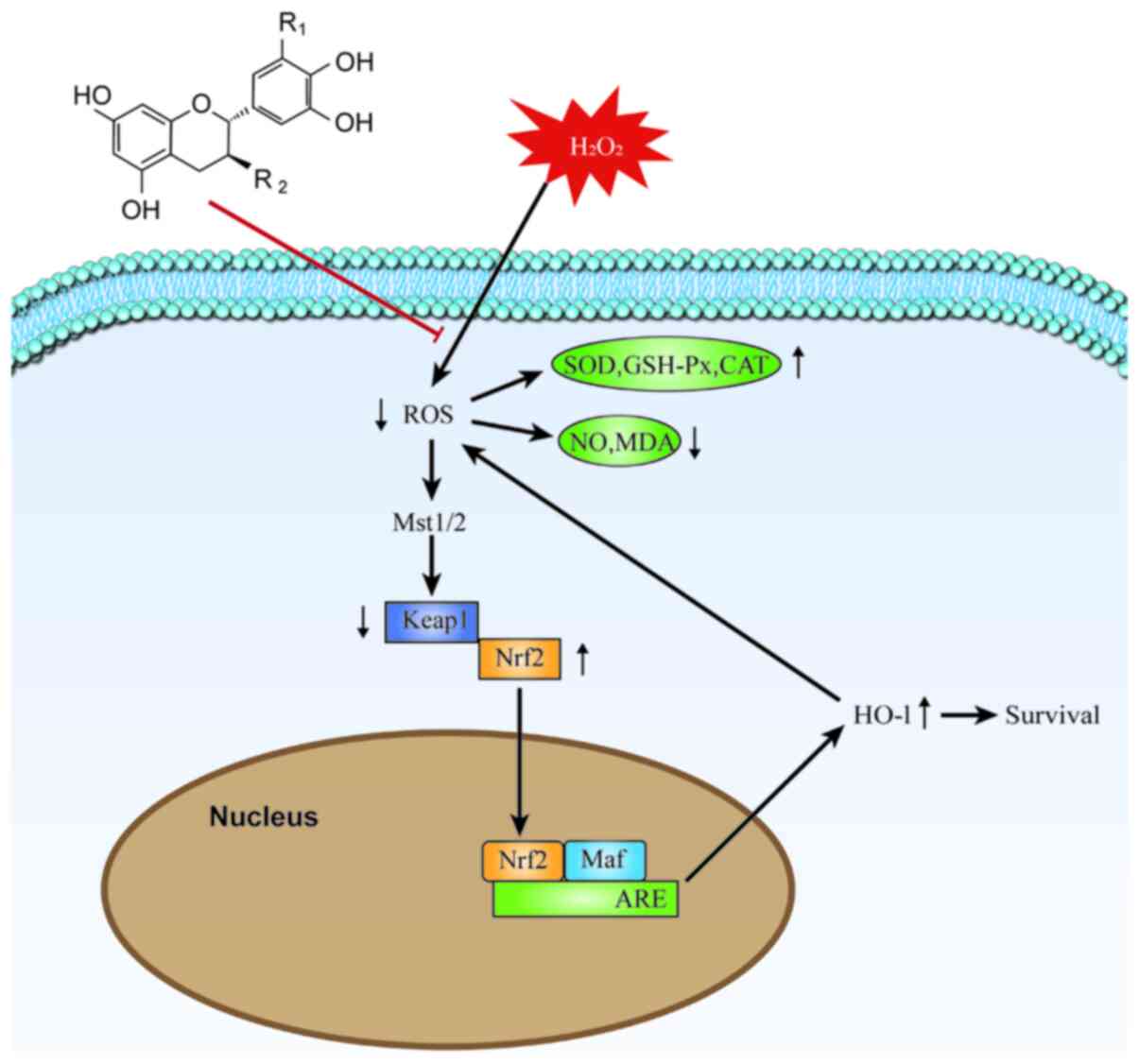
Griendling KK, Sorescu D, Lassègue B and
Ushio-Fukai M: Modulation of protein kinase activity and gene
expression by reactive oxygen species and their role in vascular
physiology and pathophysiology. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
20:2175–2183. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Moloney JN and Cotter TG: ROS signalling
in the biology of cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 80:50–64.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
He L, He T, Farrar S, Ji L, Liu T and Ma
X: Antioxidants maintain cellular redox homeostasis by elimination
of reactive oxygen species. Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:532–553.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yan Z, Zhong Y, Duan Y, Chen Q and Li F:
Antioxidant mechanism of tea polyphenols and its impact on health
benefits. Anim Nutr. 6:115–123. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xing L, Zhang H, Qi R, Tsao R and Mine Y:
Recent advances in the understanding of the health benefits and
molecular mechanisms associated with green tea polyphenols. J Agric
Food Chem. 67:1029–1043. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang D, Wang Y, Wan X, Yang CS and Zhang
J: Green tea polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate triggered
hepatotoxicity in mice: Responses of major antioxidant enzymes and
the Nrf2 rescue pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 283:65–74.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Qi G, Mi Y, Fan R, Zhao B, Ren B and Liu
X: Tea polyphenols ameliorates neural redox imbalance and
mitochondrial dysfunction via mechanisms linking the key circadian
regular Bmal1. Food Chem Toxicol. 110:189–199. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sies H: Hydrogen peroxide as a central
redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress:
Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 11:613–619. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wen ZS, Liu LJ, OuYang XK, Qu YL, Chen Y
and Ding GF: Protective effect of polysaccharides from Sargassum
horneri against oxidative stress in RAW264.7 cells. Int J Biol
Macromol. 68:98–106. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
West AP, Brodsky IE, Rahner C, Woo DK,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Walsh MC, Choi Y, Shadel GS and
Ghosh S: TLR signalling augments macrophage bactericidal activity
through mitochondrial ROS. Nature. 472:476–480. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lambeth JD: NOX enzymes and the biology of
reactive oxygen. Nat Rev Immunol. 4:181–189. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lin X, Bai D, Wei Z, Zhang Y, Huang Y,
Deng H and Huang X: Curcumin attenuates oxidative stress in
RAW264.7 cells by increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes
and activating the Nrf2-Keap1 pathway. PLoS One.
14(e0216711)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang XT, Sun XQ, Wu C, Chen JL, Yuan JJ,
Pang QF and Wang ZP: Heme oxygnease-1 induction by methylene blue
protects RAW264.7 cells from hydrogen peroxide-induced injury.
Biochem Pharmacol. 148:265–277. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang P, Geng J, Gao J, Zhao H, Li J, Shi
Y, Yang B, Xiao C, Linghu Y, Sun X, et al: Macrophage achieves
self-protection against oxidative stress-induced ageing through the
Mst-Nrf2 axis. Nat Commun. 10(755)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yang CS, Lambert JD and Sang S:
Antioxidative and anti-carcinogenic activities of tea polyphenols.
Arch Toxicol. 83:11–21. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper
PL, Wishnok JS and Tannenbaum SR: Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and
[15N]nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem. 126:131–138.
1982.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-∆∆C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wen ZS, Liu LJ, Qu YL, Ouyang XK, Yang LY
and Xu ZR: Chitosan nanoparticles attenuate hydrogen
peroxide-induced stress injury in mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells.
Mar Drugs. 11:3582–3600. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rani V, Deep G, Singh RK, Palle K and
Yadav UC: Oxidative stress and metabolic disorders: Pathogenesis
and therapeutic strategies. Life Sci. 148:183–193. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Ahmed NA, Radwan NM, Aboul Ezz HS and
Salama NA: The antioxidant effect of Green Tea Mega EGCG against
electromagnetic radiation-induced oxidative stress in the
hippocampus and striatum of rats. Electromagn Biol Med. 36:63–73.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Chen TS, Liou SY, Lin HH, Hung MY, Lin CC,
Lin YM, Lin KH, Padma VV, Yao CH, Kuo WW, et al: Oral
administration of green tea Epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces
oxidative stress and enhances restoration of cardiac function in
diabetic rats receiving autologous transplantation of
adipose-derived stem cells. Arch Physiol Biochem. 127:82–89.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Valu MV, Soare LC, Sutan NA, Ducu C, Moga
S, Hritcu L, Boiangiu RS and Carradori S: Optimization of
ultrasonic extraction to obtain erinacine A and polyphenols with
antioxidant activity from the fungal biomass of hericium
erinaceus. Foods. 9(1889)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Urbańska B and Kowalska J: Comparison of
the total polyphenol content and antioxidant activity of chocolate
obtained from roasted and unroasted cocoa beans from different
regions of the world. Antioxidants. 8(283)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Xia EQ, Deng GF, Guo YJ and Li HB:
Biological activities of polyphenols from grapes. Int J Mol Sci.
11:622–646. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xue HK, Tan JQ, Li Q, Cai X and Tang JT:
Optimization ultrasound-assisted extraction of anthocyanins from
cranberry using response surface methodology coupled with genetic
algorithm and identification anthocyanins with HPLC-MS2. J Food
Process Preserv. 45(e15378)2021.
|
|
33
|
Tan J, Li Q, Xue H and Tang J:
Ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction of anthocyanins from grape
skins: Optimization, identification, and antitumor activity. J Food
Sci. 85:3731–3744. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xue H, Tan J, Li Q, Tang J and Cai X:
Ultrasound-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction of
anthocyanins from blueberry wine residues: Optimization,
identification, and HepG2 antitumor activity. Molecules.
25(5456)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mukhtar H and Ahmad N: Cancer
chemoprevention: Future holds in multiple agents. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 158:207–210. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Khan N and Mukhtar H: Tea polyphenols for
health promotion. Life Sci. 81:519–533. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Frei B and Higdon JV: Antioxidant activity
of tea polyphenols in vivo: Evidence from animal studies. J Nutr.
133:S3275–S3284. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lagha AB and Grenier D: Tea polyphenols
inhibit the activation of NF-κB and the secretion of cytokines and
matrix metalloproteinases by macrophages stimulated with
Fusobacterium nucleatum. Sci Rep. 6(34520)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Galati G, Lin A, Sultan AM and O'Brien PJ:
Cellular and in vivo hepatotoxicity caused by green tea phenolic
acids and catechins. Free Radic Biol Med. 40:570–580.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Isbrucker RA, Edwards JA, Wolz E,
Davidovich A and Bausch J: Safety studies on epigallocatechin
gallate (EGCG) preparations. Part 2: Dermal, acute and short-term
toxicity studies. Food Chem Toxicol. 44:636–650. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Coyle CH, Philips BJ, Morrisroe SN,
Chancellor MB and Yoshimura N: Antioxidant effects of green tea and
its polyphenols on bladder cells. Life Sci. 83:12–18.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yang GY, Liao J, Li C, Chung J, Yurkow EJ,
Ho CT and Yang CS: Effect of black and green tea polyphenols on
c-jun phosphorylation and H(2)O(2) production in transformed and
non-transformed human bronchial cell lines: Possible mechanisms of
cell growth inhibition and apoptosis induction. Carcinogenesis.
21:2035–2039. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ma YF, Zhao L, Coleman DN, Gao M and Loor
JJ: Tea polyphenols protect bovine mammary epithelial cells from
hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative damage in vitro by activating
NFE2L2/HMOX1 pathways. J Dairy Sci. 102:1658–1670. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lee MJ, Maliakal P, Chen L, Meng X, Bondoc
FY, Prabhu S, Lambert G, Mohr S and Yang CS: Pharmacokinetics of
tea catechins after ingestion of green tea and
(-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate by humans: Formation of different
metabolites and individual variability. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers
Prev. 11:1025–1032. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Nakagawa K, Okuda S and Miyazawa T:
Dose-dependent incorporation of tea catechins,
(-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate and (-)-epigallocatechin, into human
plasma. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 61:1981–1985. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ullmann U, Haller J, Decourt JP, Girault
N, Girault J, Richard-Caudron AS, Pineau B and Weber P: A single
ascending dose study of epigallocatechin gallate in healthy
volunteers. J Int Med Res. 31:88–101. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Avshalumov MV, Bao L, Patel JC and Rice
ME: H2O2 signaling in the nigrostriatal
dopamine pathway via ATP-sensitive potassium channels: Issues and
answers. Antioxid Redox Signal. 9:219–231. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Mao X, Gu C, Chen D, Yu B and He J:
Oxidative stress-induced diseases and tea polyphenols. Oncotarget.
8:81649–81661. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Forman HJ, Bernardo A and Davies KJ: What
is the concentration of hydrogen peroxide in blood and plasma? Arch
Biochem Biophys. 603:48–53. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Brown GC: Reversible binding and
inhibition of catalase by nitric oxide. Eur J Biochem. 232:188–191.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
McBride AG, Borutaité V and Brown GC:
Superoxide dismutase and hydrogen peroxide cause rapid nitric oxide
breakdown, peroxynitrite production and subsequent cell death.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1454:275–288. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Jadeja RN, Upadhyay KK, Devkar RV and
Khurana S: Naturally occurring Nrf2 activators: Potential in
treatment of liver injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016(3453926)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Ma Q: Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and
toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 53:401–426. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Nguyen T, Nioi P and Pickett CB: The
Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its
activation by oxidative stress. J Biol Chem. 284:13291–13295.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Shukla K, Pal PB, Sonowal H, Srivastava SK
and Ramana KV: Aldose reductase inhibitor protects against
hyperglycemic stress by activating Nrf2-dependent antioxidant
proteins. J Diabetes Res. 2017(6785852)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Qi GY, Mi YS, Fan R, Li RN, Wang YW, Li
XY, Huang SX and Liu XB: Tea polyphenols ameliorate hydrogen
peroxide- and constant darkness-triggered oxidative stress via
modulating the Keap1/Nrf2 transcriptional signaling pathway in
HepG2 cells and mice liver. RSC Advances. 7:32198–32208. 2017.
|
|
57
|
Wang D, Zhang M, Wang T, Liu T, Guo Y and
Granato D: Green tea polyphenols mitigate the plant lectins-induced
liver inflammation and immunological reaction in C57BL/6 mice via
NLRP3 and Nrf2 signaling pathways. Food Chem Toxicol.
144(111576)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Sueoka N, Suganuma M, Sueoka E, Okabe S,
Matsuyama S, Imai K, Nakachi K and Fujiki H: A new function of
green tea: Prevention of lifestyle-related diseases. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 928:274–280. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Jian L, Xie LP, Lee AH and Binns CW:
Protective effect of green tea against prostate cancer: A
case-control study in southeast China. Int J Cancer. 108:130–135.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Miyata Y, Shida Y, Hakariya T and Sakai H:
Anti-cancer effects of green tea polyphenols against prostate
cancer. Molecules. 24(193)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|