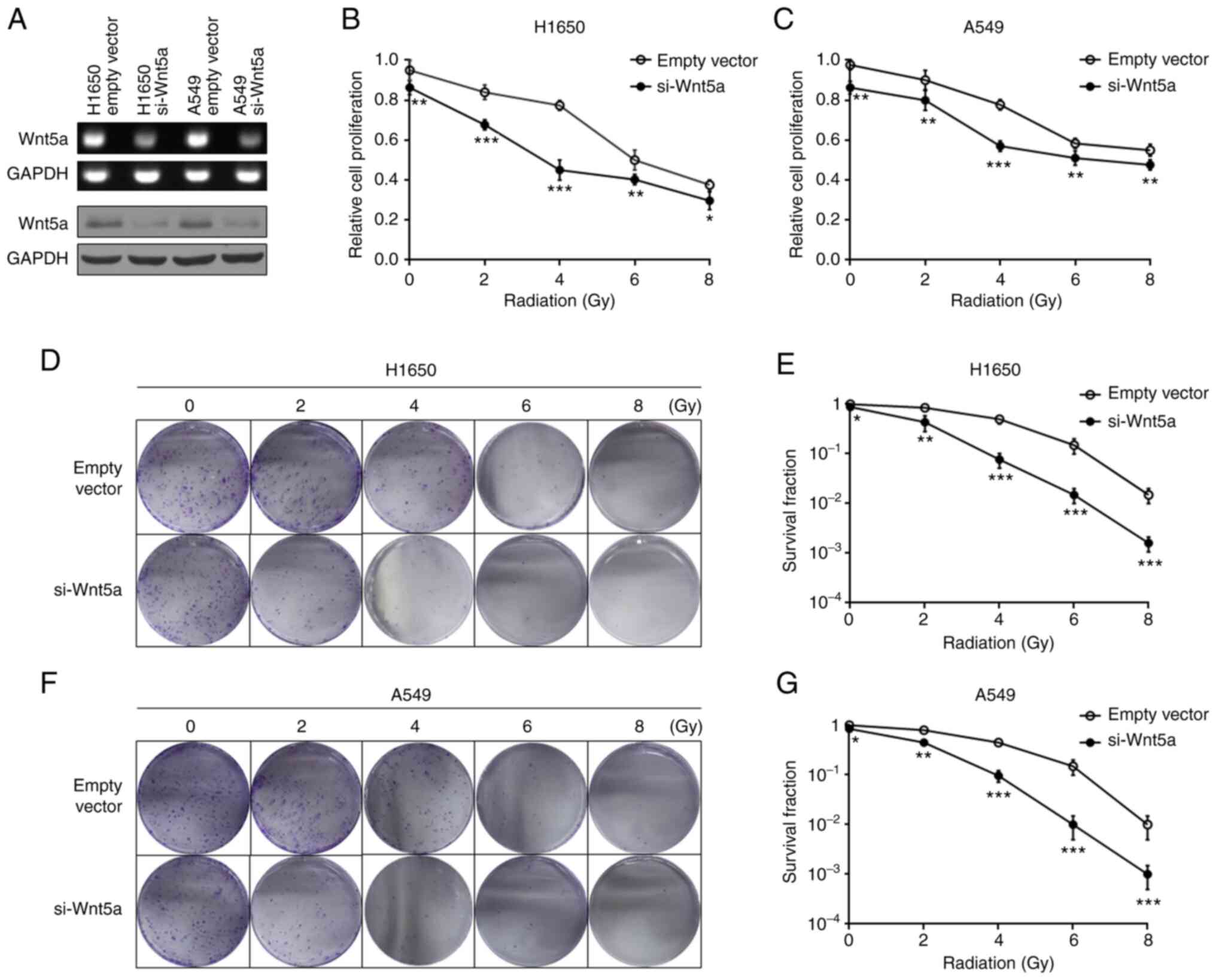
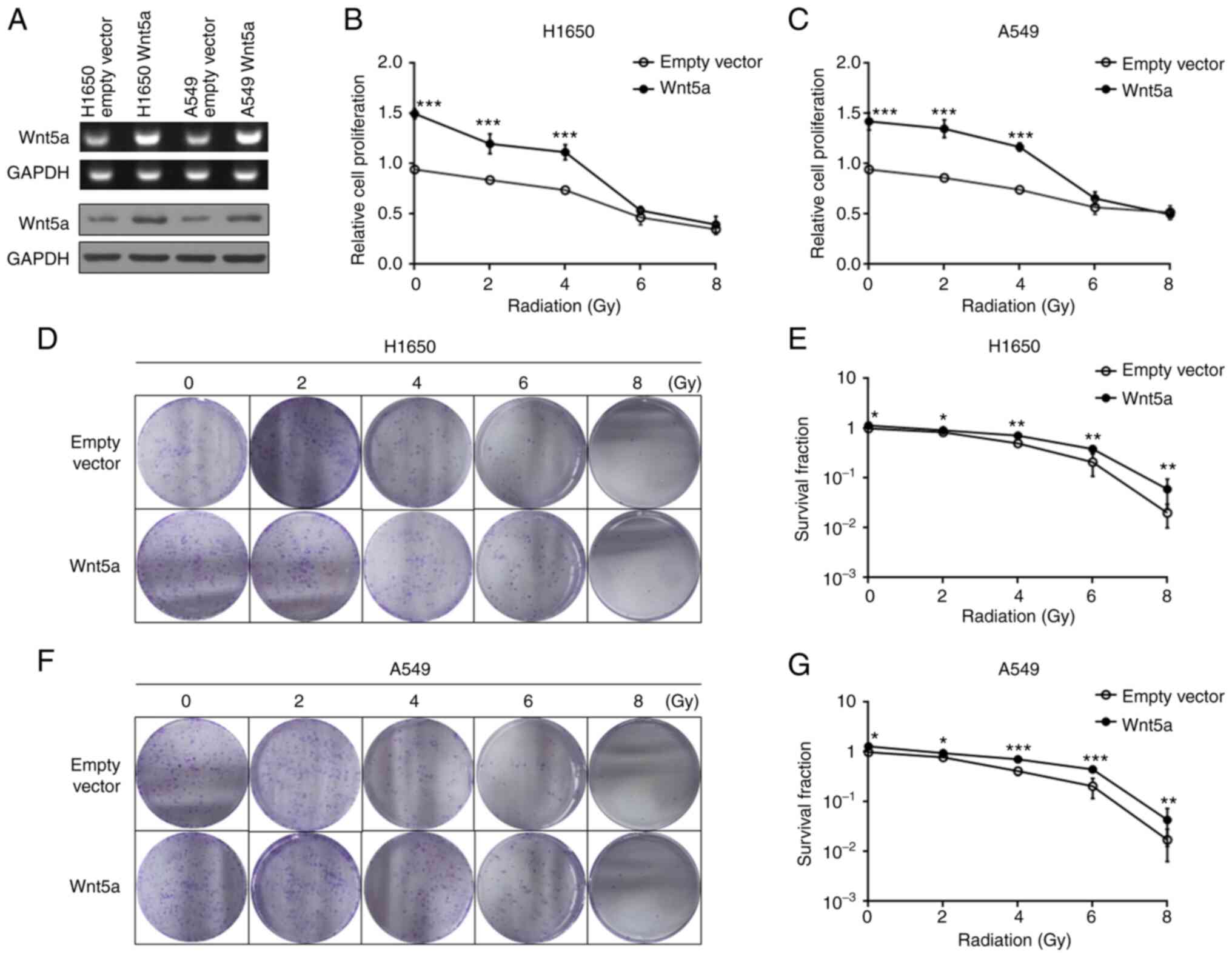
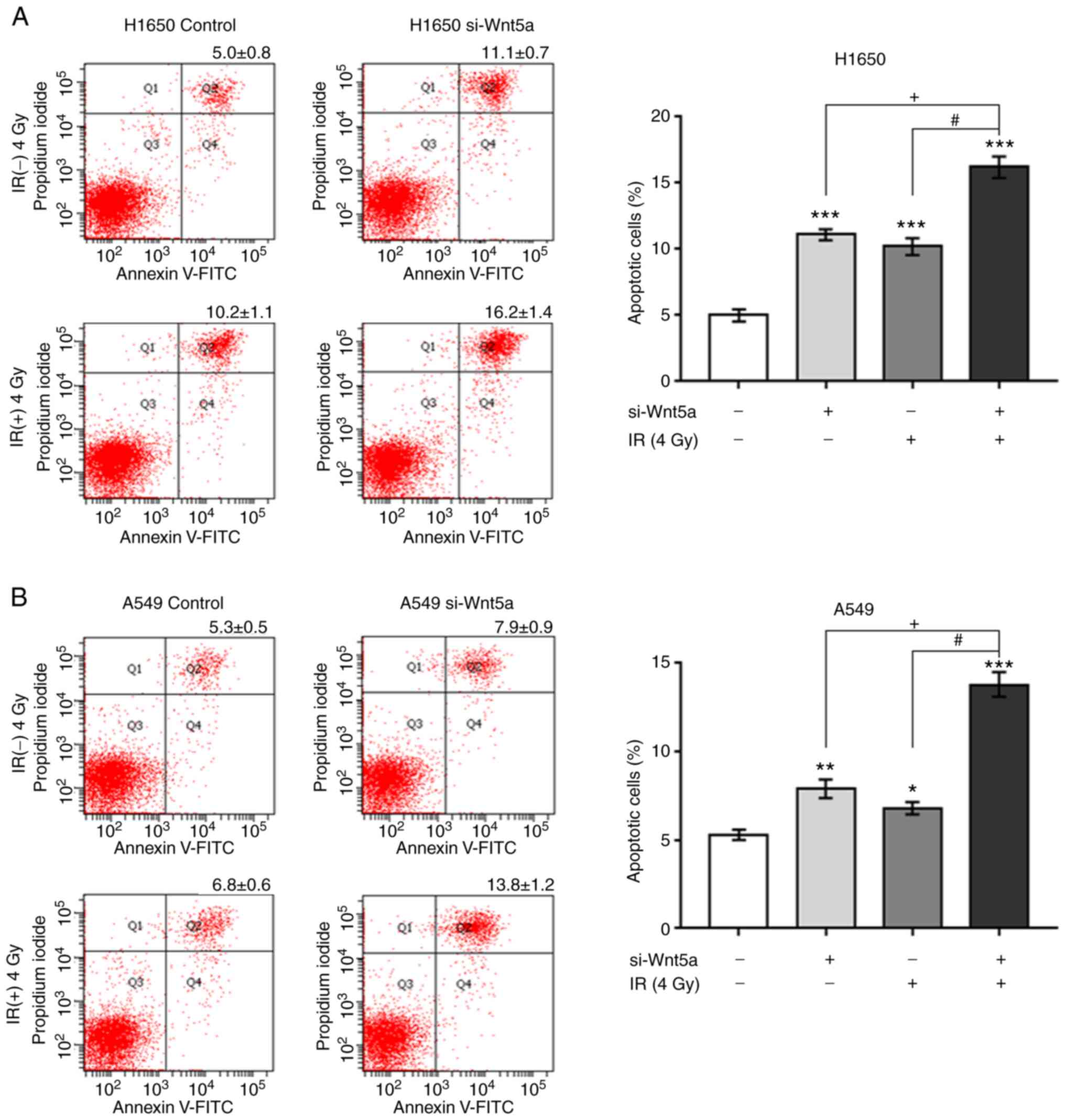
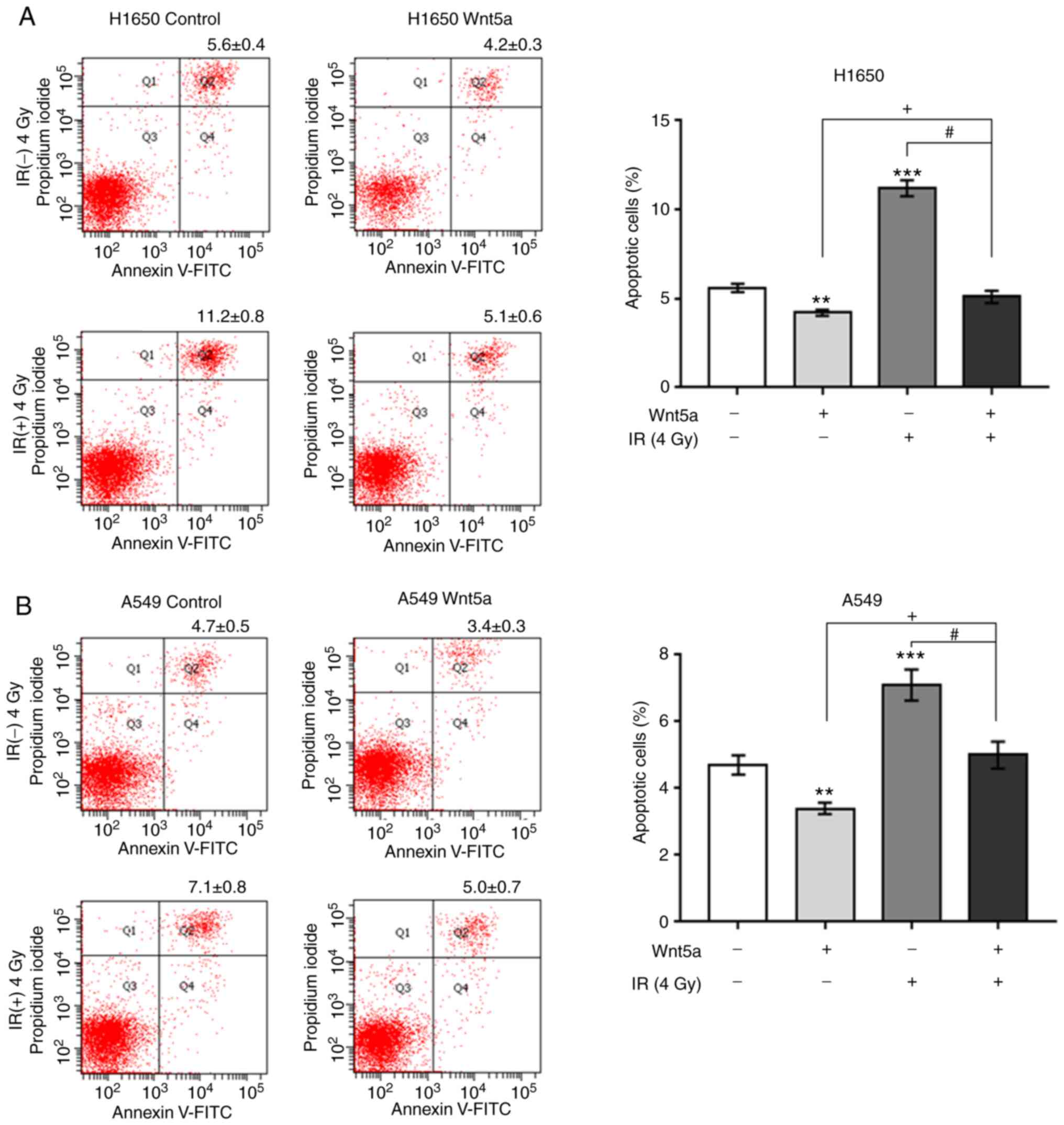
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Harris JP, Murphy JD, Hanlon AL, Le QT,
Loo BW Jr and Diehn M: A population-based comparative effectiveness
study of radiation therapy techniques in stage III non-small cell
lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 88:872–884.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kim E, Song C, Kim MY and Kim JS:
Long-term outcomes after salvage radiotherapy for postoperative
locoregionally recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer. Radiat Oncol
J. 35:55–64. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Palayoor ST, Macklis RM, Bump EA and
Coleman CN: Modulation of radiation-induced apoptosis and G2/M
block in murine T-lymphoma cells. Radiat Res. 141:235–243.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ning S and Knox SJ: Arrest and death by
apoptosis of HL60 cells irradiated with exponentially decreasing
low-dose-rate gamma radiation. Radiat Res. 151:659–669.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee SB, Gong YD, Park YI and Dong MS:
2,3,6-Trisubstituted quinoxaline derivative, a small molecule
inhibitor of the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway, suppresses
cell proliferation and enhances radiosensitivity in A549/Wnt2
cells. Biocchem Biophys Res Commun. 431:746–752. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Stewart DJ: Wnt signaling pathway in
non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
106(djt356)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bo H, Zhang S, Gao L, Chen Y, Zhang J,
Chang X and Zhu M: Upregulation of Wnt5a promotes
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of pancreatic
cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 13(496)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lee GT: Prostate cancer bone metastases
acquire resistance to androgen deprivation via WNT5A-mediated BMP-6
induction. Br J Cancer. 110:1634–1644. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kanzawa M, Semba S, Hara S, Itoh T and
Yokozaki H: WNT5A is a key regulator of the epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and cancer stem cell properties in human gastric
carcinoma cells. Pathobiology. 80:235–244. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang B, Tang Z, Gong H, Zhu L and Liu X:
Wnt5a promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and metastasis
in non-small-cell lung cancer. Biosci Rep.
37(BSR20171092)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mokhtari RB, Homayouni TS, Baluch N,
Morgatskaya E, Kumar S, Das B and Yeger H: Combination therapy in
combating cancer. Oncotarget. 8:38022–38043. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fang B and Roth JA: The role of gene
therapy in combined modality treatment strategies for cancer. Curr
Opin Mol Ther. 5:475–482. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yap TA, Omlin A and De Bono JS:
Development of therapeutic combinations targeting major cancer
signaling pathways. J Clin Oncol. 31:1592–1605. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Blagosklonny MV: Analysis of FDA approved
anticancer drugs reveals the future of cancer therapy. Cell Cycle.
3:1033–1042. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ahn SJ, Choi C, Choi YD, Kim YC, Kim KS,
Oh IJ, Ban HJ, Yoon MS, Nam TK, Jeong JU, et al: Microarray
analysis of gene expression in lung cancer cell lines treated by
fractionated irradiation. Anticancer Res. 34:4939–4948.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Whang YM, Jo U, Sung JS, Ju HJ, Kim HK,
Park KH, Lee JW, Koh IS and Kim YH: Wnt5a is associated with
cigarette smoke-related lung carcinogenesis via protein kinase C.
PLoS One. 8(e53012)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Huang Y, Liu G, Zhang B, Xu G, Xiong W and
Yang H: Wnt-5a regulates proliferation in lung cancer cells. Oncol
Rep. 23:177–181. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pukrop T and Binder C: The complex
pathways of Wnt5a in cancer progression. J Mol Med (Berl).
86:259–266. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
He TC, Sparks AB, Rago C, Hermeking H,
Zawel L, Da Costa LT, Morin PJ, Vogelstein B and Kinzler KW:
Identification of c-MYC as a target of the APC pathway. Science.
281:1509–1512. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Saegusa M, Hashimura M, Kuwata T, Hamano M
and Okayasu I: β-Catenin simultaneously induces activation of the
p53-p21WAF1 pathway and overexpression of cyclin D1 during squamous
differentiation of endometrial carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol.
164:1739–1749. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Anastas JN and Moon RT: WNT signaling
pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:11–25. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
de Sousa E, Melo F and Vermeulen L: Wnt
signaling in cancer stem cell biology. Cancers (Basel).
8(60)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Shang S, Hua F and Hu ZW: The regulation
of β-catenin activity and function in cancer: Therapeutic
opportunities. Oncotarget. 8:33972–33989. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li XQ, Yang XL, Zhang G, Wu SP, Deng XB,
Xiao SJ, Liu QZ, Yao KT and Xiao GH: Nuclear β-catenin accumulation
is associated with increased expression of Nanog protein and
predicts poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer. J Transl
Med. 11(114)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Eger A, Stockinger A, Schaffhauser B, Beug
H and Foisner R: Epithelial mesenchymal transition by c-Fos
estrogen receptor activation involves nuclear translocation of
β-catenin and upregulation of β-catenin/lymphoid enhancer binding
factor-1 transcriptional activity. J Cell Biol. 148:173–188.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xu X, Sun PL, Li JZ, Jheon S, Lee CT and
Chung JH: Aberrant Wnt1/β-catenin expression is an independent poor
prognostic marker of non-small cell lung cancer after surgery. J
Thorac Oncol. 6:716–724. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Roy LD, Sahraei M, Subramani DB, Besmer D,
Nath S, Tinder TL, Bajaj E, Shanmugam K, Lee YY, Hwang SI, et al:
MUC1 enhances invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells by inducing
epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncogene. 30:1449–1459.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Woodward WA, Chen MS, Behbod F, Alfaro MP,
Buchholz TA and Rosen JM: WNT/beta-catenin mediates radiation
resistance of mouse mammary progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 104:618–623. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wang L, Zhang XM, Li Z, Liu XJ, Chai J,
Zhang GY and Cheng YF: Overexpression of nuclear β-catenin in
rectal adenocarcinoma is associated with radioresistance. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:6876–6882. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tanaka H, Kawaguchi M, Shoda S, Miyoshi T,
Iwasaki R, Hyodo F, Hyodo F, Mori T, Hara A, Tomita H and Matsuo M:
Nuclear Accumulation of β-catenin in cancer stem cell
radioresistance and stemness in human colon cancer. Anticancer Res.
39:6575–6583. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Luo Y, Li M, Zuo X, Basourakos SP, Zhang
J, Zhao J, Han Y, Lin Y, Wang Y, Jiang Y, et al: β-catenin nuclear
translocation induced by HIF1α overexpression leads to the
radioresistance of prostate cancer. Int J Oncol. 52:1827–1840.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|