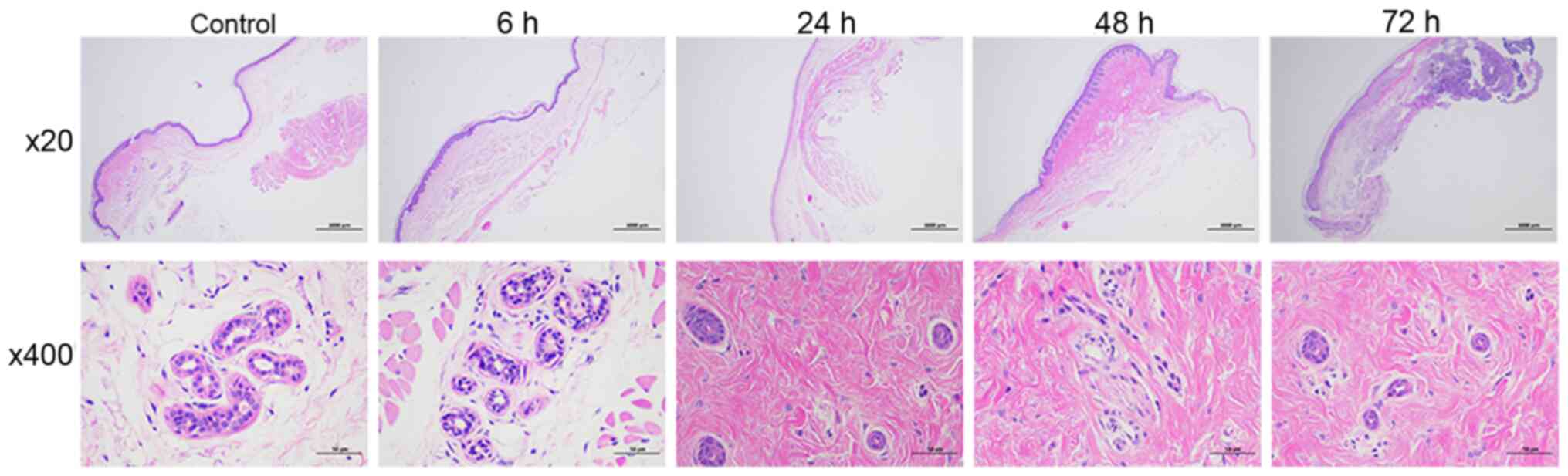
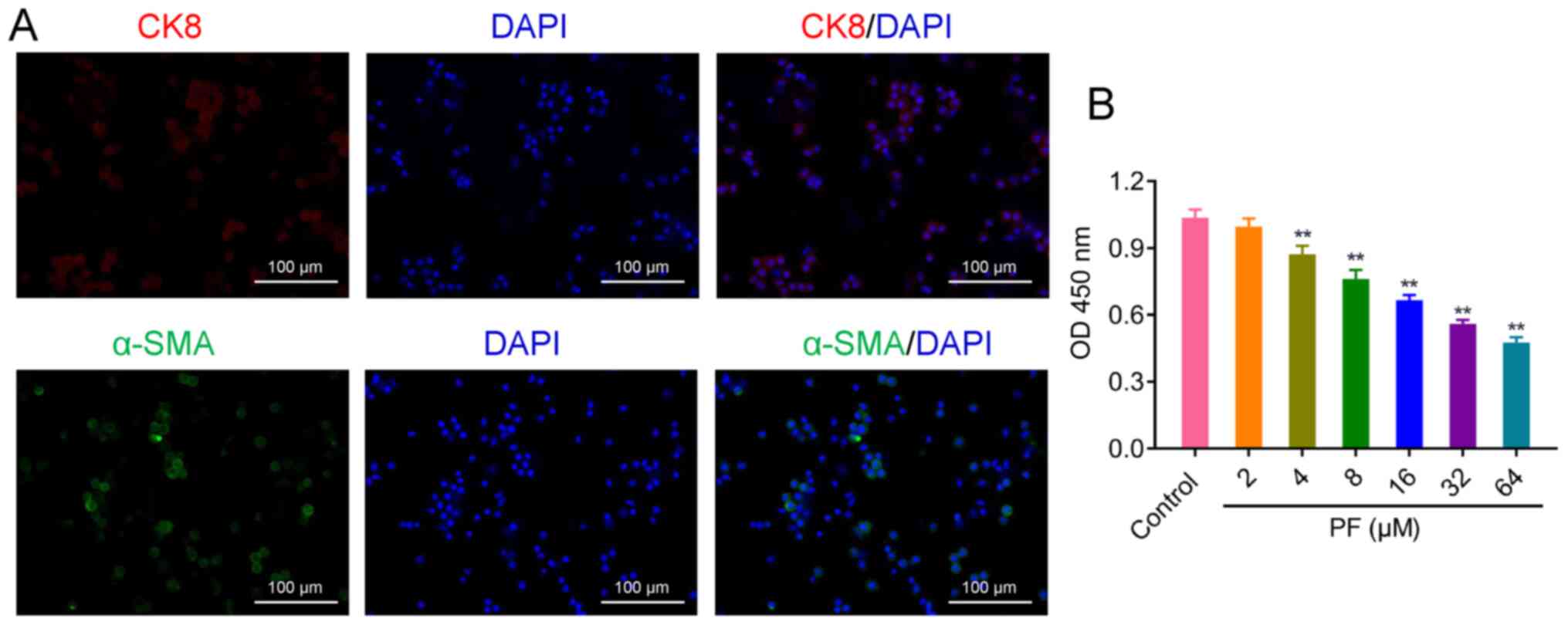
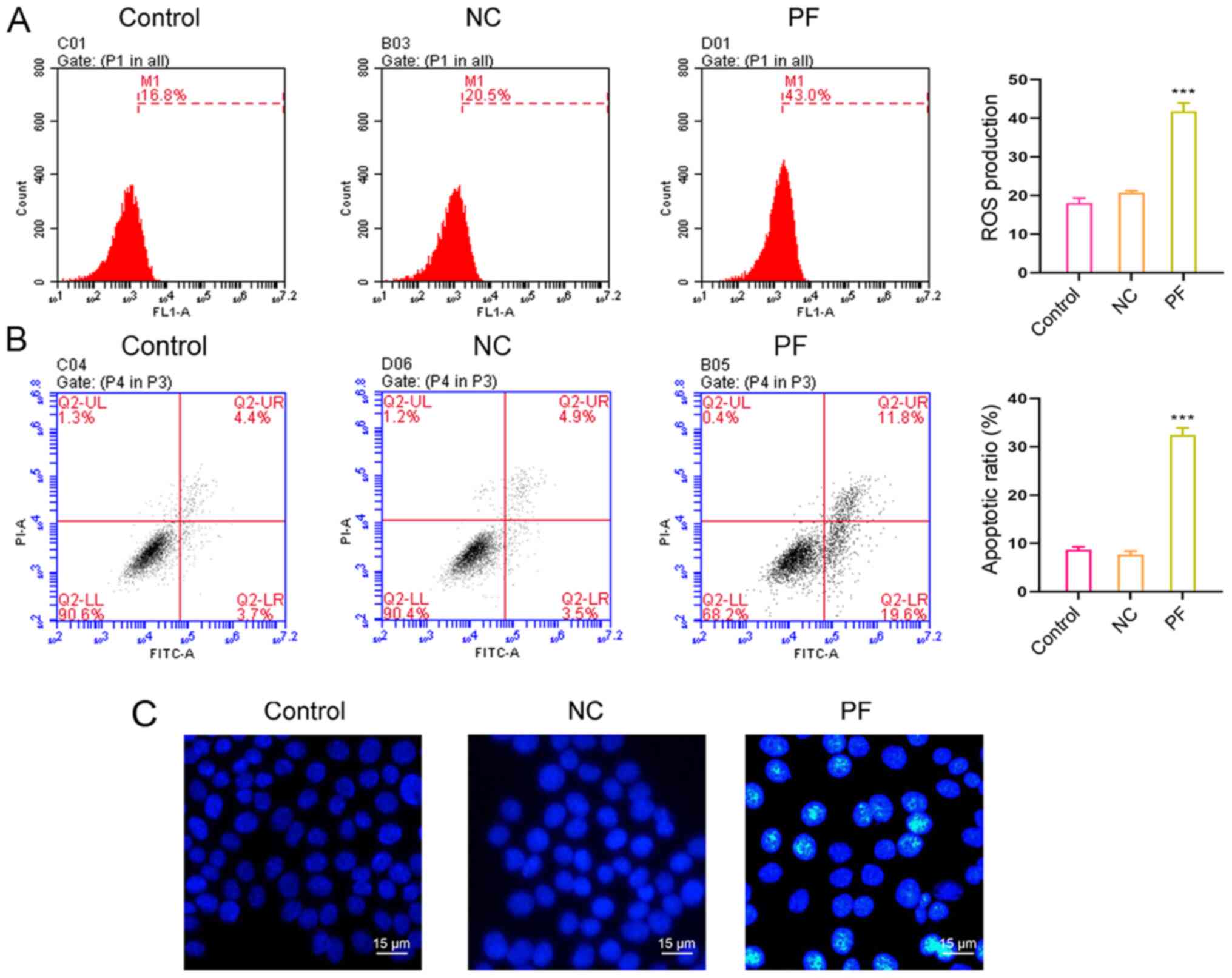
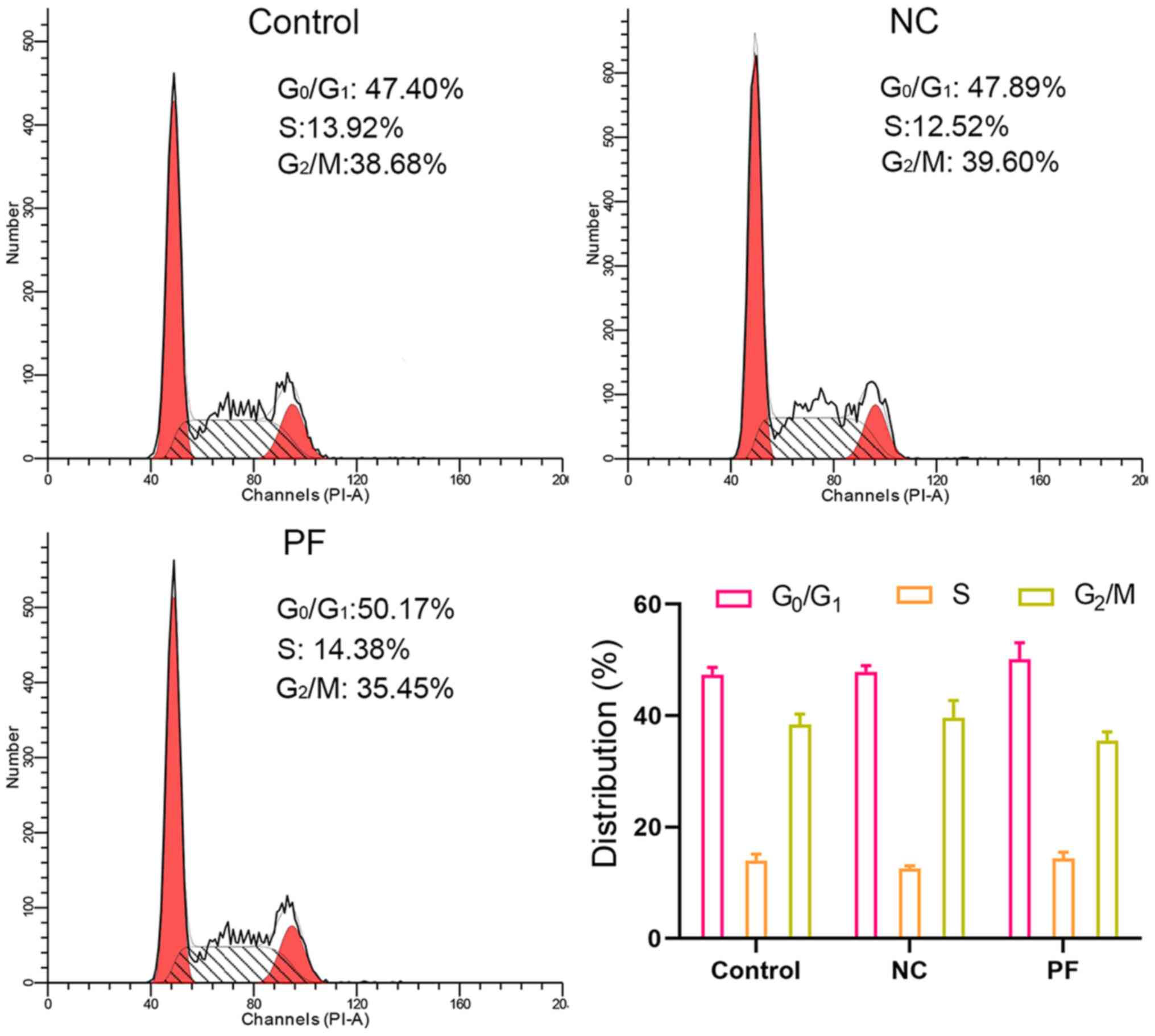
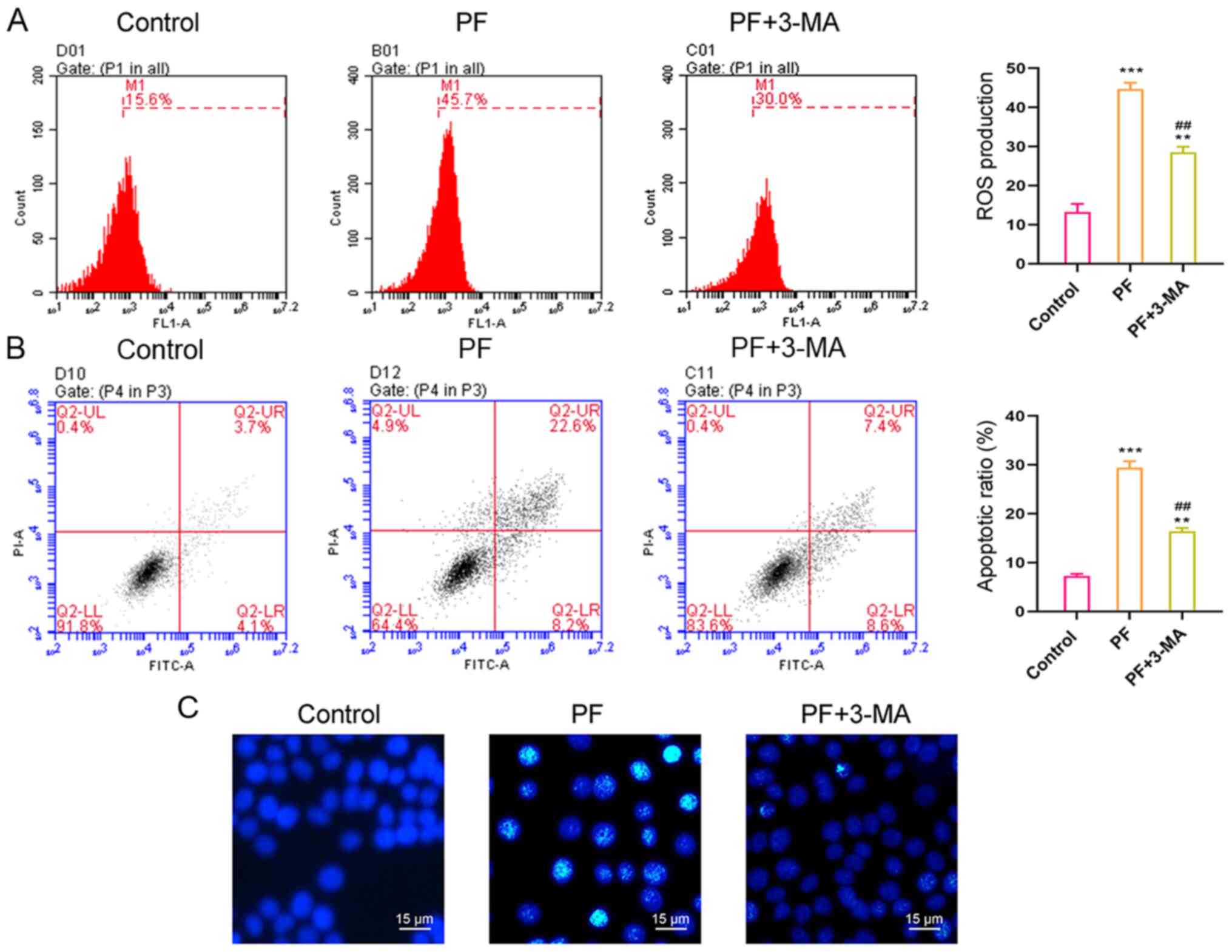
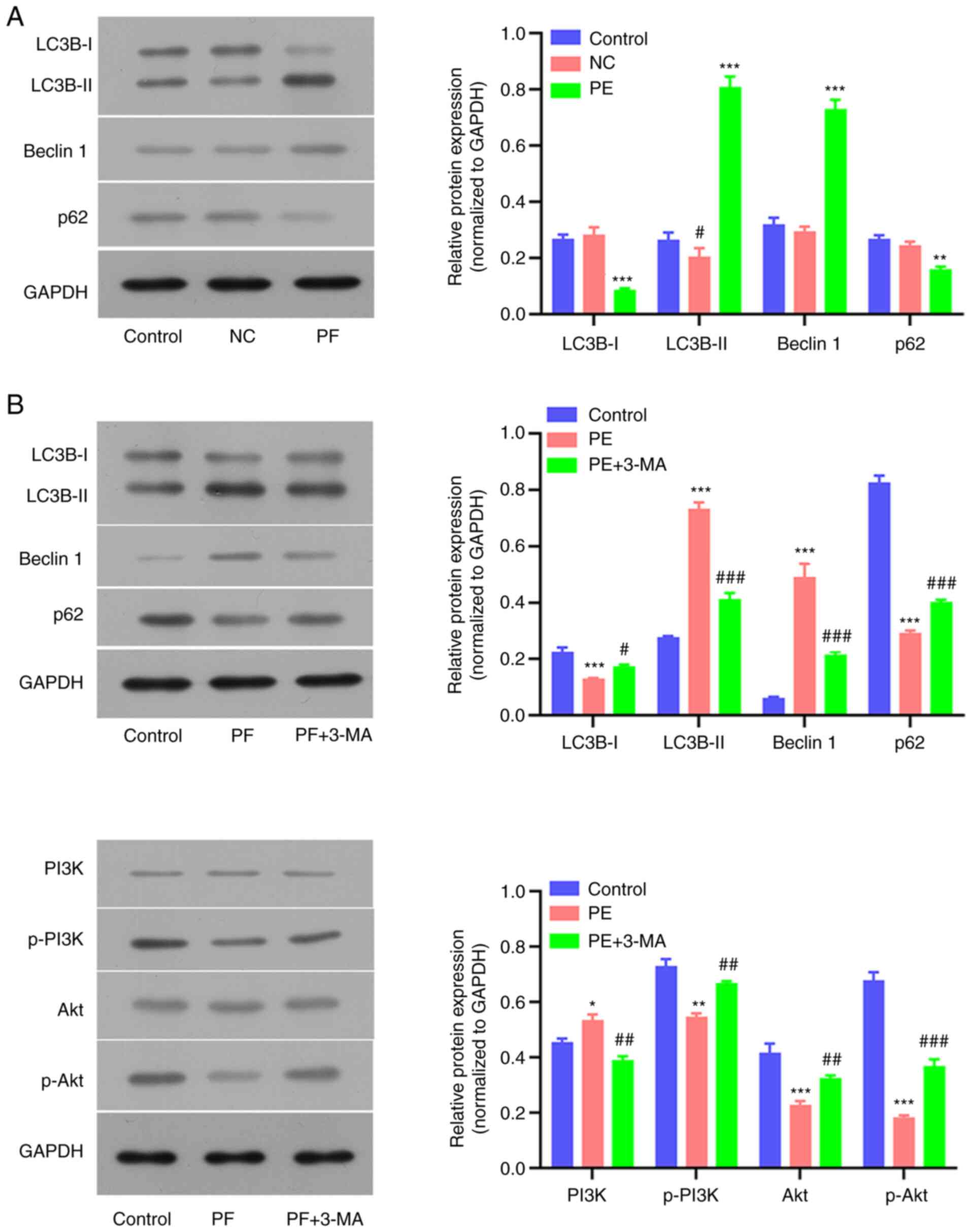
|
1
|
Hsu KC and Wang KY: Sparing subcutaneous
septa avoids skin necrosis in the treatment of axillary
bromhidrosis with suction-curettage shaving. J Cosmet Dermatol.
18:892–896. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ardon CB, Molenaar C, van Straalen KR,
Scholtes VC, Prens EP and van der Zee HH: High prevalence of
hidradenitis suppurativa in patients with perianal fistula. Int J
Colorectal Dis. 34:1337–1339. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Van TN, Manh TN, Minh PPT, Minh TT, Huu
ND, Cao KP, Huu QN, Cam VT, Huyen ML, Hau KT, et al: The
Effectiveness of Local Surgical Technique in Treatment of Axillary
Bromhidrosis. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 7:187–191.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
He J, Wang T and Dong J: A close positive
correlation between malodor and sweating as a marker for the
treatment of axillary bromhidrosis with Botulinum toxin A. J
Dermatolog Treat. 23:461–464. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kataoka A: Surgical treatment of
bromhidrosis. Rev Bras Cir Plást. 32:377–382. 2001.
|
|
6
|
Coronado MS and Opi JT: Assessment of
axillary hyperhidrosis and bromhidrosis treatment with microwave
technology. J Surg Med. 3:447–451. 2019.
|
|
7
|
Mao GY, Yang SL and Zheng JH: Etiology and
management of axillary bromidrosis: A brief review. Int J Dermatol.
47:1063–1068. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mancini M, Panasiti V, Devirgiliis V,
Pietropaolo V, Fioriti D, Nicosia R, Curzio M, Roberti V, Gobbi S,
Bottoni U, et al: Bromhidrosis induced by sphingomonas
paucimobilis: A case report. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.
22:845–848. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hashmonai M, Cameron AEP, Connery CP,
Perin N and Licht PB: The etiology of primary hyperhidrosis: A
systematic review. Clin Auton Res. 27:379–383. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhang Y, Hu S, Ge S, Wang J and He L:
Paeoniflorin inhibits IgE-mediated allergic reactions by
suppressing the degranulation of mast cells though binding with
FcεRI alpha subunits. Eur J Pharmacol. 886(173415)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Qian X, Shi X and Wang H: Effect of
paeoniflorin on the calcium ion concentration in salivary gland
cells using confocal laser scanning microscopy. Am J Transl Res.
8:3678–3688. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Manayi A, Omidpanah S, Barreca D, Ficarra
S, Daglia M, Nabavi SF and Nabavi SM: Neuroprotective effects of
paeoniflorin in neurodegenerative diseases of the central nervous
system. Phytochem Rev. 16:1173–1181. 2017.
|
|
13
|
Cao B-Y, Yang Y-P, Luo W-F, Mao CJ, Han R,
Sun X, Cheng J and Liu CF: Paeoniflorin, a potent natural compound,
protects PC12 cells from MPP+ and acidic damage via autophagic
pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. 131:122–129. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wu X, Sun X, Zhao C, Zhang J and Wang X,
Zhang A and Wang X: Exploring the pharmacological effects and
potential targets of paeoniflorin on the endometriosis of cold
coagulation and blood stasis model rats by ultra-performance liquid
chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with a pattern recognition
approach. RSC Advances. 9:20796–20805. 2019.
|
|
15
|
Hu H, Zhu Q, Su J, Wu Y, Zhu Y, Wang Y,
Fang H, Pang M, Li B, Chen S, et al: Effects of an enriched extract
of paeoniflorin, a monoterpene glycoside used in Chinese herbal
medicine, on cholesterol metabolism in a hyperlipidemic rat model.
Med Sci Monit. 23:3412–3427. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Yang B and Yu B: Paeoniflorin
protects against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a
high-fat diet in mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 38:1005–1011.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen J-Y, Wu H-X, Chen Y, Zhang LL, Wang
QT, Sun WY and Wei W: Paeoniflorin inhibits proliferation of
fibroblast-like synoviocytes through suppressing G-protein-coupled
receptor kinase 2. Planta Med. 78:665–671. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Qian G, Cao J, Chen C, Wang L, Huang X,
Ding C, Cai X, Yin F, Chu J, Li G, et al: Paeoniflorin inhibits
pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells proliferation via upregulating
A2B adenosine receptor in rat. PLoS One. 8(e69141)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ferry B, Gervasoni D and Vogt C:
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations. In: Stereotaxic Neurosurgery
in Laboratory Rodent. Springer, Paris, pp1-18, 2014.
|
|
20
|
Turkki R, Linder N, Kovanen PE, Pellinen T
and Lundin J: Identification of immune cell infiltration in
hematoxylin-eosin stained breast cancer samples: texture-based
classification of tissue morphologies. In: Proceedings of SPIE -
The International Society for Optical Engineering 9791. Medical
Imaging 2016: Digital Pathology, San Diego, p9791, 2016.
|
|
21
|
Park Y-J and Shin M-S: What is the best
method for treating osmidrosis? Ann Plast Surg. 47:303–309.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Huang Z, Zhen Y, Yin W, Ma Z and Zhang L:
Shh promotes sweat gland cell maturation in three-dimensional
culture. Cell Tissue Bank. 17:317–325. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kolakshyapati P, Li X, Chen C, Zhang M,
Tan W, Ma L and Gao C: Gene-activated matrix/bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells constructs regenerate sweat glands-like
structure in vivo. Sci Rep. 7(17630)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kurata R, Futaki S, Nakano I, Fujita F,
Tanemura A, Murota H, Katayama I, Okada F and Sekiguchi K:
Three-dimensional cell shapes and arrangements in human sweat
glands as revealed by whole-mount immunostaining. PLoS One.
12(e0178709)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Huang J, Qiu L, Ding L, Wang S, Wang J,
Zhu Q, Song F and Hu J: Ginsenoside Rb1 and paeoniflorin inhibit
transient receptor potential vanilloid-1-activated IL-8 and
PGE2 production in a human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT.
Int Immunopharmacol. 10:1279–1283. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wen J, Xu B, Sun Y, Lian M, Li Y, Lin Y,
Chen D, Diao Y, Almoiliqy M and Wang L: Paeoniflorin protects
against intestinal ischemia/reperfusion by activating LKB1/AMPK and
promoting autophagy. Pharmacol Res. 146(104308)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Che J, Zhao H, Tang J and Shi G:
Paeoniflorin attenuates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced
apoptosis and adhesion molecule expression by autophagy enhancement
in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell Biochem.
120:9291–9299. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sun X, Cao Y-B, Hu L-F, Yang YP, Li J,
Wang F and Liu CF: ASICs mediate the modulatory effect by
paeoniflorin on α-synuclein autophagic degradation. Brain Res.
1396:77–87. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chen Y, Du X, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Liu
Z, Liu C and Xie Y: Paeoniflorin protects HUVECs from
AGE-BSA-induced injury via an autophagic pathway by acting on the
RAGE. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:53–62. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li W, Zhi W, Liu F, Zhao J, Yao Q and Niu
X: Paeoniflorin inhibits VSMCs proliferation and migration by
arresting cell cycle and activating HO-1 through MAPKs and NF-κB
pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 54:103–111. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zheng Y-B, Xiao G-C, Tong S-L, Ding Y,
Wang QS, Li SB and Hao ZN: Paeoniflorin inhibits human gastric
carcinoma cell proliferation through up-regulation of microRNA-124
and suppression of PI3K/Akt and STAT3 signaling. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:7197–7207. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhao Y, Zhou G, Wang J, Jia L, Zhang P, Li
R, Shan L, Liu B, Song X, Liu S, et al: Paeoniflorin protects
against ANIT-induced cholestasis by ameliorating oxidative stress
in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 58:242–248. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wagner G, Lindroos-Christensen J,
Einwallner E, Husa J, Zapf TC, Lipp K, Rauscher S, Gröger M,
Spittler A, Loewe R, et al: HO-1 inhibits preadipocyte
proliferation and differentiation at the onset of obesity via ROS
dependent activation of Akt2. Sci Rep. 7(40881)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mittler R: ROS are good. Trends Plant Sci.
22:11–19. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang X, Liu JZ, Hu JX, Wu H, Li YL, Chen
HL, Bai H and Hai CX: ROS-activated p38 MAPK/ERK-Akt cascade plays
a central role in palmitic acid-stimulated hepatocyte
proliferation. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:539–551. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ruiz-Ramos R, Lopez-Carrillo L, Rios-Perez
AD, De Vizcaya-Ruíz A and Cebrian ME: Sodium arsenite induces ROS
generation, DNA oxidative damage, HO-1 and c-Myc proteins,
NF-kappaB activation and cell proliferation in human breast cancer
MCF-7 cells. Mutat Res. 674:109–115. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kadowaki H, Nishitoh H, Urano F, Sadamitsu
C, Matsuzawa A, Takeda K, Masutani H, Yodoi J, Urano Y, Nagano T,
et al: Amyloid β induces neuronal cell death through ROS-mediated
ASK1 activation. Cell Death Differ. 12:19–24. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Poillet-Perez L, Despouy G,
Delage-Mourroux R and Boyer-Guittaut M: Interplay between ROS and
autophagy in cancer cells, from tumor initiation to cancer therapy.
Redox Biol. 4:184–192. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li HY, Zhang J, Sun LL, Li BH, Gao HL, Xie
T, Zhang N and Ye ZM: Celastrol induces apoptosis and autophagy via
the ROS/JNK signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells: An in
vitro and in vivo study. Cell Death Dis. 6(e1604)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liu D, Lin J, Su J, Chen X, Jiang P and
Huang K: Glutamine deficiency promotes PCV2 infection through
induction of autophagy via activation of ROS-mediated JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 66:11757–11766.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Borodkina AV, Shatrova AN, Deryabin PI,
Griukova AA, Abushik PA, Antonov SM, Nikolsky NN and Burova EB:
Calcium alterations signal either to senescence or to autophagy
induction in stem cells upon oxidative stress. Aging (Albany NY).
8:3400–3418. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|