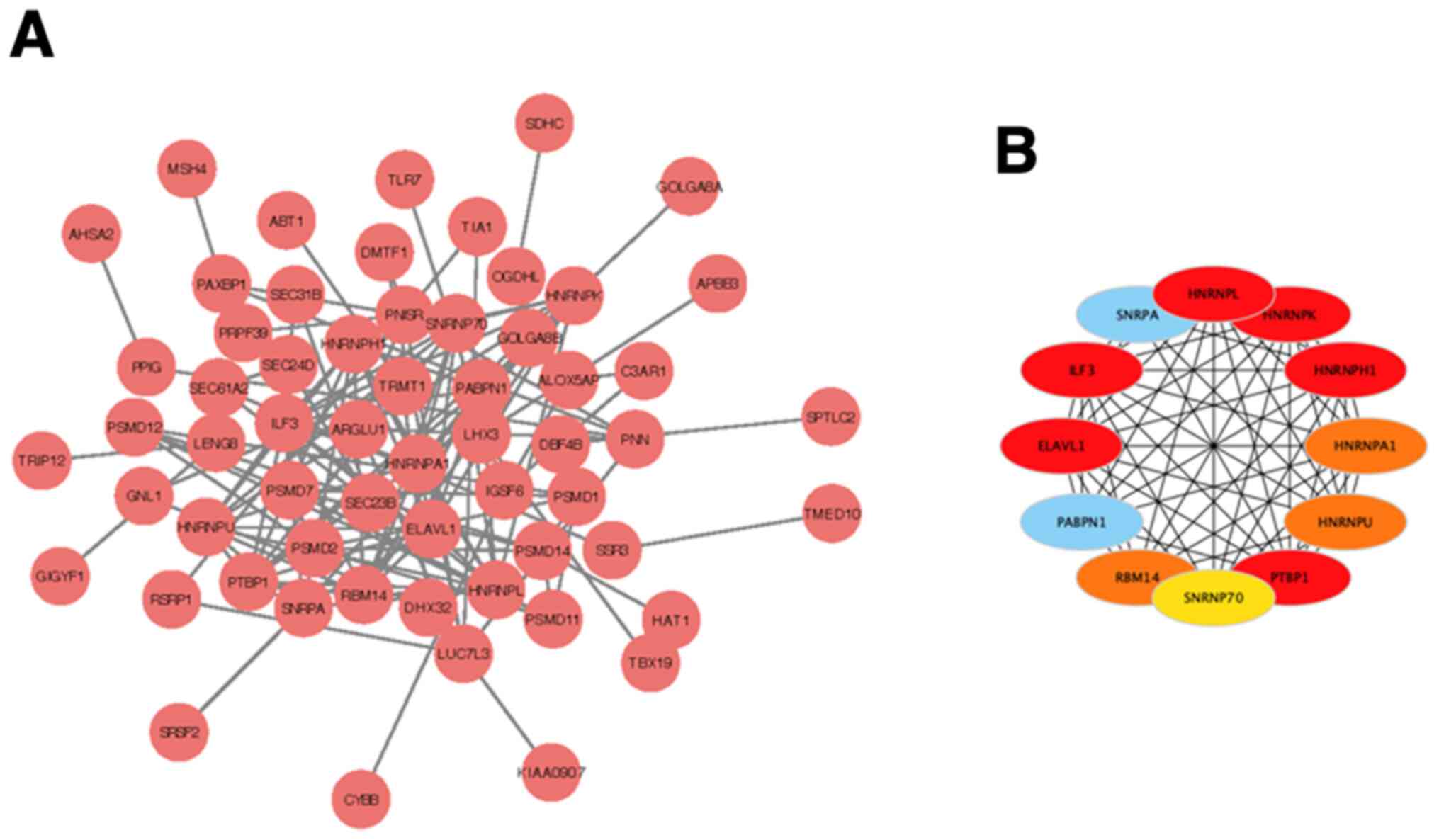
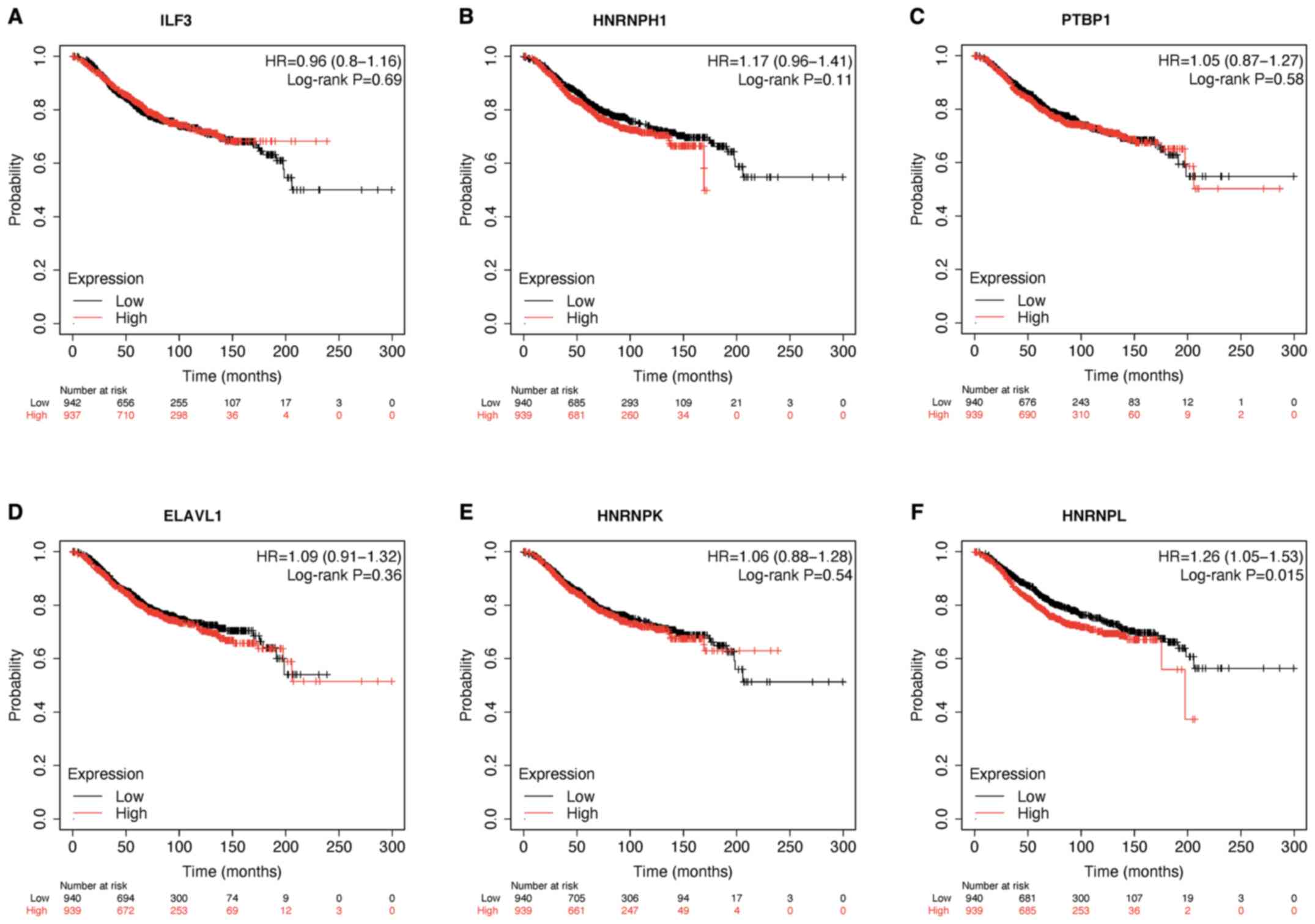
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bianchini G, Balko JM, Mayer IA, Sanders
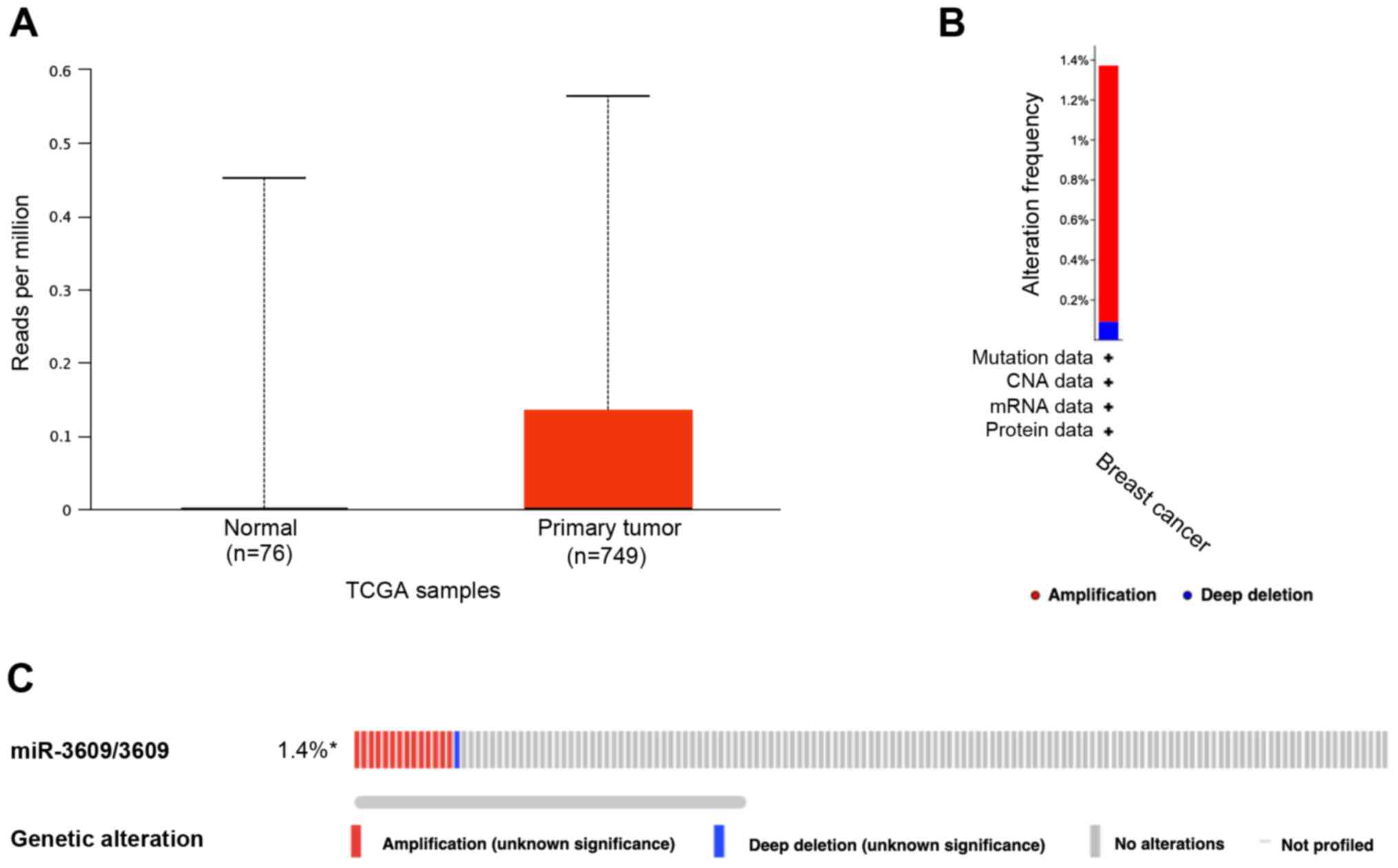
ME and Gianni L: Triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and
opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
13:674–690. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
de Ruijter TC, Veeck J, de Hoon JP, van
Engeland M and Tjan-Heijnen VC: Characteristics of triple-negative
breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 137:183–192.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jonas S and Izaurralde E: Towards a
molecular understanding of microRNA-mediated gene silencing. Nat
Rev Genet. 16:421–433. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee
M and Song SJ: Regulatory mechanism of MicroRNA expression in
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21(21)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
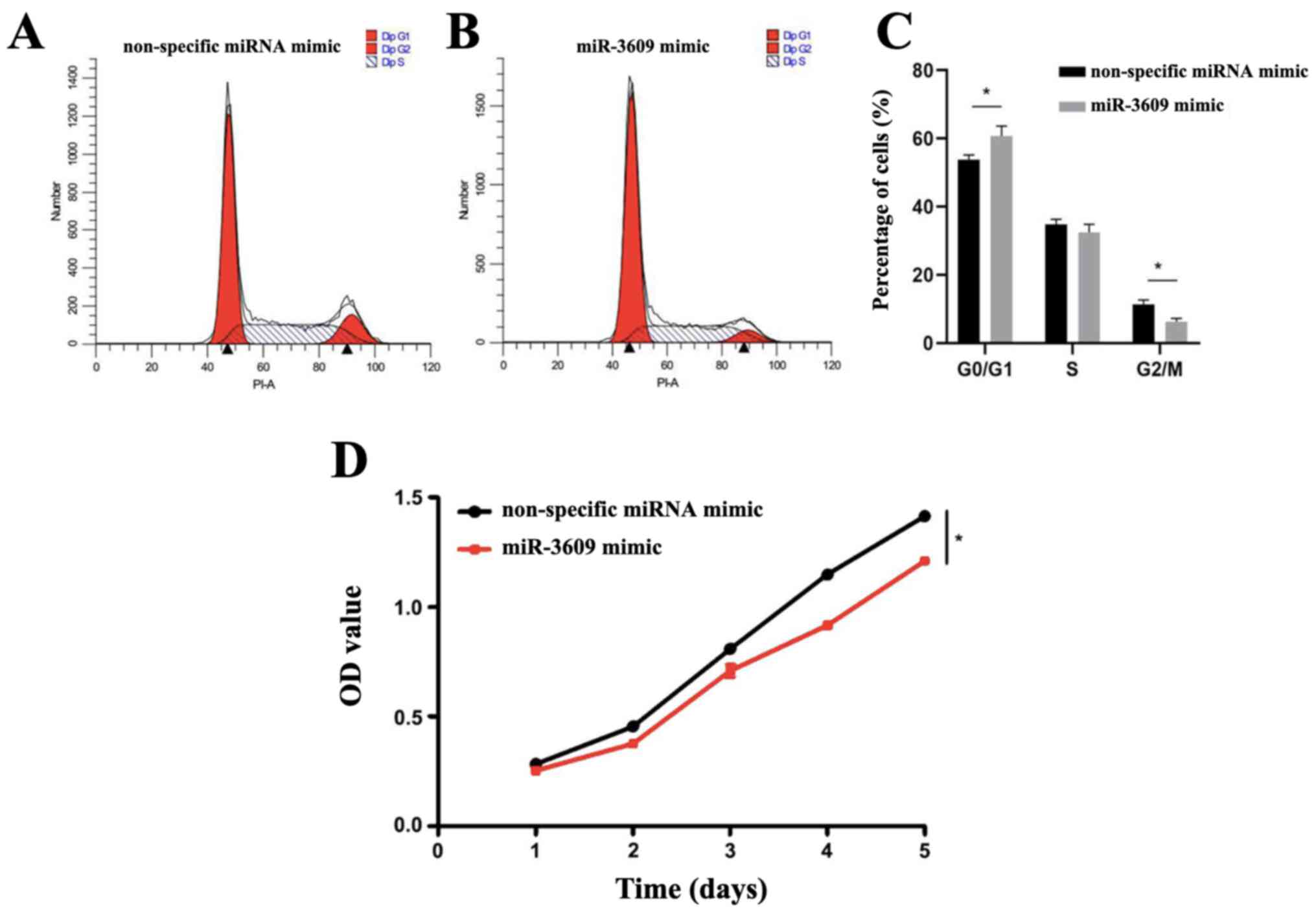
|
Ediriweera MK and Cho SK: Targeting miRNAs
by histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi): Rationalizing
epigenetics-based therapies for breast cancer. Pharmacol Ther.
206(107437)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lowery AJ, Miller N, Devaney A, McNeill
RE, Davoren PA, Lemetre C, Benes V, Schmidt S, Blake J, Ball G, et
al: MicroRNA signatures predict oestrogen receptor, progesterone
receptor and HER2/neu receptor status in breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 11(R27)2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Li S, Liu X, Zhou Y, Acharya A, Savkovic
V, Xu C, Wu N, Deng Y, Hu X, Li H, et al: Shared genetic and
epigenetic mechanisms between chronic periodontitis and oral
squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 86:216–224. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tang S and Dai Y: RNA sequencing reveals
significant miRNAs in Atypical endometrial hyperplasia. Eur J
Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 225:129–135. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mao Y, Shen J, Lu Y, Lin K, Wang H, Li Y,
Chang P, Walker MG and Li D: RNA sequencing analyses reveal novel
differentially expressed genes and pathways in pancreatic cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:42537–42547. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li D, Wang X, Yang M, Kan Q and Duan Z:
miR3609 sensitizes breast cancer cells to adriamycin by blocking
the programmed death-ligand 1 immune checkpoint. Exp Cell Res.
380:20–28. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chandrashekar DS, Bashel B, Balasubramanya
SAH, Creighton CJ, Ponce-Rodriguez I, Chakravarthi BVSK and
Varambally S: UALCAN: A portal for facilitating tumor subgroup gene
expression and survival analyses. Neoplasia. 19:649–658.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE,
Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, et
al: The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring
multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2:401–404.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
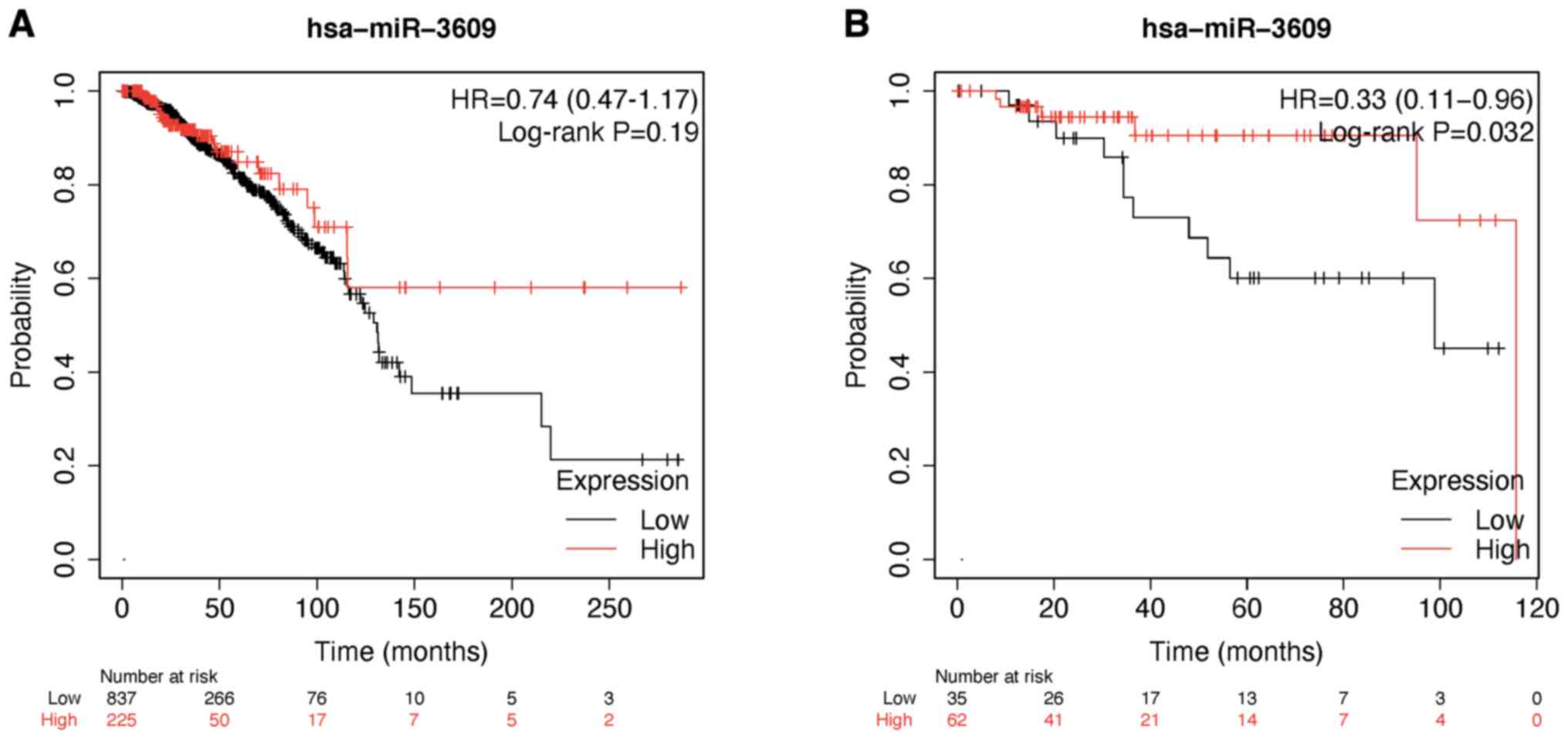
Nagy Á, Munkácsy G and Győrffy B:
Pancancer survival analysis of cancer hallmark genes. Sci Rep.
11(6047)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
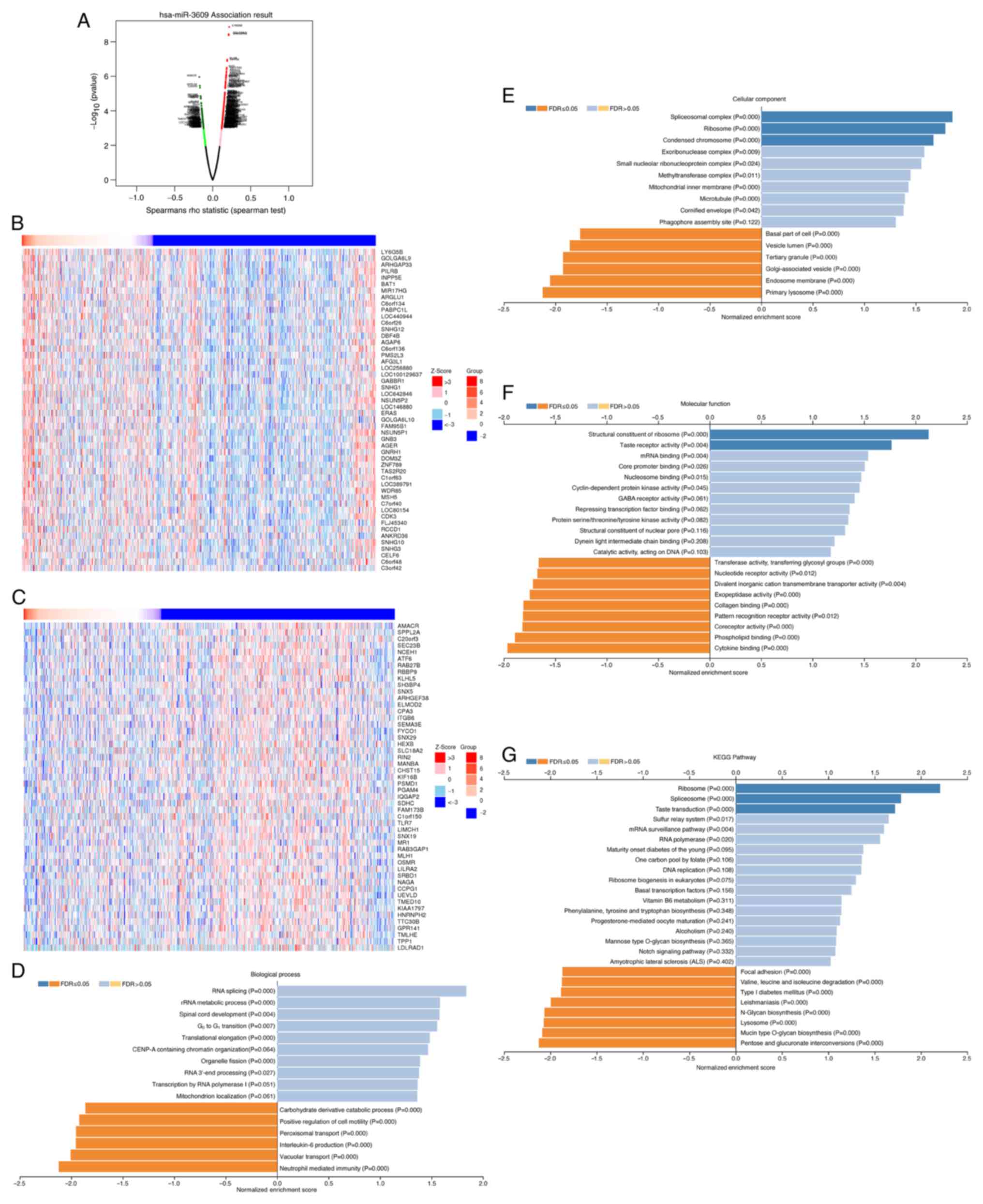
Vasaikar SV, Straub P, Wang J and Zhang B:
LinkedOmics: Analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer
types. Nucleic Acids Res. 46:D956–D963. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D607–D613.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Castella S, Bernard R, Corno M, Fradin A
and Larcher JC: Ilf3 and NF90 functions in RNA biology. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev RNA. 6:243–256. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Upadhyay R, Sanduja S, Kaza V and Dixon
DA: Genetic polymorphisms in RNA binding proteins contribute to
breast cancer survival. Int J Cancer. 132:E128–E138.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Han SP, Tang YH and Smith R: Functional
diversity of the hnRNPs: Past, present and perspectives. Biochem J.
430:379–392. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gu J, Chen Z, Chen X and Wang Z:
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNPL) in cancer. Clin
Chim Acta. 507:286–294. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xu Y, Wu W, Han Q, Wang Y, Li C, Zhang P
and Xu H: Post-translational modification control of RNA-binding
protein hnRNPK function. Open Biol. 9(180239)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li X, Han F, Liu W and Shi X: PTBP1
promotes tumorigenesis by regulating apoptosis and cell cycle in
colon cancer. Bull Cancer. 105:1193–1201. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kalimutho M, Nones K, Srihari S, Duijf
PHG, Waddell N and Khanna KK: Patterns of genomic instability in
breast cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 40:198–211. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang R, Zhu Q, Yin D, Yang Z, Guo J,
Zhang J, Zhou Y and Yu JJ: Identification and validation of an
autophagy-related lncRNA signature for patients with breast cancer.
Front Oncol. 10(597569)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gong Y, Ji P, Yang YS, Xie S, Yu TJ, Xiao
Y, Jin ML, Ma D, Guo LW, Pei YC, et al: Metabolic-pathway-based
subtyping of triple-negative breast cancer reveals potential
therapeutic targets. Cell Metab. 33:51–64.e9. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu H, Paddock MN, Wang H, Murphy CJ, Geck
RC, Navarro AJ, Wulf GM, Elemento O, Haucke V, Cantley LC, et al:
The INPP4B tumor suppressor modulates EGFR trafficking and promotes
triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 10:1226–1239.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Garrido-Castro AC, Lin NU and Polyak K:
Insights into molecular classifications of triple-negative breast
cancer: Improving patient selection for treatment. Cancer Discov.
9:176–198. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Brand A, Singer K, Koehl GE, Kolitzus M,
Schoenhammer G, Thiel A, Matos C, Bruss C, Klobuch S, Peter K, et
al: LDHA-associated lactic acid production blunts tumor
immunosurveillance by T and NK cells. Cell Metab. 24:657–671.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Brown M, Tsodikov A, Bauer KR, Parise CA
and Caggiano V: The role of human epidermal growth factor receptor
2 in the survival of women with estrogen and progesterone
receptor-negative, invasive breast cancer: The California Cancer
Registry, 1999-2004. Cancer. 112:737–747. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cortez MA, Anfossi S, Ramapriyan R, Menon
H, Atalar SC, Aliru M, Welsh J and Calin GA: Role of miRNAs in
immune responses and immunotherapy in cancer. Genes Chromosomes
Cancer. 58:244–253. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Yang Q, Cao W, Wang Z, Zhang B and Liu J:
Regulation of cancer immune escape: The roles of miRNAs in immune
checkpoint proteins. Cancer Lett. 431:73–84. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xie M, Ma L, Xu T, Pan Y, Wang Q, Wei Y
and Shu Y: Potential regulatory roles of microRNAs and long
noncoding RNAs in anticancer therapies. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
13:233–243. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Denaro N, Merlano MC and Lo Nigro C: Long
noncoding RNAs as regulators of cancer immunity. Mol Oncol.
13:61–73. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lin C-P and He L: Noncoding RNAs in cancer
development. Annu Rev Cancer Biol. 1:163–184. 2017.https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-050216-034443.
|
|
37
|
Ha M and Kim VN: Regulation of microRNA
biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:509–524. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Chen LL, Zhang ZJ, Yi ZB and Li JJ:
MicroRNA-211-5p suppresses tumour cell proliferation, invasion,
migration and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer by
directly targeting SETBP1. Br J Cancer. 117:78–88. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Breunig C, Erdem N, Bott A, Greiwe JF,
Reinz E, Bernhardt S, Giacomelli C, Wachter A, Kanthelhardt EJ,
Beißbarth T, et al: TGFβ1 regulates HGF-induced cell migration and
hepatocyte growth factor receptor MET expression via C-ets-1 and
miR-128-3p in basal-like breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 12:1447–1463.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wang DY, Gendoo DMA, Ben-David Y, Woodgett
JR and Zacksenhaus E: A subgroup of microRNAs defines
PTEN-deficient, triple-negative breast cancer patients with poorest
prognosis and alterations in RB1, MYC, and Wnt signaling. Breast
Cancer Res. 21(18)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Fitzpatrick C, Bendek MF, Briones M,
Farfán N, Silva VA, Nardocci G, Montecino M, Boland A, Deleuze JF,
Villegas J, et al: Mitochondrial ncRNA targeting induces cell cycle
arrest and tumor growth inhibition of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer
cells through reduction of key cell cycle progression factors. Cell
Death Dis. 10(423)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Xiao B, Zhang W, Chen L, Hang J, Wang L,
Zhang R, Liao Y, Chen J, Ma Q, Sun Z, et al: Analysis of the
miRNA-mRNA-lncRNA network in human estrogen receptor-positive and
estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer based on TCGA data. Gene.
658:28–35. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|