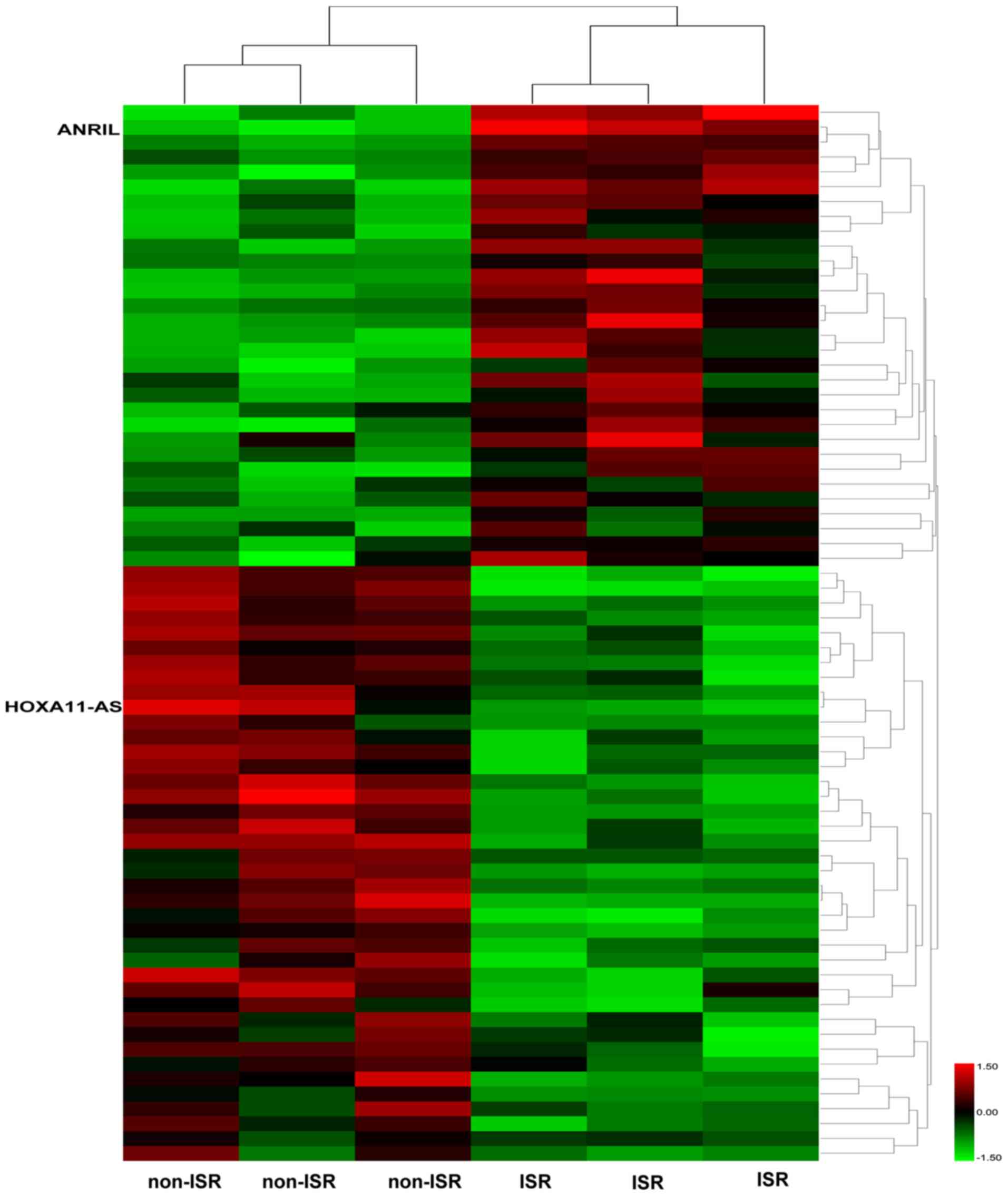
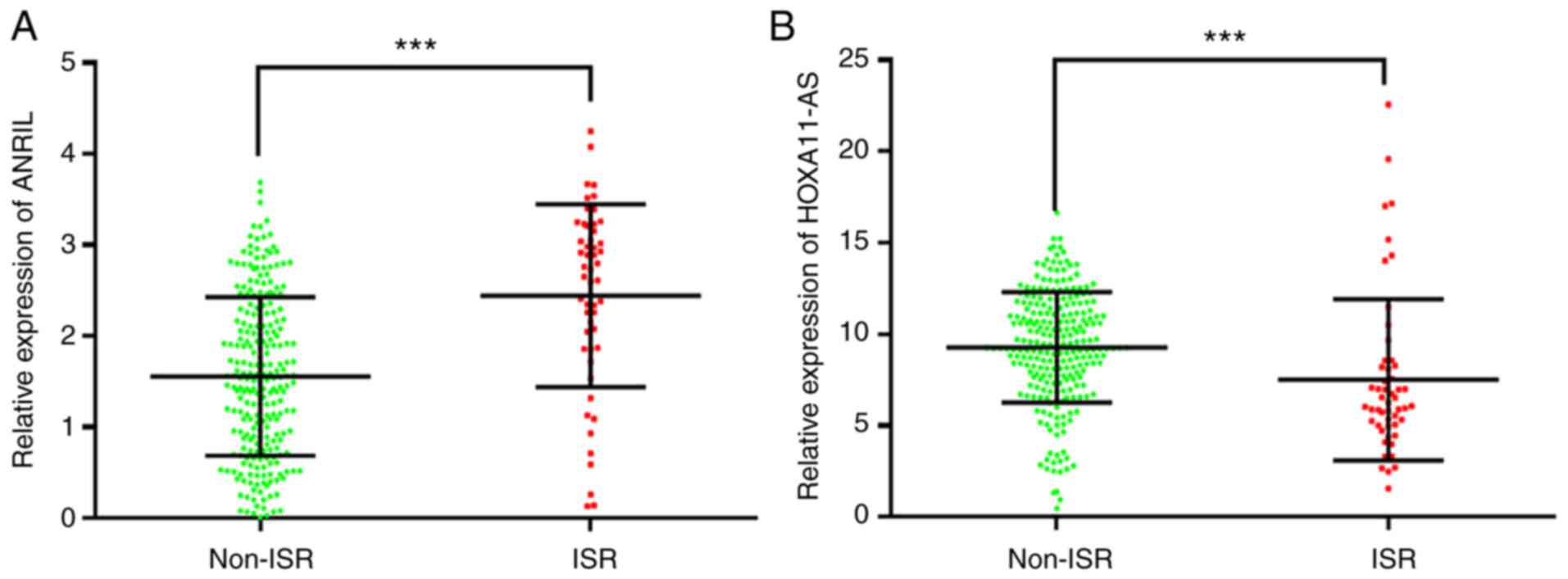
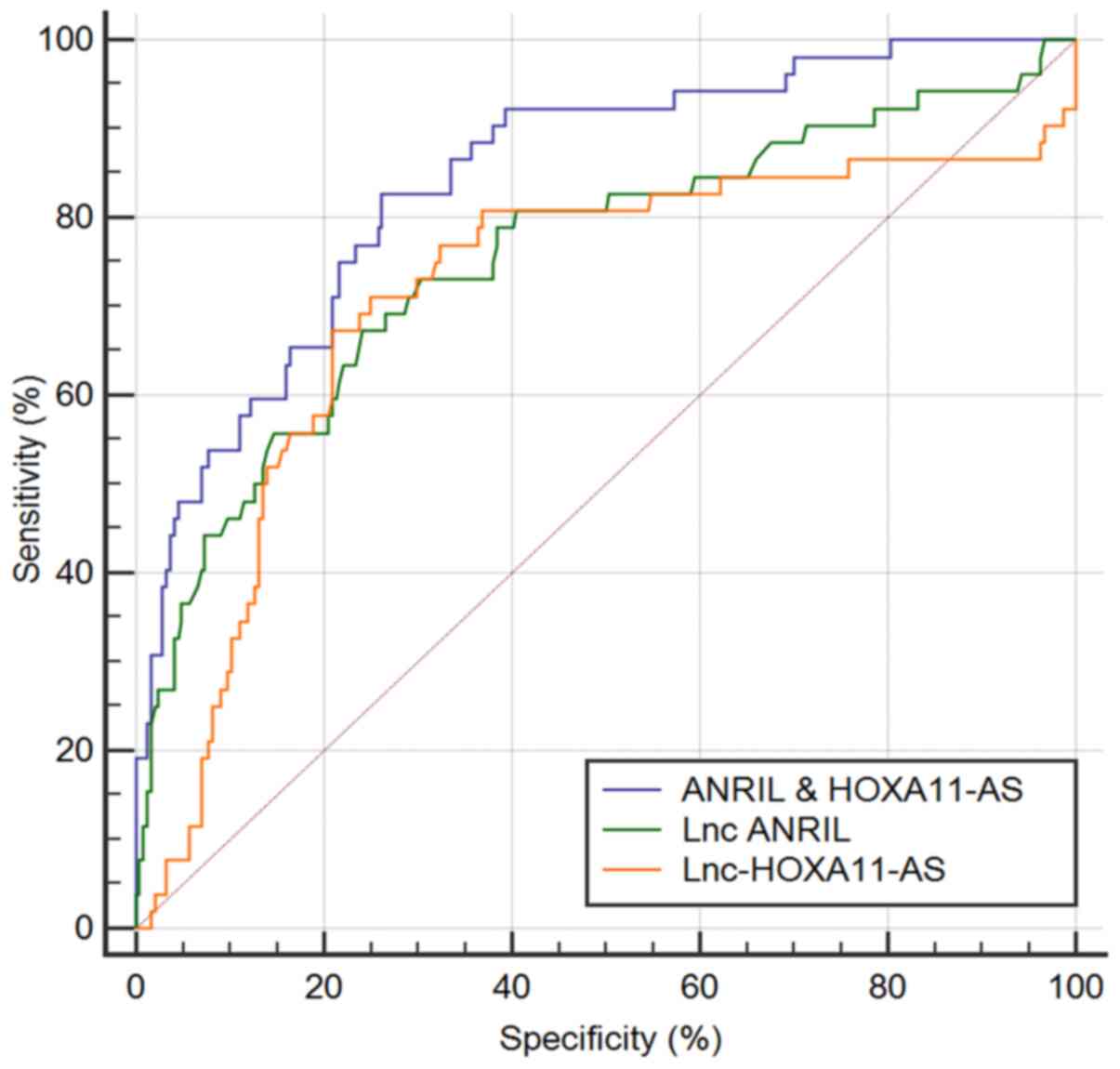
|
1
|
Hu SS, Gao RL, Liu LS, Zhu ML, Wang W and
Wang YJ: The abstract of 2018 report of Chinese cardiovascular
disease. Chin Circ Mag. 34:209–220. 2019.
|
|
2
|
Meier B: The first patient to undergo
coronary angioplasty - 23-year follow-up. N Engl J Med.
344:144–145. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lee MS and Banka G: In-stent restenosis.
Interv Cardiol Clin. 5:211–220. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Buccheri D, Piraino D, Andolina G and
Cortese B: Understanding and managing in-stent restenosis: A review
of clinical data, from pathogenesis to treatment. J Thorac Dis.
8:E1150–E1162. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Uchida S and Dimmeler S: Long noncoding
RNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res. 116:737–750.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ballantyne MD, Pinel K, Dakin R, Vesey AT,
Diver L, Mackenzie R, Garcia R, Welsh P, Sattar N, Hamilton G, et
al: Smooth muscle enriched long noncoding RNA (SMILR) regulates
cell proliferation. Circulation. 133:2050–2065. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Lai CF, Chen YT, Gu J, Nerbonne JM, Lin CH
and Yang KC: Circulating long noncoding RNA DKFZP434I0714 predicts
adverse cardiovascular outcomes in patients with end-stage renal
disease. Int J Cardiol. 277:212–219. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wang F, Su X, Liu C, Wu M and Li B:
Prognostic value of plasma long noncoding RNA ANRIL for in-stent
restenosis. Med Sci Monit. 23:4733–4739. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang P, Meng L, Liu L and Peng F: The
value of circulating exosomes-mediated lncRNA HOXA11-AS in the
proliferation of vascular endothelial cell by up-regulating SOX4.
Journal of Wenzhou Medical Unversity. 51:639–645. 2021.(In
Chinese).
|
|
11
|
Shi KQ, Wu FL, Liu WY, Zhao CC, Chen CX,
Xie YY, Wu SJ, Lin XF, Chen YP, Wong DK, et al: Non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease and risk of in-stent restenosis after bare metal
stenting in native coronary arteries. Mol Biol Rep. 41:4713–4720.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bambagioni G, Di Mario C, Torguson R,
Demola P, Ali Z, Singh V, Skinner W, Artis A, Cate TT, Zhang C, et
al: Lipid-rich plaques detected by near-infrared spectroscopy
predict coronary events irrespective of age: A Lipid Rich Plaque
sub-study. Atherosclerosis. 334:17–22. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Pleva L, Kukla P and Hlinomaz O: Treatment
of coronary in-stent restenosis: A systematic review. J Geriatr
Cardiol. 15:173–184. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li MK, Tsang AC, Tsang FC, Ho WS, Lee R,
Leung GK and Lui WM: Long-term risk of in-stent restenosis and
stent fracture for extracranial vertebral artery stenting. Clin
Neuroradiol. 29:701–706. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kumric M, Borovac JA, Martinovic D,
Ticinovic Kurir T and Bozic J: Circulating biomarkers reflecting
destabilization mechanisms of coronary artery plaques: are we
looking for the impossible? Biomolecules. 11(881)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Schmitt AM and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 29:452–463. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Thum T and Condorelli G: Long noncoding
RNAs and microRNAs in cardiovascular pathophysiology. Circ Res.
116:751–762. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li M, Wang YF, Yang XC, Xu L, Li WM, Xia
K, Zhang DP, Wu RN and Gan T: Circulating long noncoding RNA LIPCAR
acts as a novel biomarker in patients with ST-segment elevation
myocardial infarction. Med Sci Monit. 24:5064–5070. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Holdt LM, Stahringer A, Sass K, Pichler G,
Kulak NA, Wilfert W, Kohlmaier A, Herbst A, Northoff BH, Nicolaou
A, et al: Circular non-coding RNA ANRIL modulates ribosomal RNA
maturation and atherosclerosis in humans. Nat Commun.
7(12429)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chi JS, Li JZ, Jia JJ, Zhang T, Liu XM and
Yi L: Long non-coding RNA ANRIL in gene regulation and its duality
in atherosclerosis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
37:816–822. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen L, Qu H, Guo M, Zhang Y, Cui Y, Yang
Q, Bai R and Shi D: ANRIL and atherosclerosis. J Clin Pharm Ther.
45:240–248. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wei C, Zhao L, Liang H, Zhen Y and Han L:
Recent advances in unraveling the molecular mechanisms and
functions of HOXA11 AS in human cancers and other diseases
(Review). Oncol Rep. 43:1737–1754. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wang Q, Zhang J, Liu Y, Zhang W, Zhou J,
Duan R, Pu P, Kang C and Han L: A novel cell cycle-associated
lncRNA, HOXA11-AS, is transcribed from the 5-prime end of the HOXA
transcript and is a biomarker of progression in glioma. Cancer
Lett. 373:251–259. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen J, Fu Z, Ji C, Gu P, Xu P, Yu N, Kan
Y, Wu X, Shen R and Shen Y: Systematic gene microarray analysis of
the lncRNA expression profiles in human uterine cervix carcinoma.
Biomed Pharmacother. 72:83–90. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Richards EJ, Permuth-Wey J, Li Y, Chen YA,
Coppola D, Reid BM, Lin HY, Teer JK, Berchuck A, Birrer MJ, et al:
A functional variant in HOXA11-AS, a novel long non-coding RNA,
inhibits the oncogenic phenotype of epithelial ovarian cancer.
Oncotarget. 6:34745–34757. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kim HJ, Eoh KJ, Kim LK, Nam EJ, Yoon SO,
Kim KH, Lee JK, Kim SW and Kim YT: The long noncoding RNA HOXA11
antisense induces tumor progression and stemness maintenance in
cervical cancer. Oncotarget. 7:83001–83016. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yu W, Peng W, Jiang H, Sha H and Li J:
LncRNA HOXA11-AS promotes proliferation and invasion by targeting
miR-124 in human non-small cell lung cancer cells. Tumour Biol: Oct
15, 2017 (Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1177/1010428317721440.
|
|
28
|
Yu J, Hong JF, Kang J, Liao LH and Li CD:
Promotion of lncRNA HOXA11-AS on the proliferation of
hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating the expression of LATS1. Eur
Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 21:3402–3411. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu C, He T, Li Z, Liu H and Ding B:
Regulation of HOXA11-AS/miR-214-3p/EZH2 axis on the growth,
migration and invasion of glioma cells. Biomed Pharmacother.
95:1504–1513. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cui Y, Yi L, Zhao JZ and Jiang YG: Long
noncoding RNA HOXA11-AS functions as miRNA sponge to promote the
glioma tumorigenesis through targeting miR-140-5p. DNA Cell Biol.
36:822–828. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen D, Sun Q, Zhang L, Zhou X, Cheng X,
Zhou D, Ye F, Lin J and Wang W: The lncRNA HOXA11-AS functions as a
competing endogenous RNA to regulate PADI2 expression by sponging
miR-125a-5p in liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget.
8:70642–70652. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Japp NC, Souchek JJ, Sasson AR,
Hollingsworth MA, Batra SK and Junker WM: Tumor biomarker
in-solution quantification, standard production, and multiplex
detection. J Immunol Res. 2021(9942605)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Tesche C, De Cecco CN, Vliegenthart R,
Duguay TM, Stubenrauch AC, Rosenberg RD, Varga-Szemes A, Bayer RR
II, Yang J, Ebersberger U, et al: Coronary CT angiography-derived
quantitative markers for predicting in-stent restenosis. J
Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr. 10:377–383. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Parsa SF, Vafajoo A, Rostami A, Salarian
R, Rabiee M, Rabiee N, Rabiee G, Tahriri M, Yadegari A, Vashaee D,
et al: Early diagnosis of disease using microbead array technology:
A review. Anal Chim Acta. 1032:1–17. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|